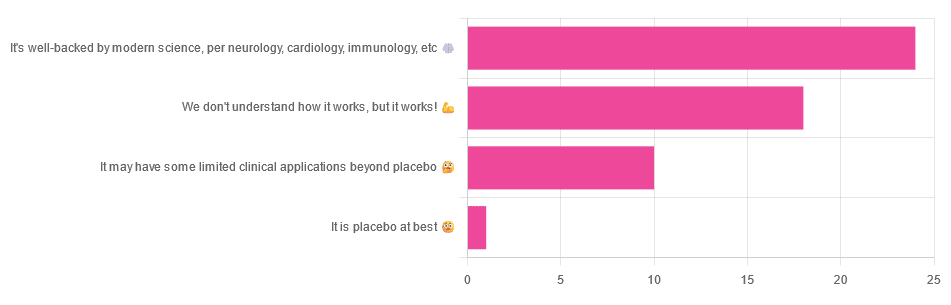
What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about how important fiber is:
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
And even how it’s arguably the most important dietary factor when it comes to avoiding heart disease:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure ← Spoiler: it’s fiber
And yes, that’s even when considered alongside other (also laudable) dietary interventions such as lowering intake of sodium, various kinds of saturated fat, and red meat.
So, what should we know about fiber, aside from “aim to get nearer 40g/day instead of the US average 16g/day”?
Soluble vs Insoluble
The first main way that dietary fibers can be categorized is soluble vs insoluble. Part of the difference is obvious, but bear with us, because there’s more to know about each:
- Soluble fiber dissolves (what a surprise) in water and, which part is important, forms a gel. This slows down things going through your intestines, which is important for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients (as well as avoiding diarrhea). Yes, you heard right: getting enough of the right kind of fiber helps you avoid diarrhea.
- Insoluble fiber does not dissolve (how shocking) in water and thus mostly passes through undigested by us (some will actually be digested by gut microbes who subsist on this, and in return for us feeding them daily, they make useful chemicals for us). This kind of fiber is also critical for healthy bowel movements, because without it, constipation can ensue.
Both kinds of fiber improve just about every metric related to blood, including improving triglycerides and improving insulin sensitivity and blood glucose levels. Thus, they help guard against various kinds of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic disease in general. Do note that because whatever’s good for your heart/blood is good for your brain (which requires a healthy heart and bloodstream to nourish it and take away waste), likely this also has a knock-on effect against cognitive decline, but we don’t have hard science for that claim so we’re going to leave that last item as a “likely”.
However, one thing’s for sure: if you want a healthy gut, heart, and brain, you need a good balance of soluble and insoluble fibers.
10 of the best for soluble fiber
| Food | Soluble Fiber Type(s) | Soluble Fiber (g per serving) | Insoluble Fiber Type(s) | Insoluble Fiber (g per serving) | Total Fiber (g per serving) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney beans (1 cup cooked) | Pectin, Resistant Starch | 1.5–2 | Hemicellulose, Cellulose | 6 | 8 |
| Lentils (1 cup cooked) | Pectin, Resistant Starch | 1.5–2 | Cellulose | 6 | 7.5 |
| Barley (1 cup cooked) | Beta-glucan | 3–4 | Hemicellulose | 2 | 6 |
| Brussels sprouts (1 cup cooked) | Pectin | 1–1.5 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 2 | 3.5 |
| Oats (1 cup cooked) | Beta-glucan | 2–3 | Cellulose | 1 | 3 |
| Apples (1 medium) | Pectin | 1–2 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 2 | 3 |
| Carrots (1 cup raw) | Pectin | 1–1.5 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 2 | 3 |
| Citrus fruits (orange, 1 medium) | Pectin | 1–1.5 | Cellulose | 1 | 2.5 |
| Flaxseeds (2 tbsp) | Mucilage, Lignin | 1–1.5 | Cellulose | 1 | 2.5 |
| Psyllium husk (1 tbsp) | Mucilage | 3–4 | Trace amounts | 0 | 3–4 |
10 of the best for insoluble fiber
| Food | Soluble Fiber Type(s) | Soluble Fiber (g per serving) | Insoluble Fiber Type(s) | Insoluble Fiber (g per serving) | Total Fiber (g per serving) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat bran (1 cup) | Trace amounts | 0 | Cellulose, Lignin | 6–8 | 6–8 |
| Black beans (1 cup cooked) | Pectin, Resistant Starch | 1.5 | Cellulose | 6 | 7.5 |
| Brown rice (1 cup cooked) | Trace amounts | 0.5 | Hemicellulose, Lignin | 2–3 | 2.5–3.5 |
| Popcorn (3 cups popped) | Trace amounts | 0.5 | Hemicellulose | 3 | 3.5 |
| Broccoli (1 cup cooked) | Pectin | 1 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 4 | 5 |
| Green beans (1 cup cooked) | Trace amounts | 0.5 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 3 | 3.5 |
| Sweet potatoes (1 cup cooked) | Pectin | 1–1.5 | Cellulose | 3 | 4.5 |
| Whole wheat bread (1 slice) | Trace amounts | 0.5 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 1 | 1.5 |
| Pears (1 medium) | Pectin | 1 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 4 | 5 |
| Almonds (1 oz) | Trace amounts | 0.5 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 2 | 2.5 |
10 of the best for a balance of both
| Food | Soluble Fiber Type(s) | Soluble Fiber (g per serving) | Insoluble Fiber Type(s) | Insoluble Fiber (g per serving) | Total Fiber (g per serving) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raspberries (1 cup) | Pectin | 1 | Cellulose | 5 | 6 |
| Edamame (1 cup cooked) | Pectin | 1 | Cellulose | 5 | 6 |
| Chia seeds (2 tbsp) | Mucilage, Pectin | 2–3 | Lignin, Cellulose | 3 | 5.5 |
| Artichokes (1 medium) | Inulin | 1 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 5 | 6 |
| Avocado (1 medium) | Pectin | ~2 | Cellulose | 4 | 6 |
| Black beans (1 cup cooked) | Pectin, Resistant Starch | 1.5 | Cellulose | 6 | 7.5 |
| Quinoa (1 cup cooked) | Pectin, Saponins | 1 | Cellulose, Hemicellulose | 3 | 4 |
| Spinach (1 cup cooked) | Pectin | 0.5 | Cellulose, Lignin | 3 | 3.5 |
| Prunes (1/2 cup) | Pectin, Sorbitol | 2 | Cellulose | 4 | 6 |
| Figs (3 medium) | Pectin | 1 | Cellulose | 2 | 3 |
You’ll notice that the above “balance” is not equal; that’s ok; we need greater quantities of insoluble than soluble anyway, so it is as well that nature provides such.
This is the same kind of balance when we talk about “balanced hormones” (does not mean all hormones are in equal amounts; means they are in the right proportions) or “balanced microbiome” (does not mean that pathogens and friendly bacteria are in equal numbers), etc.
Some notes on the above:
About those fiber types, some of the most important soluble ones to aim for are:
- Beta-glucan: found in oats and barley, it supports heart health.
- Pectin: found in fruits like apples, citrus, and pears, it helps with cholesterol control.
- Inulin: a type of prebiotic fiber found in artichokes.
- Lignin: found in seeds and wheat bran, it has antioxidant properties.
- Resistant starch: found in beans and lentils, it acts as a prebiotic for gut health.
See also: When Is A Fiber Not A Fiber? The Food Additive You Do Want
One fiber to rule them all
Well, not entirely (we still need the others) but there is a best all-rounder:
The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The “Love Drug”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Get PEA-Brained!
Today we’ll be looking at phenylethylamine, or PEA, to its friends.
Not to be mistaken for the related amino acid phenylalanine! Both ultimately have effects on the dopaminergic system, but the process and benefits are mostly quite different.
We thought we’d do this one in the week of Valentine’s Day, because of its popular association with love:
❝Phenylethylamine (PEA), an amphetamine-like substance that has been alluringly labeled the “chemical of love,” makes the best case for the love-chocolate connection since it has been shown that people in love may actually have higher levels of PEA in their brain, as surmised from the fact that their urine is richer in a metabolite of this compound. In other words, people thrashing around in the throes of love pee differently from others.❞
Source: Office for Science and Society | The Chemical of Love
What is it?
It’s an amino acid. Because we are mammals, we can synthesize it inside our bodies, so it’s not considered an “essential amino acid”, i.e. one that we need to get from our diet. It is found in some foods, though, including:
- Other animals, especially other mammals
- Various beans, legumes, nuts, seeds. In particular almonds, soybeans, lentils, and chickpeas score highly
- Fermented foods
- Chocolate (popular lore holds this to be a good source of PEA; science finds it to be a fair option, but not in the same ballpark as the other items)
Fun fact: the reason Marvel’s Venom has a penchant for eating humans and chocolate is (according to the comics) because phenylethylamine is an essential amino acid for it.
What does it do for us?
It’s a Central Nervous System (CNS) stimulant, and also helps us synthesize critical neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine (adrenaline) and serotonin:
It works similarly, but not identically, to amphetamines:
Is it safe?
We normally do this after the benefits, but “it works similarly to amphetamines” may raise an eyebrow or two, so let’s do it here:
- It is recommended to take no more than 500mg/day, with 100mg–500mg being typical doses
- It is not recommended to take it at all if you have, or have a predisposition to, any kind of psychotic disorder (especially schizophrenia, or bipolar disorder wherein you sometimes experience mania)
- This isn’t a risk for most people, but if you fall into the above category, the elevated dopamine levels could nudge you into a psychotic/manic episode that you probably don’t want.
See for example: Does phenylethylamine cause schizophrenia?
There are other contraindications too, so speak with your doctor/pharmacist before trying it.
On the other hand, if you are considering ADHD medication, then phenylethylamine could be a safer thing to try first, to see if it helps, before going to the heavy guns of actual amphetamines (as are commonly prescribed for ADHD). Same goes for depression and antidepressants.
What can I expect from PEA?
More dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Mostly the former two. Which means, you can expect stimulation.
For focus and attention, it’s so effective that it has been suggested (as we mentioned above) as a safer alternative to ADHD meds:
β-phenylethylamine, a small molecule with a large impact
…and may give similar benefits to people without ADHD, namely improved focus, attention, and mental stamina:
It also improves mood:
❝Phenylethylamine (PEA), an endogenous neuroamine, increases attention and activity in animals and has been shown to relieve depression in 60% of depressed patients. It has been proposed that PEA deficit may be the cause of a common form of depressive illness.
Effective dosage did not change with time. There were no apparent side effects. PEA produces sustained relief of depression in a significant number of patients, including some unresponsive to the standard treatments. PEA improves mood as rapidly as amphetamine but does not produce tolerance.❞
Source: Sustained antidepressant effect of PEA replacement
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it, but here is an example product on Amazon for your convenience 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
How Does One Test Acupuncture Against Placebo Anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
We asked you for your opinions on acupuncture, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of answers:
- A little under half of all respondents voted for “It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc”
- Slightly fewer respondents voted for “We don’t understand how it works, but it works!”
- A little under a fifth of respondents voted for “It may have some limited clinical applications beyond placebo”
- One (1) respondent voted for for “It’s placebo at best”
When we did a main feature about homeopathy, a couple of subscribers wrote to say that they were confused as to what homeopathy was, so this time, we’ll start with a quick definition first.
First, what is acupuncture? For the convenience of a quick definition so that we can move on to the science, let’s borrow from Wikipedia:
❝Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine in which thin needles are inserted into the body.
Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery.❞
Now, that’s not a promising start, but we will not be deterred! We will instead examine the science itself, rather than relying on tertiary sources like Wikipedia.
It’s worth noting before we move on, however, that there is vigorous debate behind the scenes of that article. The gist of the argument is:
- On one side: “Acupuncture is not pseudoscience/quackery! This has long been disproved and there are peer-reviewed research papers on the subject.”
- On the other: “Yes, but only in disreputable quack journals created specifically for that purpose”
The latter counterclaim is a) potentially a “no true Scotsman” rhetorical ploy b) potentially true regardless
Some counterclaims exhibit specific sinophobia, per “if the source is Chinese, don’t believe it”. That’s not helpful either.
Well, the waters sure are muddy. Where to begin? Let’s start with a relatively easy one:
It may have some clinical applications beyond placebo: True or False?
True! Admittedly, “may” is doing some of the heavy lifting here, but we’ll take what we can get to get us going.
One of the least controversial uses of acupuncture is to alleviate chronic pain. Dr. Vickers et al, in a study published under the auspices of JAMA (a very respectable journal, and based in the US, not China), found:
❝Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic pain and is therefore a reasonable referral option. Significant differences between true and sham acupuncture indicate that acupuncture is more than a placebo.
However, these differences are relatively modest, suggesting that factors in addition to the specific effects of needling are important contributors to the therapeutic effects of acupuncture❞
Source: Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis
If you’re feeling sharp today, you may be wondering how the differences are described as “significant” and “relatively modest” in the same text. That’s because these words have different meanings in academic literature:
- Significant = p<0.05, where p is the probability of the achieved results occurring randomly
- Modest = the differences between the test group and the control group were small
In other words, “significant modest differences” means “the sample sizes were large, and the test group reliably got slightly better results than placebo”
We don’t understand how it works, but it works: True or False
Broadly False. When it works, we generally have an idea how.
Placebo is, of course, the main explanation. And even in examples such as the above, how is placebo acupuncture given?
By inserting acupuncture needles off-target rather than in accord with established meridians and points (the lines and dots that, per Traditional Chinese Medicine, indicate the flow of qi, our body’s vital energy, and welling-points of such).
So, if a patient feels that needles are being inserted randomly, they may no longer have the same confidence that they aren’t in the control group receiving placebo, which could explain the “modest” difference, without there being anything “to” acupuncture beyond placebo. After all, placebo works less well if you believe you are only receiving placebo!
Indeed, a (Korean, for the record) group of researchers wrote about this—and how this confounding factor cuts both ways:
❝Given the current research evidence that sham acupuncture can exert not only the originally expected non-specific effects but also sham acupuncture-specific effects, it would be misleading to simply regard sham acupuncture as the same as placebo.
Therefore, researchers should be cautious when using the term sham acupuncture in clinical investigations.❞
Source: Sham Acupuncture Is Not Just a Placebo
It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc: True or False?
False, for the most part.
While yes, the meridians and points of acupuncture charts broadly correspond to nerves and vasculature, there is no evidence that inserting needles into those points does anything for one’s qi, itself a concept that has not made it into Western science—as a unified concept, anyway…
Note that our bodies are indeed full of energy. Electrical energy in our nerves, chemical energy in every living cell, kinetic energy in all our moving parts. Even, to stretch the point a bit, gravitational potential energy based on our mass.
All of these things could broadly be described as qi, if we so wish. Indeed, the ki in the Japanese martial art of aikido is the latter kinds; kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy based on our mass. Same goes, therefore for the ki in kiatsu, a kind of Japanese massage, while the ki in reiki, a Japanese spiritual healing practice, is rather more mystical.
The qi in Chinese qigong is mostly about oxygen, thus indirectly chemical energy, and the electrical energy of the nerves that are receiving oxygenated blood at higher or lower levels.
On the other hand, the efficacy of the use of acupuncture for various kinds of pain is well-enough evidenced. Indeed, even the UK’s famously thrifty NHS (that certainly would not spend money on something it did not find to work) offers it as a complementary therapy for some kinds of pain:
❝Western medical acupuncture (dry needling) is the use of acupuncture following a medical diagnosis. It involves stimulating sensory nerves under the skin and in the muscles.
This results in the body producing natural substances, such as pain-relieving endorphins. It’s likely that these naturally released substances are responsible for the beneficial effects experienced with acupuncture.❞
Source: NHS | Acupuncture
Meanwhile, the NIH’s National Cancer Institute recommends it… But not as a cancer treatment.
Rather, they recommend it as a complementary therapy for pain management, and also against nausea, for which there is also evidence that it can help.
Frustratingly, while they mention that there is lots of evidence for this, they don’t actually link the studies they’re citing, or give enough information to find them. Instead, they say things like “seven randomized clinical trials found that…” and provide links that look reassuring until one finds, upon clicking on them, that it’s just a link to the definition of “randomized clinical trial”:
Source: NIH | Nactional Cancer Institute | Acupuncture (PDQ®)–Patient Version
However, doing our own searches finds many studies (mostly in specialized, potentially biased, journals such as the Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies) finding significant modest outperformance of [what passes for] placebo.
Sometimes, the existence of papers with promising titles, and statements of how acupuncture might work for things other than relief of pain and nausea, hides the fact that the papers themselves do not, in fact, contain any evidence to support the hypothesis. Here’s an example:
❝The underlying mechanisms behind the benefits of acupuncture may be linked with the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (adrenal) axis and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin and OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathways.
In summary, strong evidence may still come from prospective and well-designed clinical trials to shed light on the potential role of acupuncture in preserving bone loss❞
Source: Acupuncture for Osteoporosis: a Review of Its Clinical and Preclinical Studies
So, here they offered a very sciencey hypothesis, and to support that hypothesis, “strong evidence may still come”.
“We must keep faith” is not usually considered evidence worthy of inclusion in a paper!
PS: the above link is just to the abstract, because the “Full Text” link offered in that abstract leads to a completely unrelated article about HIV/AIDS-related cryptococcosis, in a completely different journal, nothing to do with acupuncture or osteoporosis).
Again, this is not the kind of professionalism we expect from peer-reviewed academic journals.
Bottom line:
Acupuncture reliably performs slightly better than sham acupuncture for the management of pain, and may also help against nausea.
Beyond placebo and the stimulation of endorphin release, there is no consistently reliable evidence that is has any other discernible medical effect by any mechanism known to Western science—though there are plenty of hypotheses.
That said, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, and the logistical difficulty of testing acupuncture against placebo makes for slow research. Maybe one day we’ll know more.
For now:
- If you find it helps you: great! Enjoy
- If you think it might help you: try it! By a licensed professional with a good reputation, please.
- If you are not inclined to having needles put in you unnecessarily: skip it! Extant science suggests that at worst, you’ll be missing out on slight relief of pain/nausea.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
A Tale Of Two Cinnamons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cinnamon’s Health Benefits (But Watch Out!)
Cinnamon is enjoyed for its sweet and punchy flavor. It also has important health properties!
Let’s take a look at the science…
A Tale Of Two Cinnamons
In your local supermarket, there is likely “cinnamon” and if you’re lucky, also “sweet cinnamon”. The difference between these is critical to understand before we continue:
“Cinnamon” = Cinnamomum cassia or Cinnamomum aromaticum. This is cheapest and most readily available. It has a relatively high cinnamaldehyde content, and a high coumarin content.
“Sweet cinnamon” Cinnamomum verum or Cinnamomum zeylanicum. It has a lower cinnamaldehyde content, and/but a much lower (almost undetectable) coumarin content.
You may be wondering: what’s with the “or” in both of those cases? Each simply has two botanical names in use. It’s inconvenient and confusing, but that’s how it is.
Great! What’s cinnamaldehyde and what’s coumarin?
Cinnamaldehyde is what gives cinnamon its “spice” aspect; it’s strong and fragrant. It also gives cinnamon most of its health benefits.
As a quick aside: it’s also used as the flavoring element in cinnamon flavored vapes, and in that form, it can cause health problems. So do eat it, but we recommend not to vape it.
Coumarin is toxic in large quantities.
The recommended safe amount is 0.1mg/kg, so you could easily go over this with a couple of teaspoons of cassia cinnamon:
Toxicology and risk assessment of coumarin: focus on human data
…while in Sweet/True/Ceylon cinnamon, those levels are almost undetectable:
Medicinal properties of ‘true’ cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum): a systematic review
If you have a cinnamon sensitivity, it is likely, but not necessarily, tied to the coumarin content rather than the cinnamaldehyde content.
Summary of this section before moving on:
“Cinnamon”, or cassia cinnamon, has about 50% stronger health benefits than “Sweet Cinnamon”, also called Ceylon cinnamon.
“Cinnamon”, or cassia cinnamon, has about 250% stronger health risks than “Sweet Cinnamon”, also called Ceylon cinnamon.
The mathematics here is quite simple; sweet cinnamon is the preferred way to go.
The Health Benefits
We spent a lot of time/space today looking at the differences. We think this was not only worth it, but necessary. However, that leaves us with less time/space for discussing the actual benefits. We’ll summarize, with links to supporting science:
“Those three things that almost always go together”:
Heart and blood benefits:
- Reduces triglyceride levels
- Reduces high blood pressure
- Reduces insulin insensitivity
- Reduces fasting blood sugar levels
Neuroprotective benefits:
The science does need more testing in these latter two, though.
Where to get it?
You may be able to find sweet cinnamon in your local supermarket, or if you prefer capsule form, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
10 Tips To Reduce Morning Pain & Stiffness With Arthritis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Physiotherapist and osteoarthritis specialist Dr. Alyssa Kuhn has professional advice:
Just the tips
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Perform movements that target the range of motion in stiff joints, especially in knees and hips, to prevent them from being stuck in limited positions overnight.
- Use relaxation techniques like a hot shower, heating pad, or light reading before bed to reduce muscle tension and stiffness upon waking.
- Manage joint swelling during the day through gentle movement, compression sleeves, and self-massage .
- Maintain a balanced level of activity throughout the day to avoid excessive stiffness from either overactivity or, on the flipside, prolonged inactivity.
- Use pillows to support joints, such as placing one between your knees for hip and knee arthritis, and ensure you have a comfortable pillow for neck support.
- Eat anti-inflammatory foods prioritizing fruits and vegetables to reduce joint stiffness, and avoid foods high in added sugar, trans-fats, and saturated fats.
- Perform simple morning exercises targeting stiff areas to quickly relieve stiffness and ease into your daily routine.
- Engage in strength training exercises 2–3 times per week to build stronger muscles around the joints, which can reduce stiffness and pain.
- Ensure you get 7–8 hours of restful sleep, as poor sleep can increase stiffness and pain sensitivity the next day. 10almonds note: we realize there’s a degree of “catch 22” here, but we’re simply reporting her advice. Of course, do what you can to prioritize being able to get the best quality sleep you can.
- Perform gentle movements or stretches before bed to keep joints limber, focusing on exercises that feel comfortable and soothing.
For more on each of these plus some visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis
- Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Easy Ways To Fix Brittle, Dry, Wiry Hair
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Sam Ellis, a dermatologist, specializes in skin, hair, and nail care—and she’s here with professional knowledge:
Tackling the problem at the root
As we age, hair becomes less shiny, more brittle, coarse, wiry, or gray. More concerningly for many, hair thinning and shedding increases due to shortened growth phases and hormonal changes.
The first set of symptoms there are largely because sebum production decreases, leading to dry hair. It’s worth bearing in mind though, that factors like UV radiation, smoking, stress, and genetics contribute to hair aging too. So while we can’t do much about genetics, the modifiable factors are worth addressing.
Menopause and the corresponding “andropause” impact hair health, and hormonal shifts, not just aging, drive many hair changes. Which is good to know, because it means that HRT (mostly: topping up estrogen or testosterone as appropriate) can make a big difference. Additionally, topical/oral minoxidil and DHT blockers (such as finasteride or dutasteride) can boost hair density. These things come with caveats though, so do research any possible treatment plan before embarking on it, to be sure you are comfortable with all aspects of it—including that if you use minoxidil, while on the one hand it indeed works wonders, on the other hand, you’ll then have to keep using minoxidil for the rest of your life or your hair will fall out when you stop. So, that’s a commitment to be thought through before beginning.
Nutritional deficiencies (iron, zinc, vitamin D) and insufficient protein intake hinder hair growth, so ensure proper nutrition, with sufficient protein and micronutrients.
While we’re on the topic of “from the inside” things: take care to manage stress healthily, as stress negatively affects hair health.
Now, as for “from the outside”…
Dr. Ellis recommends moisturizing shampoos/conditioners; Virtue and Dove brands she mentions positively. She also recommends bond repair products (such as K18 and Olaplex) that restore hair integrity, and heat protectants (she recommends: Unite 7 Seconds) as well as hair oils in general that improve hair condition.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Change – by Katy Milkman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes it seems that we know everything we should be doing… We have systems and goals and principles, we know about the importance of habits, and we do our best to live them. Yet, somehow, life has other plans for us and things don’t quite come together they way they did in our genius masterplan.
So, what happened? And more importantly, what are we supposed to do about this? Katy Milkman has answers, right from the start.
Sometimes, it can be as simple as when we try to implement a change. It’s not that there’s a “wrong time” for a good change, so much that there are times that are much more likely to succeed than others… and those times can be identified and used.
Sometimes we’re falling prey to vices—which she explains how to overcome—such as:
- Impulsivity
- Procrastination
- Forgetfulness
- Laziness
We also learn some counterintuitive truths about what can boost or sabotage our confidence along the way!
Milkman writes in a compelling, almost narrative style, that makes for very easy reading. The key ideas, built up to by little (ostensibly true) stories and then revealed, become both clear and memorable. Most importantly, applicable.
Bottom line: this is a great troubleshooting guide for when you know how everything should be working, but somehow, it just doesn’t—and you’d like to fix that.
Click here to check out “How To Change” on Amazon, and get those changes rolling!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: