What’s the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest? One’s about plumbing, the other wiring
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In July 2023, rising US basketball star Bronny James collapsed on the court during practice and was sent to hospital. The 18-year-old athlete, son of famous LA Lakers’ veteran LeBron James, had experienced a cardiac arrest.
Many media outlets incorrectly referred to the event as a “heart attack” or used the terms interchangeably.
A cardiac arrest and a heart attack are distinct yet overlapping concepts associated with the heart.
With some background in how the heart works, we can see how they differ and how they’re related.

Understanding the heart
The heart is a muscle that contracts to work as a pump. When it contracts it pushes blood – containing oxygen and nutrients – to all the tissues of our body.
For the heart muscle to work effectively as a pump, it needs to be fed its own blood supply, delivered by the coronary arteries. If these arteries are blocked, the heart muscle doesn’t get the blood it needs.
This can cause the heart muscle to become injured or die, and results in the heart not pumping properly.
Heart attack or cardiac arrest?
Simply put, a heart attack, technically known as a myocardial infarction, describes injury to, or death of, the heart muscle.
A cardiac arrest, sometimes called a sudden cardiac arrest, is when the heart stops beating, or put another way, stops working as an effective pump.
In other words, both relate to the heart not working as it should, but for different reasons. As we’ll see later, one can lead to the other.
Why do they happen? Who’s at risk?
Heart attacks typically result from blockages in the coronary arteries. Sometimes this is called coronary artery disease, but in Australia, we tend to refer to it as ischaemic heart disease.
The underlying cause in about 75% of people is a process called atherosclerosis. This is where fatty and fibrous tissue build up in the walls of the coronary arteries, forming a plaque. The plaque can block the blood vessel or, in some instances, lead to the formation of a blood clot.
Atherosclerosis is a long-term, stealthy process, with a number of risk factors that can sneak up on anyone. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, diet, diabetes, stress, and your genes have all been implicated in this plaque-building process.
Other causes of heart attacks include spasms of the coronary arteries (causing them to constrict), chest trauma, or anything else that reduces blood flow to the heart muscle.
Regardless of the cause, blocking or reducing the flow of blood through these pipes can result in the heart muscle not receiving enough oxygen and nutrients. So cells in the heart muscle can be injured or die.

But a cardiac arrest is the result of heartbeat irregularities, making it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively around the body. These heartbeat irregularities are generally due to electrical malfunctions in the heart. There are four distinct types:
- ventricular tachycardia: a rapid and abnormal heart rhythm in which the heartbeat is more than 100 beats per minute (normal adult, resting heart rate is generally 60-90 beats per minute). This fast heart rate prevents the heart from filling with blood and thus pumping adequately
- ventricular fibrillation: instead of regular beats, the heart quivers or “fibrillates”, resembling a bag of worms, resulting in an irregular heartbeat greater than 300 beats per minute
- pulseless electrical activity: arises when the heart muscle fails to generate sufficient pumping force after electrical stimulation, resulting in no pulse
- asystole: the classic flat-line heart rhythm you see in movies, indicating no electrical activity in the heart.

Cardiac arrest can arise from numerous underlying conditions, both heart-related and not, such as drowning, trauma, asphyxia, electrical shock and drug overdose. James’ cardiac arrest was attributed to a congenital heart defect, a heart condition he was born with.
But among the many causes of a cardiac arrest, ischaemic heart disease, such as a heart attack, stands out as the most common cause, accounting for 70% of all cases.
So how can a heart attack cause a cardiac arrest? You’ll remember that during a heart attack, heart muscle can be damaged or parts of it may die. This damaged or dead tissue can disrupt the heart’s ability to conduct electrical signals, increasing the risk of developing arrhythmias, possibly causing a cardiac arrest.
So while a heart attack is a common cause of cardiac arrest, a cardiac arrest generally does not cause a heart attack.
What do they look like?
Because a cardiac arrest results in the sudden loss of effective heart pumping, the most common signs and symptoms are a sudden loss of consciousness, absence of pulse or heartbeat, stopping of breathing, and pale or blue-tinged skin.
But the common signs and symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, which can show up in other regions of the body such as the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. Also frequent are shortness of breath, nausea, light-headedness, looking pale, and sweating.
What’s the take-home message?
While both heart attack and cardiac arrest are disorders related to the heart, they differ in their mechanisms and outcomes.
A heart attack is like a blockage in the plumbing supplying water to a house. But a cardiac arrest is like an electrical malfunction in the house’s wiring.
Despite their different nature both conditions can have severe consequences and require immediate medical attention.
Michael Todorovic, Associate Professor of Medicine, Bond University and Matthew Barton, Senior lecturer, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Griffith University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mung Beans vs Soy Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mung beans to soy beans, we picked the soy.
Why?
Mung beans are great, but honestly, it’s not close:
In terms of macronutrients, soy has more than 2x the protein (of which, it’s also a complete protein, containing significant amounts of all essential amino acids) while mung beans have more than 2x the carbs. In their defense, mung beans also have very slightly more fiber, but the carb:fiber ratio is such that soy beans have the lower GI by far.
When it comes to vitamins, mung beans have more of vitamins A, B3, B5, and, B9, while soy beans have more of vitamins B2, B6, C, E, K, and choline, making for a moderate win for soy beans, especially as that vitamin K is more than 7x as much as mung beans have.
In the category of minerals, soy wins even more convincingly; soy beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, mung beans have more sodium.
In short, while mung beans are a very respectable option, they don’t come close to meaningfully competing with soy.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
How To Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Hearing loss is twice as common in Australia’s lowest income groups, our research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around one in six Australians has some form of hearing loss, ranging from mild to complete hearing loss. That figure is expected to grow to one in four by 2050, due in a large part to the country’s ageing population.
Hearing loss affects communication and social engagement and limits educational and employment opportunities. Effective treatment for hearing loss is available in the form of communication training (for example, lipreading and auditory training), hearing aids and other devices.
But the uptake of treatment is low. In Australia, publicly subsidised hearing care is available predominantly only to children, young people and retirement-age people on a pension. Adults of working age are mostly not eligible for hearing health care under the government’s Hearing Services Program.
Our recent study published in the journal Ear and Hearing showed, for the first time, that working-age Australians from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are at much greater risk of hearing loss than those from higher socioeconomic backgrounds.
We believe the lack of socially subsidised hearing care for adults of working age results in poor detection and care for hearing loss among people from disadvantaged backgrounds. This in turn exacerbates social inequalities.
Population data shows hearing inequality
We analysed a large data set called the Household, Income and Labour Dynamics in Australia (HILDA) survey that collects information on various aspects of people’s lives, including health and hearing loss.
Using a HILDA sub-sample of 10,719 working-age Australians, we evaluated whether self-reported hearing loss was more common among people from lower socioeconomic backgrounds than for those from higher socioeconomic backgrounds between 2008 and 2018.
Relying on self-reported hearing data instead of information from hearing tests is one limitation of our paper. However, self-reported hearing tends to underestimate actual rates of hearing impairment, so the hearing loss rates we reported are likely an underestimate.
We also wanted to find out whether people from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were more likely to develop hearing loss in the long run.
Hearing care is publicly subsidised for children.
mady70/ShutterstockWe found people in the lowest income groups were more than twice as likely to have hearing loss than those in the highest income groups. Further, hearing loss was 1.5 times as common among people living in the most deprived neighbourhoods than in the most affluent areas.
For people reporting no hearing loss at the beginning of the study, after 11 years of follow up, those from a more deprived socioeconomic background were much more likely to develop hearing loss. For example, a lack of post secondary education was associated with a more than 1.5 times increased risk of developing hearing loss compared to those who achieved a bachelor’s degree or above.
Overall, men were more likely to have hearing loss than women. As seen in the figure below, this gap is largest for people of low socioeconomic status.
Why are disadvantaged groups more likely to experience hearing loss?
There are several possible reasons hearing loss is more common among people from low socioeconomic backgrounds. Noise exposure is one of the biggest risks for hearing loss and people from low socioeconomic backgrounds may be more likely to be exposed to damaging levels of noise in jobs in mining, construction, manufacturing, and agriculture.
Lifestyle factors which may be more prevalent in lower socioeconomic communities such as smoking, unhealthy diet, and a lack of regular exercise are also related to the risk of hearing loss.
Finally, people with lower incomes may face challenges in accessing timely hearing care, alongside competing health needs, which could lead to missed identification of treatable ear disease.
Why does this disparity in hearing loss matter?
We like to think of Australia as an egalitarian society – the land of the fair go. But nearly half of people in Australia with hearing loss are of working age and mostly ineligible for publicly funded hearing services.
Hearing aids with a private hearing care provider cost from around A$1,000 up to more than $4,000 for higher-end devices. Most people need two hearing aids.
Hearing loss might be more common in low income groups because they’re exposed to more noise at work.
Dmitry Kalinovsky/ShutterstockLack of access to affordable hearing care for working-age adults on low incomes comes with an economic as well as a social cost.
Previous economic analysis estimated hearing loss was responsible for financial costs of around $20 billion in 2019–20 in Australia. The largest component of these costs was productivity losses (unemployment, under-employment and Jobseeker social security payment costs) among working-age adults.
Providing affordable hearing care for all Australians
Lack of affordable hearing care for working-age adults from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may significantly exacerbate the impact of hearing loss among deprived communities and worsen social inequalities.
Recently, the federal government has been considering extending publicly subsidised hearing services to lower income working age Australians. We believe reforming the current government Hearing Services Program and expanding eligibility to this group could not only promote a more inclusive, fairer and healthier society but may also yield overall cost savings by reducing lost productivity.
All Australians should have access to affordable hearing care to have sufficient functional hearing to achieve their potential in life. That’s the land of the fair go.
Mohammad Nure Alam, PhD Candidate in Economics, Macquarie University; Kompal Sinha, Associate Professor, Department of Economics, Macquarie University, and Piers Dawes, Professor, School of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Before You Reach For That Tylenol…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, on names: we’ve titled this with “Tylenol” because that’s a well-known brand name, but the drug name is paracetamol or acetaminophen:
- paracetamol is the drug name used by the World Health Organization, and thus also most countries.
- acetaminophen is the drug name used in Canada, Colombia, Iran, Japan, US, and Venezuela.
They are absolutely the same drug.
Firstly, obviously, do avoid overdose
The safe dosage described on the packet is generally accurate (usually around 4g/day, spaced out at 1g per 4 hours), and the dose required for toxicity is generally about 10g, or 200mg/kg body weight, whichever is lower. Since a single dose usually contains 2x 500mg = 1g, that makes overdose all too easy.
The amount required for toxicity can be misleading too, because that’s assuming…
- a healthy liver
- no other health problems
- no other medications that interact or add to the toxicity
- no medications that strain the liver (as with many pro-drugs, and drugs in general that are metabolized by the liver, which is lots).
Which is a lot of assumptions! Especially given that the liver can only process so much at once, meaning that if your liver has a lot of things to do, it can get a backlog, and you think “I’m not taking anything with this painkiller that I shouldn’t” but your liver is still metabolizing the last of last night’s glass of wine and one of your regular medications from this morning, because previously it was still metabolizing things from the day before yesterday, and so on.
See also: How To Regenerate Your Liver ← the liver is an incredible organ that does an amazing job, but it can’t do that if you don’t do this
Please don’t overdose deliberately either. Intentional overdoses make up a very large portion of acetaminophen overdoses (exact figures vary from year to year and place to place, but it’s always high), and what a lot of people doing that don’t realize is:
- it’s a very unpleasant way to die. You’ll take it, you might get some initial symptoms within the first hours or you might not, then you’ll probably feel better, and then the next day or so, you’ll enter the organs-shutting-down stage that usually will take most of a week to kill you slowly and painfully. Often your kidneys will go first but it’ll usually be liver necrosis that deals the final blow.
- it’s very difficult to treat. Stomach-pumping might work if you get it within 1 hour of overdose, and activated charcoal might help if you get it within 2 hours. Acetylcysteine may reduce the toxicity if you get it within the 8–48 hour window (depending on the speed of gastric emptying), but whether or not that will help depends on the severity of the overdose and other factors, so this is not something to bet on. After 48 hours, a liver transplant is the last resort, without which, mortality is around 95%.
Unfortunately, this means that a lot of people who do not intend to die horribly, and hoped to either die peacefully or else be saved, die horribly instead.
Ok, that was not a cheerful topic but it is important, before moving on, we’ll just put this here for anyone it may benefit:
How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To) ← this is about suicidality, in yourself or others
Secondly, that dosage is for occasional use only
The problem often starts like this:
❝Due to its perceived safety, paracetamol has long been recommended as the first line drug treatment for osteoarthritis by many treatment guidelines, especially in older people who are at higher risk of drug-related complications❞
People with chronic pain, whether high or low on the pain level of that chronic pain, can very easily get into a habit of “I’ll just take this to take the edge off”, for example when getting up in the morning (often a trigger for pain starting) or going to bed at night (one needs to sleep and the pain is a barrier to that).
But… Those events, getting up and going to bed, it means that taking the drug also becomes part of one’s morning/evening routine—with many people even metering the doses out into pill organizers for the week, with this in mind.
A large (n=582,961) study looked at two groups of people, all aged 65+:
- 180,483 people who had been prescribed paracetamol repeatedly (≥2 prescriptions within six months)
- 402,478 people of the same age who had never been prescribed paracetamol repeatedly
The findings? Bearing in mind that “≥2 prescriptions within six months” is not something generally considered excessive…
❝Acetaminophen use was associated with an increased risk of peptic ulcer bleeding (aHR 1.24; 95% CI 1.16, 1.34), uncomplicated peptic-ulcers (aHR 1.20; 95% CI 1.10, 1.31), lower gastrointestinal-bleeding (aHR 1.36; 95% CI 1.29, 1.46), heart-failure (aHR 1.09; 95% CI 1.06, 1.13), hypertension (aHR 1.07; 95% CI 1.04, 1.11), and chronic kidney disease (aHR 1.19; 95% CI 1.13, 1.24).❞
The researchers concluded:
❝Despite its perceived safety, acetaminophen is associated with several serious complications. Given its minimal analgesic effectiveness, the use of acetaminophen as the first-line oral analgesic for long-term conditions in older people requires careful reconsideration.❞
You can see the study itself here: Incidence of side effects associated with acetaminophen in people aged 65 years or more: a prospective cohort study using data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink
What to use instead?
It’s been established that taking aspirin regularly isn’t great either:
See: Low-Dose Aspirin & Anemia and Aspirin, CVD Risk, & Potential Counter-Risks
And as for ibuprofen, we don’t have an article about that yet, but it’s gut-unhealthy (harms your microbiome), and besides, anything it can do, ginger can do as well or better (in head-to-head trials; we’re not speaking hyperbolically here):
Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think ← in fact, it was even found as effective as the combination of acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and caffeine
There are other options though, and as pain is complicated and there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, we’ve compiled the following:
- Dial Down Your Pain
- Stop Pain Spreading
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief ← when painkillers aren’t helping, these things might
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cashew Nuts vs Macadamia Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cashews to macadamias, we picked the cashews.
Why?
In terms of macros, cashews have more than 2x the protein, while macadamias have nearly 2x the fat. The fats are mostly monounsaturated, so it’s still healthy in moderation, but still, we’re going to prize the protein over it and call this category a nominal win for cashews.
When it comes to vitamins, things are fairly even; cashews have more of vitamins B5, B6, B9, and E, while macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, and C.
In the category of minerals, cashews take the clear lead; cashews have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while macadamias have more calcium and manganese.
In short, enjoy both (as macadamias have their benefits too), but cashews win in total nutrient density.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hospitals worldwide are short of saline. We can’t just switch to other IV fluids – here’s why
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Last week, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration added intravenous (IV) fluids to the growing list of medicines in short supply. The shortage is due to higher-than-expected demand and manufacturing issues.
Two particular IV fluids are affected: saline and compound sodium lactate (also called Hartmann’s solution). Both fluids are made with salts.
There are IV fluids that use other components, such as sugar, rather than salt. But instead of switching patients to those fluids, the government has chosen to approve salt-based solutions by other overseas brands.
So why do IV fluids contain different chemicals? And why can’t they just be interchanged when one runs low?
Pavel Kosolapov/Shutterstock We can’t just inject water into a vein
Drugs are always injected into veins in a water-based solution. But we can’t do this with pure water, we need to add other chemicals. That’s because of a scientific principle called osmosis.
Osmosis occurs when water moves rapidly in and out of the cells in the blood stream, in response to changes to the concentration of chemicals dissolved in the blood plasma. Think salts, sugars, nutrients, drugs and proteins.
Too high a concentration of chemicals and protein in your blood stream leads it to being in a “hypertonic” state, which causes your blood cells to shrink. Not enough chemicals and proteins in your blood stream causes your blood cells to expand. Just the right amount is called “isotonic”.
Mixing the drug with the right amount of chemicals, via an injection or infusion, ensures the concentration inside the syringe or IV bag remains close to isotonic.
Australia is currently short on two salt-based IV fluids. sirnength88/Shutterstock What are the different types of IV fluids?
There are a range of IV fluids available to administer drugs. The two most popular are:
- 0.9% saline, which is an isotonic solution of table salt. This is one of the IV fluids in short supply
- a 5% solution of the sugar glucose/dextrose. This fluid is not in short supply.
There are also IV fluids that combine both saline and glucose, and IV fluids that have other salts:
- Ringer’s solution is an IV fluid which has sodium, potassium and calcium salts
- Plasma-Lyte has different sodium salts, as well as magnesium
- Hartmann’s solution (compound sodium lactate) contains a range of different salts. It is generally used to treat a condition called metabolic acidosis, where patients have increased acid in their blood stream. This is in short supply.
What if you use the wrong solution?
Some drugs are only stable in specific IV fluids, for instance, only in salt-based IV fluids or only in glucose.
Putting a drug into the wrong IV fluid can potentially cause the drug to “crash out” of the solution, meaning patients won’t get the full dose.
Or it could cause the drug to decompose: not only will it not work, but it could also cause serious side effects.
An example of where a drug can be transformed into something toxic is the cancer chemotherapy drug cisplatin. When administered in saline it is safe, but administration in pure glucose can cause life-threatening damage to a patients’ kidneys.
What can hospitals use instead?
The IV fluids in short supply are saline and Hartmann’s solution. They are provided by three approved Australian suppliers: Baxter Healthcare, B.Braun and Fresenius Kabi.
The government’s solution to this is to approve multiple overseas-registered alternative saline brands, which they are allowed to do under current legislation without it going through the normal Australian quality checks and approval process. They will have received approval in their country of manufacture.
The government is taking this approach because it may not be effective or safe to formulate medicines that are meant to be in saline into different IV fluids. And we don’t have sufficient capacity to manufacture saline IV fluids here in Australia.
The Australian Society of Hospital Pharmacists provides guidance to other health staff about what drugs have to go with which IV fluids in their Australian Injectable Drugs Handbook. If there is a shortage of saline or Hartmann’s solution, and shipments of other overseas brands have not arrived, this guidance can be used to select another appropriate IV fluid.
Why don’t we make it locally?
The current shortage of IV fluids is just another example of the problems Australia faces when it is almost completely reliant on its critical medicines from overseas manufacturers.
Fortunately, we have workarounds to address the current shortage. But Australia is likely to face ongoing shortages, not only for IV fluids but for any medicines that we rely on overseas manufacturers to produce. Shortages like this put Australian lives at risk.
In the past both myself, and others, have called for the federal government to develop or back the development of medicines manufacturing in Australia. This could involve manufacturing off-patent medicines with an emphasis on those medicines most used in Australia.
Not only would this create stable, high technology jobs in Australia, it would also contribute to our economy and make us less susceptible to future global drug supply problems.
Nial Wheate, Professor and Director Academic Excellence, Macquarie University and Shoohb Alassadi, Casual academic, pharmaceutical sciences, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleep: yes, you really do still need it!
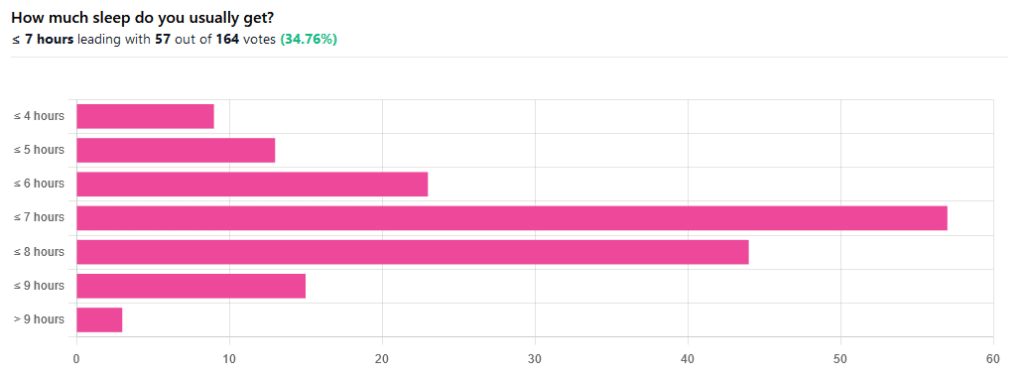
We asked you how much sleep you usually get, and got the above-pictured, below-described set of responses:
- A little of a third of all respondents selected the option “< 7 hours”
- However, because respondents also selected options such as < 6 hours, < 5 hours, and < 4 hours, so if we include those in the tally, the actual total percentage of respondents who reported getting under 7 hours, is actually more like 62%, or just under two thirds of all respondents.
- Nine respondents, which was about 5% of the total, reported usually getting under 4 hours sleep
- A little over quarter of respondents reported usually getting between 7 and 8 hours sleep
- Fifteen respondents, which was a little under 10% of the total, reported usually getting between 8 and 9 hours of sleep
- Three respondents, which was a little under 2% of the total, reported getting over 9 hours of sleep
- In terms of the classic “you should get 7–9 hours sleep”, approximately a third of respondents reported getting this amount.
You need to get 7–9 hours sleep: True or False?
True! Unless you have a (rare!) mutated ADRB1 gene, which reduces that.
The way to know whether you have this, without genomic testing to know for sure, is: do you regularly get under 6.5 hours sleep, and yet continue to go through life bright-eyed and bushy-tailed? If so, you probably have that gene. If you experience daytime fatigue, brain fog, and restlessness, you probably don’t.
About that mutated ADRB1 gene:
NIH | Gene identified in people who need little sleep
Quality of sleep matters as much as duration, and a lot of studies use the “RU-Sated” framework, which assesses six key dimensions of sleep that have been consistently associated with better health outcomes. These are:
- regularity / usual hours
- satisfaction with sleep
- alertness during waking hours
- timing of sleep
- efficiency of sleep
- duration of sleep
But, that doesn’t mean that you can skimp on the last one if the others are in order. In fact, getting a good 7 hours sleep can reduce your risk of getting a cold by three or four times (compared with six or fewer hours):
Behaviorally Assessed Sleep and Susceptibility to the Common Cold
^This study was about the common cold, but you may be aware there are more serious respiratory viruses freely available, and you don’t want those, either.
Napping is good for the health: True or False?
True or False, depending on how you’re doing it!
If you’re trying to do it to sleep less in total (per polyphasic sleep scheduling), then no, this will not work in any sustainable fashion and will be ruinous to the health. We did a Mythbusting Friday special on specifically this, a while back:
Could Just Two Hours Sleep Per Day Be Enough?
PS: you might remember Betteridge’s Law of Headlines
If you’re doing it as a energy-boosting supplement to a reasonable night’s sleep, napping can indeed be beneficial to the health, and can give benefits such as:
- Increased alertness
- Helps with learning
- Improved memory
- Boost to immunity
- Enhance athletic performance
However! There is still a right and a wrong way to go about it, and we wrote about this previously, for a Saturday Life Hacks edition of 10almonds:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
As we get older, we need less sleep: True or False
False, with one small caveat.
The small caveat: children and adolescents need 9–12 hours sleep because, uncredited as it goes, they are doing some seriously impressive bodybuilding, and that is exhausting to the body. So, an adult (with a normal lifestyle, who is not a bodybuilder) will tend to need less sleep than a child/adolescent.
But, the statement “As we get older, we need less sleep” is generally taken to mean “People in the 65+ age bracket need less sleep than younger adults”, and this popular myth is based on anecdotal observational evidence: older people tend to sleep less (as our survey above shows! For any who aren’t aware, our readership is heavily weighted towards the 60+ demographic), and still continue functioning, after all.
Just because we survive something with a degree of resilience doesn’t mean it’s good for us.
In fact, there can be serious health risks from not getting enough sleep in later years, for example:
Sleep deficiency promotes Alzheimer’s disease development and progression
Want to get better sleep?
What gets measured, gets done. Sleep tracking apps can be a really good tool for getting one’s sleep on a healthier track. We compared and contrasted some popular ones:
The Head-To-Head Of Google and Apple’s Top Apps For Getting Your Head Down
Take good care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: