Alzheimer’s may have once spread from person to person, but the risk of that happening today is incredibly low
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
An article published this week in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine documents what is believed to be the first evidence that Alzheimer’s disease can be transmitted from person to person.
The finding arose from long-term follow up of patients who received human growth hormone (hGH) that was taken from brain tissue of deceased donors.
Preparations of donated hGH were used in medicine to treat a variety of conditions from 1959 onwards – including in Australia from the mid 60s.
The practice stopped in 1985 when it was discovered around 200 patients worldwide who had received these donations went on to develop Creuztfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), which causes a rapidly progressive dementia. This is an otherwise extremely rare condition, affecting roughly one person in a million.
What’s CJD got to do with Alzehimer’s?
CJD is caused by prions: infective particles that are neither bacterial or viral, but consist of abnormally folded proteins that can be transmitted from cell to cell.
Other prion diseases include kuru, a dementia seen in New Guinea tribespeople caused by eating human tissue, scrapie (a disease of sheep) and variant CJD or bovine spongiform encephalopathy, otherwise known as mad cow disease. This raised public health concerns over the eating of beef products in the United Kingdom in the 1980s.
Human growth hormone used to come from donated organs
Human growth hormone (hGH) is produced in the brain by the pituitary gland. Treatments were originally prepared from purified human pituitary tissue.
But because the amount of hGH contained in a single gland is extremely small, any single dose given to any one patient could contain material from around 16,000 donated glands.
An average course of hGH treatment lasts around four years, so the chances of receiving contaminated material – even for a very rare condition such as CJD – became quite high for such people.
hGH is now manufactured synthetically in a laboratory, rather than from human tissue. So this particular mode of CJD transmission is no longer a risk.

National Cancer Institute/Unsplash
What are the latest findings about Alzheimer’s disease?
The Nature Medicine paper provides the first evidence that transmission of Alzheimer’s disease can occur via human-to-human transmission.
The authors examined the outcomes of people who received donated hGH until 1985. They found five such recipients had developed early-onset Alzheimer’s disease.
They considered other explanations for the findings but concluded donated hGH was the likely cause.
Given Alzheimer’s disease is a much more common illness than CJD, the authors presume those who received donated hGH before 1985 may be at higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is caused by presence of two abnormally folded proteins: amyloid and tau. There is increasing evidence these proteins spread in the brain in a similar way to prion diseases. So the mode of transmission the authors propose is certainly plausible.
However, given the amyloid protein deposits in the brain at least 20 years before clinical Alzheimer’s disease develops, there is likely to be a considerable time lag before cases that might arise from the receipt of donated hGH become evident.
When was this process used in Australia?
In Australia, donated pituitary material was used from 1967 to 1985 to treat people with short stature and infertility.
More than 2,000 people received such treatment. Four developed CJD, the last case identified in 1991. All four cases were likely linked to a single contaminated batch.
The risks of any other cases of CJD developing now in pituitary material recipients, so long after the occurrence of the last identified case in Australia, are considered to be incredibly small.
Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease (defined as occurring before the age of 65) is uncommon, accounting for around 5% of all cases. Below the age of 50 it’s rare and likely to have a genetic contribution.

perfectlab/Shutterstock
The risk is very low – and you can’t ‘catch’ it like a virus
The Nature Medicine paper identified five cases which were diagnosed in people aged 38 to 55. This is more than could be expected by chance, but still very low in comparison to the total number of patients treated worldwide.
Although the long “incubation period” of Alzheimer’s disease may mean more similar cases may be identified in the future, the absolute risk remains very low. The main scientific interest of the article lies in the fact it’s first to demonstrate that Alzheimer’s disease can be transmitted from person to person in a similar way to prion diseases, rather than in any public health risk.
The authors were keen to emphasise, as I will, that Alzheimer’s cannot be contracted via contact with or providing care to people with Alzheimer’s disease.
Steve Macfarlane, Head of Clinical Services, Dementia Support Australia, & Associate Professor of Psychiatry, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are your Kidneys Ok? Detect Early To Protect Kidney Health (Here’s How)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tomorrow (at time of publication) will be World Kidney Day (WKD). Perhaps not the most well-known initiative, but it celebrates its 21st year this year!
For those of us who celebrated our own 21st year quite some time ago now, it’s as good a reason as any to check in on our kidney health.
Here are some things they’d like us to know about Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD):
❝CKD is a silent disease, people with CKD have no signs or symptoms until the late stage of the disease.
CKD usually does not go away, instead, it progresses, unless early treatment to slow or halt the disease is ensured.
CKD can progress to kidney failure – a condition when kidneys cannot maintain their function anymore, posing a life-threatening risk.
CKD ranks number 7 in the top ten causes of death among noncommunicable diseases worldwide.
CKD increases the risk of premature death from associated cardiovascular disease.
CKD is more common among certain ethnic groups due in part to high rates of diabetes and high blood pressure.
CKD is more common among women, here is why.❞Source: World Kidney Day: Your Amazing Kidneys
How can we check our kidney health?
There are clinical tests that can be done (they’ll just need a urine sample from you; ask your doctor about it), but there’s some screening that can be done at home already:
Are Your Kidneys Healthy? Take This One-Minute Quiz To Find out
👆 this is about medical indicators; there are also non-medical factors that affect risk, including:
- Where someone lives
- Where they work
- The foods they eat
- How much exercise they do
- If they are able to get the medical care they need
For more information on this, see: Keeping Your Kidneys Healthy (Especially After 60) ← there’s a lot more to it than just hydration!
What can we do for our kidney health, besides the obvious “hydrate”?
Some top things to do include:
Hydrate, yes. See also: Things Many People Forget When It Comes To Hydration
Don’t smoke. It’s bad for everything, including your kidneys. So, just don’t. See also: Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
Look after your blood. Not just “try to keep it inside your body”, but also:
- Keep your blood sugar levels healthy (hyperglycemia can cause kidney damage)
- Keep your blood pressure healthy (hypertension can cause kidney damage)
Basically, your kidneys’ primary job of filtering blood will go much more smoothly if that blood is less problematic on the way in.
Watch your over-the-counter pill intake. A lot of PRN OTC NSAIDs (PRN = pro re nata, i.e. you take them as and when symptoms arise) (NSAIDs = Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, such as ibuprofen for example) can cause kidney damage if taken regularly.
Keep an eye on your urine. Hydration is only one side of the story, and our urine can say quite a bit about our health. Indeed, we have written about this before:
12 Things Your Urine Says About Your Health (Test At Home) ← no special equipment required!
On which note, see also: To Pee Or Not To Pee ← spoiler: there’s a flood of reasons to not hold your pee
Want to know more?
Check out the WKD website’s…
8 Golden Rules Of Kidney Disease Prevention
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why rating your pain out of 10 is tricky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“It’s really sore,” my (Josh’s) five-year-old daughter said, cradling her broken arm in the emergency department.
“But on a scale of zero to ten, how do you rate your pain?” asked the nurse.
My daughter’s tear-streaked face creased with confusion.
“What does ten mean?”
“Ten is the worst pain you can imagine.” She looked even more puzzled.
As both a parent and a pain scientist, I witnessed firsthand how our seemingly simple, well-intentioned pain rating systems can fall flat.
altanaka/Shutterstock What are pain scales for?
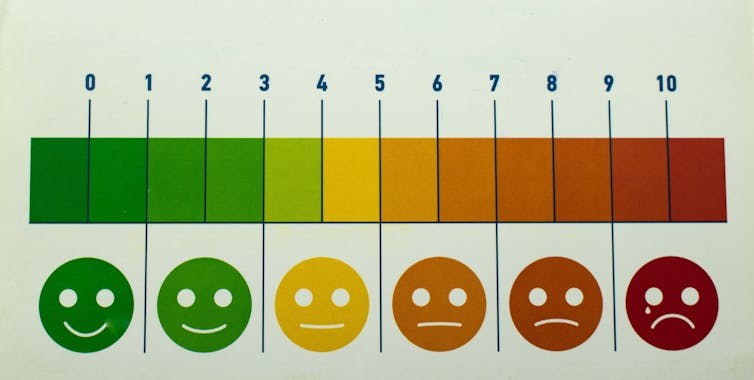
The most common scale has been around for 50 years. It asks people to rate their pain from zero (no pain) to ten (typically “the worst pain imaginable”).
This focuses on just one aspect of pain – its intensity – to try and rapidly understand the patient’s whole experience.
How much does it hurt? Is it getting worse? Is treatment making it better?
Rating scales can be useful for tracking pain intensity over time. If pain goes from eight to four, that probably means you’re feeling better – even if someone else’s four is different to yours.
Research suggests a two-point (or 30%) reduction in chronic pain severity usually reflects a change that makes a difference in day-to-day life.
But that common upper anchor in rating scales – “worst pain imaginable” – is a problem.
People usually refer to their previous experiences when rating pain. sasirin pamai/Shutterstock A narrow tool for a complex experience
Consider my daughter’s dilemma. How can anyone imagine the worst possible pain? Does everyone imagine the same thing? Research suggests they don’t. Even kids think very individually about that word “pain”.
People typically – and understandably – anchor their pain ratings to their own life experiences.
This creates dramatic variation. For example, a patient who has never had a serious injury may be more willing to give high ratings than one who has previously had severe burns.
“No pain” can also be problematic. A patient whose pain has receded but who remains uncomfortable may feel stuck: there’s no number on the zero-to-ten scale that can capture their physical experience.
Increasingly, pain scientists recognise a simple number cannot capture the complex, highly individual and multifaceted experience that is pain.
Who we are affects our pain
In reality, pain ratings are influenced by how much pain interferes with a person’s daily activities, how upsetting they find it, their mood, fatigue and how it compares to their usual pain.
Other factors also play a role, including a patient’s age, sex, cultural and language background, literacy and numeracy skills and neurodivergence.
For example, if a clinician and patient speak different languages, there may be extra challenges communicating about pain and care.
Some neurodivergent people may interpret language more literally or process sensory information differently to others. Interpreting what people communicate about pain requires a more individualised approach.
Impossible ratings
Still, we work with the tools available. There is evidence people do use the zero-to-ten pain scale to try and communicate much more than only pain’s “intensity”.
So when a patient says “it’s eleven out of ten”, this “impossible” rating is likely communicating more than severity.
They may be wondering, “Does she believe me? What number will get me help?” A lot of information is crammed into that single number. This patient is most likely saying, “This is serious – please help me.”
In everyday life, we use a range of other communication strategies. We might grimace, groan, move less or differently, use richly descriptive words or metaphors.
Collecting and evaluating this kind of complex and subjective information about pain may not always be feasible, as it is hard to standardise.
As a result, many pain scientists continue to rely heavily on rating scales because they are simple, efficient and have been shown to be reliable and valid in relatively controlled situations.
But clinicians can also use this other, more subjective information to build a fuller picture of the person’s pain.
How can we communicate better about pain?
There are strategies to address language or cultural differences in how people express pain.
Visual scales are one tool. For example, the “Faces Pain Scale-Revised” asks patients to choose a facial expression to communicate their pain. This can be particularly useful for children or people who aren’t comfortable with numeracy and literacy, either at all, or in the language used in the health-care setting.
A vertical “visual analogue scale” asks the person to mark their pain on a vertical line, a bit like imagining “filling up” with pain.
Modified visual scales are sometimes used to try to overcome communication challenges. Nenadmil/Shutterstock What can we do?
Health professionals
Take time to explain the pain scale consistently, remembering that the way you phrase the anchors matters.
Listen for the story behind the number, because the same number means different things to different people.
Use the rating as a launchpad for a more personalised conversation. Consider cultural and individual differences. Ask for descriptive words. Confirm your interpretation with the patient, to make sure you’re both on the same page.
Patients
To better describe pain, use the number scale, but add context.
Try describing the quality of your pain (burning? throbbing? stabbing?) and compare it to previous experiences.
Explain the impact the pain is having on you – both emotionally and how it affects your daily activities.
Parents
Ask the clinician to use a child-suitable pain scale. There are special tools developed for different ages such as the “Faces Pain Scale-Revised”.
Paediatric health professionals are trained to use age-appropriate vocabulary, because children develop their understanding of numbers and pain differently as they grow.
A starting point
In reality, scales will never be perfect measures of pain. Let’s see them as conversation starters to help people communicate about a deeply personal experience.
That’s what my daughter did — she found her own way to describe her pain: “It feels like when I fell off the monkey bars, but in my arm instead of my knee, and it doesn’t get better when I stay still.”
From there, we moved towards effective pain treatment. Sometimes words work better than numbers.
Joshua Pate, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney; Dale J. Langford, Associate Professor of Pain Management Research in Anesthesiology, Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University, and Tory Madden, Associate Professor and Pain Researcher, University of Cape Town
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Dyslexia Test
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
(and it’s mostly not about reading/writing!)
More than just shuffled letters
This video provides a self-test based on the Bangor Dyslexia Test (BDT). The BDT is 94% accurate in identifying dyslexia, and it includes 9 parts, with a mix of questions and tasks. Answering “yes” or struggling with tasks indicates possible dyslexia. Collecting 4+ indicators suggests dyslexia, but of course is not a replacement for official diagnosis.
It’s best to watch the video if you can, but here’s what to expect:
- Left-Right confusion: point your left hand to your right/left shoulder.
- Family history: any family members with dyslexia or struggles with reading/writing?
- Repeating numbers (order): repeat a given sequence of numbers in order.
- Letter confusion (e.g. b/d): do you confuse letters like “b” and “d” beyond age 8?
- Times tables: recite the 6, 7, and 8 times tables.
- Word manipulation: replace the letters in a word to create a new word, e.g. change “slide” (s ⇾ g) to “glide.”
- Repeating numbers (reversed): repeat a given sequence of numbers in reverse order.
- Months in reverse: recite the months of the year in reverse order.
- Subtraction: do you struggle with subtraction, e.g. 44-9 or 55-12?
Writer’s anecdote: I am not dyslexic, and/but I have an impressive level of dyscalculia (the purely numerical equivalent), to the point I’ll sometimes use a calculator to do single-digit calculations, and I am so bad at calculating ages or other differences between dates (I will have to count on my fingers or else run the severe risk of out-by-one errors). I have also been known to make mistakes counting down from 10, which really ruins dramatic tension.
In contrast, the left-right thing is interesting, because when I was first learning Arabic, I had no trouble reading/writing right-to-left, but I initially struggled so much to remember which way the “backspace” key would take me (in Arabic the backspace key backspaces to the right, despite still pointing to the left).
Anyway, for the test itself, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Reading, Better (Reading As A Cognitive Exercise)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We speak often about the importance of dietary diversity, and of that, especially diversity of plants in one’s diet, but we’ve never really focused on it as a main feature, so that’s what we’re going to do today.
Specifically, you may have heard the advice to “eat 30 different kinds of plants per week”. But where does that come from, and is it just a number out of a hat?
The magic number?
It is not, in fact, a number out of a hat. It’s from a big (n=11,336) study into what things affect the gut microbiome for better or for worse. It was an observational population study, championing “citizen science” in which volunteers tracked various things and collected and sent in various samples for analysis.
The most significant finding of this study was that those who consumed more than 30 different kinds of plants per week, had a much better gut microbiome than those who consumed fewer than 10 different kinds of plants per week (there is a bell curve at play, and it gets steep around 10 and 30):
American Gut: an Open Platform for Citizen Science Microbiome Research
Why do I care about having a good gut microbiome?
Gut health affects almost every other kind of health; it’s been called “the second brain” for the various neurotransmitters and other hormones it directly makes or indirectly regulates (which in turn affect every part of your body), and of course there is the vagus nerve connecting it directly to the brain, impacting everything from food cravings to mood swings to sleep habits.
See also:
Any other benefits?
Yes there are! Let’s not forget: as we see often in our “This or That” section, different foods can be strong or weak in different areas of nutrition, so unless we want to whip out a calculator and database every time we make food choices, a good way to cover everything is to simply eat a diverse diet.
And that goes not just for vitamins and minerals (which would be true of animal products also), but in the case of plants, a wide range of health-giving phytochemicals too:
Measuring Dietary Botanical Diversity as a Proxy for Phytochemical Exposure
Ok, I’m sold, but 30 is a lot!
It is, but you don’t have to do all 30 in your first week of focusing on this, if you’re not already accustomed to such diversity. You can add in one or two new ones each time you go shopping, and build it up.
As for “what counts”: we’re counting unprocessed or minimally-processed plants. So for example, an apple is an apple, as are dried apple slices, as is apple sauce. Any or all of those would count as 1 plant type.
Note also that we’re counting types, not totals. If you’re having apple slices with apple sauce, for some reason? That still only counts as 1.
However, while apple sauce still counts as apples (minimally processed), you cannot eat a cake and say “that’s 2 because there was wheat and sugar cane somewhere in its dim and distant history”.
Nor is your morning espresso a fruit (by virtue of coffee beans being the fruit of the plant, botanically speaking). However, it would count as 1 plant type if you eat actual coffee beans—this writer has been known to snack on such; they’re only healthy in very small portions though, because their saturated fat content is a little high.
You, however, count grains in general, as well as nuts and seeds, not just fruits and vegetables. As for herbs and spices, they count for ¼ each, except for salt, which might get lumped in with spices but is of course not a plant.
How to do it
There’s a reason we’re doing this in our Saturday Life Hacks edition. Here are some tips for getting in far more plants than you might think, a lot more easily than you might think:
- Buy things ready-mixed. This means buying the frozen mixed veg, the frozen mixed chopped fruit, the mixed nuts, the mixed salad greens etc. This way, when you’re reaching for one pack of something, you’re getting 3–5 different plants instead of one.
- Buy things individually, and mix them for storage. This is a more customized version of the above, but in the case of things that keep for at least a while, it can make lazy options a lot more plentiful. Suddenly, instead of rice with your salad you’re having sorghum, millet, buckwheat, and quinoa. This trick also works great for dried berries that can just be tipped into one’s morning oatmeal. Or, you know, millet, oats, rye, and barley. Suddenly, instead of 1 or 2 plants for breakfast you have maybe 7 or 8.
- Keep a well-stocked pantry of shelf-stable items. This is good practice anyway, in case of another supply-lines shutdown like at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. But for plant diversity, it means that if you’re making enchiladas, then instead using kidney beans because that’s what’s in the cupboard, you can raid your pantry for kidney beans, black beans, pinto beans, fava beans, etc etc. Yes, all of them; that’s a list, not a menu.
- Shop in the discount section of the supermarket. You don’t have shop exclusively there, but swing by that area, see what plants are available for next to nothing, and buy at least one of each. Figure out what to do with it later, but the point here is that it’s a good way to get suggestions of plants that you weren’t actively looking for—and novelty is invariably a step into diversity.
- Shop in a different store. You won’t be able to beeline the products you want on autopilot, so you’ll see other things on the way. Also, they may have things your usual store doesn’t.
- Shop in person, not online—at least as often as is practical. This is because when shopping for groceries online, the store will tend to prioritize showing you items you’ve bought before, or similar items to those (i.e. actually the same item, just a different brand). Not good for trying new things!
- Consider a meal kit delivery service. Because unlike online grocery shopping, this kind of delivery service will (usually) provide you with things you wouldn’t normally buy. Our sometimes-sponsor Purple Carrot is a fine option for this, but there are plenty of others too.
- Try new recipes, especially if they have plants you don’t normally use. Make a note of the recipe, and go out of your way to get the ingredients; if it seems like a chore, reframe it as a little adventure instead. Honestly, it’s things like this that keep us young in more ways than just what polyphenols can do!
- Hide the plants. Whether or not you like them; hide them just because it works in culinary terms. By this we mean; blend beans into that meaty sauce; thicken the soup with red lentils, blend cauliflower into the gravy. And so on.
One more “magic 30”, while we’re at it…
30g fiber per day makes a big (positive) difference to many aspects of health. Obviously, plants are where that comes from, so there’s a big degree of overlap here, but most of the tips we gave are different, so for double the effectiveness, check out:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are You Flourishing? (There’s a Scale)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What does it mean, to flourish? And how can you do it more?
In 2009, psychologists Diener et al developed the “Flourishing Scale”, or as it was more prosaically called originally, “Subjective Wellness Scale”. The name was changed later, as it was noted that it went beyond what was typically considered mere “wellness”.
This scale was so useful, that colleagues scrambled to see if they could improve on it, such as with PERMA (2012), which looked at:
- Positive emotion
- Engagement
- positive Relationships
- Meaning
- Accomplishment/Achievement
While popular (despite the tenuous acronym, it is a very good list of things to foster in your life), this was studied and measured scientifically and found to not be an improvement on the Flourishing Scale / SWS, so we’re going to stick to the original version for now.
We couldn’t find an interactive online quiz for the scale though (apart from this NY Times one, which is paywalled for NYT subscribers, so enjoy if you’re a NYT subscriber!), so here’s the source material, still hosted on the website of the (now deceased, as of a couple of years ago) author:
Flourishing Scale (FS) ← it’s an eight-question, ranked choice scale
How did you score? And…
What are the keys to flourishing more?
According to Jeffrey Davis M.A., of Tracking Wonder, there are five key attributes that we must develop and/or maintain:
The ability to direct and re-direct your attention
This isn’t just a task-related thing.This is about your mind itself. For example, the ability to recognize what your emotions are telling you, thank them for the message, and then set them aside. Or the ability to cut through negative thought spirals! How often have you worried about future events that didn’t transpire, or twisted yourself in knots over a past event that you can’t change?
Action: check out our previous article “The Off-Button For Your Brain” ← this is a technique for switching off racing thoughts, and it’s really good
Want more? We also did this:
The tendency to shape your time with intention and for impact
Time is an incredibly precious asset. How you use it is a very personal choice. You don’t have to maximize productivity (though you can if you want), but for example there’s a difference between:
- Deciding to spend an hour watching a TV show you really enjoy
- Wondering what’s on TV, browsing aimlessly, watching listlessly, just a distraction
In the former case, you are enjoying your time. Literally: you are experiencing joy during your time.
In the latter case, to borrow from Jim Steinman, “you were only killing time and it’ll kill you right back”!
Action: do a time audit for a week, and see where your time really goes, rather than where you expect or hope for it to go. Use this information to plan your next week more intentionally. Repeat as and when it seems like it might be useful!
The practice of constant improvement
Fun fact: you are good enough already. And you can also improve. You don’t have to, but improving in the areas that are meaningful to you can really add up over time. This could be becoming excellent at something for which already have a passion… It could also be brushing up something that you feel might be holding you back.
Action: do a quick SWOT* self-assessment. Then plan your next step from there!
*Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats. What are yours?
The ability to communicate and listen to others
A lot of this is about feedback. Giving and receiving feedback are often amongst the hardest things we do in the category of communication… Especially if the feedback is negative. How to decide what to disregard as baseless criticism, and what to take on board (and try not to take it personally), or the other way around, how to present negative feedback in a way that won’t trigger defensiveness.
Action: check out our previous article “Save Time With Better Communication” for some tips that really make relationships (of any kind) so much easier.
The commitment to positive experiences
Many things in life are not fun. Often, we know in advance that they will not be fun. The key here is the ability to make the most of a bad situation, and seek out better situations by your actions. Not like a lost person in a desert seeks water, but like a chess player who employs a general strategy to make tactical advantages more likely to appear.
Action: think about something you have to do but don’t want to. How could it be made more fun? Or failing that, how could it be made at least more comfortable?
See also: Working Smarter < Working Brighter!
Want to read more?
Check out: What Is Flourishing in Positive Psychology? (+8 Tips & PDF)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
5 Ways to Beat Menopausal Weight Gain!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As it turns out, “common” does not mean “inevitable”!
Health Coach Kait’s advice
Her 5 tips are…
- Understand your metabolism: otherwise you’re working the dark and will get random results. Learn about how different foods affect your metabolism, and note that hormonal changes due to menopause can mean that some food types have different effects now.
- Eat enough protein: one thing doesn’t change—protein helps with satiety, thus helping to avoid overeating.
- Focus on sleep: prioritizing sleep is essential for hormone regulation, and that means not just sex hormones, but also food-related hormones such as insulin, ghrelin, and leptin.
- Be smart about carbs: taking a lot of carbs at once can lead to insulin spikes and thus metabolic disorder, which in turn leads to fat in places you don’t want it (especially your liver and belly). Enjoying a low-carb diet, and/or pairing your carbs with proteins and fats, does a lot to help avoid insulin spikes too. Not mentioned in the video, but we’re going to mention here: don’t underestimate fiber’s role either, especially if you take it before the carbs, which is best for blood sugars, as it gives a buffer to the digestive process, thus slowing down absorption of carbs.
- Build muscle: if trying to avoid/lose fat, it’s tempting to focus on cardio, but we generally can’t exercise our way out of having fat, whereas having more muscle increases the body’s metabolic base rate, burning fat just by existing. So for this reason, enjoy muscle-building resistance exercises at least a few times per week.
For more information on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: