Red Light, Go!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Casting Yourself In A Healthier Light
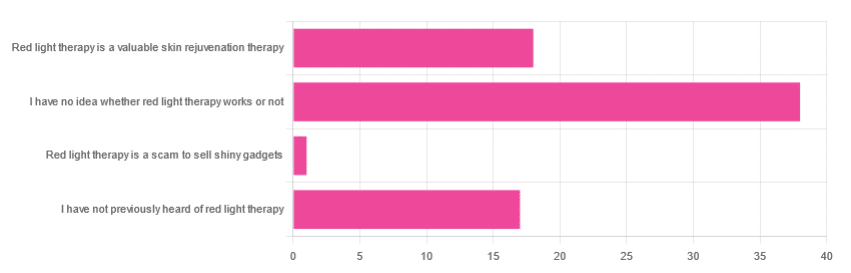
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of red light therapy (henceforth: RLT), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 51% said “I have no idea whether light therapy works or not”
- About 24% said “Red light therapy is a valuable skin rejuvenation therapy”
- About 23% said “I have not previously heard of red light therapy”
- One (1) person said: “Red light therapy is a scam to sell shiny gadgets”
A number of subscribers wrote with personal anecdotes of using red light therapy to beneficial effect, for example:
❝My husband used red light therapy after surgery on his hand. It did seem to speed healing of the incision and there is very minimal scarring. I would like to know if the red light really helped or if he was just lucky❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
And one wrote to report having observed mixed results amongst friends, per:
❝Some people it works, others I’ve seen it breaks them out❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
So, what does the science say?
RLT rejuvenates skin, insofar as it reduces wrinkles and fine lines: True or False?
True! This one’s pretty clear-cut, so we’ll just give one example study of many, which found:
❝The treated subjects experienced significantly improved skin complexion and skin feeling, profilometrically assessed skin roughness, and ultrasonographically measured collagen density.
The blinded clinical evaluation of photographs confirmed significant improvement in the intervention groups compared with the control❞
~ Dr. Alexander Wunsch & Dr. Karsten Matuschka
RLT helps speed up healing of wounds: True or False?
True! There is less science for this than the above claim, but the studies that have been done are quite compelling, for example this NASA technology study found that…
❝LED produced improvement of greater than 40% in musculoskeletal training injuries in Navy SEAL team members, and decreased wound healing time in crew members aboard a U.S. Naval submarine.❞
Read more: Effect of NASA light-emitting diode irradiation on wound healing
RLT’s benefits are only skin-deep: True or False?
False, probably, but we’d love to see more science for this, to be sure.
However, it does look like wavelengths in the near-infrared spectrum reduce the abnormal tau protein and neurofibrillary tangles associated with Alzheimer’s disease, resulting in increased blood flow to the brain, and a decrease in neuroinflammation:
Therapeutic Potential of Photobiomodulation In Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Would you like to try RLT for yourself?
There are some contraindications, for example:
- if you have photosensitivity (for obvious reasons)
- if you have Lupus (mostly because of the above)
- if you have hyperthyroidism (because if you use RLT to your neck as well as face, it may help stimulate thyroid function, which in your case is not what you want)
As ever, please check with your own doctor if you’re not completely sure; we can’t cover all bases here, and cannot speak for your individual circumstances.
For most people though, it’s very safe, and if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product on Amazon, and by all means do read reviews and shop around for the ideal device for you
Take care! 😎
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Compact Tai Chi – by Dr. Jesse Tsao
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A very frustrating thing when practicing tai chi, especially when learning, is the space typically required. We take a step this way and lunge that way and turn and now we’ve kicked a bookcase. Add a sword, and it’s goodnight to the light fixtures at the very least.
While a popular suggestion may be “do it outside”, we do not all have the luxury of living in a suitable climate. We also may prefer to practice in private, with no pressing urge to have an audience.
Tsao’s book, therefore, is very welcome. But how does he do it? The very notion of constriction is antithetical to tai chi, after all.
He takes the traditional forms, keeps the movements mostly the same, and simply changes the order of them. This way, the practitioner revolves around a central point. Occasionally, a movement will become a smaller circle than it was, but never in any way that would constrict movement.
Of course, an obvious question for any such book is “can one learn this from a book?” and the answer is complex, but we would lean towards yes, and insofar as one can learn any physical art from a book, this one does a fine job. It helps that it builds up progressively, too.
All in all, this book is a great choice for anyone who’s interested in taking up tai chi, and/but would like to do so without leaving their home.
Share This Post

The Science Of New Year’s Pre-Resolutions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Science Of New Year’s Pre-Resolutions
There’s a military dictum that “prior preparation and planning prevents p[retty] poor performance”, to paraphrase it very slightly.
Would it surprise you to know that soldiers going on the attack are not focused on the goal? Rather, they are focused on the process.
With drills and mnemonics, everything that can be controlled for in advance is; every action, every reaction, everything that can go wrong, and all the “if x then y” decisions in between pre-battle PREWAR and PAWPERSO and post-battle PACESDO (all mnemonic acronyms; the content is not important here but the principle is).
In short: take Murphy’s Law into account now, and plan accordingly!
The same goes for making your plans the winning kind
If you want your resolutions to work, you may need to make pre-resolutions now, so that you’re properly prepared:
- Do you want to make an exercise habit? Make sure now that you have the right clothes/shoes/etc, make sure that they fit you correctly, make sure you have enough of them that you can exercise when one set’s in the wash, etc.
- What grace will you allow yourself if tired, unwell, busy? What’s your back-up plan so that you still do what you can at those times when “what you can” is legitimately a bit less?
- If it’s an outdoors plan, what’s your plan for when it’s rainy? Snowy? Dangerously hot?
- What are the parameters for what counts? Make it measurable. How many exercise sessions per week, what duration?
- Do you want to make a diet habit? Make sure that you have in the healthy foods that you want to eat; know where you can and will get things. We’re often creatures of habit when it comes to shopping, so planning will be critical here!
- Do you want to cut some food/drink/substance out? Make sure you have a plan to run down or otherwise dispose of your current stock first. And make sure you have alternatives set up, and if it was something you were leaning on as a coping strategy of some kind (e.g. alcohol, cannabis, comfort-eating, etc), make sure you have an alternative coping strategy, too!
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
We promised science, so here it comes
Approach-oriented resolutions work better than avoidance-oriented ones.
This means: positively-framed resolutions work better than negatively-framed ones.
On a simple level, this means that, for example, resolving to exercise three times per week is going to work better than resolving to not consume alcohol.
But what if you really want to quit something? Just frame it positively. There’s a reason that Alcoholics Anonymous (and similar Thing Anonymous groups) measure days sober, not relapses.
So it’s not “I will not consume alcohol” but “I will get through each day alcohol-free”.
Semantics? Maybe, but it’s also science:
Why January the 1st? It’s a fresh start
Resolutions started on the 1st of January enjoy a psychological boost of a feeling of a fresh start, a new page, a new chapter.
Similar benefits can be found from starting on the 1st of a month in general, or on a Monday, or on some date that is auspicious to the person in question (religious fasts tied to calendar dates are a fine example of this).
Again, this is borne-out by science:
The Fresh Start Effect: Temporal Landmarks Motivate Aspirational Behavior
Make it a habit
Here be science:
How do people adhere to goals when willpower is low? The profits (and pitfalls) of strong habits
As for how to do that?
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Trim the middle
No, we’re not talking about your waistline. Rather, what Dr. Ayelet Fischbach refers to as “the middle problem”:
❝We’re highly motivated at the beginning. Over time, our motivation declines as we lose steam. To the extent that our goal has a clear end point, our motivation picks up again toward the end.
Therefore, people are more likely to adhere to their standards at the beginning and end of goal pursuit—and slack in the middle. We demonstrate this pattern of judgment and behavior in adherence to ethical standards (e.g., cheating), religious traditions (e.g., skipping religious rituals), and performance standards (e.g., “cutting corners” on a task).
We also show that the motivation to adhere to standards by using proper means is independent and follows a different pattern from the motivation to reach the end state of goal pursuit❞
Read: The end justifies the means, but only in the middle
How to fix this, then?
Give yourself consistent, recurring, short-term goals, with frequent review points. That way, it’s never “the middle” for long:
The fresh start effect: temporal landmarks motivate aspirational behavior
See also:
How do people protect their long-term goals from the influence of short-term motives or temptations?
Finally…
You might like this previous main feature of ours that was specifically about getting oneself through those “middle” parts:
How To Keep On Keeping On… Long Term!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
- Do you want to make an exercise habit? Make sure now that you have the right clothes/shoes/etc, make sure that they fit you correctly, make sure you have enough of them that you can exercise when one set’s in the wash, etc.

Taking A Trip Through The Evidence On Psychedelics
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.

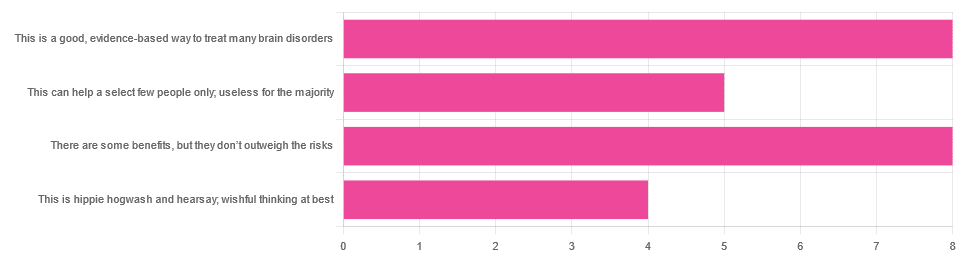
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinions on the medicinal use of psychedelics, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- 32% said “This is a good, evidence-based way to treat many brain disorders”
- 32% said “There are some benefits, but they don’t outweigh the risks”
- 20% said “This can help a select few people only; useless for the majority”
- 16% said “This is hippie hogwash and hearsay; wishful thinking at best”
Quite a spread of answers, so what does the science say?
This is hippie hogwash and hearsay; wishful thinking at best! True or False?
False! We’re tackling this one first, because it’s easiest to answer:
There are some moderately-well established [usually moderate] clinical benefits from some psychedelics for some people.
If that sounds like a very guarded statement, it is. Part of this is because “psychedelics” is an umbrella term; perhaps we should have conducted separate polls for psilocybin, MDMA, ayahuasca, LSD, ibogaine, etc, etc.
In fact: maybe we will do separate main features for some of these, as there is a lot to say about each of them separately.
Nevertheless, looking at the spread of research as it stands for psychedelics as a category, the answers are often similar across the board, even when the benefits/risks may differ from drug to drug.
To speak in broad terms, if we were to make a research summary for each drug it would look approximately like this in each case:
- there has been research into this, but not nearly enough, as “the war on drugs” may well have manifestly been lost (the winner of the war being: drugs; still around and more plentiful than ever), but it did really cramp science for a few decades.
- the studies are often small, heterogenous (often using moderately wealthy white student-age population samples), and with a low standard of evidence (i.e. the methodology often has some holes that leave room for reasonable doubt).
- the benefits recorded are often small and transient.
- in their favor, though, the risks are also generally recorded as being quite low, assuming proper safe administration*.
*Illustrative example:
Person A takes MDMA in a club, dances their cares away, has had only alcohol to drink, sweats buckets but they don’t care because they love everyone and they see how we’re all one really and it all makes sense to them and then they pass out from heat exhaustion and dehydration and suffer kidney damage (not to mention a head injury when falling) and are hospitalized and could die;
Person B takes MDMA in a lab, is overwhelmed with a sense of joy and the clarity of how their participation in the study is helping humanity; they want to hug the researcher and express their gratitude; the researcher reminds them to drink some water.
Which is not to say that a lab is the only safe manner of administration; there are many possible setups for supervised usage sites. But it does mean that the risks are often as much environmental as they are risks inherent to the drug itself.
Others are more inherent to the drug itself, such as adverse cardiac events for some drugs (ibogaine is one that definitely needs medical supervision, for example).
For those who’d like to see numbers and clinical examples of the bullet points we gave above, here you go; this is a great (and very readable) overview:
NIH | Evidence Brief: Psychedelic Medications for Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders
Notwithstanding the word “brief” (intended in the sense of: briefing), this is not especially brief and is rather an entire book (available for free, right there!), but we do recommend reading it if you have time.
This can help a select few people only; useless for the majority: True or False?
True, technically, insofar as the evidence points to these drugs being useful for such things as depression, anxiety, PTSD, addiction, etc, and estimates of people who struggle with mental health issues in general is often cited as being 1 in 4, or 1 in 5. Of course, many people may just have moderate anxiety, or a transient period of depression, etc; many, meanwhile, have it worth.
In short: there is a very large minority of people who suffer from mental health issues that, for each issue, there may be one or more psychedelic that could help.
This is a good, evidence-based way to treat many brain disorders: True or False?
True if and only if we’re willing to accept the so far weak evidence that we discussed above. False otherwise, while the jury remains out.
One thing in its favor though is that while the evidence is weak, it’s not contradictory, insofar as the large preponderance of evidence says such therapies probably do work (there aren’t many studies that returned negative results); the evidence is just weak.
When a thousand scientists say “we’re not completely sure, but this looks like it helps; we need to do more research”, then it’s good to believe them on all counts—the positivity and the uncertainty.
This is a very different picture than we saw when looking at, say, ear candling or homeopathy (things that the evidence says simply do not work).
We haven’t been linking individual studies so far, because that book we linked above has many, and the number of studies we’d have to list would be:
n = number of kinds of psychedelic drugs x number of conditions to be treated
e.g. how does psilocybin fare for depression, eating disorders, anxiety, addiction, PTSD, this, that, the other; now how does ayahuasca fare for each of those, and so on for each drug and condition; at least 25 or 30 as a baseline number, and we don’t have that room.
But here are a few samples to finish up:
- Psilocybin as a New Approach to Treat Depression and Anxiety in the Context of Life-Threatening Diseases—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials
- Therapeutic Use of LSD in Psychiatry: A Systematic Review of Randomized-Controlled Clinical Trials
- Efficacy of Psychoactive Drugs for the Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review of MDMA, Ketamine, LSD and Psilocybin
- Changes in self-rumination and self-compassion mediate the effect of psychedelic experiences on decreases in depression, anxiety, and stress.
- Psychedelic Treatments for Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review and Thematic Synthesis of Patient Experiences in Qualitative Studies
- Repeated lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) reverses stress-induced anxiety-like behavior, cortical synaptogenesis deficits and serotonergic neurotransmission decline
In closing…
The general scientific consensus is presently “many of those drugs may ameliorate many of those conditions, but we need a lot more research before we can say for sure”.
On a practical level, an important take-away from this is twofold:
- drugs, even those popularly considered recreational, aren’t ontologically evil, generally do have putative merits, and have been subject to a lot of dramatization/sensationalization, especially by the US government in its famous war on drugs.
- drugs, even those popularly considered beneficial and potentially lifechangingly good, are still capable of doing great harm if mismanaged, so if putting aside “don’t do drugs” as a propaganda of the past, then please do still hold onto “don’t do drugs alone”; trained professional supervision is a must for safety.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Beyond Burger vs Beef Burger – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing the Beyond Burger to a grass-fed beef burger, we picked the Beyond Burger—but it was very close.
Why?
The macronutrient profiles of the two are almost identical, including the amount of protein, the amount of fat, and the amount of that fat that’s saturated.
Where they stand apart is in two ways:
1) Red meat is classed as a group 2A carcinogen
2) The Beyond Burger contains more sodium (about 1/5 of the daily allowance according to the AHA, or 1/4 of the daily allowance according to the WHO)Neither of those things are great, so how to decide which is worse?
• Cancer and heart disease are both killers, with heart disease claiming more victims.
• However, we do need some sodium to live, whereas we don’t need carcinogens to live.Tie-breaker: the sodium content in the Beyond Burger is likely to be offset by the fact that it’s a fully seasoned burger and will be eaten as-is, whereas the beef burger will doubtlessly have seasonings added before it’s eaten—which may cause it to equal or even exceed the salt content of the Beyond Burger.
The cancer risk for the beef burger, meanwhile, stays one-sided.
One thing’s for sure though: neither of them are exactly a cornerstone of a healthy diet, and either are best enjoyed as an occasional indulgence.
Some further reading:
• Lesser-Known Salt Risks
• Food Choices And Cancer Risk
• Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than SaltDon’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Undoing The Damage Of Life’s Hard Knocks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes, What Doesn’t Kill Us Makes Us Insecure
We’ve written before about Complex PTSD, which is much more common than the more popularly understood kind:
Given that C-PTSD affects so many people (around 1 in 5, but really, do read the article above! It explains it better than we have room to repeat today), it seems like a good idea to share tips for managing it.
(Last time, we took all the space for explaining it, so we just linked to some external resources at the end)
What happened to you?
PTSD has (as a necessity, as part of its diagnostic criteria) a clear event that caused it, which makes the above question easy to answer.
C-PTSD often takes more examination to figure out what tapestry of circumstances (and likely but not necessarily: treatment by other people) caused it.
Often it will feel like “but it can’t be that; that’s not that bad”, or “everyone has things like that” (in which case, you’re probably one of the one in five).
The deeper questions
Start by asking yourself: what are you most afraid of, and why? What are you most ashamed of? What do you fear that other people might say about you?
Often there is a core pattern of insecurity that can be summed up in a simple, harmful, I-message, e.g:
- I am a bad person
- I am unloveable
- I am a fake
- I am easy to hurt
- I cannot keep my loved ones safe
…and so forth.
For a bigger list of common insecurities to see what resonates, check out:
Basic Fears/Insecurities, And Their Corresponding Needs/Desires
Find where they came from
You probably learned bad beliefs, and consequently bad coping strategies, because of bad circumstances, and/or bad advice.
- When a parent exclaimed in anger about how stupid you are
- When a partner exclaimed in frustration that always mess everything up
- When an employer told you you weren’t good enough
…or maybe they told you one thing, and showed you the opposite. Or maybe it was entirely non-verbal circumstances:
- When you gambled on a good idea and lost everything
- When you tried so hard at some important endeavour and failed
- When you thought someone could be trusted, and learned the hard way that you were wrong
These are “life’s difficult bits”, but when we’ve lived through a whole stack of them, it’s less like a single shattering hammer-blow of PTSD, and more like the consistent non-stop tap tap tap that ends up doing just as much damage in the long run.
Resolve them
That may sound a bit like a “and quickly create world peace” level of task, but we have tools:
Ask yourself: what if…
…it had been different? Take some time and indulge in a full-blown fantasy of a life that was better. Explore it. How would those different life lessons, different messages, have impacted who you are, your personality, your behaviour?
This is useful, because the brain is famously bad at telling real memories from false ones. Consciously, you’ll know that one was an exploratory fantasy, but to your brain, it’s still doing the appropriate rewiring. So, little by little, neuroplasticity will do its thing.
Tell yourself a better lie
We borrowed this one from the title of a very good book which we’ve reviewed previously.
This idea is not about self-delusion, but rather that we already express our own experiences as a sort of narrative, and that narrative tends to contain value judgements that are often not useful, e.g. “I am stupid”, “I am useless”, and all the other insecurities we mentioned earlier. Some simple examples might be:
- “I had a terrible childhood” → “I have come so far”
- “I should have known better” → “I am wiser now”
- “I have lost so much” → “I have experienced so much”
So, replacing that self-talk can go a long way to re-writing how secure we feel, and therefore how much trauma-response (ideally: none!) we have to stimuli that are not really as threatening as we sometimes feel they are (a hallmark of PTSD in general).
Here’s a guide to more ways:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

The Starch Solution – by Dr. John McDougall & Mary McDougall
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Carb-strong or carb-wrong? We’ve written about this ourselves before, and it comes down to clarifying questions of what and how and why. Even within the general field of carbs, even within the smaller field of starch, not all foods are equal. A slice of white bread and a baked potato are both starchy, but the latter also contains fiber, vitamins, minerals, and suchlike.
The authors make the case for a whole-foods plant-based diet in which one need not shy away from starchy foods in general; one simply must enjoy them discriminately—whole grains, and root vegetables that have not been processed to Hell and back, for examples.
The style is “old-school pop-sci” but with modern science; claims are quite well-sourced throughout, with nine pages of bibliography at the end. Right after the ninety-nine pages of recipes!
Bottom line: if you’re a carb-enjoyer, all is definitely not lost healthwise, and in fact on the contrary, this can be the foundation of a very healthy and nutrient-rich diet.
Click here to check out The Starch Solution, and enjoy the foods you love, healthily!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: