Anti-Inflammatory Pineapple Fried Rice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fried rice is not most people’s go-to when one thinks of health food, but this one is. It’s packed with plenty of nutrients, many of which are anti-inflammatory, but the real star is the pineapple (with its high bromelain content and thus particularly potent benefits).
You will need
- 2½ cups cooked wholegrain basmati rice (you can use our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe if you don’t already have leftovers to use)
- 1 cup pineapple chunks
- ½ red onion, diced
- 1 red bell pepper, diced
- ½ cup sweetcorn
- ½ peas
- 3 green onions, chopped
- 2 serrano peppers, chopped (omit if you don’t care for heat)
- 2 tbsp coconut oil
- 1 tbsp grated fresh ginger
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Fry the red onion, serrano peppers, and ginger in the coconut oil over a medium heat, stirring frequently, for about 3 minutes.
2) Add the pineapple, bell pepper, sweetcorn, peas, and black pepper, stirring frequently, for about another 3 minutes.
3) Add the rice, stirring gently but thoroughly, until fully reheated and mixed in.
4) Serve, garnishing with the green onions.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat To Beat Inflammation
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Decoding Hormone Balancing in Ads
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Time!
This is the bit whereby each week, we respond to subscriber questions/requests/etc
Have something you’d like to ask us, or ask us to look into? Hit reply to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom, and a Real Human™ will be glad to read it!
Q: As to specific health topics, I would love to see someone address all these Instagram ads targeted to women that claim “You only need to ‘balance your hormones’ to lose weight, get ripped, etc.” What does this mean? Which hormones are they all talking about? They all seem to be selling a workout program and/or supplements or something similar, as they are ads, after all. Is there any science behind this stuff or is it mostly hot air, as I suspect?
Thank you for asking this, as your question prompted yesterday’s main feature, What Does “Balancing Your Hormones” Even Mean?
That’s a great suggestion also about addressing ads (and goes for health-related things in general, not just hormonal stuff) and examining their claims, what they mean, how they work (if they work!), and what’s “technically true but may
be misleading* cause confusion”*We don’t want companies to sue us, of course.
Only, we’re going to need your help for this one, subscribers!
See, here at 10almonds we practice what we preach. We limit screen time, we focus on our work when working, and simply put, we don’t see as many ads as our thousands of subscribers do. Also, ads tend to be targeted to the individual, and often vary from country to country, so chances are good that we’re not seeing the same ads that you’re seeing.
So, how about we pull together as a bit of a 10almonds community project?
- Step 1: add our email address to your contacts list, if you haven’t already
- Step 2: When you see an ad you’re curious about, select “share” (there is usually an option to share ads, but if not, feel free to screenshot or such)
- Step 3: Send the ad to us by email
We’ll do the rest! Whenever we have enough ads to review, we’ll do a special on the topic.
We will categorically not be able to do this without you, so please do join in—Many thanks in advance!
Share This Post
-
How To Set Anxiety Aside
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Set Anxiety Aside
We’ve talked previously about how to use the “release” method to stop your racing mind.
That’s a powerful technique, but sometimes we need to be calm enough to use it. So first…
Breathe
Obviously. But, don’t underestimate the immediate power of focusing on your breath, even just for a moment.
There are many popular breathing exercises, but here’s one of the simplest and most effective, “4–4 breathing”:
- Breathe in for a count of four
- Hold for a count four
- Breathe out for a count of four
- Hold for a count of four
- Repeat
Depending on your lung capacity and what you’re used to, it may be that you need to count more quickly or slowly to make it feel right. Experiment with what feels comfortable for you, but the general goal should breathing deeply and slowly.
Identify the thing that’s causing you anxiety
We’ve also talked previously about how to use the RAIN technique to manage difficult emotions, and that’s good for handling anxiety too.
Another powerful tool is journaling.
Read: How To Use Journaling to Challenge Anxious Thoughts
If you don’t want to use any of those (very effective!) methods, that’s fine too—journaling isn’t for everyone.
You can leverage some of the same benefits by simply voicing your worries, even to yourself:
There’s an old folk tradition of “worry dolls”; these are tiny little dolls so small they can be kept in a pocket-size drawstring purse. Last thing at night, the user whispers their worries to the dolls and puts them back in their bag, where they will work on the person’s problem overnight.
We’re a health and productivity newsletter, not a dealer of magic and spells, but you can see how it works, right? It gets the worries out of one’s head, and brings about a helpful placebo effect too.
Focus on what you can control
- Most of what you worry about will not happen.
- Some of what you worry about may happen.
- Worrying about it will not help.
In fact, in some cases it may bring about what you fear, by means of the nocebo effect (like the placebo effect, but bad). Additionally, worrying drains your body and makes you less able to deal with whatever life does throw at you.
So while “don’t worry; be happy” may seem a flippant attitude, sometimes it can be best. However, don’t forget the other important part, which is actually focusing on what you can control.
- You can’t control whether your car will need expensive maintenance…
- …but you can control whether you budget for it.
- You can’t control whether your social event will go well or ill…
- …but you can control how you carry yourself.
- You can’t control whether your loved one’s health will get better or worse…
- …but you can control how you’re there for them, and you can help them take what sensible precautions they may.
…and so forth.
Look after your body as well!
Your body and mind are deeply reliant on each other. In this case, just as anxiety can drain your body’s resources, keeping your body well-nourished, well-exercised, and well-rested and can help fortify you against anxiety. For example, when it comes to diet, exercise, and sleep:
- Read: Fruit and vegetable intake is inversely associated with perceived stress across the adult lifespan
- Read: Exercise and anxiety: physical activity appears to be protective against anxiety disorders in clinical and non-clinical populations
- Read: Sleep problems predict and are predicted by generalized anxiety/depression
Don’t know where to start? How about the scientifically well-researched, evidence-based, 7-minute workout?
Share This Post
-
Anti-Aging Myths This Dermatologist Wants You To Stop Believing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dermatologist Dr. Sam Ellis lays all bare:
Bare-faced lies?
Obviously, we are hearing from a dermatologist here, so the focus is on skin aging specifically. We may well also not want to age our brain, joints, etc, but that’s not what this one is about.
So, without further ado, here are the myths she wants to bust:
- “Medical grade skincare”: the term “medical grade” is a marketing term and does not indicate superior efficacy or better ingredients.
- “Expensive skincare is more effective”: price does not always correlate with effectiveness; some high-end products justify their cost, but many do not.
- “More products = better results”: using too many products can reduce effectiveness and cause irritation; a simple routine with sunscreen and a retinoid is key.
- “Drink more water for better skin”: if you’re dehydrated, then yes, hydrate—but drinking excessive water does not improve skin appearance beyond normal hydration levels.
- “You don’t need anti-aging products until you see signs of aging”: starting skincare early, especially sun protection, helps maintain youthful skin longer.
- “Wrinkles are the first signs of aging”: hyperpigmentation and sagging are often more significant early indicators of aging than wrinkles.
- “Skincare is all you need for anti-aging”: by “skincare” here she means creams, lotions, tonics, etc, and recommends other treatments such as laser treatment and even Botox*.
- “Non-prescription retinoids are a waste of time”: over-the-counter retinoids like retinol and retinal can still be effective alternatives to prescription retinoids.
- “You must use retinoids every night”: retinoids are effective even when used a few times per week, depending on individual tolerance.
*We’re not convinced about the Botox; we’ll have to do a deep-dive research review one of these days!
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Retinoids: Retinol vs Retinal vs Retinoic Acid vs..?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
3 Day Juice Fasting? Not So Fast!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Juice fasts are trending… Again. They have been before, and this will probably not be the last time either.
The rationale is that by having nothing but fruit and/or vegetable juice for a few days, the body can clear itself of toxins while it’s not being preoccupied by dealing with what you’re eating on a daily basis.
This is not bad in theory, and in fact is a sort of parallel to the actually good advice to help the liver regenerate—by abstaining from things that the liver has to do hard work about, it has more internal resources to devote to taking care of itself.
Learn more about this: How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Just one problem
By having only juice for a few days, you are doing the opposite of what the liver needs.
In fact, by giving it what’s basically straight sugars in water with no fiber and not even any fats to slow it down, you are making your liver work overtime to deal with the flood of sugars, and it will not cope well.
Indeed, processed carbs without sufficient fiber are one of the main drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
And yes, that’s what juice is: processed carbs without fiber
(juicing is a process!)
You can read more about the science of that, here:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same? ← we get into quite some detail about how, exactly, such a harmless-seeming thing as fruit juice messes up the liver so badly
Here be (more) science
A three-day interventional study was performed on juicing and microbiome health, with three groups:
- Juice only
- Juice with whole foods
- Only whole plant-based foods
The results?
- Juice only: biggest growth in bacteria that cause inflammation and gut permeability (that’s bad; very bad)
- Juice with whole foods: the same bad effects, but much less pronounced than the juice-only group
- Only whole plant-based food: notable improvements in the microbiome
That’s what the changes were immediately post-intervention; what’s interesting to note is that the bad effects of the juice-only group also lingered longer, whereas the juice+food group enjoyed a relatively quicker recovery in the two weeks after the intervention.
Here’s the paper itself; be warned, you’ll be reading a lot about feces and saliva alongside eating and drinking:
Effects of Vegetable and Fruit Juicing on Gut and Oral Microbiome Composition
Ok, what can I do to detox?
Well, the advice we gave up top in the linked article about liver health is very sound, and also you might like to check out:
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
Want to learn more?
Here’s a video explainer from the ever-charming French biochemist Jessie Inchauspé (and our own text overview, for those who prefer reading):
Fruit Is Healthy; Juice Isn’t (Here’s Why)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Brown Rice vs Russet Potatoes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing brown rice to russet potatoes, we picked the rice.
Why?
First we’ll note: for brevity and to avoid undue repetitiveness, we’re henceforth going to just say “rice” and “potato”, respectively, but values and conclusions are still for brown rice and russet potatoes. Also, we are including the flesh and skin into the metrics for the potato (without the skin, many nutrients are no longer present).
In terms of macros, the rice has more fiber, carbs, and protein. It’s difficult to compare glycemic indices in this case, because they both need cooking before eating, and how one cooks them (and whether one cools them) along with other preparatory methods will change the GI considerably. Thus, we’ll simply go with the more nutritionally dense option, and that’s the rice.
In the category of vitamins, the rice has much more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, E, and choline, while the potato has more of vitamins C and K. A clear win for rice (and by the way, that’s 60x the vitamin E, but as potatoes don’t have much vitamin E, in practical terms, it’s actually the B-vitamins where rice’s strengths really show, as potatoes aren’t a bad source but rice is amazing).
When it comes to minerals, rice has a lot more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while potato has more calcium and potassium. Another easy win for rice.
You may be wondering about phytic acid: brown rice contains this by default, and it is something of an antinutrient (i.e., if left as-is, it reduces the bioavailability of other nutrients), and/but the phytic acid content is reduced to negligible by two things: soaking and heating (especially if those two things are combined) ← doing this the way described results in bioavailability of nutrients that’s even better than if there were just no phytic acid, albeit it requires you having the time to soak, and do so at temperature.
All in all, adding up the sections makes for an overall win for brown rice, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong? Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Half of Australians in aged care have depression. Psychological therapy could help
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While many people maintain positive emotional wellbeing as they age, around half of older Australians living in residential aged care have significant levels of depression. Symptoms such as low mood, lack of interest or pleasure in life and difficulty sleeping are common.
Rates of depression in aged care appear to be increasing, and without adequate treatment, symptoms can be enduring and significantly impair older adults’ quality of life.
But only a minority of aged care residents with depression receive services specific to the condition. Less than 3% of Australian aged care residents access Medicare-subsidised mental health services, such as consultations with a psychologist or psychiatrist, each year.
Cochrane AustraliaInstead, residents are typically prescribed a medication by their GP to manage their mental health, which they often take for several months or years. A recent study found six in ten Australian aged care residents take antidepressants.
While antidepressant medications may help many people, we lack robust evidence on whether they work for aged care residents with depression. Researchers have described “serious limitations of the current standard of care” in reference to the widespread use of antidepressants to treat frail older people with depression.
Given this, we wanted to find out whether psychological therapies can help manage depression in this group. These treatments address factors contributing to people’s distress and provide them with skills to manage their symptoms and improve their day-to-day lives. But to date researchers, care providers and policy makers haven’t had clear information about their effectiveness for treating depression among older people in residential aged care.
The good news is the evidence we published today suggests psychological therapies may be an effective approach for people living in aged care.
We reviewed the evidence
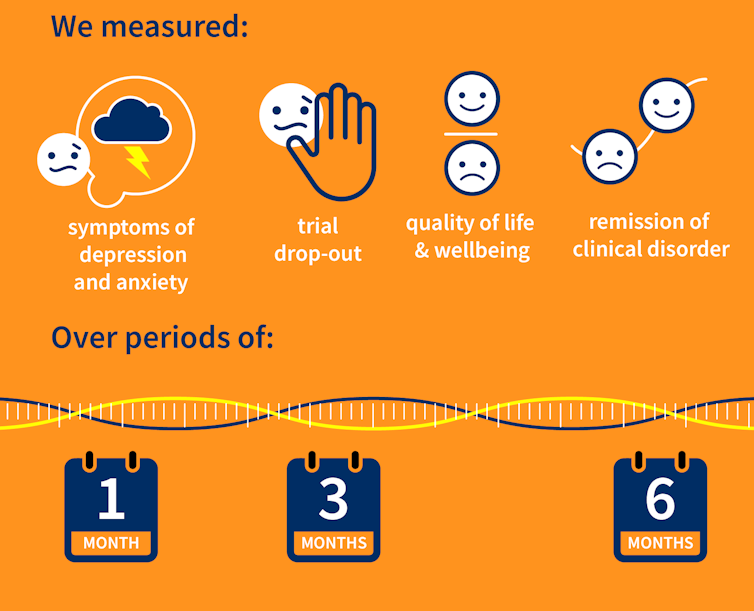
Our research team searched for randomised controlled trials published over the past 40 years that were designed to test the effectiveness of psychological therapies for depression among aged care residents 65 and over. We identified 19 trials from seven countries, including Australia, involving a total of 873 aged care residents with significant symptoms of depression.
The studies tested several different kinds of psychological therapies, which we classified as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), behaviour therapy or reminiscence therapy.
CBT involves teaching practical skills to help people re-frame negative thoughts and beliefs, while behaviour therapy aims to modify behaviour patterns by encouraging people with depression to engage in pleasurable and rewarding activities. Reminiscence therapy supports older people to reflect on positive or shared memories, and helps them find meaning in their life history.
The therapies were delivered by a range of professionals, including psychologists, social workers, occupational therapists and trainee therapists.
Cochrane AustraliaIn these studies, psychological therapies were compared to a control group where the older people did not receive psychological therapy. In most studies, this was “usual care” – the care typically provided to aged care residents, which may include access to antidepressants, scheduled activities and help with day-to-day tasks.
In some studies psychological therapy was compared to a situation where the older people received extra social contact, such as visits from a volunteer or joining in a discussion group.
What we found
Our results showed psychological therapies may be effective in reducing symptoms of depression for older people in residential aged care, compared with usual care, with effects lasting up to six months. While we didn’t see the same effect beyond six months, only two of the studies in our review followed people for this length of time, so the data was limited.
Our findings suggest these therapies may also improve quality of life and psychological wellbeing.
Psychological therapies mostly included between two and ten sessions, so the interventions were relatively brief. This is positive in terms of the potential feasibility of delivering psychological therapies at scale. The three different therapy types all appeared to be effective, compared to usual care.
However, we found psychological therapy may not be more effective than extra social contact in reducing symptoms of depression. Older people commonly feel bored, lonely and socially isolated in aged care. The activities on offer are often inadequate to meet their needs for stimulation and interest. So identifying ways to increase meaningful engagement day-to-day could improve the mental health and wellbeing of older people in aged care.
Some limitations
Many of the studies we found were of relatively poor quality, because of small sample sizes and potential risk of bias, for example. So we need more high-quality research to increase our confidence in the findings.
Many of the studies we reviewed were also old, and important gaps remain. For example, we are yet to understand the effectiveness of psychological therapies for people from diverse cultural or linguistic backgrounds.
Separately, we need better research to evaluate the effectiveness of antidepressants among aged care residents.
What needs to happen now?
Depression should not be considered a “normal” experience at this (or any other) stage of life, and those experiencing symptoms should have equal access to a range of effective treatments. The royal commission into aged care highlighted that Australians living in aged care don’t receive enough mental health support and called for this issue to be addressed.
While there have been some efforts to provide psychological services in residential aged care, the unmet need remains very high, and much more must be done.
The focus now needs to shift to how to implement psychological therapies in aged care, by increasing the competencies of the aged care workforce, training the next generation of psychologists to work in this setting, and funding these programs in a cost-effective way.
Tanya Davison, Adjunct professor, Health & Ageing Research Group, Swinburne University of Technology and Sunil Bhar, Professor of Clinical Psychology, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: