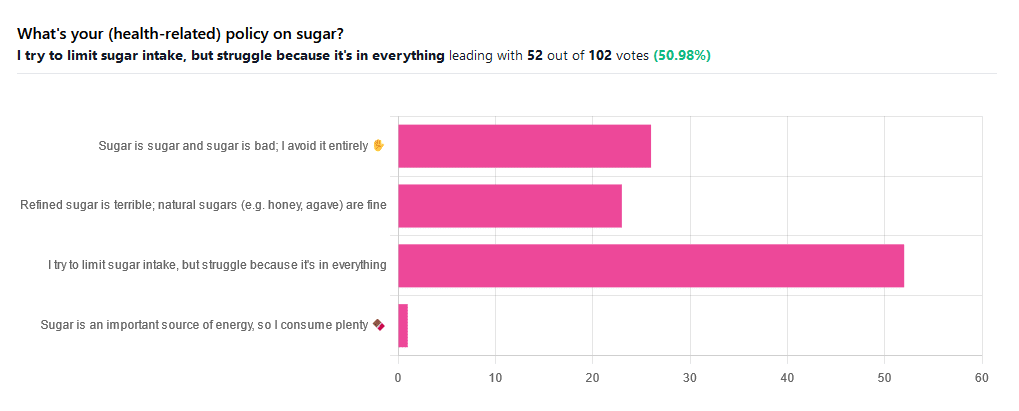The Coffee-Cortisol Connection, And Two Ways To Tweak It For Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health opinions on coffee vary from “it’s an invigorating, healthful drink” to “it will leave you a shaking frazzled wreck”. So, what’s the truth and can we enjoy it healthily? Dr. Alan Mandell weighs in:
Enjoy it, but watch out!
Dr. Mandell is speaking only for caffeinated coffee in this video, and to this end, he’s conflating the health effects of coffee and caffeine. A statistically reasonable imprecision, since most people drink coffee with its natural caffeine in, but we’ll make some adjustment to his comments below, to disambiguate which statements are true for coffee generally, and which are true for caffeine:
- Drinking
coffeecaffeine first thing in the morning may not be ideal due to dehydration from overnight water loss. Coffeecaffeine is a diuretic, which means an increase in urination, thus further dehydrating the body.- Coffee contains great antioxidants, which are of course beneficial for the health in general.
- Cortisol, the body’s stress hormone, is generally at its peak in the morning. This is, in and of itself, good and correct—it’s how we wake up.
Coffeecaffeine consumption raises cortisol levels even more, leading to increased alertness and physical readiness, but it is possible to have too much of a good thing, and in this case, problems can arise because…- Elevated cortisol from early
coffeecaffeine drinking can build tolerance, leading to the need for morecoffeecaffeine over time. - It’s better, therefore, to defer drinking
coffeecaffeine until later in the morning when cortisol levels naturally drop. - All of this means that drinking
coffeecaffeine first thing can disrupt the neuroendocrine system, leading to fatigue, depression, and general woe. - Hydrate first thing in the morning before consuming
coffeecaffeine to keep the body balanced and healthy.
What you can see from this is that coffee and caffeine are not, in fact, interchangeable words, but the basic message is clear and correct: while a little spike of cortisol in the morning is good, natural, and even necessary, a big spike is none of those things, and caffeine can cause a big spike, and since for most people caffeine is easy to build tolerance to, there will indeed consistently be a need for more, worsening the problem.
In terms of hydration, it’s good to have water (or better yet, herbal tea) on one’s nightstand to drink when one wakes up.
If coffee is an important morning ritual for you, consider finding a good decaffeinated version for at least your first cup (this writer is partial to Lavazza’s “Dek Intenso”—which is not the same as their main decaf line, by the way, so do hold out for the “Dek Intenso” if you want to try my recommendation).
Decaffeinated coffee is hydrating and will not cause a cortisol spike (unless for some reason you find coffee as a concept very stressful in which case, yes, the stressor will cause a stress response).
Anyway, for more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How (And Why) To Train Your Pre-Frontal Cortex
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Chapman’s Keys For Mental Focus
This is Dr. Sandra Chapman; she’s a cognitive neuroscientist, on a mission to, in her words, further our understanding of:
- what makes the brain stronger, faster and last longer
- what enhances human cognitive capacity, and
- what enhances the underlying brain systems across the lifespan.
To this end, she’s also the founder and Chief Director of the Center For Brain Health, where she has worked on her mission for the past 25 years (clocking up hundreds of peer-reviewed publications to her name), as well as being a professor of Behavioral and Brain Sciences at UT Dallas.
What does she want us to know?
Get your brain into gear
When it comes to your brainpower, it is “use it or lose it”, but it is also perfectly possible to use it and lose it.
Why?
Very often, what we are using our brains for is high-strain, low-yield stuff, such as multitasking, overthinking, or overthinking while multitasking. And to make it worse, we often do it without sufficient rest.
This is the equivalent of owning a Ferrari but trying to drive it in second and third gear at once by switching between the two as rapidly as possible. And doing that for 18 hours each day.
Suffice it to say, you’ll be going nowhere quickly.
An alternative “use” of brainpower is low-strain, low-yield stuff, such as having to pay close attention to a boring conversation. It’s enough to stop your mind from doing anything else, but not enough to actually stimulate you.
This is the equivalent of owning a Ferrari but keeping it idling. The wear and tear is minimal this time, but you’re not actually going anywhere either.
Better, of course, are the other two quadrants:
- low-strain, high-yield: consistently using our brain in relatively non-taxing ways that encourage its development
- high-strain, high-yield: here the Ferrari metaphor definitely fails, because unlike cars, our bodies (including our brains) are machines that benefit from judicious regular progressive overloading (but just by a bit, and with adequate recovery time between overloads).
See also: 12 Weeks To Measurably Boost Your Brain
How to do the “low-strain, low-yield” part
When it comes to “what’s the most important part of the brain to help in the face of cognitive decline?” the usual answer is either to focus on memory (hippocampi) or language (various parts, but for example Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area), since people most fear losing memory, and language is very important both socially and practically.
Those are indeed critical, and we at 10almonds stand by them, but Dr. Chapman (herself having originally trained as speech and language pathologist!) makes a strong case for adding a third brain part to the list.
Specifically, she advocates for strengthening the pre-frontal cortex, which is responsible for inhibition, task-switching, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. If that seems like a lot, do remember it’s a whole cortex and not one of the assorted important-but-small brain bits we mentioned above.
How? She has developed training programs for this, based on what she calls Strategic Memory Advanced Reasoning Tactics (SMART), to support support attention, planning, judgment and emotional management.
You can read more about those programs here:
Center For Brain Health | Our Programs
Participation in those is mostly not free, however, if you join their…
Center For Brain Health | BrainHealth Project
…then they will periodically invite you to join pilot programs, research programs, and the like, which will either be free or they-pay-you affairs—because this is how science is done, and you can read about yourself (anonymized, of course) later in peer-reviewed papers of the kind we often cite here.
If you’re not interested in any of that though, we will say that according to Dr. Chapman, the keys are:
Inhibition: be conscious of this function of your brain, and develop it. This is the function of your brain that stops you from making mistakes—or put differently: stops you from saying/doing something stupid.
Switching: do this consciously; per “I am now doing this task, now I am switching to this other task”, rather than doing the gear-grinding thing we discussed earlier
Working memory: this is effectively your brain’s RAM. Unlike the RAM of a computer (can be enhanced by adding another chip or replacing with a bigger chip), our brain’s RAM can be increased by frequent use, and especially by judicious use of progressive overloading (with rests between!) which we’ll discuss in the high-strain, high-yield section.
Flexibility: this is about creative problem-solving, openness to new ideas, and curiosity
See also: Curiosity Kills The Neurodegeneration
How to do the “high-strain, high-yield” part
Delighting this chess-playing writer, Dr. Chapman recommends chess. Although, similar games such as go (a Chinese game that looks simpler than chess but actually requires more calculation) work equally well too.
Why?
Games like chess and go cause structural changes that are particularly helpful, in terms of engaging in such foundational tasks as learning, abstract reasoning, problem-solving and self-control:
Chess Practice as a Protective Factor in Dementia
Basically, it checks (so to speak) a lot of boxes, especially for the pre-frontal cortex. Some notes:
- Focusing on the game is required for brain improvement; simply pushing wood casually will not do it. Ideally, calculating several moves ahead will allow for strong working memory use (because to calculate several moves ahead, one will have to hold increasingly many possible positions in the mind while doing so).
- The speed of play must be sufficiently slow as to allow not only for thinking, but also for what in chess is called “blunder-checking”, in other words, having decided on one’s move, pausing to consider whether it is a mistake, and actively trying to find evidence that it is. This is the crucial “inhibition habit”, and when one does it reflexively, one will make fewer mistakes. Tying this to dementia, see for example how one of the common symptoms of dementia is falling for scams that one wouldn’t have previously. How did cognitive decline make someone naïve? It didn’t, per se; it just took away their ability to, having decided what to do, pause to consider whether it was a mistake, and actively trying to find evidence that it is.
- That “conscious switching” that we talked about, rather than multitasking? In chess, there is a difference between strategy and tactics. Don’t worry about what that difference is for now (learn it if you want to take up chess), but know that strong players will only strategize while it is their opponent’s turn, and only calculate (tactics) while it is their own turn. It’s very tempting to flit constantly between one and the other, but chess requires players to have the mental discipline be able to focus on one task or the other and stick with that task until it’s the appointed time to switch.
If you feel like taking up chess, this site (and related app, if you want it) is free (it’s been funded by voluntary donations for a long time now) and good and even comes with free tuition and training tools: LiChess.org
Here’s another site that this writer (hi, it’s me) personally uses—it has great features too, but many are paywalled (I’m mostly there just because I’ve been there nearly since its inception, so I’m baked into the community now): Chess.com
Want to know more?
You might like this book by Dr. Chapman, which we haven’t reviewed yet but it did inform large parts of today’s article:
Make Your Brain Smarter: Increase Your Brain’s Creativity, Energy, and Focus – by Dr. Sandra Chapman
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Learning to Love Midlife – by Chip Conley
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While the book is titled about midlife, it could have said: midlife and beyond.
Some of the benefits discussed in this book really only kick in during one’s 50s, 60s, or 70s, usually. Which, for all but the most optimistic, is generally considered to be stretching beyond what is usually called “midlife”.
However! Chip Conley makes the argument for midlife being anywhere from one’s early 30s to mid-70s, depending on what (and how) we’re doing in life.
He talks about (as the subtitle promises) 12 reasons life gets better with age, and those reasons are grouped into 5 categories, thus:
- Physical life
- Emotional life
- Mental life
- Vocational life
- Spiritual life
It may surprise some readers that there are physical benefits that come with aging, but we do get two chapters in that category.
The writing style is very casual, yet with references to science throughout, and a bibliography for such.
Bottom line: if you’d like to make sure you’re making the most of your midlife and beyond, this a book that offers a lot of guidance on doing so!
Click here to check out Learning to Love Midlife, and age in style!
Share This Post
-
Healing Back Pain – by Dr. John Sarno
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Often when we review books with titles like this one, we preface it with a “what it’s not: a think-yourself-better book”.
In this case… It is, in fact, a think-yourself-better book. However, its many essay-length rave reviews caught our attention, and upon reading, we can report: its ideas are worth reading.
The focus of this book is on TMS, or “Tension Myoneural Syndrome”, to give it its full name. The author asserts (we cannot comment on the accuracy) that many cases of TMS are misdiagnosed as other things, from sciatica to lupus. When other treatments fail, or are simply not available (no cure for lupus yet, for example) or are unenticing (risky surgeries, for example), he offers an alternative approach.
Dr. Sarno lays out the case for TMS being internally fixable, since our muscles and nerves are all at the command of our brain. Rather than taking a physical-first approach, he takes a psychological-first approach, before building into a more holistic model.
The writing style is… A little dated and salesey and unnecessarily padded, to be honest, but the content makes it worthwhile.
Bottom line: if you have back pain, then the advice of this book, priced not much more than a box of top brand painkillers, seems a very reasonable thing to try.
Click here to check out Healing Back Pain, and see if it works for you!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Intuitive Eating Might Not Be What You Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In our recent Expert Insights main features, we’ve looked at two fairly opposing schools of thought when it comes to managing what we eat.
First we looked at:
What Flexible Dieting Really Means
…and the notion of doing things imperfectly for greater sustainability, and reducing the cognitive load of dieting by measuring only the things that are necessary.
And then in opposition to that,
What Are The “Bright Lines” Of Bright Line Eating?
…and the notion of doing things perfectly so as to not go astray, and reducing the cognitive load of dieting by having hard-and-fast rules that one does not second-guess or reconsider later when hungry.
Today we’re going to look at Intuitive Eating, and what it does and doesn’t mean.
Intuitive Eating does mean paying attention to hunger signals (each way)
Intuitive Eating means listening to one’s body, and responding to hunger signals, whether those signals are saying “time to eat” or “time to stop”.
A common recommendation is to “check in” with one’s body several times per meal, reflecting on such questions as:
- Do I have hunger pangs? Would I seek food now if I weren’t already at the table?
- If I hadn’t made more food than I’ve already eaten so far, would that have been enough, or would I have to look for something else to eat?
- Am I craving any of the foods that are still before me? Which one(s)?
- How much “room” do I feel I still have, really? Am I still in the comfort zone, and/or am I about to pass into having overeaten?
- Am I eating for pleasure only at this point? (This is not inherently bad, by the way—it’s ok to have a little more just for pleasure! But it is good to note that this is the reason we’re eating, and take it as a cue to slow down and remember to eat mindfully, and enjoy every bite)
- Have I, in fact, passed the point of pleasure, and I’m just eating because it’s in front of me, or so as to “not be wasteful”?
See also: Interoception: Improving Our Awareness Of Body Cues
And for that matter: Mindful Eating: How To Get More Out Of What’s On Your Plate
Intuitive Eating is not “80:20”
When it comes to food, the 80:20 rule is the idea of having 80% of one’s diet healthy, and the other 20% “free”, not necessarily unhealthy, but certainly not moderated either.
Do you know what else the 80:20 food rule is?
A food rule.
Intuitive Eating doesn’t do those.
The problem with food rules is that they can get us into the sorts of problems described in the studies showing how flexible dieting generally works better than rigid dieting.
Suddenly, what should have been our free-eating 20% becomes “wait, is this still 20%, or have I now eaten so much compared to the healthy food, that I’m at 110% for my overall food consumption today?”
Then one gets into “Well, I’ve already failed to do 80:20 today, so I’ll try again tomorrow [and binge meanwhile, since today is already written off]”
See also: Eating Disorders: More Varied (And Prevalent) Than People Think
It’s not “eat anything, anytime”, either
Intuitive Eating is about listening to your body, and your brain is also part of your body.
- If your body is saying “give me sugar”, your brain might add the information “fruit is healthier than candy”.
- If your body is saying “give me fat”, your brain might add the information “nuts are healthier than fried food”
- If your body is saying “give me salt”, your brain might add the information “kimchi is healthier than potato chips”
That doesn’t mean you have to swear off candy, fried food, or potato chips.
But it does mean that you might try satisfying your craving with the healthier option first, giving yourself permission to have the less healthy option afterwards if you still want it (you probably won’t).
See also:
I want to eat healthily. So why do I crave sugar, salt and carbs?
Want to know more about Intuitive Eating?
You might like this book that we reviewed previously:
Intuitive Eating – by Evelyn Tribole and Elyse Resch
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Easiest Way To Take Up Journaling
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dear Diary…
It’s well-established that journaling is generally good for mental health. It’s not a magical panacea, as evidenced by The Diaries of Franz Kafka for example (that man was not in good mental health). But for most of us, putting our thoughts and feelings down on paper (or the digital equivalent) is a good step for tidying our mind.
And as it can be said: mental health is also just health.
But…
What to write about?
It’s about self-expression (even if only you will read it), and…
❝Writing about traumatic, stressful or emotional events has been found to result in improvements in both physical and psychological health, in non-clinical and clinical populations.
In the expressive writing paradigm, participants are asked to write about such events for 15–20 minutes on 3–5 occasions.
Those who do so generally have significantly better physical and psychological outcomes compared with those who write about neutral topics.❞
Source: Emotional and physical health benefits of expressive writing
In other words, write about whatever moves you.
Working from prompts
If you read the advice above and thought “but I don’t know what moves me”, then fear not. It’s perfectly respectable to work from prompts, such as:
- What last made you cry?
- What last made you laugh?
- What was a recent meaningful moment with family?
- What is a serious mistake that you made and learned from?
- If you could be remembered for just one thing, what would you want it to be?
In fact, sometimes working from prompts has extra benefits, precisely because it challenges us to examine things we might not otherwise think about.
If a prompt asks “What tends to bring you most joy recently?” and the question stumps you, then a) you now are prompted to look at what you can change to find more joy b) you probably wouldn’t have thought of this question—most depressed people don’t, and if you cannot remember recent joy, then well, we’re not here to diagnose, but let’s just say that’s a symptom.
A quick aside: if you or a loved oneare prone to depressive episodes, here’s a good resource, by the way:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
And in the event of the mental health worst case scenario:
The six prompts we gave earlier are just ideas that came to this writer’s mind, but they’re (ok, some bias here) very good ones. If you’d like more though, here’s a good resource:
550+ Journal Prompts: The Ultimate List
The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly
While it’s not good to get stuck in ruminative negative thought spirals, it is good to have a safe outlet to express one’s negative thoughts/feelings:
Remember, your journal is (or ideally, should be) a place without censure. If you fear social consequences should your journal be read, then using an app with a good security policy and encryption options can be a good idea for journaling
Finch App is a good free option if it’s not too cutesy for your taste, because in terms of security:
- It can’t leak your data because your data never leaves your phone (unless you manually back up your data and then you choose to put it somewhere unsafe)
- It has an option to require passcode/biometrics etc to open the app
As a bonus, it also has very many optional journaling prompts, and also (optional) behavioral activation prompts, amongst more other offerings that we don’t have room to list here.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs
We asked you for your (health-related) policy on sugar. The trends were as follows:
- About half of all respondents voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Refined sugar is terrible; natural sugars (e.g. honey, agave) are fine”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad; I avoid it entirely”
- One (1) respondent voted for “Sugar is an important source of energy, so I consume plenty”
Writer’s note: I always forget to vote in these, but I’d have voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”.
Sometimes I would like to make my own [whatever] to not have the sugar, but it takes so much more time, and often money too.
So while I make most things from scratch (and typically spend about an hour cooking each day), sometimes store-bought is the regretfully practical timesaver/moneysaver (especially when it comes to condiments).
So, where does the science stand?
There has, of course, been a lot of research into the health impact of sugar.
Unfortunately, a lot of it has been funded by sugar companies, which has not helped. Conversely, there are also studies funded by other institutions with other agendas to push, and some of them will seek to make sugar out to be worse than it is.
So for today’s mythbusting overview, we’ve done our best to quality-control studies for not having financial conflicts of interest. And of course, the usual considerations of favoring high quality studies where possible Large sample sizes, good method, human subjects, that sort of thing.
Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
- Sucrose is sucrose, and is generally bad.
- Fructose is fructose, and is worse.
Both ultimately get converted into glycogen (if not used immediately for energy), but for fructose, this happens mostly* in the liver, which a) taxes it b) goes very unregulated by the pancreas, causing potentially dangerous blood sugar spikes.
This has several interesting effects:
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, it doesn’t cause insulin insensitivity (yay)
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, this leaves hyperglycemia untreated (oh dear)
- Because fructose is metabolized by the liver and converted to glycogen which is stored there, it’s one of the main contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (at this point, we’re retracting our “yay”)
Read more: Fructose and sugar: a major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
*”Mostly” in the liver being about 80% in the liver. The remaining 20%ish is processed by the kidneys, where it contributes to kidney stones instead. So, still not fabulous.
Fructose is very bad, so we shouldn’t eat too much fruit: True or False?
False! Fruit is really not the bad guy here. Fruit is good for you!
Fruit does contain fructose yes, but not actually that much in the grand scheme of things, and moreover, fruit contains (unless you have done something unnatural to it) plenty of fiber, which mitigates the impact of the fructose.
- A medium-sized apple (one of the most sugary fruits there is) might contain around 11g of fructose
- A tablespoon of high-fructose corn syrup can have about 27g of fructose (plus about 3g glucose)
Read more about it: Effects of high-fructose (90%) corn syrup on plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and normal subjects
However! The fiber content (in fruit) mitigates the impact of the fructose almost entirely anyway.
And if you take fruits that are high in sugar and/but high in polyphenols, like berries, they now have a considerable net positive impact on glycemic health:
- Polyphenols and Glycemic Control
- Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review
- Dietary polyphenols as antidiabetic agents: Advances and opportunities
You may be wondering: what was that about “unless you have done something unnatural to it”?
That’s mostly about juicing. Juicing removes much (or all) of the fiber, and if you do that, you’re basically back to shooting fructose into your veins:
- Effect of Fruit Juice on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials
- Intake of Fruit, Vegetables, and Fruit Juices and Risk of Diabetes in Women
Natural sugars like honey, agave, and maple syrup, are healthier than refined sugars: True or False?
True… Sometimes, and sometimes marginally.
This is partly because of the glycemic index and glycemic load. The glycemic index scores tail off thus:
- table sugar = 65
- maple syrup = 54
- honey = 46
- agave syrup = 15
So, that’s a big difference there between agave syrup and maple syrup, for example… But it might not matter if you’re using a very small amount, which means it may have a high glycemic index but a low glycemic load.
Note, incidentally, that table sugar, sucrose, is a disaccharide, and is 50% glucose and 50% fructose.
The other more marginal health benefits come from that fact that natural sugars are usually found in foods high in other nutrients. Maple syrup is very high in manganese, for example, and also a fair source of other minerals.
But… Because of its GI, you really don’t want to be relying on it for your nutrients.
Wait, why is sugar bad again?
We’ve been covering mostly the more “mythbusting” aspects of different forms of sugar, rather than the less controversial harms it does, but let’s give at least a cursory nod to the health risks of sugar overall:
- Obesity and associated metabolic risk
- Main contributor to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Insulin resistance and diabetes risk
- Cellular aging (shortened telomeres)
- 95% increased cancer risk
That last one, by the way, was a huge systematic review of 37 large longitudinal cohort studies. Results varied depending on what, specifically, was being examined (e.g. total sugar, fructose content, sugary beverages, etc), and gave up to 200% increased cancer risk in some studies on sugary beverages, but 95% increased risk is a respectable example figure to cite here, pertaining to added sugars in foods.
And finally…
The 56 Most Common Names for Sugar (Some Are Tricky)
How many did you know?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: