Outsmart Your Pain – by Dr. Christiane Wolf
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Wolf is a physician turned mindfulness teacher. As such, and holding an MD as well as a PhD in psychosomatic medicine, she knows her stuff.
A lot of what she teaches is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), but this book is much more specific than that. It doesn’t promise you won’t continue to experience pain—in all likelihood you will—but it does change the relationship with pain, and this greatly lessens the suffering and misery that comes with it.
For many, the most distressing thing about pain is not the sensation itself, but how crippling it can be—getting in the way of life, preventing enjoyment of other things, and making every day a constant ongoing exhausting battle… And every night, a “how much rest am I actually going to be able to get, and in what condition will I wake up, and how will I get through tomorrow?” stress-fest.
Dr. Wolf helps the reader to navigate through all these challenges and more; minimize the stress, maximize the moments of respite, and keep pain’s interference with life to a minimum. Each chapter addresses different psychological aspects of chronic pain management, and each comes with specific mindfulness meditations to explore the new ideas learned.
The style is personal and profound, while coming from a place of deep professional understanding as well as compassion.
Bottom line: if you’ve been looking for a life-ring to help you reclaim your life, this one could be it; we wholeheartedly recommend it.
Click here to check out Outsmart Your Pain, and recover the beauty and joy of life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Your Mucus Says About Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s not a sexy topic (unless perhaps you have a fetish), but it is a useful topic to know about.
So, let’s get down to business with this much-maligned bodily fluid:
What is mucus? And why?
Sometimes, it can seem that mucus only exists to be an inconvenience, and to convey disease.
And… Actually, that’s mostly true.
While some kinds of mucus have other jobs beyond the scope of today’s article (did you know semen is mostly mucus? If not, now you do), the primary job of most of our mucus is to stop things (especially pathogens) going where they shouldn’t.
So, in essence, it really does exist to be an inconvenience—to pathogens. And to convey those pathogens to where they can be disposed of safely, either outside of the body, or to be an easy meal (what with being stuck in mucus, and thus at least moderately immobilized) for our various active immune cells. To make matters worse for the pathogens, there are (usually) enzymes in our mucus that have antimicrobial properties, too.
Some of mucus’s protective role can be in other ways too, such as by lining our stomach. You know, the stomach that contains the acid that can dissolve meat, despite us also being made of meat.
The slimiest rainbow
Ok, maybe not the slimiest rainbow—there’s probably a YouTube slime channel producing more colors. But, our noses are capable of dispensing astonishing quantities of mucus sometimes, and the color can vary widely, so here’s what we can know from that:
Clear
This is as it should be, in good health. If you’re getting lots of it but it’s clear, then it’s usually allergies, but watch out in case it changes color, heralding an infection. This “clear is how it looks when in ideal health”, by the way, is why when someone is sobbing in abject grief, any mucus that shows up to add to that picture will generally be clear.
White
As above, but now inflamed. Inflammation is usually something we don’t want, but in the case of a threat from a pathogen, we actually do want acute inflammation like this—the body is assembling its armies, of which, the most visible (when they appear in mass) are white blood cells. Because of their abundant presence at this stage, the mucus will also become thicker.
Yellow
As above, but the battle is now truly underway, and the yellow color comes from dead white blood cells. This does not, however, mean the battle is necessarily going badly—the body treats its white blood cells as very disposable fighters, and their deaths in large numbers are expected and normal when doing battle.
Green
As above, but neutrophils (a specific kind of white blood cell) have joined the party. They release an enzyme that colors the mucus green—and kills a lot of pathogens. Popular lore says that green mucus means a bacterial infection, but it’s not always so; these can be deployed against viruses too, depending on various factors beyond the scope of this article (but generally pertaining to severity). In any case, this too does not mean the battle is necessarily going badly, but it does express that your body is taking it very seriously—and you should, too.
Red
Nothing to do with infections, usually—it’s just a little blood (the red kind, this time). Usually it got into the mucus because the mucus membrane got damaged, usually due to some kind of physical trauma (e.g. very vigorous nose-blowing, poking things up the nose, etc) or sometimes if the air is very dry (then the mucus itself can dry out, and become stabby inside the nose; when more mucus is produced, it gets infused with blood from the injury).
Pink
As above, but combined with the “white” stage of infection response.
Orange
As above, but combined with the “yellow” stage of infection response.
Brown
As above, but the blood has oxidized—or, as a completely alterative possibility, it could mean you have been breathing a lot of pollutants. Smoke of various kinds (from fires, from smoking, etc) can cause this.
Black
There are various possible explanations here and all of them are bad. Get thee to a doctor. Superficial examples include:
- Fungal infection (you thought toxic black mold was bad when it was on the wall of the house, wait until it’s on the walls of your respiratory system)
- Blood, in abundance, oxidized (which begs the question of what caused that, but certainly: something wrong is not right)
- Pollutants again, but this time at absurd levels of exposure
That last one might sound very transient and self-correcting, but it’s not, and it comes with many increased short- and long-term health risks.
Want to know more?
Knowledge is power, so read up, and stay well:
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- The Cold Truth About Respiratory Infections
- Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Osteoporosis & Exercises: Which To Do (And Which To Avoid)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Any idea about the latest research on the most effective exercises for osteoporosis?❞
While there isn’t much new of late in this regard, there is plenty of research!
First, what you might want to avoid:
- Sit-ups, and other exercises with a lot of repeated spinal flexion
- Running, and other high-impact exercises
- Skiing, horse-riding, and other activities with a high risk of falling
- Golf and tennis (both disproportionately likely to result in injuries to wrists, elbows, and knees)
Next, what you might want to bear in mind:
While in principle resistance training is good for building strong bones, good form becomes all the more important if you have osteoporosis, so consider working with a trainer if you’re not 100% certain you know what you’re doing:
Some of the best exercises for osteoporosis are isometric exercises:
5 Isometric Exercises for Osteoporosis (with textual explanations and illustrative GIFs)
You might also like this bone-strengthening exercise routine from corrective exercise specialist Kendra Fitzgerald:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
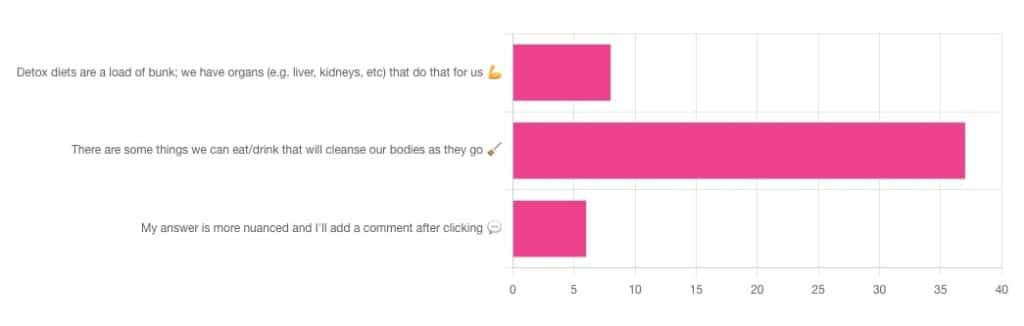
Out of the subscribers who engaged in the poll, it looks like we have a lot of confidence in at least some detox approaches being useful!
Celery juice is most people’s go-to, and indeed it was the only one to get mentioned in the comments added. So let’s take a look at that first…
Celery juice
Celery juice is enjoyed by many people, with many health benefits in mind, including to:
- reduce inflammation
- lower blood pressure
- heal the liver
- fight cancer
- reduce bloating
- support the digestive system
- increase energy
- support weight loss
- promote good mental health
An impressive list! With such an impressive list, we would hope for an impressive weight of evidence, so regular readers might be wondering why those bullet-pointed items aren’t all shiny hyperlinks to studies backing those claims. The reason is…
There aren’t any high-quality studies that back any of those claims.
We found one case study (so, a study with a sample size of one; not amazing) that observed a blood pressure change in an elderly man after drinking celery juice.
Rather than trawl up half of PubMed to show the lacklustre results in a way more befitting of Research Review Monday, though, here’s a nice compact article detailing the litany of disappointment that is science’s observations regards celery juice:
Why Are People Juicing Their Celery? – by Allison Webster, PhD, RD
A key take-away is: juicing destroys the fiber that is celery’s biggest benefit, and its phytochemicals are largely unproven to be of use.
If you enjoy celery, great! It (when not juiced) is a great source of fiber and water. If you juice it, it’s a great source of water.
Activated Charcoal
Unlike a lot of greenery—whose “cleansing” benefits mostly come from fiber and disappear when juiced—activated charcoal has a very different way of operating.
Activated charcoal is negatively charged on a molecular level*, and that—along with its porous nature—traps toxins. It really is a superpowered detox that actually works very well indeed.
But…
It works very well indeed. It will draw out toxins so well, that it’s commonly used to treat poisonings. “Wait”, we hear you say, “why was that a but”?
It doesn’t know what a toxin is. It just draws out all of the things. You took medicine recently? Not any more you didn’t. You didn’t even take that medication orally, you took it some other way? Activated charcoal does not care:
- The effect of activated charcoal on drug exposure following intravenous administration: A meta-analysis
- Activated charcoal for acute overdose: a reappraisal
Does this mean that activated charcoal can be used to “undo” a night of heavy drinking?
Sadly not. That’s one of the few things it just doesn’t work for. It won’t work for alcohol, salts, or metals:
The Use of Activated Charcoal to Treat Intoxications
*Fun chemistry mnemonic about ions:
Cations are pussitive
Anions (by process of elimination) are negative
Onions taste good in salad (remember also: Cole’s Law)
Bottom line on detox foods/drinks:
- Fiber is great; juicing removes fiber. Eat your greens (don’t drink them)!
- Activated charcoal is the heavy artillery of detoxing
- Sometimes it will remove things you didn’t want removed, though
- It also won’t help against alcohol, sadly
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Non-Alcohol Mouthwash vs Alcohol Mouthwash – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing non-alcohol mouthwash to alcohol mouthwash, we picked the alcohol.
Why?
Note: this is a contingent choice and is applicable to most, but not all, people.
In short, there has been some concern about alcohol mouthwashes increasing cancer risk, but research has shown this is only the case if you already have an increased risk of oral cancer (for example if you smoke, and/or have had an oral cancer before).
For those for whom this is not the case (for example, if you don’t smoke, and/or have no such cancer history), then best science currently shows that alcohol mouthwash does not cause any increased risk.
What about non-alcohol mouthwashes? Well, they have a different problem; they usually use chlorine-based chemicals like chlorhexidine or cetylpyridinium chloride, which are (exactly as the label promises) exceptionally good at killing oral bacteria.
(They’d kill us too, at higher doses, hence: swill and spit)
Unfortunately, much like the rest of our body, our mouth is supposed to have bacteria there and bad things happen when it doesn’t. In the case of our oral microbiome, cleaning it with such powerful antibacterial agents can kill our “good” bacteria along with the bad, which lowers the pH of our saliva (that’s bad; it means it is more acidic), and thus indirectly erodes tooth enamel.
You can read more about the science of all of the above (with references), here:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
Summary:
For most people, alcohol mouthwashes are a good way to avoid the damage that can be done by chlorhexidine in non-alcohol mouthwashes.
Here are some examples, but there will be plenty in your local supermarket:
Non-Alcohol, by Colgate | Alcohol, by Listerine
If you have had oral cancer, or if you smoke, then you may want to seek a third alternative (and also, please, stop smoking if you can).
Or, really, most people could probably skip mouthwashes, if you’ve good oral care already by other means. See also:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
(yes, it’s the same link as before, but we’re now drawing your attention to the fact it has information about toothpastes too)
If you do want other options though, might want to check out:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← miswak sticks are especially effective
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Federal Panel Prescribes New Mental Health Strategy To Curb Maternal Deaths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
BRIDGEPORT, Conn. — Milagros Aquino was trying to find a new place to live and had been struggling to get used to new foods after she moved to Bridgeport from Peru with her husband and young son in 2023.
When Aquino, now 31, got pregnant in May 2023, “instantly everything got so much worse than before,” she said. “I was so sad and lying in bed all day. I was really lost and just surviving.”
Aquino has lots of company.
Perinatal depression affects as many as 20% of women in the United States during pregnancy, the postpartum period, or both, according to studies. In some states, anxiety or depression afflicts nearly a quarter of new mothers or pregnant women.
Many women in the U.S. go untreated because there is no widely deployed system to screen for mental illness in mothers, despite widespread recommendations to do so. Experts say the lack of screening has driven higher rates of mental illness, suicide, and drug overdoses that are now the leading causes of death in the first year after a woman gives birth.
“This is a systemic issue, a medical issue, and a human rights issue,” said Lindsay R. Standeven, a perinatal psychiatrist and the clinical and education director of the Johns Hopkins Reproductive Mental Health Center.
Standeven said the root causes of the problem include racial and socioeconomic disparities in maternal care and a lack of support systems for new mothers. She also pointed a finger at a shortage of mental health professionals, insufficient maternal mental health training for providers, and insufficient reimbursement for mental health services. Finally, Standeven said, the problem is exacerbated by the absence of national maternity leave policies, and the access to weapons.
Those factors helped drive a 105% increase in postpartum depression from 2010 to 2021, according to the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
For Aquino, it wasn’t until the last weeks of her pregnancy, when she signed up for acupuncture to relieve her stress, that a social worker helped her get care through the Emme Coalition, which connects girls and women with financial help, mental health counseling services, and other resources.
Mothers diagnosed with perinatal depression or anxiety during or after pregnancy are at about three times the risk of suicidal behavior and six times the risk of suicide compared with mothers without a mood disorder, according to recent U.S. and international studies in JAMA Network Open and The BMJ.
The toll of the maternal mental health crisis is particularly acute in rural communities that have become maternity care deserts, as small hospitals close their labor and delivery units because of plummeting birth rates, or because of financial or staffing issues.
This week, the Maternal Mental Health Task Force — co-led by the Office on Women’s Health and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and formed in September to respond to the problem — recommended creating maternity care centers that could serve as hubs of integrated care and birthing facilities by building upon the services and personnel already in communities.
The task force will soon determine what portions of the plan will require congressional action and funding to implement and what will be “low-hanging fruit,” said Joy Burkhard, a member of the task force and the executive director of the nonprofit Policy Center for Maternal Mental Health.
Burkhard said equitable access to care is essential. The task force recommended that federal officials identify areas where maternity centers should be placed based on data identifying the underserved. “Rural America,” she said, “is first and foremost.”
There are shortages of care in “unlikely areas,” including Los Angeles County, where some maternity wards have recently closed, said Burkhard. Urban areas that are underserved would also be eligible to get the new centers.
“All that mothers are asking for is maternity care that makes sense. Right now, none of that exists,” she said.
Several pilot programs are designed to help struggling mothers by training and equipping midwives and doulas, people who provide guidance and support to the mothers of newborns.
In Montana, rates of maternal depression before, during, and after pregnancy are higher than the national average. From 2017 to 2020, approximately 15% of mothers experienced postpartum depression and 27% experienced perinatal depression, according to the Montana Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System. The state had the sixth-highest maternal mortality rate in the country in 2019, when it received a federal grant to begin training doulas.
To date, the program has trained 108 doulas, many of whom are Native American. Native Americans make up 6.6% of Montana’s population. Indigenous people, particularly those in rural areas, have twice the national rate of severe maternal morbidity and mortality compared with white women, according to a study in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Stephanie Fitch, grant manager at Montana Obstetrics & Maternal Support at Billings Clinic, said training doulas “has the potential to counter systemic barriers that disproportionately impact our tribal communities and improve overall community health.”
Twelve states and Washington, D.C., have Medicaid coverage for doula care, according to the National Health Law Program. They are California, Florida, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Jersey, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, and Virginia. Medicaid pays for about 41% of births in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Jacqueline Carrizo, a doula assigned to Aquino through the Emme Coalition, played an important role in Aquino’s recovery. Aquino said she couldn’t have imagined going through such a “dark time alone.” With Carrizo’s support, “I could make it,” she said.
Genetic and environmental factors, or a past mental health disorder, can increase the risk of depression or anxiety during pregnancy. But mood disorders can happen to anyone.
Teresa Martinez, 30, of Price, Utah, had struggled with anxiety and infertility for years before she conceived her first child. The joy and relief of giving birth to her son in 2012 were short-lived.
Without warning, “a dark cloud came over me,” she said.
Martinez was afraid to tell her husband. “As a woman, you feel so much pressure and you don’t want that stigma of not being a good mom,” she said.
In recent years, programs around the country have started to help doctors recognize mothers’ mood disorders and learn how to help them before any harm is done.
One of the most successful is the Massachusetts Child Psychiatry Access Program for Moms, which began a decade ago and has since spread to 29 states. The program, supported by federal and state funding, provides tools and training for physicians and other providers to screen and identify disorders, triage patients, and offer treatment options.
But the expansion of maternal mental health programs is taking place amid sparse resources in much of rural America. Many programs across the country have run out of money.
The federal task force proposed that Congress fund and create consultation programs similar to the one in Massachusetts, but not to replace the ones already in place, said Burkhard.
In April, Missouri became the latest state to adopt the Massachusetts model. Women on Medicaid in Missouri are 10 times as likely to die within one year of pregnancy as those with private insurance. From 2018 through 2020, an average of 70 Missouri women died each year while pregnant or within one year of giving birth, according to state government statistics.
Wendy Ell, executive director of the Maternal Health Access Project in Missouri, called her service a “lifesaving resource” that is free and easy to access for any health care provider in the state who sees patients in the perinatal period.
About 50 health care providers have signed up for Ell’s program since it began. Within 30 minutes of a request, the providers can consult over the phone with one of three perinatal psychiatrists. But while the doctors can get help from the psychiatrists, mental health resources for patients are not as readily available.
The task force called for federal funding to train more mental health providers and place them in high-need areas like Missouri. The task force also recommended training and certifying a more diverse workforce of community mental health workers, patient navigators, doulas, and peer support specialists in areas where they are most needed.
A new voluntary curriculum in reproductive psychiatry is designed to help psychiatry residents, fellows, and mental health practitioners who may have little or no training or education about the management of psychiatric illness in the perinatal period. A small study found that the curriculum significantly improved psychiatrists’ ability to treat perinatal women with mental illness, said Standeven, who contributed to the training program and is one of the study’s authors.
Nancy Byatt, a perinatal psychiatrist at the University of Massachusetts Chan School of Medicine who led the launch of the Massachusetts Child Psychiatry Access Program for Moms in 2014, said there is still a lot of work to do.
“I think that the most important thing is that we have made a lot of progress and, in that sense, I am kind of hopeful,” Byatt said.
Cheryl Platzman Weinstock’s reporting is supported by a grant from the National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fruit & Veg In The Fridge: Pros & Cons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What effect does refrigeration have on the nutritional value of fruit and vegetables??❞
It’s difficult to give a single definitive answer, because naturally there are a lot of different fruits and vegetables, and a lot of different climates. The answer may be different for tomatoes in Alaska vs bananas in Arizona!
However, we can still generalize at least somewhat
Refrigeration will generally slow down any degradation process, and in the case of fruit and vegetables, that can mean slowing down their “ripening” too, as applicable.
However…
Refrigeration will also impede helpful bioactivity too, and that includes quite a list of things.
Here’s a good study that’s quite illustrative; we’d summarize the conclusions but the rather long title already does that nicely:
So, this really is a case of “there are pros and cons, but probably more cons on balance”.
In practical terms, a good take-away from this can be twofold:
- don’t keep fruit and veg in the fridge unless the ambient temperature really requires it
- if the ambient temperature does require it, it’s best to get the produce in fresh each day if that’s feasible, to minimize time spent in the fridge
An extra thing not included there: often when it comes to the spoilage of fruit and veg, the problem is that it respires and oxidizes; reducing the temperature does lower the rate of those, but often a far better way is to remove the oxygen. So for example, if you get carried away and chop too many carrot batons for your hummus night, then putting them in a sealed container can go a long way to keeping them fresh.
See also: How Does the Nutritional Value of Fruits and Vegetables Change Over Time?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: