Beating Sleep Apnea
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Healthier, Natural Sleep Without Obstruction!
Obstructive Sleep Apnea, the sleep disorder in which one periodically stops breathing (and thus wakes up) repeatedly through the night, affects about 25% of men and 10% of women:
Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
Why the gender split?
There are clues that suggest it is at least partially hormonal: once women have passed menopause, the gender split becomes equal.
Are there other risk factors?
There are few risk other factors; some we can’t control, and some we can:
- Being older is riskier than being younger
- Being overweight is riskier than not being overweight
- Smoking is (what a shock) riskier than not smoking
- Chronic respiratory diseases increase risk, for example:
- Asthma
- COPD
- Long COVID*—probably. The science is young for this one so far, so we can’t say for sure until more research has been done.
- Some hormonal conditions increase risk, for example:
- Hypothyroidism
- PCOS
*However, patients already undergoing Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) treatment for obstructive sleep apnea may have an advantage when fighting a COVID infection:
What can we do about it?
Avoiding the above risk factors, where possible, is great!
If you are already suffering from obstructive sleep apnea, then you probably already know about the possibility of a CPAP device; it’s a mask that one wears to sleep, and it does what its name says (i.e. it applies continuous positive airway pressure), which keeps the airway open.
We haven’t tested these, but other people have, so here are some that the Sleep Foundation found to be worthy of note:
Sleep Foundation | Best CPAP Machines of 2024
What can we do about it that’s not CPAP?
Wearing a mask to sleep is not everyone’s preferred way to do things. There are also a plethora of surgeries available, but we’ll not review those, as those are best discussed with your doctor if necessary.
However, some lifestyle changes can help, including:
- Lose weight, if overweight. In particular, having a collar size under 16” for women or under 17” for men, is sufficient to significantly reduce the risk of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Stop smoking, if you smoke. This one, we hope, is self-explanatory.
- Stop drinking alcohol, or at least reduce intake, if you drink. People who consume alcohol tend to have more frequent, and longer, incidents of obstructive sleep apnea. See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Drinking
- Avoid sedatives and muscle relaxants, if it is safe for you to do so. Obviously, if you need them to treat some other condition you have, talk this through with your doctor. But basically, they can contribute to the “airway collapses on itself” by reducing the muscular tension that keeps your airway the shape it’s supposed to be.
- Sleep on your side, not your back. This is just plain physics, and a matter of wear the obstruction falls.
- Breathe through your nose, not through your mouth. Initially tricky to do while sleeping, but the more you practice it while awake, the more it becomes possible while asleep.
- Consider a nasal decongestant before sleep, if congestion is a problem for you, as that can help too.
For more of the science of these, see:
Cultivating Lifestyle Transformations in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
There are more medical options available not discussed here, too:
American Sleep Apnea Association | Sleep Apnea Treatment Options
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which Osteoporosis Medication, If Any, Is Right For You?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Which Osteoporosis Medication, If Any, Is Right For You?
We’ve written about osteoporosis before, so here’s a quick recap first in case you missed these:
- The Bare-bones Truth About Osteoporosis
- Exercises To Do (And Exercises To Avoid) If You Have Osteoporosis
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
All of those look and diet and/or exercise, with “diet” including supplementation. But what of medications?
So many choices (not all of them right for everyone)
The UK’s Royal Osteoporosis Society says of the very many osteoporosis meds available:
❝In terms of effectiveness, they all reduce your risk of broken bones by roughly the same amount.
Which treatment is right for you will depend on a number of things.❞
…before then going on to list a pageful of things it will depend on, and giving no specific information about what prescriptions or proscriptions may be made based on those factors.
Source: Royal Osteoporosis Society | Which medication should I take?
We’ll try to do better than that here, though we have less space. So let’s get down to it…
First line drug offerings
After diet/supplementation and (if applicable) hormones, the first line of actual drug offerings are generally biphosphates.
Biphosphates work by slowing down your osteoclasts—the cells that break down your bones. They may sound like terrible things to have in the body at all, but remember, your body is always rebuilding itself and destruction is a necessary act to facilitate creation. However, sometimes things can get out of balance, and biphosphates help tip things back into balance.
Common biphosphates include Alendronate/Fosamax, Risedronate/Actonel, Ibandronate/Boniva, and Zolendronic acid/Reclast.
A common downside is that they aren’t absorbed well by the stomach (despite being mostly oral administration, though IV versions exist too) and can cause heartburn / general stomach upset.
An uncommon downside is that messing with the body’s ability to break down bones can cause bones to be rebuilt-in-place slightly incorrectly, which can—paradoxically—cause fractures. But that’s rare and is more common if the drugs are taken in much higher doses (as for bone cancer rather than osteoporosis).
Bone-builders
If you already have low bone density (so you’re fighting to rebuild your bones, not just slow deterioration), then you may need more of a boost.
Bone-building medications include Teriparatide/Forteo, Abaloparatide/Tymlos, and Romosozumab/Evenity.
These are usually given by injection, usually for a course of one or two years.
Once the bone has been built up, it’ll probably be recommended that you switch to a biphosphate or other bone-stabilizing medication.
Estrogen-like effects, without estrogen
If your osteoporosis (or osteoporosis risk) comes from being post-menopausal, estrogen is a very common (and effective!) prescription. However, some people may wish to avoid it, if for example you have a heightened breast cancer risk, which estrogen can exacerbate.
So, medications that have estrogen-like effects post-menopause, but without actually increasing estrogen levels, include: Raloxifene/Evista, and also all the meds we mentioned in the bone-building category above.
Raloxifene/Evista specifically mimics the action of estrogen on bones, while at the same time blocking the effect of estrogen on other tissues.
Learn more…
Want a more thorough grounding than we have room for here? You might find the following resource useful:
List of 82 Osteoporosis Medications Compared (this has a big table which is sortable by various variables)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
‘Disease X’: What it is (and isn’t)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- In January 2024, the World Economic Forum hosted an event called Preparing for Disease X to discuss strategies to improve international pandemic response.
- Disease X is a term used in epidemiology to refer to potential disease threats. It is not a real disease or a global conspiracy.
- Preparation to prevent and respond to future pandemics is a necessary part of global health to keep us all safer.
During the World Economic Forum’s 54th annual meeting in Davos, Switzerland, global health experts discussed ways to strengthen health care systems in preparation for future pandemics. Conspiracy theories quickly began circulating posts about the event and the fictional disease at its center, so-called Disease X.
What is Disease X?
In 2018, the World Health Organization added Disease X to its list of Blueprint Priority Diseases that are public health risks. But, unlike the other diseases on the list, Disease X doesn’t exist. The term represents a hypothetical human disease capable of causing a pandemic. Although experts don’t know what the next Disease X will be, they can make educated guesses about where and how it may emerge—and how we can prepare for it.
Why are we hearing about Disease X now?
COVID-19 has been the deadliest infectious disease outbreak of the 21st century. It’s also an example of a Disease X: a previously unknown pathogen that spreads rapidly around the world, claiming millions of lives.
When the WEF hosted a panel of experts to discuss Disease X, it was the first exposure that many people had to a concept that global health experts have been discussing since 2018.
Even before the routine pandemic preparedness event took place, online conspiracy theorists began circulating false claims that those discussing and preparing for Disease X had sinister motives, underscoring how widespread distrust of global health entities has become in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Why does Disease X matter?
Epidemiologists use concepts like Disease X to plan for future outbreaks and avoid the mistakes of past outbreaks. The COVID-19 pandemic and the recent non-endemic outbreak of mpox highlight the importance of global coordination to efficiently prevent and respond to disease outbreaks.
Pandemics are inevitable, but the scale of their destruction doesn’t have to be. Major disease outbreaks are likely to become more frequent due to the impacts of climate change. Preparing for a pandemic now helps ensure that the world is better equipped to handle the next one.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Red Light, Go!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Casting Yourself In A Healthier Light
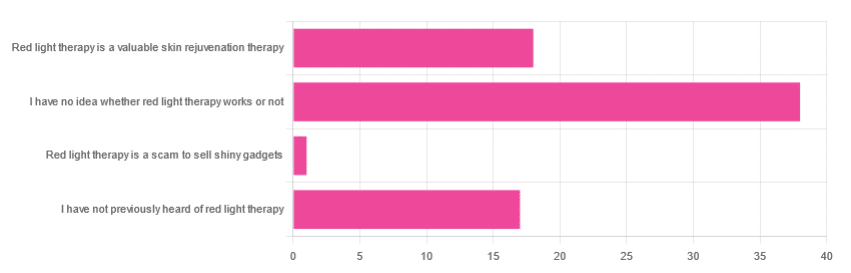
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of red light therapy (henceforth: RLT), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 51% said “I have no idea whether light therapy works or not”
- About 24% said “Red light therapy is a valuable skin rejuvenation therapy”
- About 23% said “I have not previously heard of red light therapy”
- One (1) person said: “Red light therapy is a scam to sell shiny gadgets”
A number of subscribers wrote with personal anecdotes of using red light therapy to beneficial effect, for example:
❝My husband used red light therapy after surgery on his hand. It did seem to speed healing of the incision and there is very minimal scarring. I would like to know if the red light really helped or if he was just lucky❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
And one wrote to report having observed mixed results amongst friends, per:
❝Some people it works, others I’ve seen it breaks them out❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
So, what does the science say?
RLT rejuvenates skin, insofar as it reduces wrinkles and fine lines: True or False?
True! This one’s pretty clear-cut, so we’ll just give one example study of many, which found:
❝The treated subjects experienced significantly improved skin complexion and skin feeling, profilometrically assessed skin roughness, and ultrasonographically measured collagen density.
The blinded clinical evaluation of photographs confirmed significant improvement in the intervention groups compared with the control❞
~ Dr. Alexander Wunsch & Dr. Karsten Matuschka
RLT helps speed up healing of wounds: True or False?
True! There is less science for this than the above claim, but the studies that have been done are quite compelling, for example this NASA technology study found that…
❝LED produced improvement of greater than 40% in musculoskeletal training injuries in Navy SEAL team members, and decreased wound healing time in crew members aboard a U.S. Naval submarine.❞
Read more: Effect of NASA light-emitting diode irradiation on wound healing
RLT’s benefits are only skin-deep: True or False?
False, probably, but we’d love to see more science for this, to be sure.
However, it does look like wavelengths in the near-infrared spectrum reduce the abnormal tau protein and neurofibrillary tangles associated with Alzheimer’s disease, resulting in increased blood flow to the brain, and a decrease in neuroinflammation:
Therapeutic Potential of Photobiomodulation In Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Would you like to try RLT for yourself?
There are some contraindications, for example:
- if you have photosensitivity (for obvious reasons)
- if you have Lupus (mostly because of the above)
- if you have hyperthyroidism (because if you use RLT to your neck as well as face, it may help stimulate thyroid function, which in your case is not what you want)
As ever, please check with your own doctor if you’re not completely sure; we can’t cover all bases here, and cannot speak for your individual circumstances.
For most people though, it’s very safe, and if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product on Amazon, and by all means do read reviews and shop around for the ideal device for you
Take care! 😎
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Green Curry Salmon Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These lean and healthy burgers are as quick and easy to make as they are good for entertaining. The serving-bed has its nutritional secrets too! All in all, an especially heart-healthy and brain-healthy dish.
You will need
- 4 skinless salmon fillets, cubed (Vegetarian/Vegan? Consider this Plant-Based Salmon Recipe or, since they are getting blended, simply substitute 1½ cups cooked chickpeas instead with 1 tbsp tahini)
- 2 cloves garlic, chopped
- 2 tbsp thai green curry paste
- juice of two limes, plus wedges to serve
- 1 cup quinoa
- ½ cup edamame beans, thawed if they were frozen
- large bunch fresh cilantro (or parsley if you have the “soap “cilantro tastes like soap” gene), chopped
- extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the salmon, garlic, curry paste, nutritional yeast, and half the lime juice into a food processor, and blend until smooth.
2) Remove, divide into four parts, and shape into burger patty shapes. Put them in the fridge where they can firm up while we do the next bit.
3) Cook the quinoa with the tablespoon of chia seeds added (which means boiling water and then letting it simmer for 10–15 minutes; when the quinoa is tender and unfurled a little, it’s done).
4) Drain the quinoa with a sieve, and stir in the edamame beans, the rest of the lime juice, the cilantro, and the black pepper. Set aside.
5) Using the olive oil, fry the salmon burgers for about 5 minutes on each side.
6) Serve; we recommend putting the burgers atop the rest, and adding a dash of lime at the table.
(it can also be served this way!)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Farmed Fish vs Wild–Caught
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
You May Have More Air Pollution In Your Home Than In The Street
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Certainly, gas stoves and heaters can cause indoor air pollution, with carbon monoxide (CO) being the main risk. Even if you have a CO alarm, the level at which it will go off is usually the “this will kill you tonight if you don’t do something about it soon” level, rather than the “this will slowly kill your brain cells but you’ll keep functioning otherwise, until one day you don’t” levels of CO.
Still, do by all means have a CO alarm if you have anything in your house that can release CO!
Fun fact about those stoves:
❝Just 1 kilogram of cooking fuel emits 10 quadrillion particles smaller than 3 nanometers, which matches or exceeds what’s emitted from cars with internal combustion engines.
At that rate, you might be inhaling 10-100 times more of these sub-3 nanometer particles from cooking on a gas stove indoors than you would from car exhaust while standing on a busy street.❞
But today, we’re not here about that
Rather, we are looking at some more innocent-seeming things, such as scented cleaning products and air fresheners. Notably, the biggest problem is often not even the cleaning chemicals themselves. Of course: please don’t breathe bleach fumes, etc.
But that’s an obvious risk, and today we’re about the less obvious risks.
So… What is the less obvious risk here?
It’s the fragrances. The terpenes used to hold them react with ozone in the air, to create new nanoparticles. And, just like the nanoparticles from the stove, these can reach very high concentrations indoors, and suffice it to say, if you can smell the fragrance then you have the pollutants inside you.
You can read about how badly different products score, here:
Rapid Nucleation and Growth of Indoor Atmospheric Nanocluster Aerosol during the Use of Scented Volatile Chemical Products in Residential Buildings ← you’ll need to scroll down to the table with different cleaning products and air fresheners
Further, the seemingly-harmless scented candle is, as it turns out, quite a menace too:
❝Full-scale emission experiments were conducted in the Purdue zEDGE Test House using a variety of scented candles (n = 5) and wax warmers/melts (n = 14) under different outdoor air exchange rates (AERs). Terpene concentrations were measured in real-time using a proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometer (PTR-TOF-MS). PTR-TOF-MS measurements revealed that scented candle and wax warmer/melt products emit a variety of monoterpenes (C10H16) and oxygen-containing monoterpenoids (C10H14O, C10H16O, C10H18O, C10H20O), with peak concentrations in the range of 10−1 to 102 ppb. Monoterpene EFs were much greater for scented wax warmers/melts (C10H16 EFs ∼ 102 mg per g wax consumed) compared to scented candles (C10H16 EFs ∼ 10−1 to 100 mg per g wax consumed). Significant emissions of reactive terpenes from both products, along with nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2) from candles, depleted indoor ozone (O3) concentrations. Terpene iFs were similar between the two products (iFs ∼ 103 ppm) and increased with decreasing outdoor AER. Terpene iFs during concentration decay periods were similar to, or greater than, iFs during active emission periods for outdoor AERs ≤ 3.0 h−1.
Overall, scented wax warmers/melts were found to release greater quantities of monoterpenes compared to other fragranced consumer products used in the home, including botanical disinfectants, hair care products, air fresheners, and scented sprays.❞
Put in fewer words: scented candles are bad, and wax melts (the kind with no flame, that one might easily expect to thus produce fewer emissions) are at least as bad if not worse, and both are even worse than cleaning products.
Some of the same research team conducted further studies, because of this this, finding:
❝We performed field measurements in a residential test house to investigate atmospheric nanoparticle formation from scented wax melt use. We employed a high-resolution particle size magnifier-scanning mobility particle sizer (PSMPS) and a proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometer (PTR-TOF-MS) for real-time monitoring of indoor atmospheric nanoparticle size distributions and terpene mixing ratios, respectively.
Our findings reveal that terpenes released from scented wax melts react with indoor atmospheric ozone (O3) to initiate new particle formation (NPF) events, resulting in significant indoor atmospheric nanoparticle concentrations (>106 cm–3) comparable to those emitted by combustion-based scented candles, gas stoves, diesel engines, and natural gas engines.
We show that scented wax melt-initiated NPF events can result in significant respiratory exposures, with nanoparticle respiratory tract deposited dose rates similar to those determined for combustion-based sources.
Our results challenge the perception of scented wax melts as a safer alternative to combustion-based aromatherapy❞
Read in full: Flame-Free Candles Are Not Pollution-Free: Scented Wax Melts as a Significant Source of Atmospheric Nanoparticles
In short: you might want to ditch the fragranced products!
Want to do more?
Give your household hair a makeover with this multi-vector approach to deal with different risks:
What’s Lurking In Your Household Air?
For that matter, the air is a very important factor for the health of your lungs (and thus, for the health of everything that’s fed oxygen by your lungs), and there are more things we can do in that regard as well:
Seven Things To Do For Good Lung Health!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Flossing Without Flossing?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Flossing Without Flossing?
You almost certainly brush your teeth. You might use mouthwash. A lot of people floss for three weeks at a time, often in January.
There are a lot of options for oral hygiene; variations of the above, and many alternatives too. This is a big topic, so rather than try to squeeze it all in one, this will be a several-part series.
The first part was: Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
How important is flossing?
Interdental cleaning is indeed pretty important, even though it may not have the heart health benefits that have been widely advertised:
However! The health of our gums is very important in and of itself, especially as we get older:
Flossing Is Associated with Improved Oral Health in Older Adults
But! It helps to avoid periodontal (e.g. gum) disease, not dental caries:
Flossing for the management of periodontal diseases and dental caries in adults
And! Most certainly it can help avoid a stack of other diseases:
Interdental Cleaning Is Associated with Decreased Oral Disease Prevalence
…so in short, if you’d like to have happy healthy teeth and gums, flossing is an important adjunct, and/but not a one-stop panacea.
Is it better to floss before or after brushing?
As you prefer. A team of scientists led by Dr. Claudia Silva studied this, and found that there was “no statistical difference between brush-floss and floss-brush”:
Flossing is tedious. How do we floss without flossing?
This is (mostly) about water-flossing! Which does for old-style floss what sonic toothbrushes to for old-style manual toothbrushes.
If you’re unfamiliar, it means using a device that basically power-washes your teeth, but with a very narrow high-pressure jet of water.
Do they work? Yes:
As for how it stacks up against traditional flossing, Liang et al. found:
❝In our previous single-outcome analysis, we concluded that interdental brushes and water jet devices rank highest for reducing gingival inflammation while toothpick and flossing rank last.
In this multioutcome Bayesian network meta-analysis with equal weight on gingival inflammation and bleeding-on-probing, the surface under the cumulative ranking curve was 0.87 for water jet devices and 0.85 for interdental brushes.
Water jet devices and interdental brushes remained the two best devices across different sets of weightings for the gingival inflammation and bleeding-on-probing. ❞
~ Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice
You may be wondering how safe it is if you have had dental work done, and, it appears to be quite safe, for example:
BDJ | Water-jet flossing: effect on composites
Want to try water-flossing?
Here are some examples on Amazon:
- Waterpik Complete Care 9.0 ← example of a top-end water-flossing device
- Philips Sonicare Power Flosser 3000 ← top-tier not-Waterpik-brand device
- INSMART Cordless Water Dental Flosser ← very low price and still average 4.5 star reviews, so in our opinion, a fine first choice
Bonus: if you haven’t tried interdental brushes, here’s an example for that
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: