This Is When Your Muscles Are Strongest
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Karyn Esser is a professor in the Department of Physiology and Aging at the University of Florida, where she’s also the co-director of the University of Florida Older Americans Independence Center, and she has insights to share on when it’s best to exercise:
It’s 4–5pm
Surprise, no clickbait or burying the lede!
This goes regardless of age or sex, but as we get older, it’s common for our circadian rhythm to weaken, which may result in a tendency to fluctuate a bit more.
However, since it’s healthy to keep one’s circadian rhythm as stable as reasonably possible, this is a good reason to try to keep our main exercise focused around that time of day, as it provides a sort of “anchor point” for the rest of our day to attach to, so that our body can know what time it is relative to that.
It’s also the most useful time of day to exercise, because most exercises give benefits proportional to progressive overloading, so training at our peak efficiency time will give the most efficient results. So much for those 5am runs!
On which note: while the title says “strongest” and the thumbnail has dumbbells, this does go for all different types of exercises that have been tested.
For more details on all of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

The Science of Nutrition – by Rhiannon Lambert
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While there are a lot of conflicting dietary approaches out there, the science itself is actually fairly cohesive in most regards. This book does a lot of what we do here at 10almonds, and presents the science in a clear fashion without having any particular agenda to push.
The author is a nutritionist (BSc, MSc, RNutr) and therefore provides an up-to-date evidence-based approach for eating.
As a result, the only part of this book that brings it down in this reviewer’s opinion is the section on Intermittent Fasting. Being not strictly about nutrition, she has less expertise on that topic, and it shows.
The information is largely presented in double-page spreads each answering a particular question. Because of this, and the fact there are colorful graphic representations of information too, we do recommend the print version over Kindle*.
Bottom line: if you like the notion of real science being presented in a clear and simple fashion (we like to think our subscribers do!), then you’ll surely enjoy this book.
Click here to check out the Science of Nutrition, and get a clear overview!
*Writer’s note: I realize I’ve two days in a row recommended this (yesterday because there are checkboxes to check, worksheets to complete, etc), but it’s not a new trend; just how it happened to be with these two books. I love my Kindle dearly, but sometimes print has the edge for one reason or another!
Share This Post

Tech Bliss – by Clo S., MSc.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The popular idea of a “digital detox” is simple enough, “just unplug!”, they say.
But here in the real world, not only is that often not practical for many of us, it may not always even be entirely desirable. The Internet (and our devices with all their bells and whistles) can be a source of education, joy, and connection!
So, how to find out what’s good for us and what’s not, in our daily digital practices? Clo. S. has answers… Or rather, experiments for us to do and find out for ourselves.
These experiments range from the purely practical “try this to streamline your experience” to the more personal “how does this thing make you feel?”. A lot of the experiments will be performed via your digital devices—some, without! Others are about online interpersonal dynamics, be they one-on-one or navigating a world in which it seems everyone is out to get us, our outrage, and/or our money. Still yet others are about optimizing what you do get from the parts of your digital experience that are enriching for you.
As the title suggests, there are 30 experiments, and it’s not a stretch to do them one per day for a month. But, as the author notes, it’s by no means necessary to do them like that; it’s a workbook and reference guide, not a to-do list!
(On the topic of it being a reference guide…There’s also an extensive tools directory towards the end!)
In short: this is a great book for optimizing your online experience—whatever that might mean for you personally; you can decide for yourself along the way!
Click here to get a copy of Tech Bliss: 30 Experiments For Your Digital Wellness today!
Share This Post

Who Screens The Sunscreens?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Screen The Sunscreens!

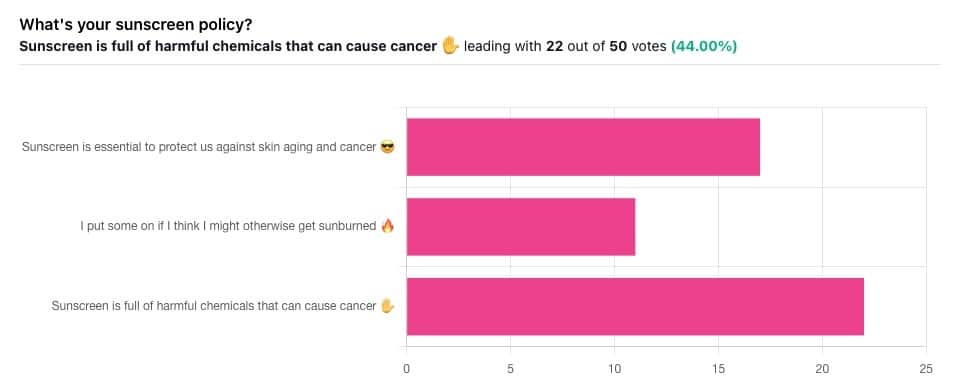
Yesterday, we asked you what your sunscreen policy was, and got a spread of answers. Apparently this one was quite polarizing!
One subscriber who voted for “Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer” wrote:
❝My mom died of complications from melanoma, so we are vigilant about sun and sunscreen. We are a family of campers and hikers and gardeners—outdoors in all seasons—and we never burn❞
Our condolences with regard to your mom! Life is so precious, and when something like that happens, it tends to stick with us. We’re glad you and your family are taking care of yourselves.
Of the subscribers who voted for “I put some on if I think I might otherwise get sunburned”, about half wrote to express uncertainties:
- uncertainty about how safe it is, and
- uncertainty about how helpful it is
…so we’re going to tackle those questions in a moment. But what of those who voted for “Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer”?
Of those, only one wrote a message, which was to say one has to be very careful of what is in the formula.
Let’s take a look, then…
Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer: True or False?
False—according to current best science. Research is ongoing!
There are four main chemicals (found in most sunscreens) that people tend to worry about:
- Abobenzone
- Oxybenzone
- Octocrylene
- Ecamsule
Now, these two sound like four brands of rocket fuel, but then, dihydrogen monoxide (DHMO), which is also found in most sunscreens, sounds like a deadly toxin too. That’s water, by the way.
But what of these four chemicals? Well, as we say, research is ongoing, but we found a study that measured all four, to see how much got into the blood, and what adverse effects, if any, this caused.
We’ll skip to their conclusion:
❝In this preliminary study involving healthy volunteers, application of 4 commercially available sunscreens under maximal use conditions resulted in plasma concentrations that exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens. The systemic absorption of sunscreen ingredients supports the need for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings. These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.❞
Now, “exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens” sounds alarming, so why did they close with the words “These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen”?
Let’s skip back up to a line from the results:
❝The most common adverse event was rash, which developed in 1 participant with each sunscreen.❞
This was most probably due to the oxybenzone, which can cause allergic skin reactions in some people.
Let us take a moment to remember the most common adverse event that occurs from not wearing sunscreen: sunburn!
You can read the full study here:
None of those ingredients have been found to be carcinogenic, even at the maximal blood plasma concentrations studied, from applications 4x/day to 75% of the body.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are absolutely very much known to cause cancer, and the effect is cumulative.
Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer: True or False?
True, unequivocally, unless we live indoors and/or otherwise never go about under sunlight.
“But our ancestors—” lived under the same sun we do, and either used sunscreen or got advanced skin aging and cancer.
Sunscreen of times past ranged from mud to mineral lotions, but it’s pretty much always existed. Even non-human animals that have skin and don’t have fur or feathers, tend to take mud-baths in sunny parts of the world.
If you’d like to avoid oxybenzone and other chemicals, though, you might have your reasons. Maybe you’re allergic, or maybe you read that it’s a potential endocrine disruptor with estrogen-like and anti-androgenic properties that you don’t want.
There are other options, to include physical blockers containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective ingredients.
If you’re interested, you can even make your own sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays (UVA is what causes skin cancer; UVB is “milder” and is what causes sunburn):
Share This Post
Related Posts

It’s Not A Bloody Trend – by Kat Brown
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one’s not a clinical book, and the author is not a clinician. However, it’s not just a personal account, either. Kat Brown is an award-winning journalist (with ADHD) and has approached this journalistically.
Not just in terms of investigative journalism, either. Rather, also with her knowledge and understanding of the industry, doing for us some meta-journalism and explaining why the press have gone for many misleading headlines.
Which in this case means for example it’s not newsworthy to say that people have gone undiagnosed and untreated for years and that many continue to go unseen; we know this also about such things as endometriosis, adenomyosis, and PCOS. But some more reactionary headlines will always get attention, e.g. “look at these malingering attention-seekers”.
She also digs into the common comorbidities of various conditions, the differences it makes to friendships, families, relationships, work, self-esteem, parenting, and more.
This isn’t a “how to” book, but there’s a lot of value here if a) you have ADHD, and/or b) you spend any amount of time with someone who does.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand “what all the fuss is about” in one book, this is the one for ADHD.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

World Menopause Day Health News Round-Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In order to provide variety in this week’s round-up, not all of this is menopause-related, but it is all important:
Menopause & CVD
Untreated menopause is associated with higher incidence of heart disease, and higher mortality. People often forget about how much estrogen does for us (well, for those of us with a physiology running on estrogen, anyway; gentlemen, your testosterone is fine for you), and think it is “just” a sex hormone, but it’s a lot more.
Read in full: Menopause transition linked to increased heart disease risk
Related: What Menopause Does To The Heart
Extraterrestrial medical technology
The much lower gravity in Earth orbit has allowed for tissue engineering techniques that Earth’s normal gravity imposes limitations on. This is big news, because it means that rather than replacing a whole liver, tissue implants could be grafted, allowing the extant liver to repair itself (something livers are famously good at, but they need enough undamaged base material to work with).
Read in full: How liver tissue from the International Space Station may transform tissue engineering
Related: How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
One thing and then another
As if endometriosis weren’t unpleasant enough in and of itself, the endothelial dysfunction inherent to it also raises cardiovascular disease risk. This is important, because while endometriosis has (like many maladies predominantly affecting women) generally been shrugged off by the medical world as an unhappy inconvenience but not life-threatening, now we know it comes with extra existential risks too:
Read in full: Understanding cardiovascular risks in endometriosis patients
Related: What You Need To Know About Endometriosis
Push-button meditation
Unlike mindfulness meditation, listening to music is a very passive experience, and thus requires less effort from the user. And yet, it has been associated with lower perceived pain levels, lower self-reported anxiety levels, less opioid use, and measurably lower heart-rate.
Read in full: Listening to music may speed up recovery from surgery, research suggests
Related: Nobody Likes Surgery, But Here’s How To Make It Much Less Bad
Cholesterol in menopause: quality over quantity
Much like previous research has shown that the quantity of LDL is not nearly so predictive of health outcomes in women as it is in men, this study into HDL and menopausal women shows that quantity of HDL does not matter nearly so much as the quality of it.
Read in full: HDL quality, not quantity, contribute to the first sign of Alzheimer’s disease in women
Related: Statins: His & Hers? ← consistent with the above, statins (to lower LDL cholesterol) generally help more for men and produce more adverse side effects for women. So again, a case of “the actual amount of cholesterol isn’t so important for women as for men”.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Water Fluoridation, Atheroma, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I watched a documentary recently on Fluoride in our drinking water & the dangers of it. Why are we poisoning our water?❞
This is a great question, and it certainly is controversial. It sounds like the documentary you watched was predominantly or entirely negative, but there’s a lot of science to back both sides of this, and it’s not even that the science is contradictory (it’s not). It’s that what differs is people’s opinions about whether benefiting one thing is worth creating a risk to another, and that means looking at:
- What is the risk associated with taking no action (error of omission)?
- What is the risk associated with taking an action (error of commission)?
The whole topic is worth a main feature, but to summarize a few key points:
- Water fluoridation is considered good for the prevention of dental cavities
- Water fluoridation aims to deliver fluoride and doses far below dangerous levels
- This requires working on consumer averages, though
- ”Where do we put the safety margins?” is to some extent a subjective question, in terms of trading off one aspect of health for another
- Too much fluoride can also be bad for the teeth (at least cosmetically, creating little white* spots)
- Detractors of fluoride tend to mostly be worried about neurological harm
- However, the doses in public water supplies are almost certainly far below the levels required to cause this harm.
- That said, again this is working on consumer averages, though.
- However, the doses in public water supplies are almost certainly far below the levels required to cause this harm.
- A good guide is: watch your teeth! Those white* spots will be “the canary in the coal mine” of more serious harm that could potentially come from higher levels due to overconsumption of fluorine.
*Teeth are not supposed to be pure white. The “Hollywood smile” is a lie. Teeth are supposed to be a slightly off-white, ivory color. Anything whiter than that is adding something else that shouldn’t be there, or stripping something off that should be there.
❝How does your diet change clean out your arteries of the bad cholesterol?❞
There’s good news and bad news here, and they can both be delivered with a one-word reply:
Slowly.
Or rather: what’s being cleaned out is mostly not the LDL (bad) cholesterol, but rather, the result of that.
When our diet is bad for cardiovascular health, our arteries get fatty deposits on their walls. Cholesterol gets stuck here too, but that’s not the main physical problem.
Our body’s natural defenses come into action and try to clean it up, but they (for example macrophages, a kind of white blood cell that consumes invaders and then dies, before being recycled by the next part of the system) often get stuck and become part of the buildup (called atheroma), which can lead to atherosclerosis and (if calcium levels are high) hardening of the arteries, which is the worst end of this.
This can then require medical attention, precisely because the body can’t remove it very well—especially if you are still maintaining a heart-unhealthy diet, thus continuing to add to the mess.
However, if it is not too bad yet, yes, a dietary change alone will reverse this process. Without new material being added to the arterial walls, the body’s continual process of rejuvenation will eventually fix it, given time (free from things making it worse) and resources.
In fact, your arteries can be one of the quickest places for your body to make something better or worse, because the blood is the means by which the body moves most things (good or bad) around the body.
All the more reason to take extra care of it, since everything else depends on it!
You might also like our previous main feature:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: