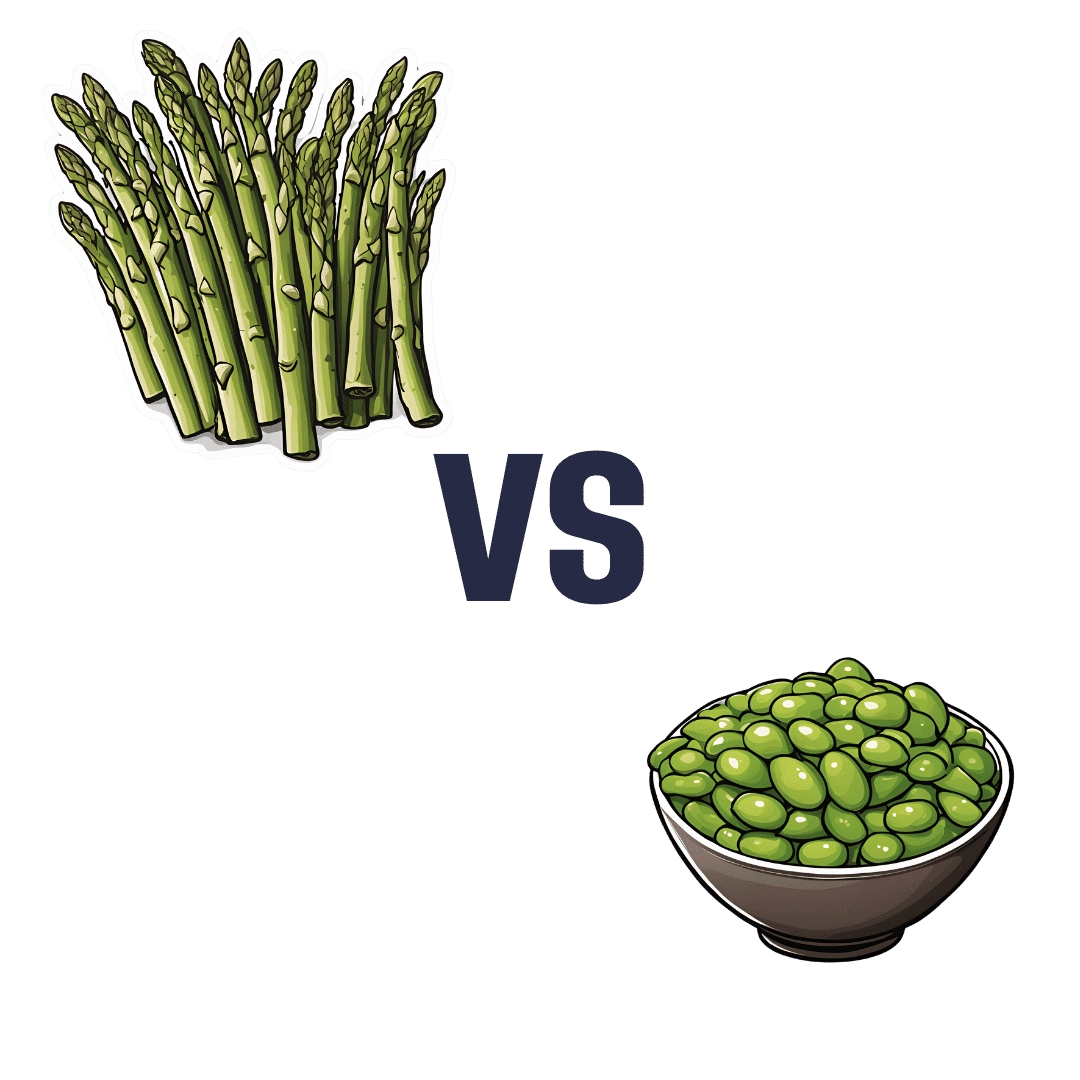
Asparagus vs Edamame – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing asparagus to edamame, we picked the edamame.
Why?
Perhaps it’s a little unfair comparing a legume to a vegetable that’s not leguminous (given legumes’ high protein content), but these two vegetables often serve a similar culinary role, and there is more to nutrition than protein. That said…
In terms of macros, edamame has a lot more protein and fiber; it also has more carbs, but the ratio is such that edamame still has the lower glycemic index. Thus, the macros category is a win for edamame in all relevant aspects.
When it comes to vitamins, things are a little closer; asparagus has more of vitamins A, B3, and C, while edamame has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and B9. All in all, a moderate win for edamame, unless we want to consider the much higher vitamin C content of asparagus as particularly more relevant.
In the category of minerals, asparagus boasts only more selenium (and more sodium, not that that’s a good thing for most people in industrialized countries), while edamame has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. An easy win for edamame.
In short, enjoy both (unless you have a soy allergy, because edamame is young soy beans), but edamame is the more nutritionally dense by far.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Fruit & Veg In The Fridge: Pros & Cons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What effect does refrigeration have on the nutritional value of fruit and vegetables??❞
It’s difficult to give a single definitive answer, because naturally there are a lot of different fruits and vegetables, and a lot of different climates. The answer may be different for tomatoes in Alaska vs bananas in Arizona!
However, we can still generalize at least somewhat
Refrigeration will generally slow down any degradation process, and in the case of fruit and vegetables, that can mean slowing down their “ripening” too, as applicable.
However…
Refrigeration will also impede helpful bioactivity too, and that includes quite a list of things.
Here’s a good study that’s quite illustrative; we’d summarize the conclusions but the rather long title already does that nicely:
So, this really is a case of “there are pros and cons, but probably more cons on balance”.
In practical terms, a good take-away from this can be twofold:
- don’t keep fruit and veg in the fridge unless the ambient temperature really requires it
- if the ambient temperature does require it, it’s best to get the produce in fresh each day if that’s feasible, to minimize time spent in the fridge
An extra thing not included there: often when it comes to the spoilage of fruit and veg, the problem is that it respires and oxidizes; reducing the temperature does lower the rate of those, but often a far better way is to remove the oxygen. So for example, if you get carried away and chop too many carrot batons for your hummus night, then putting them in a sealed container can go a long way to keeping them fresh.
See also: How Does the Nutritional Value of Fruits and Vegetables Change Over Time?
Enjoy!
Share This Post

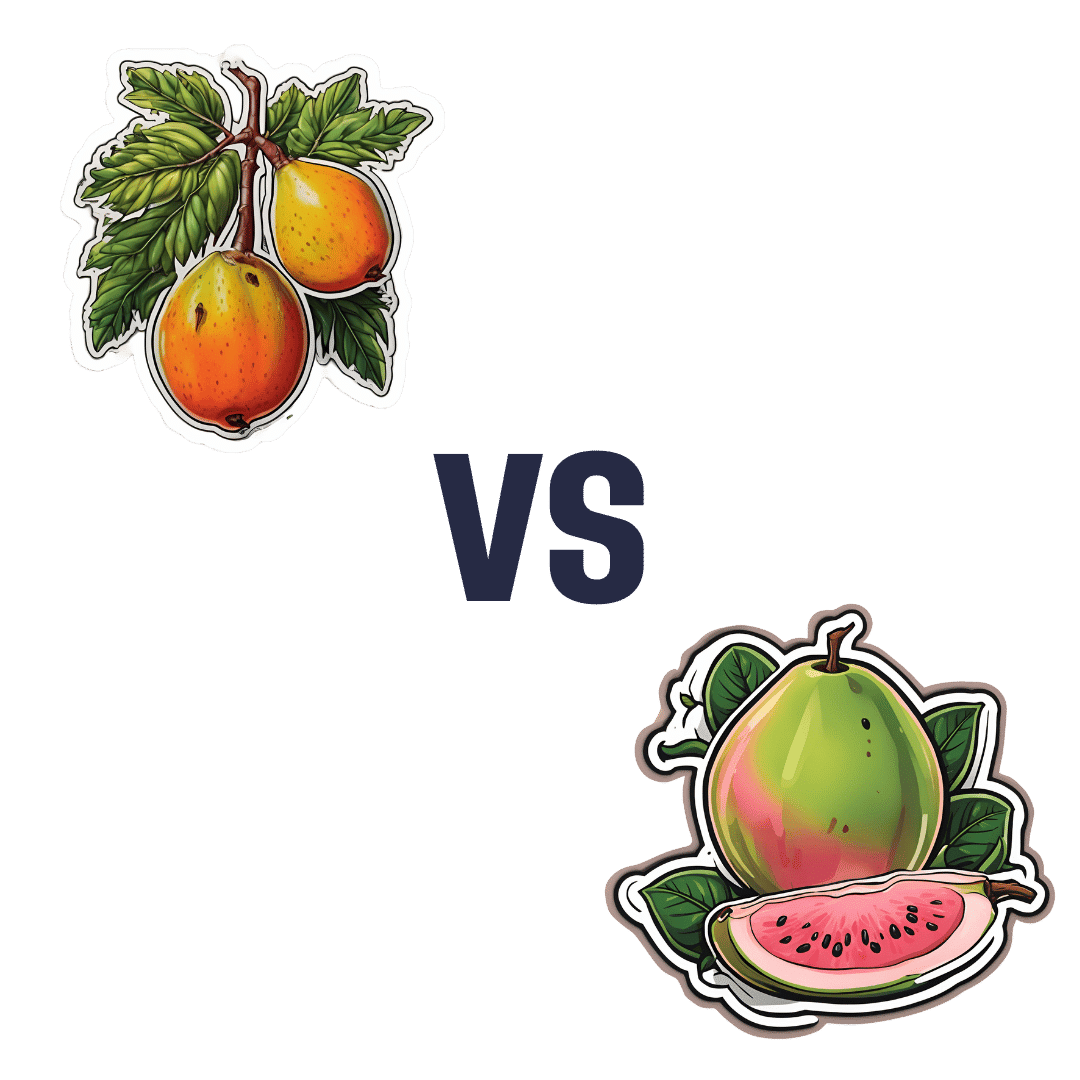
Mango vs Guava – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mango to guava, we picked the guava.
Why?
Looking at macros first, these two fruits are about equal on carbs (nominally mango has more, but it’s by a truly tiny margin), while guava has more than 3x the protein and more than 3x the fiber. A clear win for guava.
In terms of vitamins, mango has more of vitamins A, E, and K, while guava has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, B9, and C. Another win for guava.
In the category of minerals, mango is not higher in any minerals, while guava is higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc.
In short, enjoy both; both are healthy. But if you’re choosing one, there’s a clear winner here, and it’s guava.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Share This Post

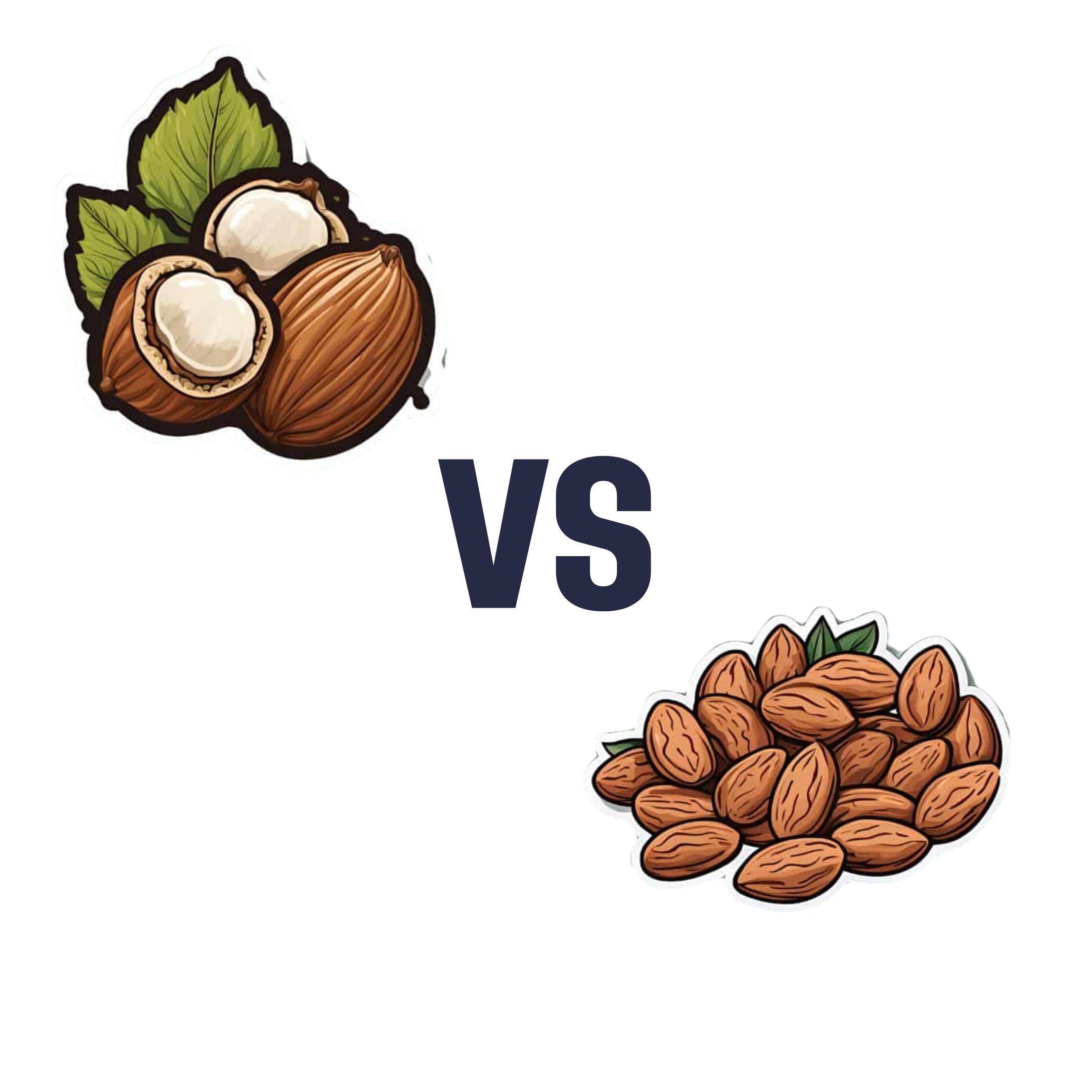
Hazelnuts vs Almonds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hazelnuts to almonds, we picked the almonds.
Why?
It’s closer than you might think! But we say almonds do come out on top.
In terms of macronutrients, almonds have notably more protein, while hazelnuts have notably more fat (healthy fats, though). Almonds are also higher in both carbs and fiber. Looking at Glycemic Index, hazelnuts’ GI is low and almonds’ GI is zero. We could call the macros category a tie, but ultimately if we need to prioritize any of these things, it’s protein and fiber, so we’ll call this a nominal win for almonds.
When it comes to vitamins, hazelnuts have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, B9 C, and K. Meanwhile, almonds have more of vitamins B2, B3, E, and choline. So, a moderate win for hazelnuts.
In the category of minerals, almonds retake the lead with more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while hazelnuts boast more copper and manganese. A clear win for almonds.
Adding up the categories, this makes for a marginal win for almonds. Of course, both of these nuts are very healthy (assuming you are not allergic), and best is to enjoy both if possible.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts

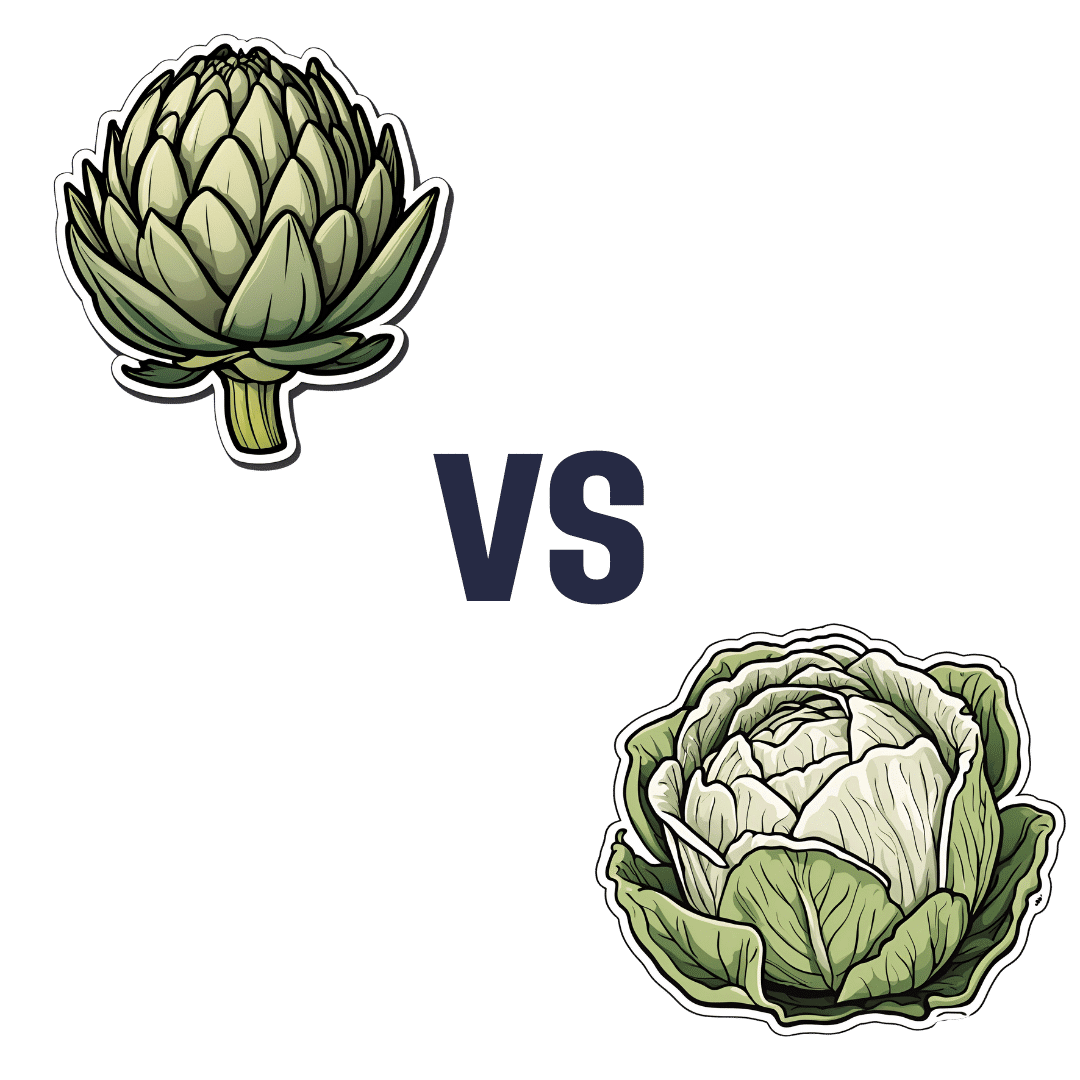
Artichoke vs Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing artichoke to cabbage, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Looking at the macros first of all, artichoke has more than 2x the protein; it also has nearly 2x the carbs, but to more than counterbalance that, it has more than 2x the fiber. An easy win for artichoke in the macros category.
In the category of vitamins, both are very respectable; artichoke has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B9, E, and choline, while cabbage has more of vitamins A, C, and K. Superficially, that’s a 7:3 win for artichoke, but the margins of difference for artichoke’s vitamins are very small (meaning cabbage is hot on its heels for those vitamins), whereas cabbage’s A, C, and K are with big margins of difference (3–7x more), and arguably those vitamins are higher priority in the sense that B-vitamins of various kinds are found in most foods, whereas A, C, and K aren’t, and while E isn’t either, artichoke had a tiny margin of difference for that. All in all, we’re calling this category a tie, as an equally fair argument could be made for either vegetable here.
When it comes to minerals, there’s a much clearer winner: artichoke has a lot more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while cabbage has a tiny bit more selenium. The two vegetables are equal on calcium.
Adding up two clear artichoke wins and a tie, makes for an overall clear win for artichoke. Of course, enjoy both though; diversity is almost always best of all!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Breaking Free from Emotional Eating – Geneen Roth
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The isn’t a book about restrictive dieting, or even willpower. Rather, it’s about making the unconscious conscious, and changing your relationship with food from being one of compulsion, to one of choice, wherein you also get the choice of saying “no”.
Roth takes us through the various ways in which life seems to conspire to take consciousness away from eating, from obvious distractions such as TV, to less obvious ones, like “it doesn’t count if you’re not sitting down”. She also tackles other psychological aspects, such as those people get from parents—which can be a big factor for many.
Importantly, she teaches us that when it comes to “have your cake and eat it”, you can also, in fact, have your cake and not eat it. That’s an option too. Its mere presence in our house is not the boss of us. However, overcoming the “this then that” automatic process that goes from having to eating, is something that Roth gives quite some attention to, offering a number of reframes to make it a lot easier.
The style is friendly, conversational, pop-science, and the format dates it a little—this is very much a book formatted the way pop-science books were formatted 20–50 years ago (the book itself is from 2003, for what it’s worth). However, a lack of modern format doesn’t take away from its very valuable insights, and if anything, the older format rather promotes reading a book from cover to cover, which can be beneficial.
Bottom line: if emotional or compulsive eating is something that you’ve found tricky to overcome, then this book can help make it a lot easier.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Walking… Better.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Walking… Better.
We recently reviewed “52 Ways To Walk” by Annabel Streets. You asked us to share some more of our learnings from that book, and… Obviously we can’t do all 52, nor go into such detail, but here are three top tips inspired by that book…
Walk in the cold!
While cold weather is often seen as a reason to not walk, in fact, it has numerous health benefits, the most exciting of which might be:
Walking in the cold causes us to convert white and yellow fat into the healthier brown fat. If you didn’t know about this, neither did scientists until about 15 years ago.
In fact, scientists didn’t even know that adult humans could even have brown adipose tissue! It was really quite groundbreaking.
In case you missed it: The Changed Metabolic World with Human Brown Adipose Tissue: Therapeutic Visions
Work while you walk!
Obviously this is only appropriate for some kinds of work… but if in your life you have any kind of work that is chiefly thinking, a bunch of it can be done while walking.
Open your phone’s note-taking app, lock the screen and pocket your phone, and think on some problem that you need to solve. Whenever you have an “aha” moment, take out your phone and make a quick note on the go.
For that matter, if you have the money and space (or are fortunate to have an employer disposed towards facilitating such), you could even set up a treadmill desk… At worst, it wouldn’t harm your work (and it’ll be a LOT better than sitting for so long).
Walk within an hour of waking!
No, this doesn’t mean that if you don’t get out of the house within 60 minutes you say “Oh no, missed the window, guess it’s a day in today”
But it does mean: in the evening, make preparations to head out first thing in the morning. Set out your clothes and appropriate footwear, find your flask to fill with the beverage of your choice in the morning and set that with them.
Then, when morning arrives… do your morning necessaries (e.g. some manner of morning ablutions and perhaps a light breakfast), make that drink for your flask, and hit the road.
Why? We’ll tell you a secret:
You ever wondered why some people seem to be more able to keep a daylight-regulated circadian rhythm than others? It’s not just about smartphones and coffees…
This study found that getting sunlight (not electric light, not artificial sunlight, but actual sunlight, from the sun, even if filtered through partial cloud) between 08:30—09:00 resulted in higher levels of a protein called PER2. PER2 is critical for setting circadian rhythms, improving metabolism, and fortifying blood vessels.
Besides, on a more simplistic level, it’s also a wonderful and energizing start to a healthy and productive day!
Read: Beneficial effects of daytime light exposure on daily rhythms, metabolic state and affect
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: