The End of Old Age – by Dr. Marc Agronin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book is not: a book about ending aging. For that, you would want to check out “Ending Aging”, by Dr. Aubrey de Grey.
What this book actually is: a book about the purpose of aging. As in: “aging: to what end?”, and then the book answers that question.
Rather than viewing aging as solely a source of decline, this book (while not shying away from that) resolutely examines the benefits of old age—from clinically defining wisdom, to exploring the many neurological trade-offs (e.g., “we lose this thing but we get this other thing in the process”), and the assorted ways in which changes in our brain change our role in society, without relegating us to uselessness—far from it!
The style of the book is deep and meaningful prose throughout. Notwithstanding the author’s academic credentials and professional background in geriatric psychiatry, there’s no hard science here, just comprehensible explanations of psychiatry built into discussions that are often quite philosophical in nature (indeed, the author additionally has a degree in psychology and philosophy, and it shows).
Bottom line: if you’d like your own aging to be something you understand better and can actively work with rather than just having it happen to you, then this is an excellent book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wanna read more?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’ve Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
Q: Tips for reading more and managing time for it?
A: We talked about this a little bit in yesterday’s edition, so you may have seen that, but aside from that:
- If you don’t already have one, consider getting a Kindle or similar e-reader. They’re very convenient, and also very light and ergonomic—no more wrist strain as can occur with physical books. No more eye-strain, either!
- Consider making reading a specific part of your daily routine. A chapter before bed can be a nice wind-down, for instance! What’s important is it’s a part of your day that’ll always, or at least almost always, allow you to do a little reading.
- If you drive, walk, run, or similar each day, a lot of people find that’s a great time to listen to an audiobook. Please be safe, though!
- If your lifestyle permits such, a “reading retreat” can be a wonderful vacation! Even if you only “retreat” to your bedroom, the point is that it’s a weekend (or more!) that you block off from all other commitments, and curl up with the book(s) of your choice.
Share This Post
-
Spark – by Dr. John Ratey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that exercise is good for mental health as well as physical. So, what’s so revolutionary about this “revolutionary new science of exercise and the brain”?
A lot of it has to do with the specific neuroscience of how exercise has not only a mood-boosting effect (endorphins) and neuroprotective effect (helping to guard against cognitive decline), but also promotes neuroplasticity… e.g., the creation and strengthening of neural pathways, as well as boosting the structure of the brain in some parts such as the cerebellum.
The book also covers not just “exercise has these benefits”, but also the “how this works” of all kinds of brain benefits, including:
- against Alzheimer’s
- mitigating ADHD
- managing menopause
- dealing with addiction
…and more. And once we understand how something works, we’re far more likely to be motivated to actually do the kinds of exercises that give the specific benefits we want/need. Which is very much the important part!
In short: this book will tell you what you need to know to get you doing the exercises you need to enjoy those benefits—very much worth it!
Share This Post
-
How to Permanently Loosen a Tight Psoas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Is Your Psoas?
Your psoas is a deep muscle in your lower back and hip area that connects your spine to your thigh bone. It helps you bend your hips and spine, making it a hip flexor.
In today’s video, Your Wellness Nerd (the YouTube channel behind the video below) has revealed some great tips on loosening said tight hip flexors!
How to loosen them
First off, the big reveal…your tight psoas is likely stemming from an overlooked cause: your lower back! The video kicks off with a simple technique to loosen up that stiff area in your lower back. All you need is a foam roller.
But, before diving into the exercises, it’s essential to gauge your current flexibility. A basic hip flexor stretch serves as a pre-test.
Note: the goal here isn’t to stretch, but rather to feel how tight you are.
After testing, it’s time to roll…literally. Working through the lower back, use your roller or tennis ball to any find stiff spots and loosen them out; those spots are likely increasing the tension on your psoas.
After some rolling, retest with the hip flexor stretch. Chances are, you’ll feel more mobility and less tightness right away.
Note: this video focuses on chronic psoas issues. If you have sore psoas from a muscular workout, you may want to read our piece on speeding up muscle recovery.
Is That All?
But wait, there’s more! The video also covers two more exercises specifically targeting the psoas. This one’s hard to describe, so we recommend watching the video. However, to provide an overview, you’re doing the “classic couch stretch”, but with a few alterations.
Next, the tennis ball technique zeroes in on specific tight spots in the psoas. By lying on the ball and adjusting its position around the hip area, you can likely release some deeply held tension.
Additionally, some of our readers advocate for acupuncture for psoas relief – we’ve done an acupuncture myth-busting article here for reference.
Other Sources
If you’re looking for some more in-depth guides on stretching your psoas, and your body in general, we’ve made a range of 1-minute summaries of books that specifically target stretching:
- 11 Minutes to Pain-Free Hips (perfect for psoas muscles)
- Stretching Scientifically
- Stretching & Mobility
- Stretching to Stay Young
The final takeaway? If you’re constantly battling tight psoas muscles despite trying different exercises and stretches, it might be time to look at your lower back and your daily habits. This video isn’t just a band-aid fix; it’s about addressing the root cause for long-term relief:
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Staring At The Sun – by Dr. Irvin Yalom
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A quick note first: there are two editions of this book; the content is the same, but the cover is different. So if in your region it has a bright yellow cover and the subtitle is the excitable “Overcoming The Terror Of Death” rather than the more measured “Being At Peace With Your Own Mortality”, that is why; different regional publishers made different choices.
For most of us, dying is the last thing we want to do. We may fear it; we may ignore it; we may try to beat it—but it’s a constant existential threat whether we want it or not.
This book is about “death anxiety”, either direct (conscious fear of impending death) or sublimated (not necessarily realising what we’re avoiding thinking about it). In its broadest sense, the fear of death can be described as rational. But angst about it probably won’t help, so this book looks to help us overcome that.
The style of the book is largely anecdotal, in which the author uses examples from his therapeutic practice to illustrate ways in which the fear of death can manifest, and ways in which it can be managed healthily.
Subjective criticism: while this author developed existential therapy, many of the ideas in this book lean heavily on the psychodynamic approach derived from Freud, and this reviewer isn’t a fan of that. But nevertheless, many of the examples here are thought-provoking and useful, so it is not too strong a criticism.
Bottom line: there are many ways to manage one’s mortality, and this book brings attention to a range of possibilities.
Click here to check out Staring At The Sun, and manage your mortality!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Body: A Guide for Occupants – by Bill Bryson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Better known for his writings on geography and history, here Bryson puts his mind to anatomy and physiology. How well does he do?
Very well, actually—thanks no doubt to the oversight of the veritable flock of consulting scientists mentioned in the acknowledgements. To this reviewer’s knowledge, no mistakes made it through into publication.
That said, Bryson’s love of history does shine through, and in this case, the book is as much a telling of medical history, as it is of the human body. That’s a feature not a bug, though, as not only is it fascinating in and of itself, but also, it’d be difficult to fully understand where we’re at in science, without understanding how we got here.
The style of the book is easy-reading narrative prose, but packed with lots of quirky facts, captivating anecdotes, and thought-provoking statistics. For example:
- The least effective way to spread germs is kissing. It proved ineffective among volunteers (in what sounds like a fun study) who had been successfully infected with the cold virus. Sneezes and coughs weren’t much better. The only really reliable way to transfer cold germs was physically by touch.
- The United States has 4% of the world’s population but consumes 80% of its opiates.
- Allowing a fever to run its course (within limits) could be the wisest thing. An increase of only a degree or so in body temperature slows the replication rate of viruses by a factor of 200.
Still, these kinds of things are woven together so well, that it doesn’t feel at all like reading a trivia list!
Bottom line: if you’d like to know a lot more about anatomy and physiology, but prefer a very casual style rather than sitting down with a stack of textbooks, this book is a great option.
Click here to check out The Body, and learn more about yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I’ve recovered from a cold but I still have a hoarse voice. What should I do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cold, flu, COVID and RSV have been circulating across Australia this winter. Many of us have caught and recovered from one of these common upper respiratory tract infections.
But for some people their impact is ongoing. Even if your throat isn’t sore anymore, your voice may still be hoarse or croaky.
So what happens to the voice when we get a virus? And what happens after?
Here’s what you should know if your voice is still hoarse for days – or even weeks – after your other symptoms have resolved.
Why does my voice get croaky during a cold?
A healthy voice is normally clear and strong. It’s powered by the lungs, which push air past the vocal cords to make them vibrate. These vibrations are amplified in the throat and mouth, creating the voice we hear.
The vocal cords are two elastic muscles situated in your throat, around the level of your laryngeal prominence, or Adam’s apple. (Although everyone has one, it tends to be more pronounced in males.) The vocal cords are small and delicate – around the size of your fingernail. Any small change in their structure will affect how the voice sounds.
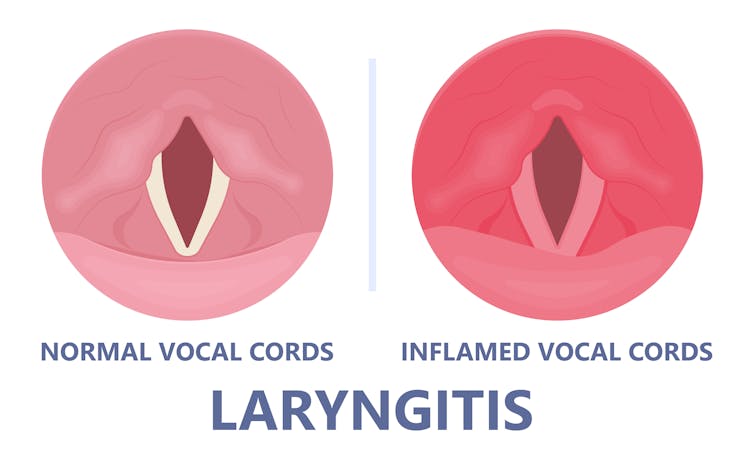
When the vocal cords become inflamed – known as laryngitis – your voice will sound different. Laryngitis is a common part of upper respiratory tract infections, but can also be caused through misuse.
Viruses such as the common cold can inflame the vocal cords. Pepermpron/Shutterstock Catching a virus triggers the body’s defence mechanisms. White blood cells are recruited to kill the virus and heal the tissues in the vocal cords. They become inflamed, but also stiffer. It’s harder for them to vibrate, so the voice comes out hoarse and croaky.
In some instances, you may find it hard to speak in a loud voice or have a reduced pitch range, meaning you can’t go as high or loud as normal. You may even “lose” your voice altogether.
Coughing can also make things worse. It is the body’s way of trying to clear the airways of irritation, including your own mucus dripping onto your throat (post-nasal drip). But coughing slams the vocal cords together with force.
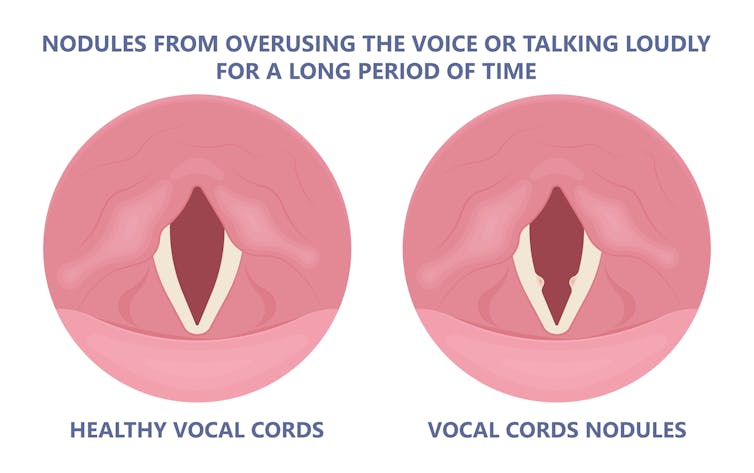
Chronic coughing can lead to persistent inflammation and even thicken the vocal cords. This thickening is the body trying to protect itself, similar to developing a callus when a pair of new shoes rubs.
Thickening on your vocal cords can lead to physical changes in the vocal cords – such as developing a growth or “nodule” – and further deterioration of your voice quality.
Coughing and exertion can cause inflamed vocal cords to thicken and develop nodules. Pepermpron/Shutterstock How can you care for your voice during infection?
People who use their voices a lot professionally – such as teachers, call centre workers and singers – are often desperate to resume their vocal activities. They are more at risk of forcing their voice before it’s ready.
The good news is most viral infections resolve themselves. Your voice is usually restored within five to ten days of recovering from a cold.
Occasionally, your pharmacist or doctor may prescribe cough suppressants to limit additional damage to the vocal cords (among other reasons) or mucolytics, which break down mucus. But the most effective treatments for viral upper respiratory tract infections are hydration and rest.
Drink plenty of water, avoid alcohol and exposure to cigarette smoke. Inhaling steam by making yourself a cup of hot water will also help clear blocked noses and hydrate your vocal cords.
Rest your voice by talking as little as possible. If you do need to talk, don’t whisper – this strains the muscles.
Instead, consider using “confidential voice”. This is a soft voice – not a whisper – that gently vibrates your vocal cords but puts less strain on your voice than normal speech. Think of the voice you use when communicating with someone close by.
During the first five to ten days of your infection, it is important not to push through. Exerting the voice by talking a lot or loudly will only exacerbate the situation. Once you’ve recovered from your cold, you can speak as you would normally.
What should you do if your voice is still hoarse after recovery?
If your voice hasn’t returned to normal after two to three weeks, you should seek medical attention from your doctor, who may refer you to an ear nose and throat specialist.
If you’ve developed a nodule, the specialist would likely refer you to a speech pathologist who will show you how to take care of your voice. Many nodules can be treated with voice therapy and don’t require surgery.
You may have also developed a habit of straining your vocal cords, if you forced yourself to speak or sing while they were inflamed. This can be a reason why some people continue to have a hoarse voice even when they’ve recovered from the cold.
In those cases, a speech pathologist may play a valuable role. They may teach you to exercises that make voicing more efficient. For example, lip trills (blowing raspberries) are a fun and easy way you can learn to relax the voice. This can help break the habit of straining your voice you may have developed during infection.
Yeptain Leung, Postdoctoral Research and Lecturer of Speech Pathology, School of Health Sciences, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: