Waist Size Worries: Age-Appropriate Solutions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝My BMI is fine, but my waist is too big. What do I do about that? I am 5′ 5″ tall and 128 pounds and 72 years old.❞
It’s hard to say without knowing about your lifestyle (and hormones, for that matter)! But, extra weight around the middle in particular is often correlated with high levels of cortisol, so you might find this of benefit:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Clean Needles Save Lives. In Some States, They Might Not Be Legal.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Kim Botteicher hardly thinks of herself as a criminal.
On the main floor of a former Catholic church in Bolivar, Pennsylvania, Botteicher runs a flower shop and cafe.
In the former church’s basement, she also operates a nonprofit organization focused on helping people caught up in the drug epidemic get back on their feet.
The nonprofit, FAVOR ~ Western PA, sits in a rural pocket of the Allegheny Mountains east of Pittsburgh. Her organization’s home county of Westmoreland has seen roughly 100 or more drug overdose deaths each year for the past several years, the majority involving fentanyl.
Thousands more residents in the region have been touched by the scourge of addiction, which is where Botteicher comes in.
She helps people find housing, jobs, and health care, and works with families by running support groups and explaining that substance use disorder is a disease, not a moral failing.
But she has also talked publicly about how she has made sterile syringes available to people who use drugs.
“When that person comes in the door,” she said, “if they are covered with abscesses because they have been using needles that are dirty, or they’ve been sharing needles — maybe they’ve got hep C — we see that as, ‘OK, this is our first step.’”
Studies have identified public health benefits associated with syringe exchange services. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says these programs reduce HIV and hepatitis C infections, and that new users of the programs are more likely to enter drug treatment and more likely to stop using drugs than nonparticipants.
This harm-reduction strategy is supported by leading health groups, such as the American Medical Association, the World Health Organization, and the International AIDS Society.
But providing clean syringes could put Botteicher in legal danger. Under Pennsylvania law, it’s a misdemeanor to distribute drug paraphernalia. The state’s definition includes hypodermic syringes, needles, and other objects used for injecting banned drugs. Pennsylvania is one of 12 states that do not implicitly or explicitly authorize syringe services programs through statute or regulation, according to a 2023 analysis. A few of those states, but not Pennsylvania, either don’t have a state drug paraphernalia law or don’t include syringes in it.
Those working on the front lines of the opioid epidemic, like Botteicher, say a reexamination of Pennsylvania’s law is long overdue.
There’s an urgency to the issue as well: Billions of dollars have begun flowing into Pennsylvania and other states from legal settlements with companies over their role in the opioid epidemic, and syringe services are among the eligible interventions that could be supported by that money.
The opioid settlements reached between drug companies and distributors and a coalition of state attorneys general included a list of recommendations for spending the money. Expanding syringe services is listed as one of the core strategies.
But in Pennsylvania, where 5,158 people died from a drug overdose in 2022, the state’s drug paraphernalia law stands in the way.
Concerns over Botteicher’s work with syringe services recently led Westmoreland County officials to cancel an allocation of $150,000 in opioid settlement funds they had previously approved for her organization. County Commissioner Douglas Chew defended the decision by saying the county “is very risk averse.”
Botteicher said her organization had planned to use the money to hire additional recovery specialists, not on syringes. Supporters of syringe services point to the cancellation of funding as evidence of the need to change state law, especially given the recommendations of settlement documents.
“It’s just a huge inconsistency,” said Zoe Soslow, who leads overdose prevention work in Pennsylvania for the public health organization Vital Strategies. “It’s causing a lot of confusion.”
Though sterile syringes can be purchased from pharmacies without a prescription, handing out free ones to make drug use safer is generally considered illegal — or at least in a legal gray area — in most of the state. In Pennsylvania’s two largest cities, Philadelphia and Pittsburgh, officials have used local health powers to provide legal protection to people who operate syringe services programs.
Even so, in Philadelphia, Mayor Cherelle Parker, who took office in January, has made it clear she opposes using opioid settlement money, or any city funds, to pay for the distribution of clean needles, The Philadelphia Inquirer has reported. Parker’s position signals a major shift in that city’s approach to the opioid epidemic.
On the other side of the state, opioid settlement funds have had a big effect for Prevention Point Pittsburgh, a harm reduction organization. Allegheny County reported spending or committing $325,000 in settlement money as of the end of last year to support the organization’s work with sterile syringes and other supplies for safer drug use.
“It was absolutely incredible to not have to fundraise every single dollar for the supplies that go out,” said Prevention Point’s executive director, Aaron Arnold. “It takes a lot of energy. It pulls away from actual delivery of services when you’re constantly having to find out, ‘Do we have enough money to even purchase the supplies that we want to distribute?’”
In parts of Pennsylvania that lack these legal protections, people sometimes operate underground syringe programs.
The Pennsylvania law banning drug paraphernalia was never intended to apply to syringe services, according to Scott Burris, director of the Center for Public Health Law Research at Temple University. But there have not been court cases in Pennsylvania to clarify the issue, and the failure of the legislature to act creates a chilling effect, he said.
Carla Sofronski, executive director of the Pennsylvania Harm Reduction Network, said she was not aware of anyone having faced criminal charges for operating syringe services in the state, but she noted the threat hangs over people who do and that they are taking a “great risk.”
In 2016, the CDC flagged three Pennsylvania counties — Cambria, Crawford, and Luzerne — among 220 counties nationwide in an assessment of communities potentially vulnerable to the rapid spread of HIV and to new or continuing high rates of hepatitis C infections among people who inject drugs.
Kate Favata, a resident of Luzerne County, said she started using heroin in her late teens and wouldn’t be alive today if it weren’t for the support and community she found at a syringe services program in Philadelphia.
“It kind of just made me feel like I was in a safe space. And I don’t really know if there was like a come-to-God moment or come-to-Jesus moment,” she said. “I just wanted better.”
Favata is now in long-term recovery and works for a medication-assisted treatment program.
At clinics in Cambria and Somerset Counties, Highlands Health provides free or low-cost medical care. Despite the legal risk, the organization has operated a syringe program for several years, while also testing patients for infectious diseases, distributing overdose reversal medication, and offering recovery options.
Rosalie Danchanko, Highlands Health’s executive director, said she hopes opioid settlement money can eventually support her organization.
“Why shouldn’t that wealth be spread around for all organizations that are working with people affected by the opioid problem?” she asked.
In February, legislation to legalize syringe services in Pennsylvania was approved by a committee and has moved forward. The administration of Gov. Josh Shapiro, a Democrat, supports the legislation. But it faces an uncertain future in the full legislature, in which Democrats have a narrow majority in the House and Republicans control the Senate.
One of the bill’s lead sponsors, state Rep. Jim Struzzi, hasn’t always supported syringe services. But the Republican from western Pennsylvania said that since his brother died from a drug overdose in 2014, he has come to better understand the nature of addiction.
In the committee vote, nearly all of Struzzi’s Republican colleagues opposed the bill. State Rep. Paul Schemel said authorizing the “very instrumentality of abuse” crossed a line for him and “would be enabling an evil.”
After the vote, Struzzi said he wanted to build more bipartisan support. He noted that some of his own skepticism about the programs eased only after he visited Prevention Point Pittsburgh and saw how workers do more than just hand out syringes. These types of programs connect people to resources — overdose reversal medication, wound care, substance use treatment — that can save lives and lead to recovery.
“A lot of these people are … desperate. They’re alone. They’re afraid. And these programs bring them into someone who cares,” Struzzi said. “And that, to me, is a step in the right direction.”
At her nonprofit in western Pennsylvania, Botteicher is hoping lawmakers take action.
“If it’s something that’s going to help someone, then why is it illegal?” she said. “It just doesn’t make any sense to me.”
This story was co-reported by WESA Public Radio and Spotlight PA, an independent, nonpartisan, and nonprofit newsroom producing investigative and public-service journalism that holds power to account and drives positive change in Pennsylvania.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Cashew & Chickpea Balti
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to curries, the humble balti is perhaps the best when you don’t have all day to let something simmer. Filled with healthful spices, this one also comes complete with lots of fiber as well as healthy proteins and fats, with most of its calories coming from the nuts themselves, and the haricot paste base makes for a deliciously creamy curry without having to add anything unhealthy.
You will need
- 1 cup cashews, soaked in warm water for at least 5 minutes, and drained (if allergic, omit)
- 1 can chickpeas (keep the water)
- 1 can haricot beans (keep the water)
- 1 can crushed tomatoes
- 2 medium (or 3 small) red onions, sliced
- red or green chilis, quantity per your preference re heat, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- ½ oz fresh ginger, peeled and finely chopped
- 1 tbsp tomato paste
- 1 tbsp garam masala
- 1 tbsp ground coriander
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 2 tsp turmeric
- 1 tsp mustard seeds (if allergic, omit)
- 1 tsp sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp coriander seeds
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Avocado oil, for frying (extra virgin olive-oil, or cold-pressed coconut oil, are fine alternatives)
- Garnish: handful fresh cilantro, chopped (or parsley, if you have the “cilantro tastes like soap” gene)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a large sauté pan (we’re going to need space to work; a large wok is traditional but a sauté pan is convenient), and add the garlic, ginger, mustard seeds, and coriander seeds, stirring for about 2 minutes, then add the onions and chilis, stirring for another 3 minutes. The onions and chilis won’t be fully cooked yet, but that’s fine, we just needed to get them started.
2) Add the crushed tomatoes, stirring them in, and when they get to temperature, turn the heat down to a simmer.
3) Add the chickpeas to the pan, but separately put the chickpea water into a high-speed blender.
4) Add the haricot beans, including the water they came in, to the high-speed blender, as well as the tomato paste and the remaining spices (including the MSG or salt), and blend on high until smooth. Add the curry paste (that’s what you’ve just made in the blender) to the pan, and stir in well.
5) Add the cashews, stirring in well. Taste, and adjust any spices if necessary for your liking. If the onions still aren’t fully cooked, let them simmer until they are, but it shouldn’t take long.
10almonds tip: if perchance you made it too spicy, you can add a little lime juice and the acidity will counteract the heat. Adding lemon juice, lime juice, or some kind of vinegar (depending on what works with the flavor profile of your recipe) is a good last resort to have up your sleeve for fixing a dish that got too spicy.
6) Add the garnish, and serve—we recommend serving it with our Tasty Versatile Rice, but any carb is fine.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we hit 5/5 again today!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
3 Day Juice Fasting? Not So Fast!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Juice fasts are trending… Again. They have been before, and this will probably not be the last time either.
The rationale is that by having nothing but fruit and/or vegetable juice for a few days, the body can clear itself of toxins while it’s not being preoccupied by dealing with what you’re eating on a daily basis.
This is not bad in theory, and in fact is a sort of parallel to the actually good advice to help the liver regenerate—by abstaining from things that the liver has to do hard work about, it has more internal resources to devote to taking care of itself.
Learn more about this: How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Just one problem
By having only juice for a few days, you are doing the opposite of what the liver needs.
In fact, by giving it what’s basically straight sugars in water with no fiber and not even any fats to slow it down, you are making your liver work overtime to deal with the flood of sugars, and it will not cope well.
Indeed, processed carbs without sufficient fiber are one of the main drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
And yes, that’s what juice is: processed carbs without fiber
(juicing is a process!)
You can read more about the science of that, here:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same? ← we get into quite some detail about how, exactly, such a harmless-seeming thing as fruit juice messes up the liver so badly
Here be (more) science
A three-day interventional study was performed on juicing and microbiome health, with three groups:
- Juice only
- Juice with whole foods
- Only whole plant-based foods
The results?
- Juice only: biggest growth in bacteria that cause inflammation and gut permeability (that’s bad; very bad)
- Juice with whole foods: the same bad effects, but much less pronounced than the juice-only group
- Only whole plant-based food: notable improvements in the microbiome
That’s what the changes were immediately post-intervention; what’s interesting to note is that the bad effects of the juice-only group also lingered longer, whereas the juice+food group enjoyed a relatively quicker recovery in the two weeks after the intervention.
Here’s the paper itself; be warned, you’ll be reading a lot about feces and saliva alongside eating and drinking:
Effects of Vegetable and Fruit Juicing on Gut and Oral Microbiome Composition
Ok, what can I do to detox?
Well, the advice we gave up top in the linked article about liver health is very sound, and also you might like to check out:
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
Want to learn more?
Here’s a video explainer from the ever-charming French biochemist Jessie Inchauspé (and our own text overview, for those who prefer reading):
Fruit Is Healthy; Juice Isn’t (Here’s Why)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Millet vs Rye – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing millet to rye, we picked the rye.
Why?
In terms of macros, they’re about equal on protein, and rye has more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which give it the lower glycemic index, so we say rye wins this category.
In the category of vitamins, millet has more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, and B9, while rye has more of vitamins A, B5, E, and K. Notionally, that’s a 4:4 tie, though rye’s margins of difference are an order of magnitude greater, so we say rye takes a marginal victory on this one.
When it comes to minerals, there’s nothing to debate here: millet has more copper, while rye has more calcium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. An easy win for rye on this one.
Adding up the sections gives the overall win to rye, but there is one other thing worth mentioning: millet is naturally gluten-free, but rye is not, so if you are avoiding gluten for any reason, you’ll want to pick the millet in this case.
See also: Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Aside from that, by all means enjoy either or both, in moderation! Diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Grains: Bread Of Life, Or Cereal Killer?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Myth of Normal – by Dr. Gabor Maté and Daniel Maté
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of popular beliefs (and books!) start with the assumption that everyone is, broadly speaking, “normal”. That major diversions from “normal” happen only to other people… And that minor diversions from “normal” are just something to suck up and get over—magically effecting a return to “normalcy”.
Dr. Maté, however, will have none of these unhelpful brush-offs, and observes that in fact most if not all of us have been battered by the fates one way or another. We just:
- note that we have more similarities than differences, and
- tend to hide our own differences (to be accepted) or overlook other people’s (to make them more acceptable).
How is this more helpful? Well, the above approach isn’t always, but Mate has an improvement to offer:
We must see flawed humans (including ourselves) as the product of our environments… and/but see this a reason to look at improving those environments!
Beyond that…
The final nine chapters of the books he devotes to “pathways to wholeness” and, in a nutshell, recovery. Recovery from whatever it was for you. And if you’ve had a life free from anything that needs recovering from, then congratulations! You doubtlessly have at least one loved one who wasn’t so lucky, though, so this book still makes for excellent reading.
Dr. Maté was awarded the Order of Canada for his medical work and writing. His work has mostly been about addiction, trauma, stress, and childhood development. He co-wrote this book with his son, Daniel.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mental illness, psychiatric disorder or psychological problem. What should we call mental distress?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We talk about mental health more than ever, but the language we should use remains a vexed issue.
Should we call people who seek help patients, clients or consumers? Should we use “person-first” expressions such as person with autism or “identity-first” expressions like autistic person? Should we apply or avoid diagnostic labels?
These questions often stir up strong feelings. Some people feel that patient implies being passive and subordinate. Others think consumer is too transactional, as if seeking help is like buying a new refrigerator.
Advocates of person-first language argue people shouldn’t be defined by their conditions. Proponents of identity-first language counter that these conditions can be sources of meaning and belonging.
Avid users of diagnostic terms see them as useful descriptors. Critics worry that diagnostic labels can box people in and misrepresent their problems as pathologies.
Underlying many of these disagreements are concerns about stigma and the medicalisation of suffering. Ideally the language we use should not cast people who experience distress as defective or shameful, or frame everyday problems of living in psychiatric terms.
Our new research, published in the journal PLOS Mental Health, examines how the language of distress has evolved over nearly 80 years. Here’s what we found.
Engin Akyurt/Pexels Generic terms for the class of conditions
Generic terms – such as mental illness, psychiatric disorder or psychological problem – have largely escaped attention in debates about the language of mental ill health. These terms refer to mental health conditions as a class.
Many terms are currently in circulation, each an adjective followed by a noun. Popular adjectives include mental, mental health, psychiatric and psychological, and common nouns include condition, disease, disorder, disturbance, illness, and problem. Readers can encounter every combination.
These terms and their components differ in their connotations. Disease and illness sound the most medical, whereas condition, disturbance and problem need not relate to health. Mental implies a direct contrast with physical, whereas psychiatric implicates a medical specialty.
Mental health problem, a recently emerging term, is arguably the least pathologising. It implies that something is to be solved rather than treated, makes no direct reference to medicine, and carries the positive connotations of health rather than the negative connotation of illness or disease.
Is ‘mental health problem’ actually less pathologising? Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Arguably, this development points to what cognitive scientist Steven Pinker calls the “euphemism treadmill”, the tendency for language to evolve new terms to escape (at least temporarily) the offensive connotations of those they replace.
English linguist Hazel Price argues that mental health has increasingly come to replace mental illness to avoid the stigma associated with that term.
How has usage changed over time?
In the PLOS Mental Health paper, we examine historical changes in the popularity of 24 generic terms: every combination of the nouns and adjectives listed above.
We explore the frequency with which each term appears from 1940 to 2019 in two massive text data sets representing books in English and diverse American English sources, respectively. The findings are very similar in both data sets.
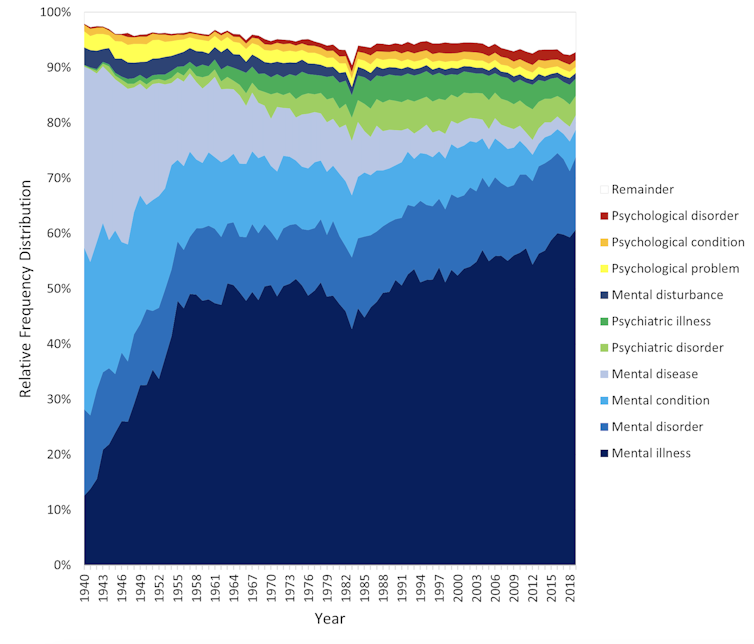
The figure presents the relative popularity of the top ten terms in the larger data set (Google Books). The 14 least popular terms are combined into the remainder.
Relative popularity of alternative generic terms in the Google Books corpus. Haslam et al., 2024, PLOS Mental Health. Several trends appear. Mental has consistently been the most popular adjective component of the generic terms. Mental health has become more popular in recent years but is still rarely used.
Among nouns, disease has become less widely used while illness has become dominant. Although disorder is the official term in psychiatric classifications, it has not been broadly adopted in public discourse.
Since 1940, mental illness has clearly become the preferred generic term. Although an assortment of alternatives have emerged, it has steadily risen in popularity.
Does it matter?
Our study documents striking shifts in the popularity of generic terms, but do these changes matter? The answer may be: not much.
One study found people think mental disorder, mental illness and mental health problem refer to essentially identical phenomena.
Other studies indicate that labelling a person as having a mental disease, mental disorder, mental health problem, mental illness or psychological disorder makes no difference to people’s attitudes toward them.
We don’t yet know if there are other implications of using different generic terms, but the evidence to date suggests they are minimal.
The labels we use may not have a big impact on levels of stigma. Pixabay/Pexels Is ‘distress’ any better?
Recently, some writers have promoted distress as an alternative to traditional generic terms. It lacks medical connotations and emphasises the person’s subjective experience rather than whether they fit an official diagnosis.
Distress appears 65 times in the 2022 Victorian Mental Health and Wellbeing Act, usually in the expression “mental illness or psychological distress”. By implication, distress is a broad concept akin to but not synonymous with mental ill health.
But is distress destigmatising, as it was intended to be? Apparently not. According to one study, it was more stigmatising than its alternatives. The term may turn us away from other people’s suffering by amplifying it.
So what should we call it?
Mental illness is easily the most popular generic term and its popularity has been rising. Research indicates different terms have little or no effect on stigma and some terms intended to destigmatise may backfire.
We suggest that mental illness should be embraced and the proliferation of alternative terms such as mental health problem, which breed confusion, should end.
Critics might argue mental illness imposes a medical frame. Philosopher Zsuzsanna Chappell disagrees. Illness, she argues, refers to subjective first-person experience, not to an objective, third-person pathology, like disease.
Properly understood, the concept of illness centres the individual and their connections. “When I identify my suffering as illness-like,” Chappell writes, “I wish to lay claim to a caring interpersonal relationship.”
As generic terms go, mental illness is a healthy option.
Nick Haslam, Professor of Psychology, The University of Melbourne and Naomi Baes, Researcher – Social Psychology/ Natural Language Processing, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: