Will there soon be a cure for HIV?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, is a chronic health condition that can be fatal without treatment. People with HIV can live healthy lives by taking antiretroviral therapy (ART), but this medication must be taken daily in order to work, and treatment can be costly. Fortunately, researchers believe a cure is possible.
In July, a seventh person was reportedly cured of HIV following a 2015 stem cell transplant for acute myeloid leukemia. The patient stopped taking ART in 2018 and has remained in remission from HIV.
Read on to learn more about HIV, the promise of stem cell transplants, and what other potential cures are on the horizon.
What is HIV?
HIV infects and destroys the immune system’s cells, making people more susceptible to infections. If left untreated, HIV will severely impair the immune system and progress to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). People living with untreated AIDS typically die within three years.
People with HIV can take ART to help their immune systems recover and to reduce their viral load to an undetectable level, which slows the progression of the disease and prevents them passing the virus to others.
How can stem cell transplants cure HIV?
Several people have been cured of HIV after receiving stem cell transplants to treat leukemia or lymphoma. Stem cells are produced by the spongy tissue located in the center of some bones, and they can turn into new blood cells.
A mutation on the CCR5 gene prevents HIV from infecting new cells and creates resistance to the virus, which is why some HIV-positive people have received stem cells from donors carrying this mutation. (One person was reportedly cured of HIV after receiving stem cells without the CCR5 mutation, but further research is needed to understand how this occurred.)
Despite this promising news, experts warn that stem cell transplants can be fatal, so it’s unlikely this treatment will be available to treat people with HIV unless a stem cell transplant is needed to treat cancer. People with HIV are at an increased risk for blood cancers, such as Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which stem cell transplants can treat.
Additionally, finding compatible donors with the CCR5 mutation who share genetic heritage with patients of color can be challenging, as donors with the mutation are typically white.
What are other potential cures for HIV?
In some rare cases, people who started ART shortly after infection and later stopped treatment have maintained undetectable levels of HIV in their bodies. There have also been some people whose bodies have been able to maintain low viral loads without any ART at all.
Researchers are studying these cases in their search for a cure.
Other treatment options researchers are exploring include:
- Gene therapy: In addition to stem cell transplants, gene therapy for HIV involves removing genes from HIV particles in patients’ bodies to prevent the virus from infecting other cells.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment is typically used in cancer patients to teach their immune systems how to fight off cancer. Research has shown that giving some HIV patients antibodies that target the virus helps them reach undetectable levels of HIV without ART.
- mRNA technology: mRNA, a type of genetic material that helps produce proteins, has been used in vaccines to teach cells how to fight off viruses. Researchers are seeking a way to send mRNA to immune system cells that contain HIV.
When will there be a cure for HIV?
The United Nations and several countries have pledged to end HIV and AIDS by 2030, and a 2023 UNAIDS report affirmed that reaching this goal is possible. However, strategies to meet this goal include HIV prevention and improving access to existing treatment alongside the search for a cure, so we still don’t know when a cure might be available.
How can I find out if I have HIV?
You can get tested for HIV from your primary care provider or at your local health center. You can also purchase an at-home HIV test from a drugstore or online. If your at-home test result is positive, follow up with your health care provider to confirm the diagnosis and get treatment.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pear vs Peach – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pears to peaches, we picked the peaches.
Why?
Both are great! But peaches are exceptional in some ways that pears just can’t match up to:
In terms of macros, pears have more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which results in an approximately equal glycemic index. Thus, we’ll say that pears win this round by virtue of being the nutritionally denser option.
Looking at the vitamins, pears have (slightly) more of vitamins B6, B9, and K, while peaches have (much) more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, C, E, and choline—thus sweeping this category easily for peaches.
In the category of minerals, pears have more calcium and copper, while peaches have more iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. This time, the margins of difference for each mineral are comparably low (i.e. pears are close behind peaches on all those minerals), but still, by strength of numbers, it’s a clear win for peaches.
When it comes to polyphenols, not only do peaches have more, but also, they have anticancer properties that pears don’t—see our link below for more about that!
Meanwhile, adding up the sections makes for an overall win for peaches, but as ever when it comes to fruits, by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← peaches in the #2 spot! They induce cell death in cancer cells while sparing healthy ones
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Could my glasses be making my eyesight worse?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So, you got your eyesight tested and found out you need your first pair of glasses. Or you found out you need a stronger pair than the ones you have. You put them on and everything looks crystal clear. But after a few weeks things look blurrier without them than they did before your eye test. What’s going on?
Some people start to wear spectacles for the first time and perceive their vision is “bad” when they take their glasses off. They incorrectly interpret this as the glasses making their vision worse. Fear of this might make them less likely to wear their glasses.
But what they are noticing is how much better the world appears through the glasses. They become less tolerant of a blurry world when they remove them.
Here are some other things you might notice about eyesight and wearing glasses.
Lazy eyes?
Some people sense an increasing reliance on glasses and wonder if their eyes have become “lazy”.
Our eyes work in much the same way as an auto-focus camera. A flexible lens inside each eye is controlled by muscles that let us focus on objects in the distance (such as a footy scoreboard) by relaxing the muscle to flatten the lens. When the muscle contracts it makes the lens steeper and more powerful to see things that are much closer to us (such as a text message).
From the age of about 40, the lens in our eye progressively hardens and loses its ability to change shape. Gradually, we lose our capacity to focus on near objects. This is called “presbyopia” and at the moment there are no treatments for this lens hardening.
Optometrists correct this with prescription glasses that take the load of your natural lens. The lenses allow you to see those up-close images clearly by providing extra refractive power.
Once we are used to seeing clearly, our tolerance for blurry vision will be lower and we will reach for the glasses to see well again.
The wrong glasses?
Wearing old glasses, the wrong prescription (or even someone else’s glasses) won’t allow you to see as well as possible for day-to-day tasks. It could also cause eyestrain and headaches.
Incorrectly prescribed or dispensed prescription glasses can lead to vision impairment in children as their visual system is still in development.
But it is more common for kids to develop long-term vision problems as a result of not wearing glasses when they need them.
By the time children are about 10–12 years of age, wearing incorrect spectacles is less likely to cause their eyes to become lazy or damage vision in the long term, but it is likely to result in blurry or uncomfortable vision during daily wear.
Registered optometrists in Australia are trained to assess refractive error (whether the eye focuses light into the retina) as well as the different aspects of ocular function (including how the eyes work together, change focus, move around to see objects). All of these help us see clearly and comfortably.
Younger children with progressive vision impairments may need more frequent eye tests. Shutterstock What about dirty glasses?
Dirty or scratched glasses can give you the impression your vision is worse than it actually is. Just like a window, the dirtier your glasses are, the more difficult it is to see clearly through them. Cleaning glasses regularly with a microfibre lens cloth will help.
While dirty glasses are not commonly associated with eye infections, some research suggests dirty glasses can harbour bacteria with the remote but theoretical potential to cause eye infection.
To ensure best possible vision, people who wear prescription glasses every day should clean their lenses at least every morning and twice a day where required. Cleaning frames with alcohol wipes can reduce bacterial contamination by 96% – but care should be taken as alcohol can damage some frames, depending on what they are made of.
When should I get my eyes checked?
Regular eye exams, starting just before school age, are important for ocular health. Most prescriptions for corrective glasses expire within two years and contact lens prescriptions often expire after a year. So you’ll need an eye check for a new pair every year or so.
Kids with ocular conditions such as progressive myopia (short-sightedness), strabismus (poor eye alignment), or amblyopia (reduced vision in one eye) will need checks at least every year, but likely more often. Likewise, people over 65 or who have known eye conditions, such as glaucoma, will be recommended more frequent checks.
Eye checks can detect broader health issues. Shutterstock An online prescription estimator is no substitute for a full eye examination. If you have a valid prescription then you can order glasses online, but you miss out on the ability to check the fit of the frame or to have them adjusted properly. This is particularly important for multifocal lenses where even a millimetre or two of misalignment can cause uncomfortable or blurry vision.
Conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure, can affect the eyes so regular eye checks can also help flag broader health issues. The vast majority of eye conditions can be treated if caught early, highlighting the importance of regular preventative care.
James Andrew Armitage, Professor of Optometry and Course Director, Deakin University and Nick Hockley, Lecturer in Optometric Clinical Skills, Director Deakin Collaborative Eye Care Clinic, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How Metformin Slows Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Metformin And How It Slows Down Aging
That’s a bold claim for a title, but the scientific consensus is clear, and this Research Review Monday we’re going to take a look at exactly that!
Metformin is a common diabetes-management drug, used to lower blood sugar levels in people who either don’t have enough insulin or the insulin isn’t being recognized well enough by the body.
However, it also slows aging, which is a quality it’s also been studied for for more than a decade. We’ll look at some of the more recent research, though. Let’s kick off with an initial broad statement, from the paper “The Use of Metformin to Increase the Human Healthspan”, as part of the “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology” series:
In recent years, more attention has been paid to the possibility of using metformin as an anti-aging drug. It was shown to significantly increase the lifespan in some model organisms and delay the onset of age-associated declines. Growing amounts of evidence from clinical trials suggest that metformin can effectively reduce the risk of many age-related diseases and conditions, including cardiometabolic disorders, neurodegeneration, chronic inflammation and frailty.
How does it work?
That’s still being studied, but the scientific consensus is that it works by inducing hormesis—the process by which minor stress signals cells to start repairing themselves. How does it induce that hormesis? Again, still being studied, but it appears to do it by activating a specific enzyme; namely, the AMP-activated protein kinase:
Read: Metformin-enhances resilience via hormesis
It also has been found to slow aging by means of an anti-inflammatory effect, as a bonus!
Any bad news?
Well, firstly, in most places it’s only prescribed for diabetes management, not for healthy life extension. A lot of anti-aging enthusiasts have turned to the grey market online to get it, and we can’t recommend that.
Secondly, it does have some limitations:
- Its bioavailability isn’t great in tablet form (the form in which it is most commonly given)
- It has quite a short elimination half-life (around 6 hours), which makes it great to fix transient hyperglycemia in diabetics—job done and it’s out—but presents a logistical challenge when it comes to something so pernicious as aging.
- Some people are non-responders (a non-responder, in medicine, is someone for whom a drug simply doesn’t work, for no obvious reason)
Want to know more? Check out:
Metformin in aging and aging-related diseases: clinical applications and relevant mechanism
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
This Is Your Brain on Food – by Dr. Uma Naidoo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Diet will fix your brain” is a bold claim that often comes from wishful thinking and an optimistic place where anecdote is louder than evidence. But, diet does incontrovertibly also affect brain health. So, what does Dr. Naidoo bring to the table?
The author is a Harvard-trained psychiatrist, a professional chef who graduated with her culinary school’s most coveted award, and a trained-and-certified nutritionist. Between those three qualifications, it’s safe to she knows her stuff when it comes to the niche that is nutritional psychiatry. And it shows.
She takes us through the neurochemistry involved, what chemicals are consumed, made, affected, inhibited, upregulated, etc, what passes through the blood-brain barrier and what doesn’t, what part the gut really plays in its “second brain” role, and how we can leverage that—as well as mythbusting a lot of popular misconceptions about certain foods and moods.
There’s hard science in here, but presented in quite a pop-science way, making for a very light yet informative read.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand what your food is doing to your brain (and what it could be doing instead), then this is a top-tier book for you!
Click here to check out This Is Your Brain On Food, and get to know yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Non-Alcohol Mouthwash vs Alcohol Mouthwash – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing non-alcohol mouthwash to alcohol mouthwash, we picked the alcohol.
Why?
Note: this is a contingent choice and is applicable to most, but not all, people.
In short, there has been some concern about alcohol mouthwashes increasing cancer risk, but research has shown this is only the case if you already have an increased risk of oral cancer (for example if you smoke, and/or have had an oral cancer before).
For those for whom this is not the case (for example, if you don’t smoke, and/or have no such cancer history), then best science currently shows that alcohol mouthwash does not cause any increased risk.
What about non-alcohol mouthwashes? Well, they have a different problem; they usually use chlorine-based chemicals like chlorhexidine or cetylpyridinium chloride, which are (exactly as the label promises) exceptionally good at killing oral bacteria.
(They’d kill us too, at higher doses, hence: swill and spit)
Unfortunately, much like the rest of our body, our mouth is supposed to have bacteria there and bad things happen when it doesn’t. In the case of our oral microbiome, cleaning it with such powerful antibacterial agents can kill our “good” bacteria along with the bad, which lowers the pH of our saliva (that’s bad; it means it is more acidic), and thus indirectly erodes tooth enamel.
You can read more about the science of all of the above (with references), here:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
Summary:
For most people, alcohol mouthwashes are a good way to avoid the damage that can be done by chlorhexidine in non-alcohol mouthwashes.
Here are some examples, but there will be plenty in your local supermarket:
Non-Alcohol, by Colgate | Alcohol, by Listerine
If you have had oral cancer, or if you smoke, then you may want to seek a third alternative (and also, please, stop smoking if you can).
Or, really, most people could probably skip mouthwashes, if you’ve good oral care already by other means. See also:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
(yes, it’s the same link as before, but we’re now drawing your attention to the fact it has information about toothpastes too)
If you do want other options though, might want to check out:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← miswak sticks are especially effective
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
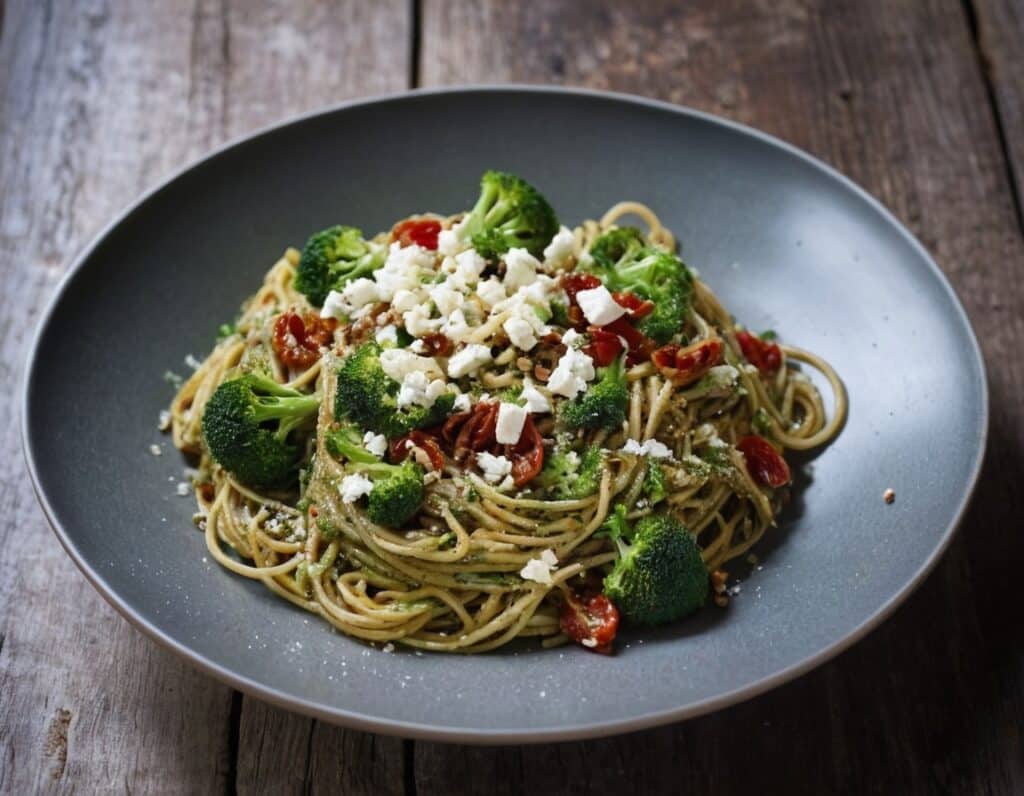
Gut-Healthy Spaghetti Chermoula
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chermoula is a Maghreb relish/marinade (it’s used for both purposes); it’s a little like chimichurri but with distinctly N. African flavors. The gut-healthiness starts there (it’s easy to forget that olives—unless fresh—are a fermented food full of probiotic Lactobacillus sp. and thus great for the gut even beyond their fiber content), and continues in the feta, the vegetables, and the wholewheat nature of the pasta. The dish can be enjoyed at any time, but it’s perfect for warm summer evenings—perhaps dining outside, if you’ve place for that.
You will need
- 9oz wholewheat spaghetti (plus low-sodium salt for its water)
- 10oz broccoli, cut into small florets
- 3oz cilantro (unless you have the soap gene)
- 3oz parsley (whether or not you included the cilantro)
- 3oz green olives, pitted, rinsed
- 1 lemon, pickled, rinsed
- 1 bulb garlic
- 3 tbsp pistachios, shelled
- 2 tbsp mixed seeds
- 1 tsp cumin
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- ½ cup extra virgin olive oil
- For the garnish: 3oz feta (or plant-based equivalent), crumbled, 3oz sun-dried tomatoes, diced, 1 tsp cracked black pepper
Note: why are we rinsing the things? It’s because while picked foods are great for the gut, the sodium can add up, so there’s no need to bring extra brine with them too. By doing it this way, there’ll be just the right amount for flavor, without overdoing it.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the spaghetti as you normally would, but when it’s a minute or two from being done, add the broccoli in with it. When it’s done, drain and rinse thoroughly to get rid of excess starch and salt, and also because cooling it even temporarily (as in this case) lowers its glycemic index.
2) Put the rest of the ingredients into a food processor (except the olive oil and the garnish), and blitz thoroughly until no large coarse bits remain. When that’s done, add the olive oil, and pulse it a few times to combine. We didn’t add the olive oil previously, because blending it so thoroughly in that state would have aerated it in a way we don’t want.
3) Put ⅔ of the chermoula you just made into the pan you used for cooking the spaghetti, and set it over a medium heat. When it starts bubbling, return the spaghetti and broccoli to the pan, mixing gently but thoroughly. If the pasta threatens to stick, you can add a little more chermoula, but go easy on it. Any leftover chermoula that you didn’t use today, can be kept in the fridge and used later as a pesto.
4) Serve! Add the garnish as you do.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Less Obvious Probiotics Benefits
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- What Matters Most For Your Heart? ← spoiler: this is why, while we do watch the sodium, we care more about the fiber
- All about Olive Oil: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: