Strength training has a range of benefits for women. Here are 4 ways to get into weights
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Picture a gym ten years ago: the weights room was largely a male-dominated space, with women mostly doing cardio exercise. Fast-forward to today and you’re likely to see women of all ages and backgrounds confidently navigating weights equipment.
This is more than just anecdotal. According to data from the Australian Sports Commission, the number of women participating in weightlifting (either competitively or not) grew nearly five-fold between 2016 and 2022.
Women are discovering what research has long shown: strength training offers benefits beyond sculpted muscles.

Health benefits
Osteoporosis, a disease in which the bones become weak and brittle, affects more women than men. Strength training increases bone density, a crucial factor for preventing osteoporosis, especially for women negotiating menopause.
Strength training also improves insulin sensitivity, which means your body gets better at using insulin to manage blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Regular strength training contributes to better heart health too.
There’s a mental health boost as well. Strength training has been linked to reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.

Improved confidence and body image
Unlike some forms of exercise where progress can feel elusive, strength training offers clear and tangible measures of success. Each time you add more weight to a bar, you are reminded of your ability to meet your goals and conquer challenges.
This sense of achievement doesn’t just stay in the gym – it can change how women see themselves. A recent study found women who regularly lift weights often feel more empowered to make positive changes in their lives and feel ready to face life’s challenges outside the gym.
Strength training also has the potential to positively impact body image. In a world where women are often judged on appearance, lifting weights can shift the focus to function.
Instead of worrying about the number on the scale or fitting into a certain dress size, women often come to appreciate their bodies for what they can do. “Am I lifting more than I could last month?” and “can I carry all my groceries in a single trip?” may become new measures of physical success.

Lifting weights can also be about challenging outdated ideas of how women “should” be. Qualitative research I conducted with colleagues found that, for many women, strength training becomes a powerful form of rebellion against unrealistic beauty standards. As one participant told us:
I wanted something that would allow me to train that just didn’t have anything to do with how I looked.
Society has long told women to be small, quiet and not take up space. But when a woman steps up to a barbell, she’s pushing back against these outdated rules. One woman in our study said:
We don’t have to […] look a certain way, or […] be scared that we can lift heavier weights than some men. Why should we?
This shift in mindset helps women see themselves differently. Instead of worrying about being objects for others to look at, they begin to see their bodies as capable and strong. Another participant explained:
Powerlifting changed my life. It made me see myself, or my body. My body wasn’t my value, it was the vehicle that I was in to execute whatever it was that I was executing in life.
This newfound confidence often spills over into other areas of life. As one woman said:
I love being a strong woman. It’s like going against the grain, and it empowers me. When I’m physically strong, everything in the world seems lighter.
Feeling inspired? Here’s how to get started
1. Take things slow
Begin with bodyweight exercises like squats, lunges and push-ups to build a foundation of strength. Once you’re comfortable, add external weights, but keep them light at first. Focus on mastering compound movements, such as deadlifts, squats and overhead presses. These exercises engage multiple joints and muscle groups simultaneously, making your workouts more efficient.
2. Prioritise proper form
Always prioritise proper form over lifting heavier weights. Poor technique can lead to injuries, so learning the correct way to perform each exercise is crucial. To help with this, consider working with an exercise professional who can provide personalised guidance and ensure you’re performing exercises correctly, at least initially.

3. Consistency is key
Like any fitness regimen, consistency is key. Two to three sessions a week are plenty for most women to see benefits. And don’t be afraid to occupy space in the weights room – remember you belong there just as much as anyone else.
4. Find a community
Finally, join a community. There’s nothing like being surrounded by a group of strong women to inspire and motivate you. Engaging with a supportive community can make your strength-training journey more enjoyable and rewarding, whether it’s an in-person class or an online forum.
Are there any downsides?
Gym memberships can be expensive, especially for specialist weightlifting gyms. Home equipment is an option, but quality barbells and weightlifting equipment can come with a hefty price tag.
Also, for women juggling work and family responsibilities, finding time to get to the gym two to three times per week can be challenging.
If you’re concerned about getting too “bulky”, it’s very difficult for women to bulk up like male bodybuilders without pharmaceutical assistance.
The main risks come from poor technique or trying to lift too much too soon – issues that can be easily avoided with some guidance.
Erin Kelly, Lecturer and PhD Candidate, Discipline of Sport and Exercise Science, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Some women’s breasts can’t make enough milk, and the effects can be devastating
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many new mothers worry about their milk supply. For some, support from a breastfeeding counsellor or lactation consultant helps.
Others cannot make enough milk no matter how hard they try. These are women whose breasts are not physically capable of producing enough milk.
Our recently published research gives us clues about breast features that might make it difficult for some women to produce enough milk. Another of our studies shows the devastating consequences for women who dream of breastfeeding but find they cannot.
Some breasts just don’t develop
Unlike other organs, breasts are not fully developed at birth. There are key developmental stages as an embryo, then again during puberty and pregnancy.
At birth, the breast consists of a simple network of ducts. Usually during puberty, the glandular (milk-making) tissue part of the breast begins to develop and the ductal network expands. Then typically, further growth of the ductal network and glandular tissue during pregnancy prepares the breast for lactation.
But our online survey of women who report low milk supply gives us clues to anomalies in how some women’s breasts develop.
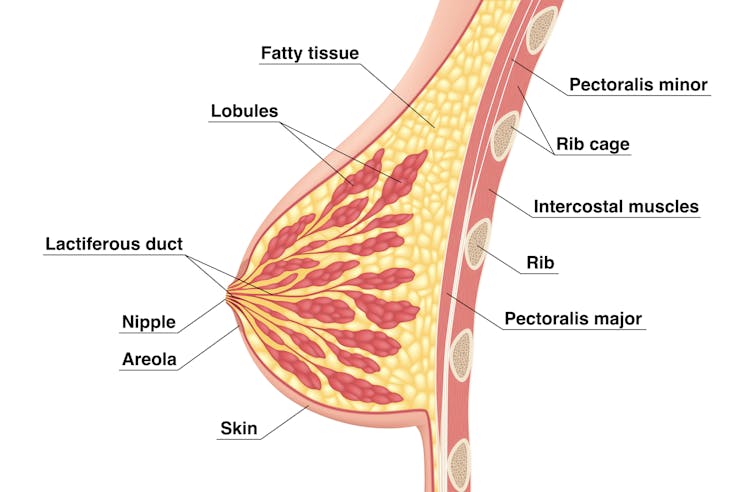
We’re not talking about women with small breasts, but women whose glandular tissue (shown in this diagram as “lobules”) is underdeveloped and have a condition called breast hypoplasia.
Sometimes not enough glandular tissue, shown here as lobules, develop.
Tsuyna/ShutterstockWe don’t know how common this is. But it has been linked with lower rates of exclusive breastfeeding.
We also don’t know what causes it, with much of the research conducted in animals and not humans.
However, certain health conditions have been associated with it, including polycystic ovary syndrome and other endocrine (hormonal) conditions. A high body-mass index around the time of puberty may be another indicator.
Could I have breast hypoplasia?
Our survey and other research give clues about who may have breast hypoplasia.
But it’s important to note these characteristics are indicators and do not mean women exhibiting them will definitely be unable to exclusively breastfeed.
Indicators include:
- a wider than usual gap between the breasts
- tubular-shaped (rather than round) breasts
- asymmetric breasts (where the breasts are different sizes or shapes)
- lack of breast growth in pregnancy
- a delay in or absence of breast fullness in the days after giving birth
In our survey, 72% of women with low milk supply had breasts that did not change appearance during pregnancy, and about 70% reported at least one irregular-shaped breast.
The effects
Mothers with low milk supply – whether or not they have breast hyoplasia or some other condition that limits their ability to produce enough milk – report a range of emotions.
Research, including our own, shows this ranges from frustration, confusion and surprise to intense or profound feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair.
Some mothers describe “breastfeeding grief” – a prolonged sense of loss or failure, due to being unable to connect with and nourish their baby through breastfeeding in the way they had hoped.
These feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair can trigger symptoms of anxiety and depression for some women.
Feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair were common.
Bricolage/ShutterstockOne woman told us:
[I became] so angry and upset with my body for not being able to produce enough milk.
Many women’s emotions intensified when they discovered that despite all their hard work, they were still unable to breastfeed their babies as planned. A few women described reaching their “breaking point”, and their experience felt “like death”, “the worst day of [my] life” or “hell”.
One participant told us:
I finally learned that ‘all women make enough milk’ was a lie. No amount of education or determination would make my breasts work. I felt deceived and let down by all my medical providers. How dare they have no answers for me when I desperately just wanted to feed my child naturally.
Others told us how they learned to accept their situation. Some women said they were relieved their infant was “finally satisfied” when they began supplementing with formula. One resolved to:
prioritise time with [my] baby over pumping for such little amounts.
Where to go for help
If you are struggling with low milk supply, it can help to see a lactation consultant for support and to determine the possible cause.
This will involve helping you try different strategies, such as optimising positioning and attachment during breastfeeding, or breastfeeding/expressing more frequently. You may need to consider taking a medication, such as domperidone, to see if your supply increases.
If these strategies do not help, there may be an underlying reason why you can’t make enough milk, such as insufficient glandular tissue (a confirmed inability to make a full supply due to breast hypoplasia).
Even if you have breast hypoplasia, you can still breastfeed by giving your baby extra milk (donor milk or formula) via a bottle or using a supplementer (which involves delivering milk at the breast via a tube linked to a bottle).
More resources
The following websites offer further information and support:
- Australian Breastfeeding Association
- Lactation Consultants of Australia and New Zealand
- Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne
- Supply Line Breastfeeders Support Group of Australia Facebook support group
- IGT And Low Milk Supply Support Group Facebook support group
- Breastfeeding Medicine Network Australia/New Zealand
- Supporting breastfeeding grief (a collection of resources).
Shannon Bennetts, a research fellow at La Trobe University, contributed to this article.
Renee Kam, PhD candidate and research officer, La Trobe University and Lisa Amir, Professor in Breastfeeding Research, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
We Hope This Email Blows Your Tits Clean Off
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Right Kind Of “Email Hacks”!
Are you a Gmailer or an Outlookista? Whatever your preference, you’re probably facing many of the same challenges that most of us face in our work and personal lives:
Email’s greatest strength (its ease of accessibility) brings about its greatest problem (our inboxes are cluttered and chaotic), not to mention that each of us are usually managing a whole flock of email addresses.
Sometimes we put productivity resources up against each other; that’s not what we’re going to do today! Each of these can play a role alongside each other; grab as many as will make your life easier:
ProtonMail: this is an email client; it’s the nicest, simplest, easiest, free email client that doesn’t track, let alone share, everything you do.
Bonus: there also exists ProtonCalendar (it’s a calendar that doesn’t share your data), ProtonDrive (it’s a cloud storage provider that doesn’t share your data) and, because they’re indeed serious about your privacy, ProtonVPN (it’s a VPN that, of course, doesn’t share your data).
Clean Email: maybe you’re stuck with the email provider you have. It happens. But it doesn’t have to be a chaotic mess. This tool will make tidying your email (and keeping it tidy!) a simplified dream.
See How Clean Your Email Can Get With Just A Few Clicks!
Right Inbox: a Gmail extension with many useful features, including read receipts, emails scheduled for later (e.g: time your email to send at 7am to look like a morning lark when in fact you’re peacefully snoozing), add unforwardable “For Your Eyes Only” notes to emails, and more.
Power Up Your Gmail With The Right Inbox Extension!
Email Finder: find the verified work email address of any person, so long as you know what company you’re looking for them in! No more “I thought it was lastname.firstname@ and it was firstname.lastname@”, no more “the wrong John Smith”, no more “undelivered” bounceback notices. Just: your email delivered.
Never Hear From The Mailer Daemon Again, With Email Finder!
Unroll.me: love your subscriptions, but hate the clutter? Unroll.me aggregates them for you in a virtual roll-up, with an “unroll” button to read them.
Get What You Really Want From Your Subscriptions, With Unroll.Me!
On which note, anything you’d like to hear more of from us? Let us know! You can always just hit reply, or use the feedback widget at the bottom of this email
Share This Post
-
Change Your Brain, Change Your Life – by Dr. Daniel G. Amen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
To what extent can we change our brains, and to what extent are we stuck with what we have?
Dr. Amen tells us that being mindful of both ends of this is critical:
- Neuroplasticity means we can, indeed, change our brains
- We do, however, have fundamental “brain types” based on our neurochemistry and physical brain structure
He argues for the use of brain imaging technology to learn more about the latter… In order to better go about doing what we can with the former.
The book looks at how these different brain types can lead to situations where what works as a treatment for one person can often not work for another. It’s also prescriptive, about what sorts of treatments (and lifestyle adjustments) are more likely to do better for each.
Where the book excels is in giving ideas and pointers for exploration… Things to take to one’s doctor, and—for example—request certain tests, and then what to do with those.
Where the book is a little light is on including hard science in the explanations. The hard science is referred to, but is considered beyond the scope of the book, or perhaps beyond the interest of the reader. That’s unfortunate, as we’d have liked to have seen more of it, rather than taking claims at face value without evidence.
Bottom line: this is distinctly “pop science” in presentation, but can give a lot of great ideas for learning more about our own brains and brain health… And then optimizing such.
Click here to check out “Change Your Brain; Change Your Life” on Amazon today!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Reduce Chronic Stress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sunday Stress-Buster
First, an important distinction:
- Acute stress (for example, when stepping out of your comfort zone, engaging in competition, or otherwise focusing on something that requires your full attention for best performance) is generally a good thing. It helps you do you your best. It’s sometimes been called “eustress”, “good stress”.
- Chronic stress (for example, when snowed under at work and you do not love it, when dealing with a serious illness, and/or faced with financial problems) is unequivocally a bad thing. Our body is simply not made to handle that much cortisol (the stress hormone) all the time.
Know the dangers of too much cortisol
We covered this as a main feature last month: Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
…but it bears mentioning again and for those who’ve joined us since then:
A little spike of cortisol now and again can be helpful. Having it spiking all the time, or even a perpetual background low-to-moderate level, can be ruinous to the health in so many ways.
The good news is, the physiological impact of stress on the body (which ranges from face-and-stomach fat deposits, to rapid aging), can be reversed—even the biological aging!
Read: Biological age is increased by stress and restored upon recovery ← this study is so hot-of-the-press that it was published literally two days ago
Focus on what you can control
A lot of things that cause you stress may be outside of your control. Focus on what is within your control. Oftentimes, we are so preoccupied with the stress, that we employ coping strategies that don’t actually deal with the problem.
That’s a maladaptive response to an evolutionary quirk—our bodies haven’t caught up with modern life, and on an evolutionary scale, are still priming us to deal with sabre-toothed tigers, not financial disputes, for example.
But, how to deal with the body’s “wrong” response?
First, deal with the tiger. There isn’t one, but your body doesn’t know that. Do some vigorous exercise, or if that’s not your thing, tense up your muscles strongly for a few seconds and then relax them, doing each part of your body. This is called progressive relaxation, and how it works is basically tricking your body into thinking you successfully fled the tiger, or fought the tiger and won.
Next, examine what the actual problem is, that’s causing you stress. You’re probably heavily emotionally attached to the problem, or else it wouldn’t be stressing you. So, imagine what advice you would give to help a friend deal with the same problem, and then do that.
Better yet: enlist an actual friend (or partner, family member, etc) to help you. We are evolved to live in a community, engaged in mutual support. That’s how we do well; that’s how we thrive best.
By dealing with the problem—or sometimes even just having support and/or something like a plan—your stress will evaporate soon enough.
The power of “…and then what?”
Sometimes, things are entirely out of your control. Sometimes, bad things are entirely possible; perhaps even probable. Sometimes, they’re so bad, that it’s difficult to avoid stressing about the possible outcomes.
If something seems entirely out of your control and/or inevitable, ask yourself:
“…and then what?”
Writer’s storytime: when I was a teenager, sometimes I would go out without a coat, and my mother would ask, pointedly, “But what will you do if it rains?!”
I’d reply “I’ll get wet, of course”
This attitude can go just the same for much more serious outcomes, up to and including death.
So when you find yourself stressing about some possible bad outcome, ask yourself, “…and then what?”.
- What if this is cancer? Well, it might be. And then what? You might seek cancer treatment.
- What if I can’t get treatment, or it doesn’t work? Well, you might die. And then what?
In Dialectic Behavior Therapy (DBT), this is called “radical acceptance” and acknowledges bad possible/probable/known outcomes, allows one to explore the feelings, and come up with a plan for managing the situation, or even just coming to terms with the fact that sometimes, suffering is inevitable and is part of the human condition.
It’ll still be bad—but you won’t have added extra suffering in the form of stress.
Breathe.
Don’t underestimate the power of relaxed deep breathing to calm the rest of your body, including your brain.
Also: we’ve shared this before, a few months ago, but this 8 minute soundscape was developed by sound technicians working with a team of psychologists and neurologists. It’s been clinically tested, and found to have a much more relaxing effect(in objective measures of lowering heart rate and lowering cortisol levels, as well as in subjective self-reports) than merely “relaxing music”.
Try it and see for yourself:
! Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Who Screens The Sunscreens?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Screen The Sunscreens!
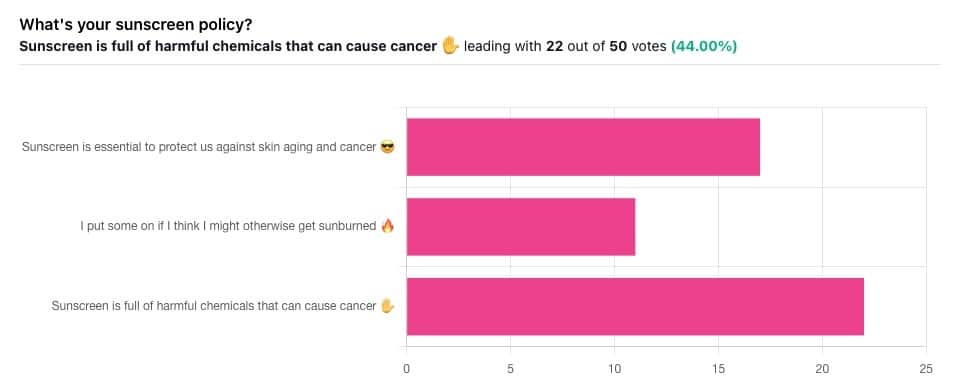
Yesterday, we asked you what your sunscreen policy was, and got a spread of answers. Apparently this one was quite polarizing!
One subscriber who voted for “Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer” wrote:
❝My mom died of complications from melanoma, so we are vigilant about sun and sunscreen. We are a family of campers and hikers and gardeners—outdoors in all seasons—and we never burn❞
Our condolences with regard to your mom! Life is so precious, and when something like that happens, it tends to stick with us. We’re glad you and your family are taking care of yourselves.
Of the subscribers who voted for “I put some on if I think I might otherwise get sunburned”, about half wrote to express uncertainties:
- uncertainty about how safe it is, and
- uncertainty about how helpful it is
…so we’re going to tackle those questions in a moment. But what of those who voted for “Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer”?
Of those, only one wrote a message, which was to say one has to be very careful of what is in the formula.
Let’s take a look, then…
Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer: True or False?
False—according to current best science. Research is ongoing!
There are four main chemicals (found in most sunscreens) that people tend to worry about:
- Abobenzone
- Oxybenzone
- Octocrylene
- Ecamsule
Now, these two sound like four brands of rocket fuel, but then, dihydrogen monoxide (DHMO), which is also found in most sunscreens, sounds like a deadly toxin too. That’s water, by the way.
But what of these four chemicals? Well, as we say, research is ongoing, but we found a study that measured all four, to see how much got into the blood, and what adverse effects, if any, this caused.
We’ll skip to their conclusion:
❝In this preliminary study involving healthy volunteers, application of 4 commercially available sunscreens under maximal use conditions resulted in plasma concentrations that exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens. The systemic absorption of sunscreen ingredients supports the need for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings. These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.❞
Now, “exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens” sounds alarming, so why did they close with the words “These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen”?
Let’s skip back up to a line from the results:
❝The most common adverse event was rash, which developed in 1 participant with each sunscreen.❞
This was most probably due to the oxybenzone, which can cause allergic skin reactions in some people.
Let us take a moment to remember the most common adverse event that occurs from not wearing sunscreen: sunburn!
You can read the full study here:
None of those ingredients have been found to be carcinogenic, even at the maximal blood plasma concentrations studied, from applications 4x/day to 75% of the body.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are absolutely very much known to cause cancer, and the effect is cumulative.
Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer: True or False?
True, unequivocally, unless we live indoors and/or otherwise never go about under sunlight.
“But our ancestors—” lived under the same sun we do, and either used sunscreen or got advanced skin aging and cancer.
Sunscreen of times past ranged from mud to mineral lotions, but it’s pretty much always existed. Even non-human animals that have skin and don’t have fur or feathers, tend to take mud-baths in sunny parts of the world.
If you’d like to avoid oxybenzone and other chemicals, though, you might have your reasons. Maybe you’re allergic, or maybe you read that it’s a potential endocrine disruptor with estrogen-like and anti-androgenic properties that you don’t want.
There are other options, to include physical blockers containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective ingredients.
If you’re interested, you can even make your own sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays (UVA is what causes skin cancer; UVB is “milder” and is what causes sunburn):
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nutrivore – by Dr. Sarah Ballantyne
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The core idea of this book is that foods can be assigned a numerical value according to their total nutritional value, and that this number can be used to guide a person’s diet such that we will eat, in aggregate, a diet that is more nutritious. So far, so simple.
What Dr. Ballantyne also does, besides explaining and illustrating this system (there are chapters explaining the calculation system, and appendices with values), is also going over what to consider important and what we can let slide, and what things we might need more of to address a wide assortment of potential health concerns. And yes, this is definitely a “positive diet” approach, i.e. it focuses on what to add in, not what to cut out.
The premise of the “positive diet” approach is simple, by the way: if we get a full set of good nutrients, we will be satisfied and not crave unhealthy food.
She also offers a lot of helpful “rules of thumb”, and provides a variety of cheat-sheets and suchlike to make things as easy as possible.
There’s also a recipes section! Though, it’s not huge and it’s probably not necessary, but it’s just one more “she’s thinking of everything” element.
Bottom line: if you’d like a single-volume “Bible of” nutrition-made-easy, this is a very usable tome.
Click here to check out Nutrivore, and start filling up your diet!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: