Make Your Negativity Work For You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s The Right Balance?
We’ve written before about positivity the pitfalls and perils of toxic positivity:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
…as well as the benefits that can be found from selectively opting out of complaining:
A Bone To Pick… Up And Then Put Back Where We Found It
So… What place, if any, does negativity usefully have in our lives?
Carrot and Stick
We tend to think of “carrot and stick” motivation being extrinsic, i.e. there is some authority figure offering is reward and/or punishment, in response to our reactions.
In those cases when it really is extrinsic, the “stick” can still work for most people, by the way! At least in the short term.
Because in the long term, people are more likely to rebel against a “stick” that they consider unjust, and/or enter a state of learned helplessness, per “I’ll never be good enough to satisfy this person” and give up trying to please them.
But what about when you have your own carrot and stick? What about when it comes to, for example, your own management of your own healthy practices?
Here it becomes a little different—and more effective. We’ll get to that, but first, bear with us for a touch more about extrinsic motivation, because here be science:
We will generally be swayed more easily by negative feelings than positive ones.
For example, a study was conducted as part of a blood donation drive, and:
- Group A was told that their donation could save a life
- Group B was told that their donation could prevent a death
The negative wording given to group B boosted donations severalfold:
Read the paper: Life or Death Decisions: Framing the Call for Help
We have, by the way, noticed a similar trend—when it comes to subject lines in our newsletters. We continually change things up to see if trends change (and also to avoid becoming boring), but as a rule, the response we get from subscribers is typically greater when a subject line is phrased negatively, e.g. “how to avoid this bad thing” rather than “how to have this good thing”.
How we can all apply this as individuals?
When we want to make a health change (or keep up a healthy practice we already have)…
- it’s good to note the benefits of that change/practice!
- it’s even better to note the negative consequences of not doing it
For example, if you want to overcome an addiction, you will do better for your self-reminders to be about the bad consequences of using, more than the good consequences of abstinence.
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
This goes even just for things like diet and exercise! Things like diet and exercise can seem much more low-stakes than substance abuse, but at the end of the day, they can add healthy years onto our lives, or take them off.
Because of this, it’s good to take time to remember, when you don’t feel like exercising or do feel like ordering that triple cheeseburger with fries, the bad outcomes that you are planning to avoid with good diet and exercise.
Imagine yourself going in for that quadruple bypass surgery, asking yourself whether the unhealthy lifestyle was worth it. Double down on the emotions; imagine your loved ones grieving your premature death.
Oof, that was hard-hitting
It was, but it’s effective—if you choose to do it. We’re not the boss of you! Either way, we’ll continue to send the same good health advice and tips and research and whatnot every day, with the same (usually!) cheery tone.
One last thing…
While it’s good to note the negative, in order to avoid the things that lead to it, it’s not so good to dwell on the negative.
So if you get caught in negative thought spirals or the like, it’s still good to get yourself out of those.
If you need a little help with that sometimes, check out these:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dates vs Prunes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to prunes, we picked the prunes.
Why?
First let’s note: we’re listing the second fruit here as “prunes” rather than “plums”, since prunes are dehydrated plums, and it makes more sense to compare the dried fruit to dates which are invariably dried too. Otherwise, the water weight of plums would unfairly throw out the nutrient proportions per 100g (indeed, upon looking up numbers, dates would overwhelmingly beat plums easily in the category of pretty much every nutrient).
So let’s look at the fairer comparison:
In terms of macros, dates have a little more protein, carbohydrate, and fiber. This is because while both are dried, prunes are usually sold with more water remaining than dates; indeed, per 100g prunes still have 30g water weight to dates’ 20g water weight. This makes everything close, but we are going to call this category a nominal win for dates. Mind you, hydration is still good, but please do not rely on dried fruit for your hydration!
When it comes to vitamins, dates have more of vitamins B5 and B9, while prunes have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, C, E, K, and choline. A clear win for prunes here.
In the category of minerals, it’s a similar story: dates have more iron, magnesium, and selenium, while prunes have more calcium, copper, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Another win for prunes.
In short, enjoy either or both, but prunes win on overall nutritional density!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Professional-Style Dental Cleaning At Home?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You know the scene: your dentist is rummaging around inside your mouth with an implement that looks like a medieval torture device; you wince at a sudden sharp pain, only to be told “if you flossed, you wouldn’t be bleeding now”.
For most of us, going to the dentist isn’t near the top of our “favorite things to do” list, but it is of course a necessity of (healthy) life.
So, what can we do to minimize suffering in the dentist’s chair?
First, the basics
Of course, good oral hygiene is the absolute baseline, but with so many choices out there, which is best? We examined an array of options in this three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing Without Flossing?
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← we recommend the miswak! Not only does it clean the teeth as well as or better than traditional brushing, but also it changes the composition of saliva to improve the oral microbiome, effectively turning your saliva into a biological mouthwash that kills unwanted microbes and is comfortable for the ones that should be there.
In fact, caring for the composition of one’s saliva, and thus one’s oral microbiome, is so important that we did a main feature on that, a little later:
Make Your Saliva Better For Your Teeth ← this is especially important if you take any meds that affect the composition of your saliva (scroll down to the table of meds). Your medications’ leaflets won’t tell you that it does that directly, but they will list “dry mouth” as one of the potential side effects (and you’ll probably know if you have a medication that gives you a dry mouth).
Next, level up
For this one, we’ll drop some links to some videos we’ve featured (for those who prefer text, worry not, your faithful writer has added text-based overviews):
- How To Regrow Receding Gums
- Tooth Remineralization: How To Heal Your Teeth Naturally
- Tartar Removal At Home & How To Prevent Tartar
Now, that last one sounds slightly more exciting than it is—it is about using chemical processes to gradually lessen the tartar over time, with a six-month timeframe.
So, what if you want to do one better than that?
Finally… Buckle up, this one’s fun
Ok, so “fun” and “dental care” don’t usually go hand-in-hand, and maybe your sense of fun differs from this writer’s, but hey. The thing is, we’re going to get hands-on with dental tools.
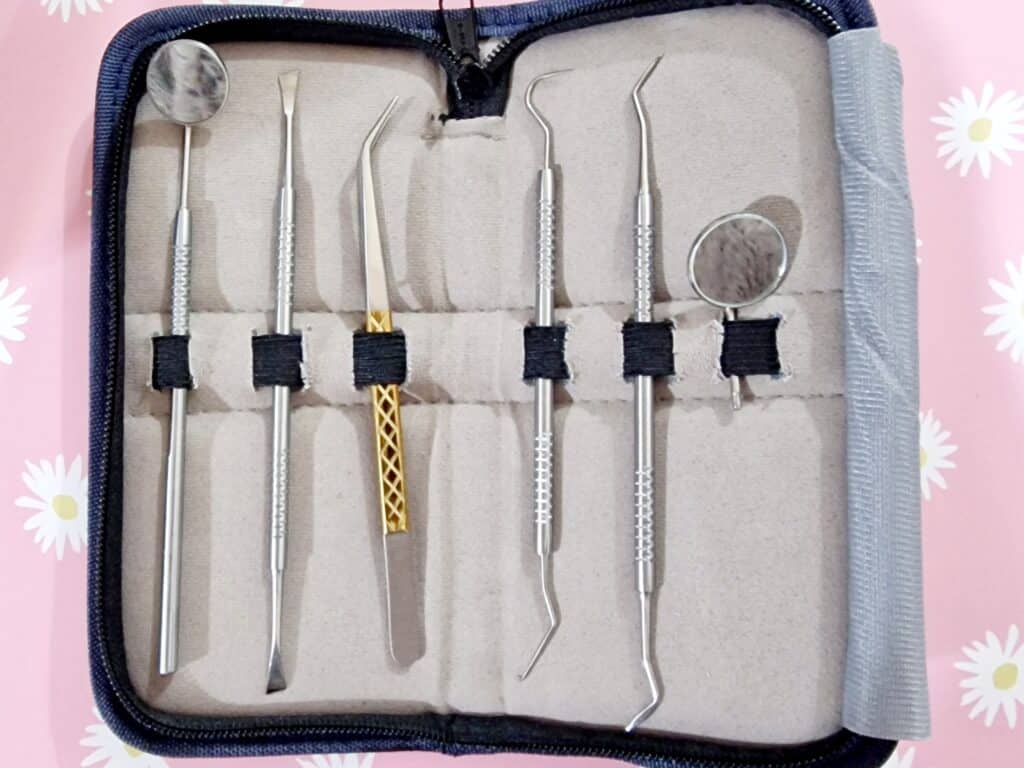
Specifically, these dental tools:
👆 these are literally the tools this writer has; if you look in the specula (the round mirror bits), you can see the reflection of the fluffy gray bathrobe I was wearing when I took the picture!
You can get tools like these easily online; here’s an example product on Amazon; do also shop around of course, and we recommend checking the reviews to ensure good quality.
Writer’s story on why I have these: once upon a time, a wisdom tooth came through at 45°, ploughing through the molar next to it, which then needed removing.
However, my teeth have the interesting anatomical quirk that I have hooked/barbed roots, which does not make tooth extraction easy; it had to come out sidewise, and the process was somewhat bungled by an inexperienced dental surgeon.
When the anesthetic wore off, it was the most pain I’ve ever been in in my life.
After that, I wasn’t a very regular returner to the dentist, and in 2013, I fell into a very deep depression for unrelated reasons, and during that period, I got some plaque/tartar buildup on some of my teeth due to lack of care, that then just stayed until I decided to take care of it more recently, which I am happy to say, I’ve now done (my teeth are the happiest and healthiest they’ve ever been), and I’m going to share how, with you.
So, here’s how to do it… First, you’ll need those tools, of course.
You will also want a good quality backlit magnifying mirror. Again, here’s an example product on Amazon ← this is the exact kind this writer has, and it’s very good.
You may be thinking: “wait a minute, this is scary, those are dangerous and I’m not a dentist!”
If so, then a few quick things to bear in mind:
- If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
- These things do look scarier than they are once you get used to them. Do you use metal silverware when eating? Technically you could stab yourself with a fork any time, or damage your teeth with it, but when was the last time you did that?
- With regard to manual dexterity, if you have the manual dexterity required to paint your nails, floss your teeth, sew by hand, or write with a pen, then you have the manual dexterity to do this, too.
Now, about the tools:
- Speculum / magnifying speculum: the one with the mirror. This is useful for looking at the backs of teeth.
- Tweezers: the one with the gold grip in the photo above. You probably won’t need to use these, but we’re sure you know how to use tweezers in general.
- Dental explorer: the one with the big wicked-looking hook on one end, and a tiny (almost invisible in the photo) hook on the other end. This is for examining cavities, not for manipulating things. Best leave that to your dentist if you have cavities.
- Dental pick: this is the one to the right of the dental explorer, and it is for cleaning in the crevices between teeth. One end is quite blunt; the other is pointier, and you can choose which end to use depending on what fits into the shape of the crevice between your teeth.
- Dental scraper: this is the one with chisel ends. One end curves very slightly to the left, the other, very slightly to the right. This is for ergonomics depending on which hand you’re using, and which side you’re scraping (you’ll become very aware that your teeth, even if they look straight, curve very slightly at the edges.
You’ll be using these last two for the actual tartar removal, selecting the tool appropriate to cleaning the flat surface of a tooth, or the crevice where the teeth meet (not like flossing! That part, yes, but under no circumstances is this thing going all the way through to the other side, it’s just for getting into to nook that the scraper can’t so easily clean, that’s all).
A word on using metal against your teeth: a scary prospect, initially! However…
While steel is indeed harder than the enamel of your teeth, the enamel of your teeth is much harder than the plaque/tartar/calculus that you will be removing. Therefore, the technique to use is very gently scrape, starting as gently as humanly possible until you get a feel for it.
Unlike the dentist, you will have an advantage here in that you have biofeedback, and bone conduction of the sounds in your mouth, so you can exercise much more restraint than your dentist can. With the correct minimum of pressure, the tool should glide smoothly down enamel, but when it’s scraping tartar, it should make a very fine sandpapery noise.
This is why “or write with a pen” was one of the skills we mentioned earlier; it’s the same thing; you don’t press with a pen so hard that it goes through the paper, so don’t press so hard with the tool that it damages your enamel, that’s all.
Because of the differential in hardness between the tartar and the enamel, it’s really very easy to remove the tartar without harming the enamel, provided one is gentle.
Final word of warning; we’ll repeat: If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
Also, while this kind of cleaning can be done safely at home, we recommend against doing anything more complicated than that.
See for example: Can You Repair Your Own Teeth At Home? ← the short answer is “no”, or not beyond tooth remineralization, anyway, and kits that say otherwise are potentially misleading, or stop-gap solutions at best.
One last time: always consult with a professional and get their advice (ours is not advice; it’s just information).
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How Old Is Too Old For HRT?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I think you guys do a great job. Wondering if I can suggest a topic? Older women who were not offered hormone replacement therepy because of a long term study that was misread. Now, we need science to tell us if we are too old to benefit from begininng to take HRT. Not sure how old your readers are on average but it would be a great topic for older woman. Thanks❞
Thank you for the kind words, and the topic suggestion!
About the menopause and older age thereafter
We’ve talked a bit before about the menopause, for example:
What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
And we’ve even discussed the unfortunate social phenomenon of post-menopausal women thinking “well, that’s over and done with now, time to forget about that”, because spoiler, it will never be over and done with—your body is always changing every day, and will continue to do so until you no longer have a body to change.
This means, therefore, that since changes are going to happen no matter what, the onus is on us to make the changes as positive (rather than negative) as possible:
Menopause, & When Not To Let Your Guard Down
About cancer risk
It sounds like you know this one, but for any who were unaware: indeed, there was an incredibly overblown and misrepresented study, and even that was about older forms of HRT (being conjugated equine estrogens, instead of bioidentical estradiol):
As for those who have previously had breast cancer or similar, there is also:
The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
Is it too late?
Fortunately, there is a quick and easy test to know whether you are too old to benefit:
First, find your pulse, by touching the first two fingers of one hand, against the wrist of the other. If you’re unfamiliar with where to find the pulse at the wrist, here’s a quick explainer.
Or if you prefer a video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Did you find it?
Good; in that case, it’s not too late!
Scientists have tackled this question, looking at women of various ages, and finding that when comparing age groups taking HRT, disease risk changes do not generally vary much by age i.e., someone at 80 gets the same relative benefit from HRT as someone at 50, with no extra risks from the HRT. For example, if taking HRT at 50 reduces a risk by n% compared to an otherwise similar 50-year-old not on HRT, then doing so at 80 reduces the same risk by approximately the same percentage, compared to an otherwise similar 80-year-old not on HRT.
There are a couple of exceptions, such as in the case of already having advanced atherosclerotic lesions (in which specific case HRT could increase inflammation; not something it usually does), or in the case of using conjugated equine estrogens instead of modern bioidentical estradiol (as we talked about before).
Thus, for the most part, HRT is considered safe and effective regardless of age:
How old is too old for hormone therapy?
👆 that’s from 2015 though, so how about a new study, from 2024?
❝Compared with never use or discontinuation of menopausal hormone therapy after age 65 years, the use of estrogen monotherapy beyond age 65 years was associated with significant risk reductions in mortality (19% or adjusted hazards ratio, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.79-0.82), breast cancer (16%), lung cancer (13%), colorectal cancer (12%), congestive heart failure (CHF) (5%), venous thromboembolism (3%), atrial fibrillation (4%), acute myocardial infarction (11%), and dementia (2%).❞
❝Among senior Medicare women, the implications of menopausal hormone therapy use beyond age 65 years vary by types, routes, and strengths. In general, risk reductions appear to be greater with low rather than medium or high doses, vaginal or transdermal rather than oral preparations, and with estradiol rather than conjugated estrogen.❞
Read in full: Use of menopausal hormone therapy beyond age 65 years and its effects on women’s health outcomes by types, routes, and doses
As for more immediately-enjoyable benefits (improved mood, healthier skin, better sexual function, etc), yes, those also are benefits that people enjoy at least into their eighth decade:
See: Use of hormone therapy in Swedish women aged 80 years or older
What about…
Statistically speaking, most people who take HRT have a great time with it and consider it life-changing in a good way. However, nothing is perfect; sometimes going on HRT can have a shaky start, and for those people, there may be some things that need addressing. So for that, check out:
HRT Side Effects & Troubleshooting
And also, while estrogen monotherapy is very common, it is absolutely worthwhile to consider also taking progesterone alongside it:
Progesterone Menopausal HRT: When, Why, And How To Benefit
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Art Of Letting Go – by Nick Trenton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: is this a basic CBT book? And, for the most part, no, it’s not.
It does touch on some of the time-tested CBT techniques, but a large part of the book is about reframing things in a different way, that’s a little more DBT-ish, and even straying into BA. But enough of the initialisms, let’s give an example:
It can be scary to let go of the past, or of present or future possibilities (bad ones as well as good!). However, it’s hard to consciously do something negative (same principle as “don’t think of a pink elephant”), so instead, look at it as taking hold of the present/future—and thus finding comfort and security in a new reality rather than an old memory or a never-actual imagining.
So, this book has a lot of ideas like that, and if even one of them helps, then it was worth reading.
The writing style is comprehensive, and goes for the “tell them what you’re gonna tell them; tell them; then tell them what you told them” approach, which a) is considered good for learning b) can feel a little like padding nonetheless.
Bottom line: this reviewer didn’t personally love the style, but the content made up for it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
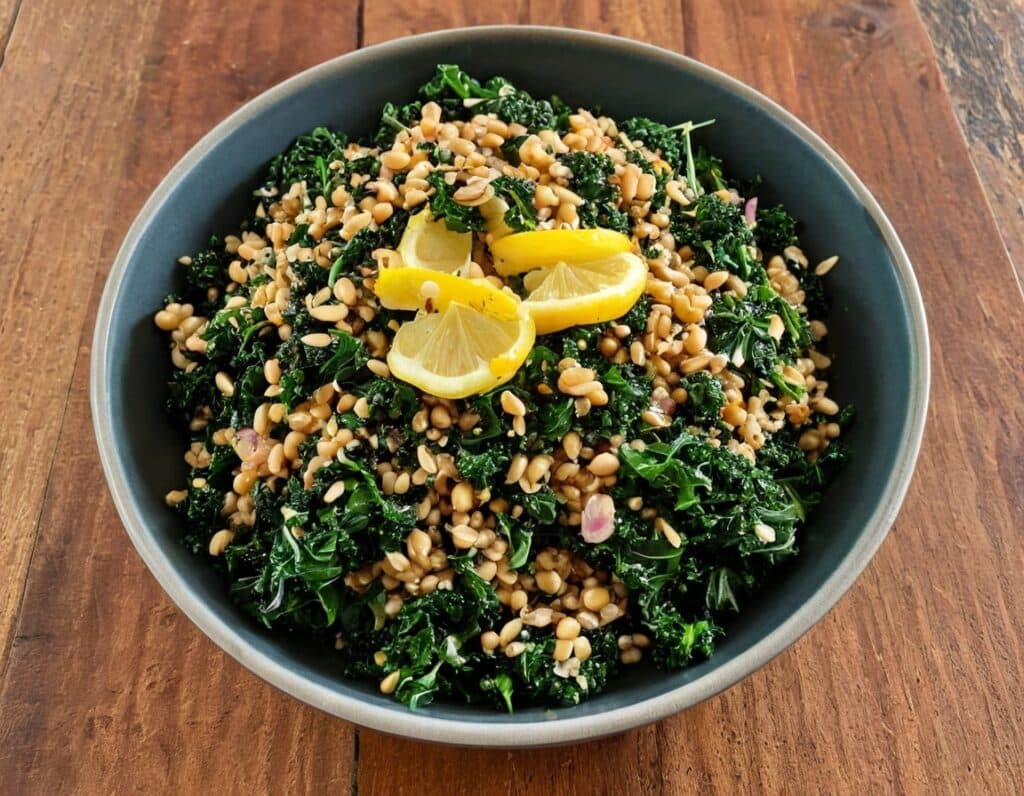
SMOL Bowl With Sautéed Greens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whole grains are good, and gluten is bad for some people. Today’s dish has four whole grains, and no gluten (assuming no cross-contamination, so look for the gluten-free label if that’s important to you). Breafast? Brunch? Lunch? Supper, even? This is good at any time of day, packed with nutrients and full of flavor!
You will need (per person)
- 1 cup mixed cooked grains of equal parts sorghum, millet, oats, lentils (SMOL)—these can be cooked in bulk in advance and frozen in portions, as it’s often good to used mixed grains, and these four are a great combination for many purposes.
- ½ cup low sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made this yourself from vegetable offcuts you kept in the freezer until you had enough for this purpose, but failing that, low-sodium stock cubes can be bought at most large supermarkets).
- ½ cup finely chopped red onion
- 6 oz cavolo nero, finely chopped
- 1 small carrot, finely chopped
- 3 cloves garlic, finely chopped
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- To serve: 1 lemon wedge
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the stock to a sauté pan over a medium heat, and add the onion, garlic, and carrot. Stir frequently for about 7 minutes.
2) Add the cavolo nero and miso paste, stirring for another 4 minutes. If there is any liquid remaining, drain it off now.
3) Warm the SMOL mixture (microwave is fine) and spoon it into a bowl, topping with the nutritional yeast and black pepper. Finally, add the hot cavolo nero mixture.
4) Serve with the lemon wedge on the side, to add a dash of lemon at will.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Longans vs Lychees – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing longans to lychees, we picked the lychees.
Why?
These two fruits are more closely related than they look from the outside, both being members of the soapberry family. However, there are some differences:
In terms of macros, longans have more protein while lychees have more carbs, and they are equal on fiber, giving longans the lower glycemic index. They’re both good, but longans nominally take the win on this one.
When it comes to vitamins, longans have more of vitamins B1, B2, and C, while lychees have more of vitamins B3, B6, B9, E, K, and choline, making for a respectable win for lychees in this category.
In the category of minerals, longans have more copper and potassium, while lychees have more calcium, iron, manganese phosphorus, and zinc. Thus, a win for lychees here too.
It’s worth looking at polyphenols too—lychees have around 10x more, which is notable.
Adding up the categories makes for an overall win for lychees, but by all means enjoy either or both! Diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods ← longans and lychees both make the list
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: