Undoing The Damage Of Life’s Hard Knocks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes, What Doesn’t Kill Us Makes Us Insecure
We’ve written before about Complex PTSD, which is much more common than the more popularly understood kind:
Given that C-PTSD affects so many people (around 1 in 5, but really, do read the article above! It explains it better than we have room to repeat today), it seems like a good idea to share tips for managing it.
(Last time, we took all the space for explaining it, so we just linked to some external resources at the end)
What happened to you?
PTSD has (as a necessity, as part of its diagnostic criteria) a clear event that caused it, which makes the above question easy to answer.
C-PTSD often takes more examination to figure out what tapestry of circumstances (and likely but not necessarily: treatment by other people) caused it.
Often it will feel like “but it can’t be that; that’s not that bad”, or “everyone has things like that” (in which case, you’re probably one of the one in five).
The deeper questions
Start by asking yourself: what are you most afraid of, and why? What are you most ashamed of? What do you fear that other people might say about you?
Often there is a core pattern of insecurity that can be summed up in a simple, harmful, I-message, e.g:
- I am a bad person
- I am unloveable
- I am a fake
- I am easy to hurt
- I cannot keep my loved ones safe
…and so forth.
For a bigger list of common insecurities to see what resonates, check out:
Basic Fears/Insecurities, And Their Corresponding Needs/Desires
Find where they came from
You probably learned bad beliefs, and consequently bad coping strategies, because of bad circumstances, and/or bad advice.
- When a parent exclaimed in anger about how stupid you are
- When a partner exclaimed in frustration that always mess everything up
- When an employer told you you weren’t good enough
…or maybe they told you one thing, and showed you the opposite. Or maybe it was entirely non-verbal circumstances:
- When you gambled on a good idea and lost everything
- When you tried so hard at some important endeavour and failed
- When you thought someone could be trusted, and learned the hard way that you were wrong
These are “life’s difficult bits”, but when we’ve lived through a whole stack of them, it’s less like a single shattering hammer-blow of PTSD, and more like the consistent non-stop tap tap tap that ends up doing just as much damage in the long run.
Resolve them
That may sound a bit like a “and quickly create world peace” level of task, but we have tools:
Ask yourself: what if…
…it had been different? Take some time and indulge in a full-blown fantasy of a life that was better. Explore it. How would those different life lessons, different messages, have impacted who you are, your personality, your behaviour?
This is useful, because the brain is famously bad at telling real memories from false ones. Consciously, you’ll know that one was an exploratory fantasy, but to your brain, it’s still doing the appropriate rewiring. So, little by little, neuroplasticity will do its thing.
Tell yourself a better lie
We borrowed this one from the title of a very good book which we’ve reviewed previously.
This idea is not about self-delusion, but rather that we already express our own experiences as a sort of narrative, and that narrative tends to contain value judgements that are often not useful, e.g. “I am stupid”, “I am useless”, and all the other insecurities we mentioned earlier. Some simple examples might be:
- “I had a terrible childhood” → “I have come so far”
- “I should have known better” → “I am wiser now”
- “I have lost so much” → “I have experienced so much”
So, replacing that self-talk can go a long way to re-writing how secure we feel, and therefore how much trauma-response (ideally: none!) we have to stimuli that are not really as threatening as we sometimes feel they are (a hallmark of PTSD in general).
Here’s a guide to more ways:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Strawberries vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing strawberries to cherries, we picked the cherries.
Why?
Both are great, and an argument could be made for either! But here’s our rationale:
In terms of macros, as with most fruits they are both mostly water, and have similar carbs and fiber. Nominally, cherries have the lower glycemic index, so we could call this category nominally a win for cherries, but honestly, they’re both low-GI foods and nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating strawberries, so it’s fairer to consider this category a tie.
Looking at the vitamins, strawberries have more of vitamins C, B9, E, and K, while cherries have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, and choline. Thus, a modest win for cherries here.
When it comes to minerals, strawberries see their day: strawberries have more iron, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus, while cherries have more calcium, copper, and potassium. By the numbers, a win for strawberries.
So far, so tied!
What swings it into cherries’ favor is cherries’ slew of specific phytochemical benefits, including cherry-specific anti-inflammatory properties, sleep-improving abilities, and post-exercise recovery boosts, as well as anti-diabetic benefits above and beyond the normal “this is a fruit” level.
In short, both are very respectable fruits, but cherries have some extra qualities that are just special.
Of course, as ever, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Cherries’ Health Benefits Simply Pop
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
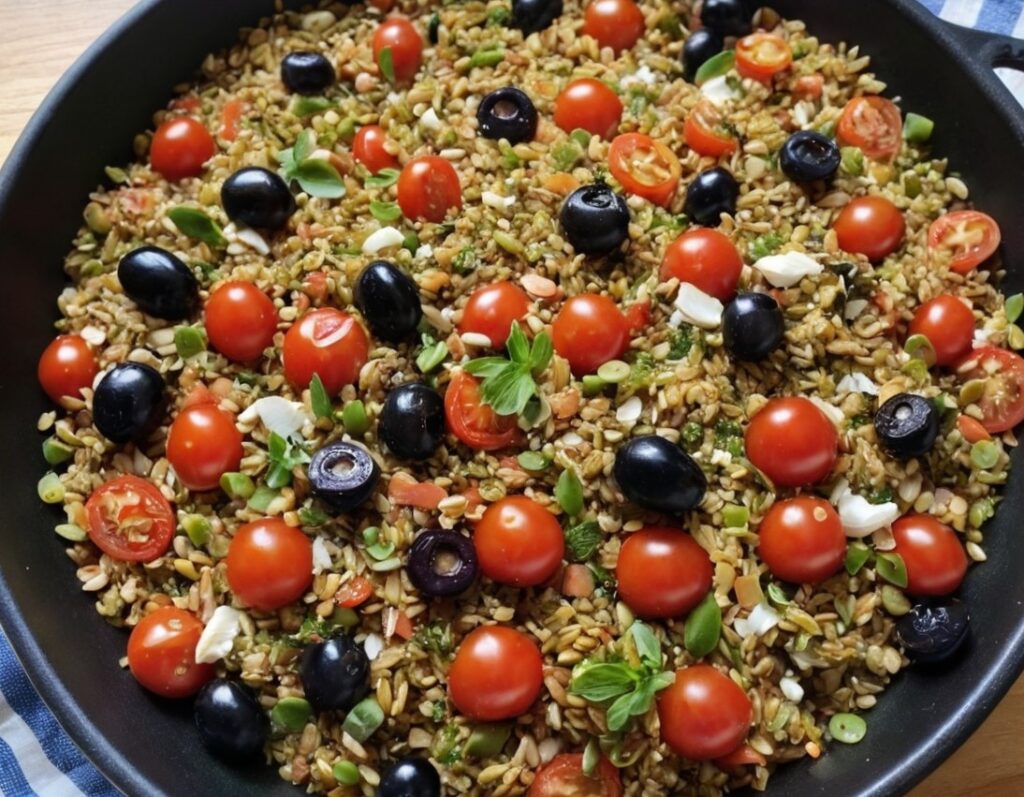
Freekeh Tomato Feast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber-dense freekeh stars in this traditional Palestinian dish, and the whole recipe is very gut-healthy, not to mention delicious and filling, as well as boasting generous amounts of lycopene and other phytonutrients:
You will need
- 1 cup dried freekeh (if avoiding gluten, substitute a gluten-free grain, or pseudograin such as buckwheat; if making such a substitution, then also add 1 tbsp nutritional yeast—for the flavor as well as the nutrients)
- 1 medium onion, thinly sliced
- 1 2oz can anchovies (if vegan/vegetarian, substitute 1 can kimchi)
- 1 14oz can cherry tomatoes
- 1 cup halved cherry tomatoes, fresh
- ½ cup black olives, pitted
- 1 5oz jar roasted peppers, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 sprig fresh thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Place a heavy-based (cast iron, if you have it) sauté pan over a medium heat. Add some olive oil, then the onion, stirring for about 5 minutes.
2) Add the anchovies, herbs and spices (including the garlic), and stir well to combine. The anchovies will probably soon melt into the onion; that’s fine.
3) Add the canned tomatoes (but not the fresh), followed by the freekeh, stirring well again to combine.
4) Add 2 cups boiling water, and simmer with the lid on for about 40 minutes. Stir occasionally and check the water isn’t getting too low; top it up if it’s getting dry and the freekeh isn’t tender yet.
5) Add the fresh chopped cherry tomatoes and the chopped peppers from the jar, as well as the olives. Stir for just another 2 minutes, enough to let the latest ingredients warm through.
6) Serve, adding a garnish if you wish:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Proteinaholic – by Dr. Garth Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein is important, yes. However, you can have too much of a good thing, and you can also get it from bad sources that do more harm than good.
That’s what this book is about, and how to go about understanding the science in a world where marketing has outstripped the conclusions of research scientists.
Firstly, let’s mention that Dr. Davis’ main issue here is (as the subtitle suggests) about animal proteins, not plant-based proteins. The former are associated with very many health risks that the latter are not. And yes, even just the lean protein, not considering the animal fat.
He does not argue that the reader must, or even necessarily needs to, adopt a vegan diet. However, he does argue for minimizing animal proteins, and getting more plants in.
A lot of the book is about the research to back this approach, and specifically, it’s largely a polemic against animal protein. He also shares anecdotes throughout, about his own health journey—from an overweight cheeseburger-fueled heart attack machine with exciting cholesterol levels, to a healthy, muscular, plant-fueled advocate for healthier eating.
He talks us through the science at hand, including chapters for each of the main health risks associated with meat consumption, as well as how the science got misrepresented by popular marketing for [not necessarily, but usually] meat-heavy diets such as Atkins and Paleo. That yes, they will give short term weight loss, but bring extra health risks in the longer term, and how.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut down your meat consumption but worry “will I get enough protein?”, this book will set your mind at ease with an abundance of science.
Click here to check out Proteinaholic, and give your body better!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Art Of Letting Go – by Nick Trenton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: is this a basic CBT book? And, for the most part, no, it’s not.
It does touch on some of the time-tested CBT techniques, but a large part of the book is about reframing things in a different way, that’s a little more DBT-ish, and even straying into BA. But enough of the initialisms, let’s give an example:
It can be scary to let go of the past, or of present or future possibilities (bad ones as well as good!). However, it’s hard to consciously do something negative (same principle as “don’t think of a pink elephant”), so instead, look at it as taking hold of the present/future—and thus finding comfort and security in a new reality rather than an old memory or a never-actual imagining.
So, this book has a lot of ideas like that, and if even one of them helps, then it was worth reading.
The writing style is comprehensive, and goes for the “tell them what you’re gonna tell them; tell them; then tell them what you told them” approach, which a) is considered good for learning b) can feel a little like padding nonetheless.
Bottom line: this reviewer didn’t personally love the style, but the content made up for it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How light can shift your mood and mental health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
It’s spring and you’ve probably noticed a change in when the Sun rises and sets. But have you also noticed a change in your mood?
We’ve known for a while that light plays a role in our wellbeing. Many of us tend to feel more positive when spring returns.
But for others, big changes in light, such as at the start of spring, can be tough. And for many, bright light at night can be a problem. Here’s what’s going on.
llaszlo/Shutterstock An ancient rhythm of light and mood
In an earlier article in our series, we learned that light shining on the back of the eye sends “timing signals” to the brain and the master clock of the circadian system. This clock coordinates our daily (circadian) rhythms.
“Clock genes” also regulate circadian rhythms. These genes control the timing of when many other genes turn on and off during the 24-hour, light-dark cycle.
But how is this all linked with our mood and mental health?
Circadian rhythms can be disrupted. This can happen if there are problems with how the body clock develops or functions, or if someone is routinely exposed to bright light at night.
When circadian disruption happens, it increases the risk of certain mental disorders. These include bipolar disorder and atypical depression (a type of depression when someone is extra sleepy and has problems with their energy and metabolism).
Light on the brain
Light may also affect circuits in the brain that control mood, as animal studies show.
There’s evidence this happens in humans. A brain-imaging study showed exposure to bright light in the daytime while inside the scanner changed the activity of a brain region involved in mood and alertness.
Another brain-imaging study found a link between daily exposure to sunlight and how the neurotransmitter (or chemical messenger) serotonin binds to receptors in the brain. We see alterations in serotonin binding in several mental disorders, including depression.
Our mood can lift in sunlight for a number of reasons, related to our genes, brain and hormones. New Africa/Shutterstock What happens when the seasons change?
Light can also affect mood and mental health as the seasons change. During autumn and winter, symptoms such as low mood and fatigue can develop. But often, once spring and summer come round, these symptoms go away. This is called “seasonality” or, when severe, “seasonal affective disorder”.
What is less well known is that for other people, the change to spring and summer (when there is more light) can also come with a change in mood and mental health. Some people experience increases in energy and the drive to be active. This is positive for some but can be seriously destabilising for others. This too is an example of seasonality.
Most people aren’t very seasonal. But for those who are, seasonality has a genetic component. Relatives of people with seasonal affective disorder are more likely to also experience seasonality.
Seasonality is also more common in conditions such as bipolar disorder. For many people with such conditions, the shift into shorter day-lengths during winter can trigger a depressive episode.
Counterintuitively, the longer day-lengths in spring and summer can also destabilise people with bipolar disorder into an “activated” state where energy and activity are in overdrive, and symptoms are harder to manage. So, seasonality can be serious.
Alexis Hutcheon, who experiences seasonality and helped write this article, told us:
[…] the season change is like preparing for battle – I never know what’s coming, and I rarely come out unscathed. I’ve experienced both hypomanic and depressive episodes triggered by the season change, but regardless of whether I’m on the ‘up’ or the ‘down’, the one constant is that I can’t sleep. To manage, I try to stick to a strict routine, tweak medication, maximise my exposure to light, and always stay tuned in to those subtle shifts in mood. It’s a time of heightened awareness and trying to stay one step ahead.
So what’s going on in the brain?
One explanation for what’s going on in the brain when mental health fluctuates with the change in seasons relates to the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine.
Serotonin helps regulate mood and is the target of many antidepressants. There is some evidence of seasonal changes in serotonin levels, potentially being lower in winter.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in reward, motivation and movement, and is also a target of some antidepressants. Levels of dopamine may also change with the seasons.
But the neuroscience of seasonality is a developing area and more research is needed to know what’s going on in the brain.
How about bright light at night?
We know exposure to bright light at night (for instance, if someone is up all night) can disturb someone’s circadian rhythms.
This type of circadian rhythm disturbance is associated with higher rates of symptoms including self-harm, depressive and anxiety symptoms, and lower wellbeing. It is also associated with higher rates of mental disorders, such as major depression, bipolar disorder, psychotic disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (or PTSD).
Why is this? Bright light at night confuses and destabilises the body clock. It disrupts the rhythmic regulation of mood, cognition, appetite, metabolism and many other mental processes.
But people differ hugely in their sensitivity to light. While still a hypothesis, people who are most sensitive to light may be the most vulnerable to body clock disturbances caused by bright light at night, which then leads to a higher risk of mental health problems.
Bright light at night disrupts your body clock, putting you at greater risk of mental health issues. Ollyy/Shutterstock Where to from here?
Learning about light will help people better manage their mental health conditions.
By encouraging people to better align their lives to the light-dark cycle (to stabilise their body clock) we may also help prevent conditions such as depression and bipolar disorder emerging in the first place.
Healthy light behaviours – avoiding light at night and seeking light during the day – are good for everyone. But they might be especially helpful for people at risk of mental health problems. These include people with a family history of mental health problems or people who are night owls (late sleepers and late risers), who are more at risk of body clock disturbances.
Alexis Hutcheon has lived experience of a mental health condition and helped write this article.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Jacob Crouse, Research Fellow in Youth Mental Health, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney; Emiliana Tonini, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney, and Ian Hickie, Co-Director, Health and Policy, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Beetroot vs Red Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to red cabbage, we picked the red cabbage.
Why?
Both are great, and both have their strengths!
In terms of macros, beetroot has very slightly more protein, carbs, and fiber, but the margins of difference are very small in each case. However, in terms of glycemic index, red cabbage has the considerably lower glycemic index, of 32 (low) as opposed to beetroot’s GI of 64 (medium). On the strength of this GI difference, we call this category a win for red cabbage.
In the category of vitamins, beetroot has more of vitamin B9, while red cabbage has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, C, E, K, and choline. By strength of numbers and also by having very large margins of difference on most of those, red cabbage is the clear winner here.
When it comes to minerals, beetroot has more copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while red cabbage has more calcium (and about ⅓ of the sodium). By the numbers, this is a win for beetroot, though it’s worth noting that the margins of difference were small, i.e. red cabbage was right behind beetroot on each of those.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall red cabbage win, but as we say, beetroot is great too, especially when it comes to minerals!
As ever, enjoy either or both; diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
No, beetroot isn’t vegetable Viagra. But here’s what it can do!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: