The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Hormone Balancing Act
We’ve written before about menopausal HRT:
What You Should Have Been Told About Menopause Beforehand
…and even specifically about the considerations when it comes to breast cancer risk:
Menopausal Hormone Replacement Therapy
this really does bear reading, by the way—scroll down to the bit about breast cancer risk, because it’s not a simple increased/decreased risk; it can go either way, and which way it goes will depend on various factors including your medical history and what HRT, if any, you are taking.
Hormone Modulating Therapy
Hormone modulating therapy, henceforth HMT, is something a little different.
Instead of replacing hormones, as hormone replacement therapy does, guess what hormone modulating therapy does instead? That’s right…
MHT can modulate hormones by various means, but the one we’re going to talk about today does it by blocking estrogen receptors,
Isn’t that the opposite of what we want?
You would think so, but since for many people with an increased breast cancer risk, the presence of estrogen increases that risk, which leaves menopausal (peri- or post) people in an unfortunate situation, having to choose between increased breast cancer risk (with estrogen), or osteoporosis and increased dementia risk, amongst other problems (without).
However, the key here (in fact, that’s a very good analogy) is in how the blocker works. Hormones and their receptors are like keys and locks, meaning that the wrong-shaped hormone won’t accidentally trigger it. And when the right-shaped hormone comes along, it gets activated and the message (in this case, “do estrogenic stuff here!” gets conveyed). A blocker is sufficiently similar to fit into the receptor, without being so similar as to otherwise act as the hormone.
In this case, it has been found that HMT blocking estrogen receptors was sufficient to alleviate the breast cancer risk, while also being associated with a 7% lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease or related dementias, with that risk reduction being even greater for some demographics depending on race and age. Black women in the 65–74 age bracket enjoyed a 24% relative risk reduction, with white women of the same age getting an 11% relative risk reduction. Black women enjoyed the same benefits after that age, whereas white women starting it at that age did not get the same benefits. The conclusion drawn from this is that it’s good to start this at 65 if relevant and practicable, especially if white, because the protective effect is strongest when gained aged 65–69.
Here’s a pop-science article that goes into the details more deeply than we have room for here:
Hormone therapy for breast cancer linked with lower dementia risk
And here’s the paper itself; we highly recommend reading at least the abstract, because it goes into the numbers in much more detail than we reasonably can here. It’s a huge cohort study of 18,808 women aged 65 years or older, so this is highly relevant data:
Want to learn more?
If you’d like a much deeper understanding of breast cancer risk management, including in the context of hormone therapy, you might like this excellent book that we reviewed recently:
The Smart Woman’s Guide to Breast Cancer – by Dr. Jenn Simmons
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
12 Questions For Better Brain Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We usually preface our “Expert Insights” pieces with a nice banner that has a stylish tall cutout that allows us to put a photo of the expert in. Today we’re not doing that, because for today’s camera-shy expert, we could only find one photo, and it’s a small, grainy, square headshot that looks like it was taken some decades ago, and would not fit our template at all. You can see it here, though!
In any case, Dr. Linda Selwa is a neurologist and neurophysiologist with nearly 40 years of professional experience.
The right questions to ask
As a neurologist, she found that one of the problems that results in delayed interventions (and thus, lower efficacy of those interventions) is that people don’t know there’s anything to worry about until a degenerative brain condition has degenerated past a certain point. With that in mind, she bids us ask ourselves the following questions, and discuss them with our primary healthcare providers as appropriate:
- Sleep: Are you able to get sufficient sleep to feel rested?
- Affect, mood and mental health: Do you have concerns about your mood, anxiety, or stress?
- Food, diet and supplements: Do you have concerns about getting enough or healthy enough food, or have any questions about supplements or vitamins?
- Exercise: Do you find ways to fit physical exercise into your life?
- Supportive social interactions: Do you have regular contact with close friends or family, and do you have enough support from people?
- Trauma avoidance: Do you wear seatbelts and helmets, and use car seats for children?
- Blood pressure: Have you had problems with high blood pressure at home or at doctor visits, or do you have any concerns about blood pressure treatment or getting a blood pressure cuff at home?
- Risks, genetic and metabolic factors: Do you have trouble controlling blood sugar or cholesterol? Is there a neurological disease that runs in your family?
- Affordability and adherence: Do you have any trouble with the cost of your medicines?
- Infection: Are you up to date on vaccines, and do you have enough information about those vaccines?
- Negative exposures: Do you smoke, drink more than one to two drinks per day, or use non-prescription drugs? Do you drink well water, or live in an area with known air or water pollution?
- Social and structural determinants of health: Do you have concerns about keeping housing, having transportation, having access to care and medical insurance, or being physically or emotionally safe from harm?
You will note that some of these are well-known (to 10almonds readers, at least!) risk factors for cognitive decline, but others are more about systemic and/or environmental considerations, things that don’t directly pertain to brain health, but can have a big impact on it anyway.
About “concerns”: in the case of those questions that ask “do you have concerns about…?”, and you’re not sure, then yes, you do indeed have concerns.
About “trouble”: as for these kinds of health-related questionnaires in general, if a question asks you “do you have trouble with…?” and your answer is something like “no, because I have a special way of dealing with that problem” then the answer for the purposes of the questionnaire is yes, you do indeed have trouble.
Note that you can “have trouble with” something that you simultaneously “have under control”—just as a person can have no trouble at all with something that they leave very much out of control.
Further explanation on each of the questions
If you’re wondering what is meant by any of these, or what counts, or why the question is even being asked, then we recommend you check out Dr. Selwa et al’s recently-published paper, then all is explained in there, in surprisingly easy-to-read fashion:
Emerging Issues In Neurology: The Neurologist’s Role in Promoting Brain Health
If you scroll past the abstract, introduction, and disclaimers, then you’ll be straight into the tables of information about the above 12 factors.
Want to be even more proactive?
Check out:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Big Think’s #1 Antidote To Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Why This Video Is Important
A lot of what we talk about here at 10almonds is focused on healthy aging. We want you – our lovely readers – to not only live for a long time, but also be healthy enough to enjoy that “long time”.
We’ve talked about anything from Dr. Greger’s eight anti-aging interventions, to the specific benefits of resveratrol or metformin in combatting aging, to even reducing stress-induced aging.
So, why is this video important? It goes beyond just talking about what we know about living longer, but also focuses on how we should live longer; there’s a big difference between living a long life but never leaving your house vs. living a long life beyond your front door.
The Takeaways
The core message that Big Think wants to convey is that our lifestyle is our best bet in slowing the aging process. Our bodies are adaptive systems, responding positively to healthy lifestyle choices. They focus on exercise: regular physical activity increases healthspan, consequently extending lifespan.
A key takeaway is the difference between physical activity and exercise. While any movement counts as physical activity, exercise is a deliberate, health-focused activity. It benefits the brain by releasing growth factors that strengthen critical areas like the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
The video encourages embracing physical activity in any form available to you, from gardening to walking. The goal isn’t to hit a specific number of steps but to stay active in a way that suits your lifestyle.
Science may not solve death. Yet. But focusing on maintaining a healthy, functioning state for as long as possible is the real victory in the battle against aging. And, at the moment, exercise seems to be our best bet:
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hormonal Health: Is It Really A Balancing Act?
Have you ever wondered what “balancing your hormones” actually means?
The popular view is that men’s hormones look like this:
Testosterone (less) ⟷ Testosterone (more)
…And that women’s hormones look more like this:
♀︎ Estrogen ↭ Progesterone ⤵︎
⇣⤷ FSH ⤦ ↴ ☾ ⤹⤷ Luteinizing Hormone ⤦
DHEA ↪︎ Gonadotrophin ⤾
↪︎ Testosterone? ⥅⛢
Clear as mud, right?
But, don’t worry, Supplements McHerbal Inc will sell you something guaranteed to balance your hormones!
How can a supplement (or dietary adjustment) “balance” all that hotly dynamic chaos, and make everything “balanced”?
The truth is, “balanced” in such a nebulous term, and this is why you will not hear endocrinologists using it. It’s used in advertising to mean “in good order”, and “not causing problems”, and “healthy”.
In reality, our hormone levels depend on everything from our diet to our age to our anatomy to our mood to the time of the day to the phase of the moon.
Not that the moon has an influence on our physiology at all—that’s a myth—but you know, 28 day cycle and all. And, yes, half the hormones affect the levels of the others, either directly or indirectly.
Trying to “balance” them would be quite a game of whack-a-mole, and not something that a “cure-all” single “hormone-balancing” supplement could do.
So why aren’t we running this piece on Friday, for our “mythbusting” section? Well, we could have, but the more useful information is yet to come and will take up more of today’s newsletter than the myth-busting!
What, then, can we do to untangle the confusion of these hormones?
Well first, let’s understand what they do, in the most simple terms possible:
- Estrogen—the most general feminizing hormone from puberty onwards, busiest in the beginning of the menstrual cycle, and starts getting things ready for ovulation.
- Progesterone—secondary feminizing hormone, fluffs the pillows for the oncoming fertilized egg to be implanted, increases sex drive, and adjusts metabolism accordingly. Busiest in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
- Testosterone—is also present, contributes to sex drive, is often higher in individuals with PCOS. If menopause is untreated, testosterone will also rise, because there will be less estrogen
- (testosterone and estrogen “antagonize” each other, which is the colorfully scientific way of saying they work against each other)
- DHEA—Dehydroepiandrosterone, supports production of testosterone (and estrogen!). Sounds self-balancing, but in practice, too much DHEA can thus cause elevated testosterone levels, and thus hirsutism.
- Gonadotrophin—or more specifically human chorionic gonadotrophin, HcG, is “the pregnancy hormone“, present only during pregnancy, and has specific duties relating to such. This is what’s detected in (most) pregnancy test kits.
- FSH—follicle stimulating hormone, is critical to ovulation, and is thus essential to female fertility. On the other hand, when the ovaries stop working, FSH levels will rise in a vain attempt to encourage the ovulation that isn’t going to happen anymore.
- Luteinizing hormone—says “go” to the new egg and sends it on its merry way to go get fertilized. This is what’s detected by ovulation prediction kits.
Sooooooo…
What, for most women, most often is meant by a “hormonal imbalance” is:
- Low levels of E and/or P
- High levels of DHEA and/or T
- Low or High levels of FSH
In the case of low levels of E and/or P, the most reliable way to increase these is, drumroll please… To take E and/or P. That’s it, that’s the magic bullet.
Bonus Tip: take your E in the morning (this is when your body will normally make more and use more) take your P in the evening (it won’t make you sleepy, but it will improve your sleep quality when you do sleep)
In the case of high levels of DHEA and/or T, then that’s a bit more complex:
- Taking E will antagonize (counteract) the unwanted T.
- Taking T-blockers (such as spironolactone or bicalutamide) will do what it says on the tin, and block T from doing the jobs it’s trying to do, but the side-effects are considered sufficient to not prescribe them to most people.
- Taking spearmint or saw palmetto will lower testosterone’s effects
- Scientists aren’t sure how or why spearmint works for this
- Saw palmetto blocks testosterone’s conversion into a more potent form, DHT, and so “detoothes” it a bit. It works similarly to drugs such as finasteride, often prescribed for androgenic alopecia, called “male pattern baldness”, but it affects plenty of women too.
In the case of low levels of FSH, eating leafy greens will help.
In the case of high levels of FSH, see a doctor. HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy) may help. If you’re not of menopausal age, it could be a sign something else is amiss, so it could be worth getting that checked out too.
What can I eat to boost my estrogen levels naturally?
A common question. The simple answer is:
- Flaxseeds and soy contain plant estrogens that the body can’t actually use as such (too incompatible). They’ve lots of high-quality nutrients though, and the polyphenols and isoflavones can help with some of the same jobs when it comes to sexual health.
- Fruit, especially peaches, apricots, blueberries, and strawberries, contain a lot of lignans and also won’t increase your E levels as such, but will support the same functions and reduce your breast cancer risk.
- Nuts, especially almonds (yay!), cashews, and pistachios, contain plant estrogens that again can’t be used as bioidentical estrogen (like you’d get from your ovaries or the pharmacy) but do support heart health.
- Leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables support a lot of bodily functions including good hormonal health generally, in ways that are beyond the scope of this article, but in short: do eat your greens!
Note: because none of these plant-estrogens or otherwise estrogenic nutrients can actually do the job of estradiol (the main form of estrogen in your body), this is why they’re still perfectly healthy for men to eat too, and—contrary to popular “soy boy” social myths—won’t have any feminizing effects whatsoever.
On the contrary, most of the same foods support good testosterone-related health in men.
The bottom line:
- Our hormones are very special, and cannot be replaced with any amount of herbs or foods.
- We can support our body’s natural hormonal functions with good diet, though.
- Our hormones naturally fluctuate, and are broadly self-correcting.
- If something gets seriously out of whack, you need an endocrinologist, not a homeopath or even a dietician.
In case you missed it…
We gave a more general overview of supporting hormonal health (including some hormones that aren’t sex hormones but are really important too), back in February.
Check it out here: Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them
Want to read more?
Anthea Levi, RD, takes much the same view:
❝For some ‘hormone-balancing’ products, the greatest risk might simply be lost dollars. Others could come at a higher cost.❞
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How to Fall Back Asleep After Waking Up in the Middle of the Night
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michael Bruce, the Sleep Doctor, addresses a common concern: waking up in the middle of the night and struggling to fall back asleep.
Understanding the Wake-Up
Firstly, why are we waking up during the night?
Waking up between 2 AM and 3 AM is said to be normal, and linked to your core body temperature. As your body core temperature drops, to trigger melatonin release, and then rises again, you get into a lighter stage of sleep. This lighter stage of sleep makes you more prone to waking up.
Note, there are also some medical conditions (such as sleep apnea) that can cause you to wake up during the night.
But, what can we do about it? Aside from constantly shifting sleeping position (Should I be sleeping on my back? On my left? Right?)
Avoid the Clock
The first step is to resist the urge to check the time. It’s easy to be tempted to have a look at the clock, however, doing so can increase anxiety, making it harder to fall back asleep. As Dr. Bruce says, sleep is like love—the less you chase it, the more it comes.
It may be useful to point your alarm clock (if you still have one of those) the opposite direction to your bed.
Embracing Non-Sleep Deep Rest (NSDR)
Whilst this may not help you fall back asleep, it’s worth pointing out that just lying quietly in the dark without moving still offers rejuvenation. This revujenating stage is called Non-Sleep Deep Rest (otherwise known as NSDR)
If you’re not familiar with NSDR, check out our overview of Andrew Huberman’s opinions on NSDR here.
So, you can reassure yourself that whilst you may not be asleep, you are still resting.
Keep Your Heart Rate Down
To fall back asleep, it’s best if your heart rate is below 60 bpm. So, Dr. Bruce advises avoiding void getting up unnecessarily, as moving around can elevate your heart rate.
On a similar vain, he introduces the 4-7-8 breathing technique, which is designed to lower your heart rate. The technique is simple:
- Breathe in for 4 seconds.
- Hold for 7 seconds.
- Exhale for 8 seconds.
Repeat this cycle gently to calm your body and mind.
As per any of our Video Breakdowns, we only try to capture the most important pieces of information in text; the rest can be garnered from the video itself:
Wishing you a thorough night’s rest!
Do you know any other good videos on sleep? Send them to us via email!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
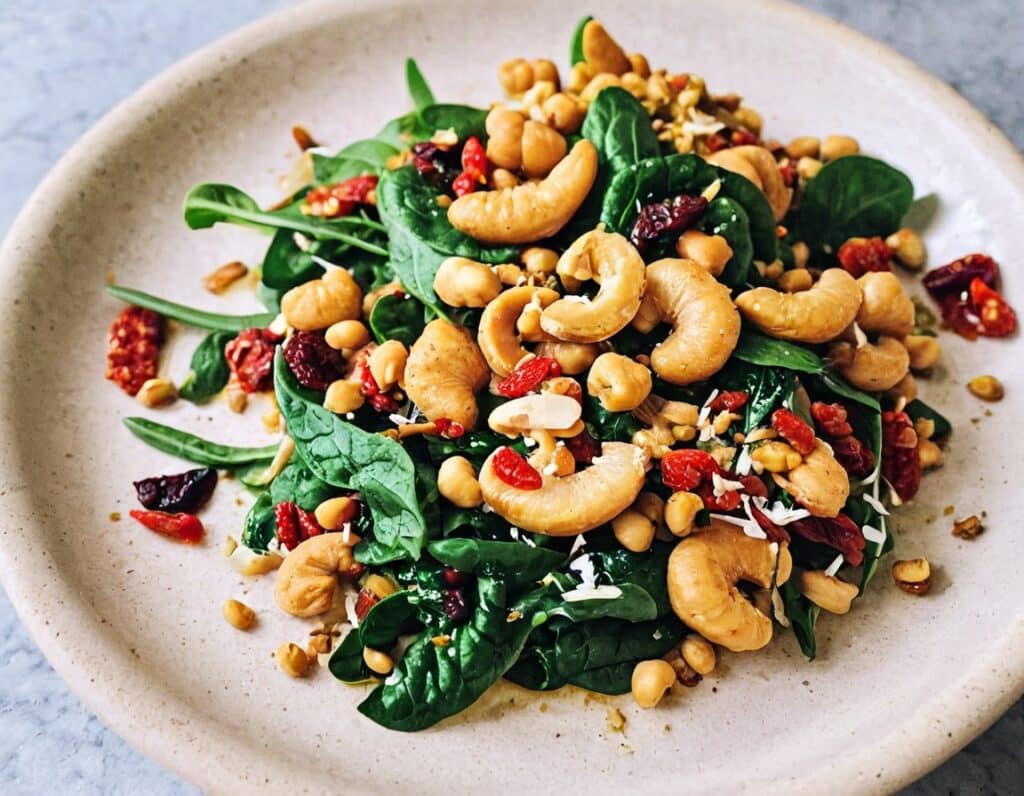
Protein Immune Support Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to get enough protein from a salad, without adding meat? Cashews and chickpeas have you more than covered! Along with the leafy greens and an impressive array of minor ingredients full of healthy phytochemicals, this one’s good for your muscles, bones, skin, immune health, and more.
You will need
- 1½ cups raw cashews (if allergic, omit; the chickpeas and coconut will still carry the dish for protein and healthy fats)
- 2 cans (2x 14oz) chickpeas, drained
- 1½ lbs baby spinach leaves
- 2 large onions, finely chopped
- 3 oz goji berries
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp dessicated coconut
- 1 tbsp dried cumin
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a pan; add the onions and cook for about 3 minutes.
2) Add the garlic and cook for a further 2 minutes.
3) Add the spinach, and cook until it wilts.
4) Add the remaining ingredients except the coconut, and cook for another three minutes.
5) Heat another pan (dry); add the coconut and toast for 1–2 minutes, until lightly golden. Add it to the main pan.
6) Serve hot as a main, or an attention-grabbing side:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ageless Athletes – by Dr. Jim Madden
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is an approach to strength and fitness training specifically for the 50+ crowd, and/but even more specifically for the 50+ crowd who do not wish to settle for mediocrity. In short, it’s for those who not only wish to stay healthy and have good mobility, but also who wish to be and remain athletic.
It does not assume extant athleticism, but nor does it assume complete inexperience. It provides a fairly ground-upwards entry to a training program that then quickly proceeds to competitive levels of athleticism.
The author himself details his own journey from being in his 30s, overweight and unfit, to being in his 50s and very athletic, with before and after photos. Granted, those are 20 years in between, but all the same, it’s a good sign when someone gets stronger and fitter with age, rather than declining.
The style of the book is quite casual, and/but after the introductory background and pep talk, is quite pragmatic and drops the additional fluff. In particular, older readers may enjoy the “Old Workhorse” protocol, as a tailored measured progression system.
In terms of expected equipment by the way, some is bodyweight and some is with weights; kettlebells in particular feature strongly, since this is about functional strength and not bodybuilding.
In the category of criticism, he does refer to his other books and generally assumes the reader is reading all his work, so it may not be for everyone as a standalone book.
Bottom line: if you’re 50+ and are wondering how to gain/maintain a high level athleticism, this book can definitely help with that.
Click here to check out Ageless Athlete, and go from strength to strength!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: