Fixing Fascia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fascia: Why (And How) You Should Take Care Of Yours
Fascia is the web-like layer of connective tissue that divides your muscles and organs from each other. It simultaneously holds some stuff in place, and allows other parts to glide over each other with minimal friction.
At least, that’s what it’s supposed to do.
Like any body part, it can go wrong. More on this later. But first…
A quick note on terms
It may seem like sometimes people say “myofascial” because it sounds fancier, but it does actually have a specific meaning too:
- “Fascia” is what we just described above
- “Myofascial” means “of or relating to muscles and fascia”
For example, “myofascial release” means “stopping the fascia from sticking to the muscle where it shouldn’t” and “myofascial pain” means “pain that has to do with the muscles and fascia”. See also:
Myofascial vs Fascia: When To Use Each One? What To Consider
Why fascia is so ignored
For millennia, it was mostly disregarded as a “neither this nor that” tissue that just happens to be in the body. We didn’t pay attention to it, just like we mostly don’t pay attention to the air around us.
But, much like the air around us, we sure pay attention when something goes wrong with it!
However, even in more recent years, we’ve been held back until quite new developments like musculoskeletal ultrasound that could show us problems with the fascia.
What can go wrong
It’s supposed to be strong, thin, supple, and slippery. It holds on in the necessary places like a spiderweb, but for the most part, it is evolved for minimum friction.
Some things can cause it to thicken and become sticky in the wrong places. Things such as:
- Physical trauma, e.g. an injury or surgery—but we repeat ourselves, because a surgery is an injury! It’s a (usually) necessary injury, but an injury nonetheless.
- Compensation for pain. If a body part hurts for some reason, and your posture changes to accommodate that, doing so can mess up your fascia, and cause you different problems somewhere else entirely.
- This is not witchcraft; think of how, when using a corded vacuum cleaner, sometimes the cord can get snagged on something in the next room and we nearly break something because we expected it to just come with us and it didn’t? It’s like that.
- Repetitive movements (repetitive strain injury is partly a myofascial issue)
- Not enough movement: when it comes to range of motion, it’s “use it or lose it”.
- The human body tries its best to be as efficient as possible for us! So eventually it will go “Hey, I notice you never move more than 30º in this direction, so I’m going to stop making fascia that allows you to go past that point, and I’ll just dump the materials here instead”
“I’ll just dump the materials here instead” is also part of the problem—it creates what we colloquially call “knots”, which are not so much part of the muscle as the fascia that covers it. That’s an actual physical sticky lumpy bit.
What to do about it
Firstly, avoid the above things! But, if for whatever reason something has gone wrong and you now have sticky lumpy fascia that doesn’t let you move the way you’d like (if you have any mobility/flexibility issues that aren’t for another known reason, then this is usually it), there are things can be done:
- Heat—is definitely not a cure-all, but it’s a good first step before doing the other things. A heating pad or a warm bath are great.
- Here’s an example of a neck+back+shoulders heating pad; you can get them for different body parts, or just use an electric blanket!
- Massage—ideally, by someone else who knows what they are doing. Self-massage is possible, as is teaching oneself (there are plenty of video tutorials available), but skilled professional therapeutic myofascial release massage is the gold standard.
- Foam rollers are a great no-skill way to get going with self-massage, whether because that’s what’s available to you, or because you just want something you can do between sessions. Here’s an example of the kind we mean.
- Acupuncture—triggering localized muscular relaxation, an important part of myofascial release, is something acupuncture is good at.
- See also: Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture ← noteworthily, the strongest criticism of acupuncture for pain relief is that it performs only slightly better than sham acupuncture, but taken in practical terms, all that really means is “sticking little needles in does work, even if not necessarily by the mechanism acupuncturists believe”
- Calisthenics—Pilates, yoga, and other forms of body movement training can help gradually get one’s fascia to where and how it’s supposed to be.
- This is that “use it or lose it” bodily efficiency we talked about!
Remember, the body is always rebuilding itself. It never stops, until you die. So on any given day, you get to choose whether it rebuilds itself a little bit worse or a little bit better.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Health & Happiness From Outside & In
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A friend in need…
In a recent large (n=3,486) poll across the US:
- 90% of people aged 50 and older say they have at least one close friend
- 75% say they have enough close friends
- 70% of those with a close friend say they can definitely count on them to provide health-related support
However, those numbers shrink by half when it comes to people whose physical and/or mental health is not so great, resulting in a negative feedback loop of fewer close friends whom one sees less often, and progressively worse physical and/or mental health. In other words, the healthier you are, the more likely you are to have a friend who’ll support you in your health:
Read in full: Friendships promote healthier living in older adults, says new survey
Related: How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Kindness makes a difference to healthcare outcomes
Defining kindness as action-oriented, positively focused, and purposeful in nature, this sets kindness apart from compassion and empathy, when it’s otherwise often been conflated with those, and thus overlooked. This also means that kindness can still be effected when clinicians are too burned-out to be compassionate, and/or when patients are not in a state of mind where empathy is useful.
Furthermore, unkindness (again, as defined by this review) was found in large studies to be the root cause of ¾ of patient harm events in hospital settings. This means that far from being a wishy-washy abstraction, kindness/unkindness can be a very serious factor when it comes to healthcare outcomes:
Read in full: Review suggests kindness could make for better health care
Related: The Human Touch vs AI, The Doctor That Never Tires
The gift of health?
🎵 Last Christmas, I gave you my heart
Which turned out to be a silly idea
This year, to save me from tears
I’ll just get you a Fitbit or something🎵Health & happiness go hand in hand, so does that make health stuff a good gift? It can do! But there are also plenty of opportunities for misfires.
For example, getting someone a gym membership when they don’t have time for that may not help them at all, and sports equipment that they’ll use once and then leave to gather dust might not be great either. In contrast, the American Heart Association recommends to first consider what they enjoy doing, and work with that, and ideally make it something versatile and/or portable. Wearable gadgets are a fine option for many, but a gift doesn’t have to be fancy to be good—with a blood pressure monitoring cuff being a suggestion from Dr. Sperling (a professor of preventative cardiology):
Read in full: Oh, there’s no gift like health for the holidays
Related: Here’s Where Activity Trackers Help (And Also Where They Don’t)
How you use social media matters more than how much
A study commissioned by the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre found that while the quantity of time one spends on social media is not associated (positively or negatively) with loneliness, they did find a correlation between passive (as opposed to engaged) use of social media, and loneliness. In other words, people who were chatting with friends less, were more lonely! Shocking news.
While the findings may seem obvious, it does present a call-to-action for anyone who is feeling lonely: to use social media not just to see what everyone else is up to, but also, to reach out to people.
Read in full: Unpacking the link between social media and loneliness
Related: Make Social Media Work For Your Mental Health Rather Than Against It
Gut-only antidepressants
Many antidepressants work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain; a new study suggests that targeting antidepressants to work only in the gut (which is where serotonin is made, not the brain) could not only be an effective treatment for mood disorders, but also cause fewer adverse side-effects:
Read in full: Antidepressants may act in gut to reduce depression and anxiety
Related: Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Frozen/Thawed/Refrozen Meat: How Much Is Safety, And How Much Is Taste?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What You Can (And Can’t) Safely Do With Frozen Meat
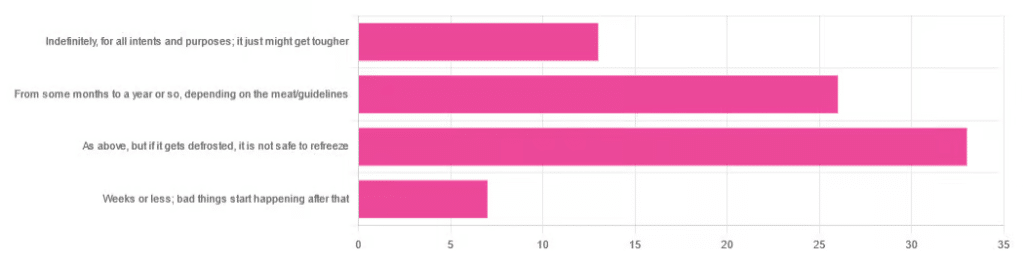
Yesterday, we asked you:
❝You have meat in the freezer. How long is it really safe to keep it?❞
…and got a range of answers, mostly indicating to a) follow the instructions (a very safe general policy) and b) do not refreeze if thawed because that would be unsafe. Fewer respondents indicated that meat could be kept for much longer than guidelines say, or conversely, that it should only be kept for weeks or less.
So, what does the science say?
Meat can be kept indefinitely (for all intents and purposes) in a freezer; it just might get tougher: True or False?
False, assuming we are talking about a normal household electrical freezer that bottoms out at about -18℃ / 0℉.
Fun fact: cryobiologists cryopreserve tissue samples (so basically, meat) at -196℃ / -320℉, and down at those temperatures, the tissues will last a lot longer than you will (and, for all practical purposes: indefinitely). There are other complications with doing so (such as getting the sample through the glass transition point without cracking it during the vitrification process) but those are beyond the scope of this article.
If you remember back to your physics or perhaps chemistry classes at school, you’ll know that molecules move more quickly at higher temperatures, and more slowly at lower ones, only approaching true stillness as they near absolute zero (-273℃ / -459℉ / 0K ← we’re not saying it’s ok, although it is; rather, that is zero kelvin; no degree sign is used with kelvins)
That means that when food is frozen, the internal processes aren’t truly paused; it’s just slowed to a point of near imperceptibility.
So, all the way up at the relatively warm temperatures of a household freezer, a lot of processes are still going on.
What this means in practical terms: those guidelines saying “keep in the freezer for up to 4 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 9 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 12 months” etc are being honest with you.
More or less, anyway! They’ll usually underestimate a little to be on the safe side—but so should you.
Bad things start happening within weeks at most: True or False?
False, for all practical purposes. Again, assuming a normal and properly-working household freezer as described above.
(True, technically but misleadingly: the bad things never stopped; they just slowed down to a near imperceptible pace—again, as described above)
By “bad” here we should clarify we mean “dangerous”. One subscriber wrote:
❝Meat starts losing color and flavor after being in the freezer for too long. I keep meat in the freezer for about 2 months at the most❞
…and as a matter of taste, that’s fair enough!
It is unsafe to refreeze meat that has been thawed: True or False?
False! Assuming it has otherwise been kept chilled, just the same as for fresh meat.
Food poisoning comes from bacteria, and there is nothing about the meat previously having been frozen that will make it now have more bacteria.
That means, for example…
- if it was thawed (but chilled) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been chilled for that period of time (so probably: use it or freeze it, unless it’s been more than a few days)
- if it was thawed (and at room temperature) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been at room temperature for that period of time (so probably: throw it out, unless the period of time is very small indeed)
The USDA gives for 2 hours max at room temperature before considering it unsalvageable, by the way.
However! Whenever you freeze meat (or almost anything with cells, really), ice crystals will form in and between cells. How much ice crystallization occurs depends on several variables, with how much water there is present in the food is usually the biggest factor (remember that animal cells are—just like us—mostly water).
Those ice crystals will damage the cell walls, causing the food to lose structural integrity. When you thaw it out, the ice crystals will disappear but the damage will be left behind (this is what “freezer burn” is).
So if your food seems a little “squishy” after having been frozen and thawed, that’s why. It’s not rotten; it’s just been stabbed countless times on a microscopic level.
The more times you freeze and thaw and refreeze food, the more this will happen. Your food will degrade in structural integrity each time, but the safety of it won’t have changed meaningfully.
Want to know more?
Further reading:
You can thaw and refreeze meat: five food safety myths busted
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Quit Drinking – by Rebecca Dolton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many “quit drinking” books focus on tips you’ve heard already—cut down like this, rearrange your habits like that, make yourself accountable like so, add a reward element this way, etc.
Dolton takes a different approach.
She focuses instead on the underlying processes of addiction, so as to not merely understand them to fight them, but also to use them against the addiction itself.
This is not just a social or behavioral analysis, by the way, and goes into some detail into the physiological factors of the addiction—including such things as the little-talked about relationship between addiction and gut flora. Candida albans, found in most if not all humans to some extent, gets really out of control when given certain kinds of sugars (including those from alcohol); it grows, eventually puts roots through the intestinal walls (ouch!) and the more it grows, the more it demands the sugars it craves, so the more you feed it.
Quite a motivator to not listen to such cravings! It’s not even you that wants it, it’s the Candida!
Anyway, that’s just one example; there are many. The point here is that this is a well-researched, well-written book that sets itself apart from many of its genre.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Wouldn’t It Be Nice To Have Regenerative Superpowers?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Best-Laid Schemes of Mice and Medical Researchers…
This is Dr. Ellen Heber-Katz. She’s an internationally-renowned immunologist and regeneration biologist, but her perhaps greatest discovery was accidental.
Unlike in Robert Burns’ famous poem, this one has a happy ending!
But it did involve the best-laid schemes of mice and medical researchers, and how they did indeed “gang gagly“ (or in the English translation, “go awry”).
How it started…
Back in 1995, she was conducting autoimmune research, and doing a mouse study. Her post-doc assistant was assigned to punch holes in the ears of mice that had received an experimental treatment, to distinguish them from the control group.
However, when the mice were later checked, none of them had holes (nor even any indication there ever had been holes punched)—the experiment was ruined, though the post-doc swore she did her job correctly.
So, they had to start from scratch in the new year, but again, a second batch of mice repeated the trick. No holes, no wounds, no scarring, not disruption to their fur, no damage to the cartilage that had been punched through.
In a turn of events worthy of a superhero origin story, they discovered that their laboratory-made autoimmune disease had accidentally given the mice super-healing powers of regeneration.
In the animal kingdom, this is akin to a salamander growing a new tail, but it’s not something usually found in mammals.
Read: A New Murine Model for Mammalian Wound Repair and Regeneration
How it’s going…
Dr. Heber-Katz and colleagues took another 20 years of work to isolate hypoxia-inducible factor-1a (HIF-1a) as a critical molecule that, if blocked, would eliminate the regenerative response.
Further, a drug (which they went on to patent), 1,4-dihydrophenonthrolin-4-one-3-carboxylic acid (1,4-DPCA), chemically induced this regenerative power:
See: Drug-induced regeneration in adult mice
Another 5 years later, they found that this same drug can be used to stimulate the regrowth of bones, too:
And now…
The research is continuing. Here’s the latest, a little over a month ago:
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition: an organizing principle of mammalian regeneration
Regrowing nerves has also been added into the list of things the drug can do.
What about humans?
Superpowered mice are all very well and good, but when can we expect this in humans?
The next step is testing the drug in larger animals, which she hopes to do next year, followed eventually by studies in humans.
Read the latest:
Regrowing nerves and healing without scars? A scientist’s career-long quest comes closer to fruition
Very promising!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Know When You’re Healing Emotionally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The healing process can be humbling but rewarding, leading to deep fulfillment and inner peace. Discomfort in healing can be part of growth and self-integration. Because of that, progress sometimes looks and/or feels like progress… And sometimes it doesn’t. Here’s how to recognize it, though:
Small but important parts of a bigger process
Nine signs indicating you are healing:
- Allowing emotions: you acknowledge and process both negative and positive emotions instead of suppressing them.
- Improved boundaries: you improve at expressing and maintaining boundaries, overcoming fear of rejection, guilt, and shame.
- Acceptance of past: you accept difficult past experiences and their impact, reducing their hold over you.
- Less reactivity: you become less reactive and more thoughtful in responses, practicing emotional self-regulation.
- Non-linear healing: you understand that healing involves ups and downs and isn’t a straightforward journey.
- Stepping out of your comfort zone: you start taking brave steps that previously induced fear or anxiety.
- Handling disappointments: you accept setbacks and respond to them healthily, without losing motivation.
- Inner peace: you develop a sense of wholeness, and forgiveness for yourself and others, reducing self-sabotage.
- Welcoming support: you become more open to seeking and accepting help, moving beyond pride and shame.
In short: healing (especially the very first part: accepting that something needs healing) can be uncomfortable but lead to much better places in life. It’s okay if healing is slow; everyone’s journey is different, and doing your best is enough.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Why You Can’t Just “Get Over” Trauma
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sesame & Peanut Tofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yesterday we learned how to elevate tofu from “nutrition” to “nutritious tasty snack” with our Basic Baked Tofu recipe; today we’re expanding on that, to take it from “nutritious tasty snack” to “very respectable meal”.
You will need
For the tofu:
- The Basic Baked Tofu that we made yesterday (consider making this to be “step zero” of today’s recipe if you don’t already have a portion in the fridge)
For the sauce:
- ⅓ cup peanut butter, ideally with no added sugar or salt (if allergic to peanuts specifically, use almond butter; if allergic to nuts generally, use tahini)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated or crushed
- 1 tbsp tamarind paste
- 1½ tbsp tamari sauce (or low-sodium soy sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tbsp sambal oelek (or sriracha sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
- ½ tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- ½ tsp MSG (or else omit; do not substitute with salt in this case unless you have a particular craving)
- zest of 1 lime
For the vegetables:
- 14 oz broccolini / tenderstem broccoli, thick ends trimmed (failing that, any broccoli)
- 6 oz shelled edamame
- 1½ tsp toasted sesame oil
For serving:
- 4 cups cooked rice (we recommend our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe)
- ½ cup raw cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 5 minutes and then drained (if allergic, substitute cooked chickpeas, rinsed and drained)
- 1 tbsp toasted sesame seeds
- 1 handful chopped cilantro, unless you have the “this tastes like soap” gene, in which case substitute chopped parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the sauce ingredients in a bowl and whisk well (or use a blender if you have one that’s comfortable with this relatively small quantity of ingredients). Taste it, and adjust the ingredient ratios if you’d like more saltiness, sweetness, sourness, spiciness, umami.
2) Prepare a bowl with cold water and some ice. Steam the broccolini and edamame for about 3 minutes; as soon as they become tender, dump them into the ice bathe to halt the cooking process. Let them chill for a few minutes, then drain, dry, and toss in the sesame oil.
3) Reheat the tofu if necessary (an air fryer is great for this), and then combine with half of the sauce in a bowl, tossing gently to coat well.
4) Add a little extra water to the remaining sauce, enough to make it pourable, whisking to an even consistency.
5) Assemble; do it per your preference, but we recommend the order: rice, vegetables, tofu, cashews, sauce, sesame seeds, herbs.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: