Hair Growth: Caffeine and Minoxidil Strategies
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Questions and Answers at 10almonds
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
This newsletter has been growing a lot lately, and so have the questions/requests, and we love that! In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
Hair growth strategies for men combing caffeine and minoxidil?
Well, the strategy for that is to use caffeine and minoxidil! Some more specific tips, though:
- Both of those things need to be massaged (gently!) into your scalp especially around your hairline.
- In the case of caffeine, that boosts hair growth. No extra thought or care needed for that one.
- In the case of minoxidil, it reboots the hair growth cycle, so if you’ve only recently started, don’t be surprised (or worried) if you see more shedding in the first three months. It’s jettisoning your old hairs because new ones were just prompted (by the minoxidil) to start growing behind them. So: it will get briefly worse before it gets better, but then it’ll stay better… provided you keep using it.
- If you’d like other options besides minoxidil, finasteride is a commonly prescribed oral drug that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which latter is what tells your hairline to recede.
- If you’d like other options besides prescription drugs, saw palmetto performs comparably to finasteride (and works the same way).
- You may also want to consider biotin supplementation if you don’t already enjoy that
- Consider also using a dermaroller on your scalp. If you’re unfamiliar, this is a device that looks like a tiny lawn aerator, with many tiny needles, and you roll it gently across your skin.
- It can be used for promoting hair growth, as well as for reducing wrinkles and (more slowly) healing scars.
- It works by breaking up the sebum that may be blocking new hair growth, and also makes the skin healthier by stimulating production of collagen and elastin (in response to the thousands of microscopic wounds that the needles make).
- Sounds drastic, but it doesn’t hurt and doesn’t leave any visible marks—the needles are that tiny. Still, practise good sterilization and ensure your skin is clean when using it.
See: How To Use A Dermaroller ← also explains more of the science of it
PS: this question was asked in the context of men, but the information goes the same for women suffering from androgenic alepoceia—which is a lot more common than most people think!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Women want to see the same health provider during pregnancy, birth and beyond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hazel Keedle, Western Sydney University and Hannah Dahlen, Western Sydney University
In theory, pregnant women in Australia can choose the type of health provider they see during pregnancy, labour and after they give birth. But this is often dependent on where you live and how much you can afford in out-of-pocket costs.
While standard public hospital care is the most common in Australia, accounting for 40.9% of births, the other main options are:
- GP shared care, where the woman sees her GP for some appointments (15% of births)
- midwifery continuity of care in the public system, often called midwifery group practice or caseload care, where the woman sees the same midwife of team of midwives (14%)
- private obstetrician care (10.6%)
- private midwifery care (1.9%).
Given the choice, which model would women prefer?
Our new research, published BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, found women favoured seeing the same health provider throughout pregnancy, in labour and after they have their baby – whether that’s via midwifery group practice, a private midwife or a private obstetrician.
Assessing strengths and limitations
We surveyed 8,804 Australian women for the Birth Experience Study (BESt) and 2,909 provided additional comments about their model of maternity care. The respondents were representative of state and territory population breakdowns, however fewer respondents were First Nations or from culturally or linguistically diverse backgrounds.
We analysed these comments in six categories – standard maternity care, high-risk maternity care, GP shared care, midwifery group practice, private obstetric care and private midwifery care – based on the perceived strengths and limitations for each model of care.
Overall, we found models of care that were fragmented and didn’t provide continuity through the pregnancy, birth and postnatal period (standard care, high risk care and GP shared care) were more likely to be described negatively, with more comments about limitations than strengths.
What women thought of standard maternity care in hospitals
Women who experienced standard maternity care, where they saw many different health care providers, were disappointed about having to retell their story at every appointment and said they would have preferred continuity of midwifery care.
Positive comments about this model of care were often about a midwife or doctor who went above and beyond and gave extra care within the constraints of a fragmented system.
The model of care with the highest number of comments about limitations was high-risk maternity care. For women with pregnancy complications who have their baby in the public system, this means seeing different doctors on different days.
Some respondents received conflicting advice from different doctors, and said the focus was on their complications instead of their pregnancy journey. One woman in high-risk care noted:
The experience was very impersonal, their focus was my cervix, not preparing me for birth.
Why women favoured continuity of care
Overall, there were more positive comments about models of care that provided continuity of care: private midwifery care, private obstetric care and midwifery group practice in public hospitals.
Women recognised the benefits of continuity and how this included informed decision-making and supported their choices.
The model of care with the highest number of positive comments was care from a privately practising midwife. Women felt they received the “gold standard of maternity care” when they had this model. One woman described her care as:
Extremely personable! Home visits were like having tea with a friend but very professional. Her knowledge and empathy made me feel safe and protected. She respected all of my decisions. She reminded me often that I didn’t need her help when it came to birthing my child, but she was there if I wanted it (or did need it).
However, this is a private model of care and women need to pay for it. So there are barriers in accessing this model of care due to the cost and the small numbers working in Australia, particularly in regional, rural and remote areas, among other barriers.
Women who had private obstetricians were also positive about their care, especially among women with medical or pregnancy complications – this type of care had the second-highest number of positive comments.
This was followed by women who had continuity of care from midwives in the public system, which was described as respectful and supportive.
However, one of the limitations about continuity models of care is when the woman doesn’t feel connected to her midwife or doctor. Some women who experienced this wished they had the opportunity to choose a different midwife or doctor.
What about shared care with a GP?
While shared care between the GP and hospital model of care is widely promoted in the public maternity care system as providing continuity, it had a similar number of negative comments to those who had fragmented standard hospital care.
Considering there is strong evidence about the benefits of midwifery continuity of care, and this model of care appears to be most acceptable to women, it’s time to expand access so all Australian women can access continuity of care, regardless of their location or ability to pay.
Hazel Keedle, Senior Lecturer of Midwifery, Western Sydney University and Hannah Dahlen, Professor of Midwifery, Associate Dean Research and HDR, Midwifery Discipline Leader, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Stop Sabotaging Your Gut
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Robynne Chutkan. She’s an integrative gastroenterologist, and founder of the Digestive Center for Wellness, in Washington DC, which for the past 20 years has been dedicated to uncovering the root causes of gastrointestinal disorders, while the therapeutic side of things has been focused on microbial optimization, nutritional therapy, mind-body techniques, and lifestyle changes.
In other words, maximal health for minimal medicalization.
So… What does she want us to know?
Live dirty
While attentive handwashing is important to avoid the spread of communicable diseases*, excessive cleanliness in general can result in an immune system that has no idea how to deal with pathogens when exposure does finally occur.
*See also: The Truth About Handwashing
This goes doubly for babies: especially those who were born by c-section and thus missed out on getting colonized by vaginal bacteria, and especially those who are not breast-fed, and thus miss out on nutrients given in breast milk that are made solely for the benefit of certain symbiotic bacteria (humans can’t even digest those particular nutrients, we literally evolved to produce some nutrients solely for the bacteria).
See also: Breast Milk’s Benefits That Are (So Far) Not Replicable
However, it still goes for the rest of us who are not babies, too. We could, Dr. Chutkan tells us, stand to wash less in general, and definitely ease up on antibacterial soaps and so forth.
See also: Should You Shower Daily?
Take antibiotics only if absolutely necessary (and avoid taking them by proxy)
Dr. Chutkan describes antibiotics as the single biggest threat to our microbiome, not just because of overprescription, but also the antibiotics that are used in animal agriculture and thus enter the food chain (and thus, enter us, if we eat animal products).
Still, while the antibiotics meat/dairy-enjoyers will get from food are better avoided, antibiotics actually taken directly are even worse, and are absolutely a “scorched earth” tactic against whatever they’re being prescribed for.
See also: Antibiotics? Think Thrice ← which also brings up “Four Ways Antibiotics Can Kill You”; seriously, the risks of antibiotics are not to be underestimated, including the risks associated only with them working exactly as intended—let alone if something goes wrong.
Probiotics won’t save you
While like any gastroenterologist (or really, almost any person in general), she notes that probiotics can give a boost to health. However, she wants us to know about two shortcomings that are little-discussed:
1) Your body has a collection of microbiomes each with their own needs, and while it is possible to take “generally good” bacteria in probiotics and assume they’ll do good, taking Lactobacillus sp. will do nothing for a shortage of Bifidobacteria sp, and even taking the correct genus can have similar shortcomings if a different species of that genus is needed, e.g. taking L. acidophilus will do nothing for a shortage of L. reuteri.
It’d be like a person with a vitamin D deficiency taking vitamin B12 supplements and wondering why they’re not getting better.
2) Probiotics are often wasted if not taken mindfully of their recipient environment. For example, most gut bacteria only live for about 20 minutes in the gut. They’re usually inactive in the supplement form, they’re activated in the presence of heat and moisture and appropriate pH etc, and then the clock is ticking for them to thrive or die.
This means that if you take a supplement offering two billion strains of good gut bacteria, and you take it on an empty stomach, then congratulations, 20 minutes later, they’re mostly dead, because they had nothing to eat. Or if you take it after drinking a soda, congratulations, they’re mostly dead because not only were they starved, but also their competing “bad” microbes weren’t starved and changed the environment to make it worse for the “good” ones.
For this reason, taking probiotics with (or immediately after) plenty of fiber is best.
This is all accentuated if you’re recovering from using antibiotics, by the way.
Imagine: a nuclear war devastates the population of the Earth. Some astronauts manage to safely return, finding a mostly-dead world covered in nuclear winter. Is the addition of a few astronauts going to quickly repopulate the world? No, of course not. They are few, the death toll is many, and the environment is very hostile to life. A hundred years later, the population will be pretty much the same—a few straggling survivors.
It’s the same after taking antibiotics, just, generations pass in minutes instead of decades. You can’t wipe out almost everything beneficial in the gut, create a hostile environment there, throw in a couple of probiotic gummies, and expect the population to bounce back.
That said, although “probiotics will not save you”, they can help provided you give them a nice soft bed of fiber to land on, some is better than none, and guessing at what strains are needed is better than giving nothing.
See also: How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make, Really?
What she recommends
So to recap, we’ve had:
- Wash less, and/or with less harsh chemicals
- Avoid antibiotics like the plague, unless you literally have The Plague, for which the treatment is indeed antibiotics
- Avoid antibiotic-contaminated foods, which in the US is pretty much all animal products unless it’s, for example, your own back-yard hens whom you did not give antibiotics. Do not fall for greenwashing aesthetics in the packaging of “happy cows” and their beef, milk, etc, “happy hens” and their meat, eggs, etc… If it doesn’t explicitly claim to be free from the use of antibiotics, then antibiotics were almost certainly used.
- Dr. Chutkan herself is not even vegan, by the way, but very much wants us to be able to make informed choices about this, and does recommend at least a “plants-forward” diet, for the avoiding-antibiotics reason and for the plenty-of-fiber reason, amongst others.
- Consider probiotics, but don’t expect them to work miracles by themselves; you’ve got to help them to help you.
- Dr. Chutkan also recommends getting microbiome tests done if you think something might be amiss, and then you can supplement with probiotics in a more targetted fashion instead of guessing at what species is needed where.
She also recommends, of course, a good gut-healthy diet in general, especially “leafy green things that were recently alive; not powders”, beans, and nuts, while avoiding gut-unhealthy things such as sugars-without-fiber, alcohol, or some gut-harmful additives (such as most artificial sweeteners, although stevia is a gut-healthy exception, and sucralose is ok in moderation).
For more on gut-healthy eating, check out:
Make Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
Want to know more from Dr. Chutkan?
We recently reviewed an excellent book of hers:
The Anti-Viral Gut: Tackling Pathogens From The Inside Out – by Dr. Robynne Chutkan
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Why do some people’s hair and nails grow quicker than mine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Throughout recorded history, our hair and nails played an important role in signifying who we are and our social status. You could say, they separate the caveman from businessman.
It was no surprise then that many of us found a new level of appreciation for our hairdressers and nail artists during the COVID lockdowns. Even Taylor Swift reported she cut her own hair during lockdown.
So, what would happen if all this hair and nail grooming got too much for us and we decided to give it all up. Would our hair and nails just keep on growing?
The answer is yes. The hair on our head grows, on average, 1 centimeter per month, while our fingernails grow an average of just over 3 millimetres.
When left unchecked, our hair and nails can grow to impressive lengths. Aliia Nasyrova, known as the Ukrainian Rapunzel, holds the world record for the longest locks on a living woman, which measure an impressive 257.33 cm.
When it comes to record-breaking fingernails, Diana Armstrong from the United States holds that record at 1,306.58 cm.
Most of us, however, get regular haircuts and trim our nails – some with greater frequency than others. So why do some people’s hair and nails grow more quickly?
Jari Lobo/Pexels Remind me, what are they made out of?
Hair and nails are made mostly from keratin. Both grow from matrix cells below the skin and grow through different patterns of cell division.
Nails grow steadily from the matrix cells, which sit under the skin at the base of the nail. These cells divide, pushing the older cells forward. As they grow, the new cells slide along the nail bed – the flat area under the fingernail which looks pink because of its rich blood supply.
Nails, like hair, are made mostly of keratin. Scott Gruber/Unsplash A hair also starts growing from the matrix cells, eventually forming the visible part of the hair – the shaft. The hair shaft grows from a root that sits under the skin and is wrapped in a sac known as the hair follicle.
This sac has a nerve supply (which is why it hurts to pull out a hair), oil-producing glands that lubricate the hair and a tiny muscle that makes your hair stand up when it’s cold.
At the follicle’s base is the hair bulb, which contains the all-important hair papilla that supplies blood to the follicle.
Matrix cells near the papilla divide to produce new hair cells, which then harden and form the hair shaft. As the new hair cells are made, the hair is pushed up above the skin and the hair grows.
But the papilla also plays an integral part in regulating hair growth cycles, as it sends signals to the stem cells to move to the base of the follicle and form a hair matrix. Matrix cells then get signals to divide and start a new growth phase.
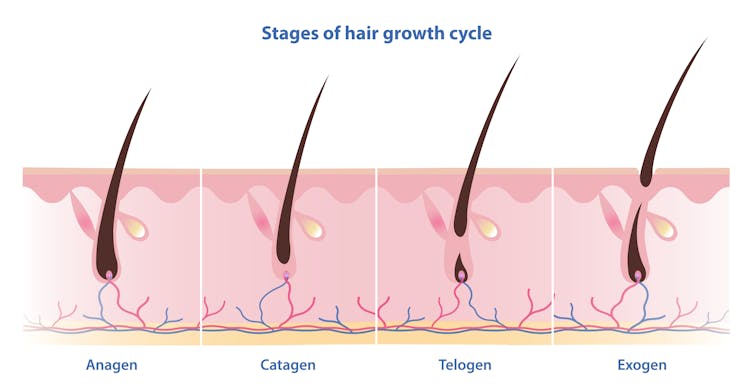
Unlike nails, our hair grows in cycles
Scientists have identified four phases of hair growth, the:
- anagen or growth phase, which lasts between two and eight years
- catagen or transition phase, when growth slows down, lasting around two weeks
- telogen or resting phase, when there is no growth at all. This usually lasts two to three months
- exogen or shedding phase, when the hair falls out and is replaced by the new hair growing from the same follicle. This starts the process all over again.
Hair follicles enter these phases at different times so we’re not left bald. Mosterpiece/Shutterstock Each follicle goes through this cycle 10–30 times in its lifespan.
If all of our hair follicles grew at the same rate and entered the same phases simultaneously, there would be times when we would all be bald. That doesn’t usually happen: at any given time, only one in ten hairs is in the resting phase.
While we lose about 100–150 hairs daily, the average person has 100,000 hairs on their head, so we barely notice this natural shedding.
So what affects the speed of growth?
Genetics is the most significant factor. While hair growth rates vary between individuals, they tend to be consistent among family members.
Nails are also influenced by genetics, as siblings, especially identical twins, tend to have similar nail growth rates.
Genetics have the biggest impact on growth speed. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels But there are also other influences.
Age makes a difference to hair and nail growth, even in healthy people. Younger people generally have faster growth rates because of the slowing metabolism and cell division that comes with ageing.
Hormonal changes can have an impact. Pregnancy often accelerates hair and nail growth rates, while menopause and high levels of the stress hormone cortisol can slow growth rates.
Nutrition also changes hair and nail strength and growth rate. While hair and nails are made mostly of keratin, they also contain water, fats and various minerals. As hair and nails keep growing, these minerals need to be replaced.
That’s why a balanced diet that includes sufficient nutrients to support your hair and nails is essential for maintaining their health.
Nutrition can impact hair and nail growth. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels Nutrient deficiencies may contribute to hair loss and nail breakage by disrupting their growth cycle or weakening their structure. Iron and zinc deficiencies, for example, have both been linked to hair loss and brittle nails.
This may explain why thick hair and strong, well-groomed nails have long been associated with perception of good health and high status.
However, not all perceptions are true.
No, hair and nails don’t grow after death
A persistent myth that may relate to the legends of vampires is that hair and nails continue to grow after we die.
In reality, they only appear to do so. As the body dehydrates after death, the skin shrinks, making hair and nails seem longer.
Morticians are well aware of this phenomenon and some inject tissue filler into the deceased’s fingertips to minimise this effect.
So, it seems that living or dead, there is no escape from the never-ending task of caring for our hair and nails.
Michelle Moscova, Adjunct Associate Professor, Anatomy, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Doesn’t Lycopene Do?
Lycopene is an antioxidant carotenoid famously found in tomatoes; it actually appears in even higher levels in watermelon, though. If you are going to get it from tomato, know that cooking improves the lycopene content rather than removing it (watermelon, on the other hand, can be enjoyed as-is and already has the higher lycopene content).
Antioxidant properties
Let’s reiterate the obvious first, for the sake of being methodical and adding a source. Lycopene is a potent antioxidant with multiple health benefits:
Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits
…and as such, it does all the things you might reasonably expect and antioxidant to do. For example…
Anti-inflammatory properties
In particular, it regulates macrophage activity, reducing inflammation while improving immune response:
Lycopene Regulates Macrophage Immune Response through the Autophagy Pathway Mediated by RIPK1
As can be expected of most antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, it also has…
Anticancer properties
Scientific papers tend to be “per cancer type”, so we’re just going to give one example, but there’s pretty much evidence for its utility against most if not all types of cancer. We’re picking prostate cancer though, as it’s one that’s been studied the most in the context of lycopene intake—in this study, for example, it was found that men who enjoyed at least two servings of lycopene-rich tomato sauce per week were 30% less likely to develop prostate cancer than those who didn’t:
Dietary lycopene intake and risk of prostate cancer defined by ERG protein expression
If you’d like to see something more general, however, then check out:
Potential Use of Tomato Peel, a Rich Source of Lycopene, for Cancer Treatment
It also fights Candida albicans
Ok, this is not (usually) so life-and-death as cancer, but reducing our C. albicans content (specifically: in our gut) has a lot of knock-on effects for other aspects of our health, so this isn’t one to overlook:
The title does not make this clear, but yes: this does mean it has an antifungal effect. We mention this because often cellular apoptosis is good for an overall organism, but in this case, it simply kills the Candida.
It’s good for the heart
A lot of studies focus just on triglyceride markers (which lycopene improves), but more tellingly, here’s a 10-year observational study in which diets rich in lycopene were associated to a 17–26% lower risk of heart disease:
Relationship of lycopene intake and consumption of tomato products to incident CVD
…and a 39% overall reduced mortality in, well, we’ll let the study title tell it:
…which means also:
It’s good for the brain
As a general rule of thumb, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain (because the brain needs healthy blood flow to stay healthy, and is especially vulnerable when it doesn’t get that), and in this case that rule of thumb is also borne out by the post hoc evidence, specifically yielding a 31% decreased incidence of stroke:
Dietary and circulating lycopene and stroke risk: a meta-analysis of prospective studies
Is it safe?
As a common food product, it is considered very safe.
If you drink nothing but tomato juice all day for a long time, your skin will take on a reddish hue, which will go away if you stop getting all your daily water intake in tomato juice.
In all likelihood, even if you went to extremes, you would get sick from the excess of vitamin A (generally present in the same foods) sooner than you’d get sick from the excess of lycopene.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, and also we recommend simply enjoying tomatoes, watermelons, etc, but if you do want a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Seasonal Affective Disorder (Beyond Sunlight!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those of us in the Northern Hemisphere, the time of increasing darkness is upon us again. Depending on our latitude, the sun barely rises before it skitters off again. And depending on other factors of our geography, we might not get much sun during that time (writer’s example: the ancient bog from which I write has been surrounded by fog for two weeks now).
So, what to do about it?
Firstly, we can make the most of whatever sun we do get (especially in the morning, if possible), and we can of course make some use of artificial sunlight. To save doubling up, we’ll link to what we previously wrote about optimizing both of those things:
‘Tis To Season To Be SAD-Savvy
More ways to get serotonin
Sunlight, of course, triggers our bodies to make serotonin, and hence we often make less of it during winter. But, there are other ways to get serotonin too, and one of the best ways is spending time in nature. Yes, even if the weather is gloomy, provided there are still visible green things and you are seeing them, it will promote serotonin production.
Of course, it may not be the season for picnics, but a morning walk through a local park or other green space is ideal.
On which note, gardening remains a good activity. Not a lot of people do so much gardening after a certain point in the year, but in one way, it’s more important than ever to get some soil under your fingernails:
There are bacteria in soil (specifically: Mycobacterium vaccae) that work similarly to antidepressants.
When something is described as having an effect similar to antidepressants, it’s usually hyperbole. In this case, it’s medicine, and literally works directly on the serotonergic system (as do many, but not all, antidepressants).
See also: Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
While many antidepressants are selective serotonin uptake inhibitors (i.e., they slow the rate at which your brain loses serotonin), Mycobacterium vaccae increases the rate at which you produce serotonin. So, you feel happier, more relaxed, while also feeling more energized.
^this one’s a mouse study, but we’re including it because it covers exactly how it works in the brain, which is something that the ethics board wouldn’t let them do on humans, due to the need for slicing the brains up for examination.
As to how to benefit: touching soil will get you “infected” by the bacteria, yes, even if you wash your hands later. Growing food in the soil and eating the good (including if you wash and cook it) is even better.
Boost the other “happiness chemicals”
Serotonin is just one “happiness hormone”, other feel-good neurotransmitters that are just as important include dopamine and oxytocin.
Dopamine is most associated with being the “reward chemical”, so it pays to do things that you find rewarding. If you’re stuck for ideas, engaging in small acts of kindness is a sure-fire way to get dopamine flowing and lift your own mood as well as theirs.
See also: 10 Ways To Naturally Boost Dopamine
Oxytocin, meanwhile is the “cuddle chemical”, and can be triggered even if you have nobody to cuddle*. If you do, by the way, make it at least 20–30 seconds, as that’s generally how long it takes to get oxytocin flowing.
*Vividly imagining it has much the same effect, since the brain can’t tell the difference. Alternatively, looking at pictures/videos (your choice) of small cute animals tends to work for most people also.
For more on these things, check out: Neurotransmitter Cheatsheet
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Carrots vs Broccoli – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing carrots to broccoli, we picked the broccoli.
Why?
These are both excellent candidates that should be in everyone’s diet, but there’s a clear winner:
In terms of macros, carrots have 50% more carbs for the same fiber (giving carrots the relatively higher glycemic index, though really, nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating carrots, which are a low-GI food already), while broccoli has more protein. By the numbers, it’s a nominal win for broccoli here, but really, both are great.
In the category of vitamins, carrots have more of vitamins A and B3, while broccoli has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline. An easy win for broccoli. We’d like to emphasize, though, that this doesn’t mean carrots don’t have lots of vitamins—they do—it’s just that broccoli has even more!
When it comes to minerals, carrots are genuinely great, and/but not higher in any minerals than broccoli, while broccoli has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. So again, a clear win for broccoli, despite carrots’ fortitude.
All in all, an overwhelming win for broccoli, though once again, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: