Proteinaholic – by Dr. Garth Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein is important, yes. However, you can have too much of a good thing, and you can also get it from bad sources that do more harm than good.
That’s what this book is about, and how to go about understanding the science in a world where marketing has outstripped the conclusions of research scientists.
Firstly, let’s mention that Dr. Davis’ main issue here is (as the subtitle suggests) about animal proteins, not plant-based proteins. The former are associated with very many health risks that the latter are not. And yes, even just the lean protein, not considering the animal fat.
He does not argue that the reader must, or even necessarily needs to, adopt a vegan diet. However, he does argue for minimizing animal proteins, and getting more plants in.
A lot of the book is about the research to back this approach, and specifically, it’s largely a polemic against animal protein. He also shares anecdotes throughout, about his own health journey—from an overweight cheeseburger-fueled heart attack machine with exciting cholesterol levels, to a healthy, muscular, plant-fueled advocate for healthier eating.
He talks us through the science at hand, including chapters for each of the main health risks associated with meat consumption, as well as how the science got misrepresented by popular marketing for [not necessarily, but usually] meat-heavy diets such as Atkins and Paleo. That yes, they will give short term weight loss, but bring extra health risks in the longer term, and how.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut down your meat consumption but worry “will I get enough protein?”, this book will set your mind at ease with an abundance of science.
Click here to check out Proteinaholic, and give your body better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
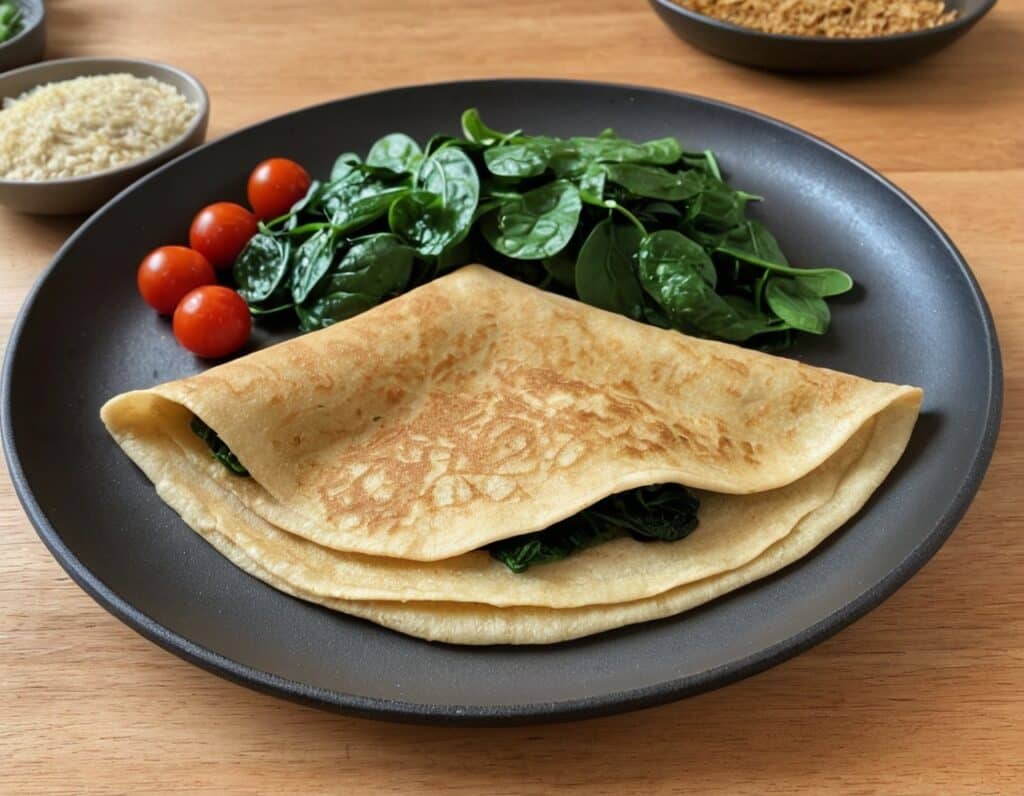
Savory Protein Crêpe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pancakes have a bad reputation healthwise, but they don’t have to be so. Here’s a very healthy crêpe recipe, with around 20g of protein per serving (which is about how much protein most people’s body’s can use at one sitting) and a healthy dose of fiber too:
You will need
Per crêpe:
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend oat milk for this)
- 2 oz chickpea flour (also called garbanzo bean flour, or gram flour)
- 1 tsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp ras el-hanout (optional but tasty and contains an array of beneficial phytochemicals)
- 1 tsp dried mixed herbs
- ⅛ tsp MSG or ¼ tsp low-sodium salt
For the filling (also per crêpe):
- 6 cherry tomatoes, halved
- Small handful baby spinach
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix the dry crêpe ingredients in a bowl, and then stir in the milk, whisking to mix thoroughly. Leave to stand for at least 5 minutes.
2) Meanwhile, heat a little olive oil in a skillet, add the tomatoes and fry for 1 minute, before adding the spinach, stirring, and turning off the heat. As soon as the spinach begins to wilt, set it aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil either in the same skillet (having been carefully wiped clean) or a crêpe pan if you have one, and pour in a little of the batter you made, tipping the pan so that it coats the pan evenly and thinly. Once the top is set, jiggle the pan to see that it’s not stuck, and then flip your crêpe to finish on the other side.
If you’re not confident of your pancake-tossing skills, or your pan isn’t good enough quality to permit this, you can slide it out onto a heatproof chopping board, and use that to carefully turn it back into the pan to finish the other side.
4) Add the filling to one half of the crêpe, and fold it over, pushing down at the edges with a spatula to make a seal, cooking for another 30 seconds or so. Alternatively, you can just serve a stack of crêpes and add the filling at the table, folding or rolling per personal preference:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
‘Emergency’ or Not, Covid Is Still Killing People. Here’s What Doctors Advise to Stay Safe.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With around 20,000 people dying of covid in the United States since the start of October, and tens of thousands more abroad, the covid pandemic clearly isn’t over. However, the crisis response is, since the World Health Organization and the Biden administration ended their declared health emergencies last year.
Let’s not confuse the terms “pandemic” and “emergency.” As Abraar Karan, an infectious disease physician and researcher at Stanford University, said, “The pandemic is over until you are scrunched in bed, feeling terrible.”
Pandemics are defined by neither time nor severity, but rather by large numbers of ongoing infections worldwide. Emergencies are acute and declared to trigger an urgent response. Ending the official emergency shifted the responsibility for curbing covid from leaders to the public. In the United States, it meant, for example, that the government largely stopped covering the cost of covid tests and vaccines.
But the virus is still infecting people; indeed, it is surging right now.
With changes in the nature of the pandemic and the response, KFF Health News spoke with doctors and researchers about how to best handle covid, influenza, and other respiratory ailments spreading this season.
A holiday wave of sickness has ensued as expected. Covid infections have escalated nationwide in the past few weeks, with analyses of virus traces in wastewater suggesting infection rates as high as last year’s. More than 73,000 people died of covid in the U.S. in 2023, meaning the virus remains deadlier than car accidents and influenza. Still, compared with last year’s seasonal surge, this winter’s wave of covid hospitalizations has been lower and death rates less than half.
“We’re seeing outbreaks in homeless shelters and in nursing homes, but hospitals aren’t overwhelmed like they have been in the past,” said Salvador Sandoval, a doctor and health officer at the Merced County public health department in California. He attributes that welcome fact to vaccination, covid treatments like Paxlovid, and a degree of immunity from prior infections.
While a new coronavirus variant, JN.1, has spread around the world, the current vaccines and covid tests remain effective.
Other seasonal illnesses are surging, too, but rates are consistent with those of previous years. Between 9,400 and 28,000 people died from influenza from Oct. 1 to Jan. 6, estimates the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and millions felt so ill from the flu that they sought medical care. Cases of pneumonia — a serious condition marked by inflamed lungs that can be triggered by the flu, covid, or other infections — also predictably rose as winter set in. Researchers are now less concerned about flare-ups of pneumonia in China, Denmark, and France in November and December, because they fit cyclical patterns of the pneumonia-causing bacteria Mycoplasma pneumoniae rather than outbreaks of a dangerous new bug.
Public health researchers recommend following the CDC guidance on getting the latest covid and influenza vaccines to ward off hospitalization and death from the diseases and reduce chances of getting sick. A recent review of studies that included 614,000 people found that those who received two covid vaccines were also less likely to develop long covid; often involving fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and joint pain, the condition is marked by the development or continuation of symptoms a few months after an infection and has been debilitating for millions of people. Another analysis found that people who had three doses of covid vaccines were much less likely to have long covid than those who were unvaccinated. (A caveat, however, is that those with three doses might have taken additional measures to avoid infections than those who chose to go without.)
It’s not too late for an influenza vaccine, either, said Helen Chu, a doctor and epidemiologist at the University of Washington in Seattle. Influenza continues to rise into the new year, especially in Southern states and California. Last season’s shot appeared to reduce adults’ risk of visits to the emergency room and urgent care by almost half and hospitalization by more than a third. Meanwhile, another seasonal illness with a fresh set of vaccines released last year, respiratory syncytial virus, appears to be waning this month.
Another powerful way to prevent covid, influenza, common colds, and other airborne infections is by wearing an N95 mask. Many researchers say they’ve returned to socializing without one but opt for the masks in crowded, indoor places when wearing one would not be particularly burdensome. Karan, for example, wears his favorite N95 masks on airplanes. And don’t forget good, old-fashioned hand-washing, which helps prevent infections as well.
If you do all that and still feel sick? Researchers say they reach for rapid covid tests. While they’ve never been perfect, they’re often quite helpful in guiding a person’s next steps.
When President Joe Biden declared the end of the public health emergency last year, many federally funded testing sites that sent samples to laboratories shut their doors. As a result, people now mainly turn to home covid tests that signal an infection within 15 minutes and cost around $6 to $8 each at many pharmacies. The trick is to use these tests correctly by taking more than one when there’s reason for concern. They miss early infections more often than tests processed in a lab, because higher levels of the coronavirus are required for detection — and the virus takes time to multiply in the body. For this reason, Karan considers other information. “If I ran into someone who turned out to be sick, and then I get symptoms a few days later,” he said, “the chance is high that I have whatever they had, even if a test is negative.”
A negative result with a rapid test might mean simply that an infection hasn’t progressed enough to be detected, that the test had expired, or that it was conducted wrong. To be sure the culprit behind symptoms like a sore throat isn’t covid, researchers suggest testing again in a day or two. It often takes about three days after symptoms start for a test to register as positive, said Karan, adding that such time estimates are based on averages and that individuals may deviate from the norm.
If a person feels healthy and wants to know their status because they were around someone with covid, Karan recommends testing two to four days after the exposure. To protect others during those uncertain days, the person can wear an N95 mask that blocks the spread of the virus. If tests remain negative five days after an exposure and the person still feels fine, Chu said, they’re unlikely to be infected — and, if they are, viral levels would be so low that they would be unlikely to pass the disease to others.
Positive tests, on the other hand, reliably flag an infection. In this case, people can ask a doctor whether they qualify for the antiviral drug Paxlovid. The pills work best when taken immediately after symptoms begin so that they slash levels of the virus before it damages the body. Some studies suggest the medicine reduces a person’s risk of long covid, too, but the evidence is mixed. Another note on tests: Don’t worry if they continue to turn out positive for longer than symptoms last; the virus may linger even if it’s no longer replicating. After roughly a week since a positive test or symptoms, studies suggest, a person is unlikely to pass the virus to others.
If covid is ruled out, Karan recommends tests for influenza because they can guide doctors on whether to prescribe an antiviral to fight it — or if instead it’s a bacterial infection, in which case antibiotics may be in order. (One new home test diagnoses covid and influenza at the same time.) Whereas antivirals and antibiotics target the source of the ailment, over-the-counter medications may soothe congestion, coughs, fevers, and other symptoms. That said, the FDA recently determined that a main ingredient in versions of Sudafed, NyQuil, and other decongestants, called phenylephrine, is ineffective.
Jobs complicate a personal approach to staying healthy. Emergency-era business closures have ended, and mandates on vaccination and wearing masks have receded across the country. Some managers take precautions to protect their staff. Chu, for example, keeps air-purifying devices around her lab, and she asks researchers to stay home when they feel sick and to test themselves for covid before returning to work after a trip.
However, occupational safety experts note that many employees face risks they cannot control because decisions on if and how to protect against outbreaks, such as through ventilation, testing, and masking, are left to employers. Notably, people with low-wage and part-time jobs — occupations disproportionately held by people of color — are often least able to control their workplace environments.
Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the National Council for Occupational Safety and Health, said the lack of national occupational standards around airborne disease protection represents a fatal flaw in the Biden administration’s decision to relinquish its control of the pandemic.
“Every workplace needs to have a plan for reducing the threat of infectious disease,” she said. “If you only focus on the individual, you fail workers.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resistance Is Useful!
At 10almonds we talk a lot about the importance of regular moderate exercise (e.g. walking, gardening, housework, etc), and with good reason: getting in those minutes (at least 150 minutes per week, so, a little over 20 minutes per day, or 25 minutes per day with one day off) is the exericise most consistently linked to better general health outcomes and reduced mortality risk.
We also often come back to mobility, because at the end of the day, being able to reach for something from a kitchen cabinet without doing oneself an injury is generally more important in life than being able to leg-press a car.
Today though, we’re going to talk about resistance training.
What is resistance training?
It can be weight-lifting, or it can be bodyweight exercises. In those cases, what you’re resisting is gravity. It can also be exercises with resistance bands or machines. In all cases, it’s about building and/or maintaining strength.
Why does it matter?
Let’s say you’re not an athlete, soldier, or laborer, and the heaviest thing you have to pick up is a bag of groceries. Strength still matters, for two main reasons:
- Muscle strength correlates to bone strength. You can’t build (or maintain) strong muscles on weak bones, so if you take care of your muscles, then your body will keep your bones strong too.
- That’s assuming you have a good diet as well—but today’s not about that. If you’d like to know more about eating for bone health though, do check out this previous article about that!
- Muscle strength correlates to balance and stability. You can’t keep yourself from falling over if you are physically frail.
Both of those things matter, because falls and fractures often have terrible health outcomes (e.g., slower recovery and more complications) the older we get. So, we want to:
- Ideally, not fall in the first place
- If we do fall, have robust bones
See also: Effects of Resistance Exercise on Bone Health
How much should we do?
Let’s go to the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research on this one:
❝There is strong evidence to support the benefits of resistance exercise for countering many age-related processes of sarcopenia, muscle weakness, mobility loss, chronic disease, disability, and even premature mortality.
In addition, this Position Statement provides specific evidence-based practice recommendations to aid in the implementation of resistance exercise programs for healthy older adults and those with special considerations.
While there are instances where low-intensity, low-volume programs are appropriate (i.e., beginning programs for individuals with frailty or CVDs), the greatest benefits are possible with progression to moderate to higher intensity programs.❞
~ Fragala et al
Read the statement in full:
There’s a lot of science there and it’s well worth reading if you have the time. It’s particularly good at delineating how much is not enough vs how much is too much, and the extent to which we should (or shouldn’t) train to exhaustion.
If you don’t fancy that, though, and/or just want to start with something accessible and work your way up, the below is a very good (and also evidence-based) start-up plan:
Healthline’s Exercise Plan For Seniors—For Strength, Balance, & Flexibility
(it has a weekly planner, step-by-step guides to the exercises, and very clear illustrative animations of each)
Share This Post
- Muscle strength correlates to bone strength. You can’t build (or maintain) strong muscles on weak bones, so if you take care of your muscles, then your body will keep your bones strong too.
Related Posts
-
Creamy Fortifying Cauliflower Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As delicious as it is super-easy to make, this one is full of protein, fiber, healthy fats, and some of the most health-giving spices around.
You will need
- 1 quart low-sodium vegetable stock
- 1 large cauliflower, cut into florets
- 1 large onion, finely chopped
- 2 cans cannellini (or other white) beans, drained and rinsed
- 1 cup raw cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 5 minutes, and drained (if allergic, substitute chickpeas)
- 1 bulb (yes, a whole bulb) garlic, roughly chopped
- 5 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 10 fresh sprigs of thyme (keep them whole!)
- 1 large fresh sprig of rosemary (keep this whole too!)
- zest of 1 lemon
- 1 tbsp red chili flakes
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp MSG or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- ½ tsp ground turmeric
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Tightly tie up the sprigs of rosemary and thyme with kitchen twine (shining a bright light on it and asking it invasive questions is optional)
2) Heat some olive oil to a medium heat in your biggest sauté pan or similar. Add the onions, and cook for about 10 minutes, stirring as necessary. We are not trying to outright caramelize them here, but we do want them browned a little.
3) Add the garlic and cook for another 2 minutes, stirring frequently.
4) Add the vegetable stock, and stir, ensuring no onion is stuck to the base of the pan. Add the cauliflower, cashews, beans, nooch, pepper, turmeric, and MSG/salt, stirring to combine. Don’t worry if the cauliflower isn’t all submerged; it’ll be fine in a little while.
5) Add the herbs, submerging them in the soup (still tied up bouquet garni style).
6) Bring to a boil, reduce to a simmer and cook for 15–20 minutes; the cauliflower will be soft when it’s ready.
7) Remove the bouquet garni, and blend the soup until thick and creamy. You can do this with an immersion blender, but to get the smoothest soup, you’ll need to use a stand blender. Either ensure yours is safe for hot liquids, or else allow to cool, blend, and reheat later. This is important, as otherwise your blender could explode.
8) Serve, using the lemon zest and chili for the garnish:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Origin of Everyday Moods – by Dr. Robert Thayer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First of all, what does this title mean by “everyday moods”? By this the author is referring to the kinds of moods we have just as a matter of the general wear-and-tear of everyday life—not the kind that come from major mood disorders and/or serious trauma.
The latter kinds of mood take less explaining, in any case. Dr. Thayer, therefore, spends his time on the less obvious ones—which in turn are the ones that affect most of the most, every day.
Critical to Dr. Thayer’s approach is the mapping of moods by four main quadrants:
- High energy, high tension
- High energy, low tension
- Low energy, high tension
- Low energy, low tension
…though this can be further divided into 25 sectors, if we rate each variable on a scale of 0–4. But for the first treatment, it suffices to look at whether energy and tension are high or low, respectively, and which we’d like to have more or less of.
Then (here be science) how to go about achieving that in the most efficient, evidence-based ways. So, it’s not just a theoretical book; it has great practical value too.
The style of the book is accessible, and walks a fine line between pop-science and hard science, which makes it a great book for laypersons and academics alike.
Bottom line: if you’d like the cheat codes to improve your moods and lessen the impact of bad ones, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out The Origin of Everyday Moods, and manage yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Retinoids: Retinol vs Retinal vs Retinoic Acid vs..?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I’m confused about retinol, retinal, retinoin, retinoids, etc, and of course every product claims to be the best, what’s the actual science on it?❞
Before we get into these skincare products, let’s first note that for most people, what’s best for the skin is good sleep and hydration, a plants-centric whole foods diet, and good stress management:
See for example: Of Brains And Breakouts: The Brain Skin Doctor
However, the world of potions and lotions can be an alluring one, and there is some merit there too. So, in a nutshell:
- Retinoids are the overall class of chemicals, and not a specific type
- Retinoic acid is the strongest form of this chemical and is prescription-controlled in most places
- “Retinoin” is probably tretinoin (all-trans retinoic acid) with the “t” having falling off; we can only find it being used as a product name, not an actual substance
- Retinal, when it’s not an adjective referring to the retina (the part of the eye that receives refocussed light) and is instead a noun, is a less potent retinoid than the prescription-only kinds, but still stronger than retinol
- Retinol is a much less potent form, and is the most widely found in skincare products
- Retinoic acid is the strongest form of this chemical and is prescription-controlled in most places
All of them work the same way; it is only how serious they are about it that differs.
The mechanism of action is that they speed up the turnover (shedding cycle) of skin, so that cells are replaced sooner. As with any non-cancerous human tissue, this means that the tissue itself (in this case, your skin) will be biologically younger than if it had been replaced later.
The downside, of course, of this is that—while trying to make your skin healthier and more beautiful—the first thing that will happen is skin shedding. Depending on the retinoid type, dose, and the health of your skin to start with, this may mean anything from needing to exfoliate in the morning, to having to go to hospital with what looks like the world’s worst sunburn. For this reason, it is recommended to start with weaker products and lower doses, and work up carefully.
A note on doses: the recommended doses for these products are always truly tiny, like “use a pea-sized amount of this 0.05% serum on your face”. Take them seriously until you’re absolutely sure from experience that your skin can handle more.
Also, a tip: wear gloves when you apply any of the above products. This is because your fingers are also covered in skin, and if you don’t use gloves, then half the product that you intended for your face will be absorbed into your fingers instead.
You can learn more about the science of retinoids here, in our article about tretinoin, the usually prescription-only form of retinoic acid:
Tretinoin: Undo The Sun’s Damage To Your Skin
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product of retinal (stronger than retinol) on Amazon 😎
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Retinoids are the overall class of chemicals, and not a specific type