Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer – by Dr. Patrick Walsh & Janet Farrar Worthington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate cancer is not glamorous or fun, and neither is this book.
Nevertheless, it’s a disease that affects 12% of men in general, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing every year after that.
So, if you have a prostate or love someone who has one, this book is worthwhile reading—yes, even as a preventative.
Like many cancers, prostate cancer is easy to treat if caught very early, becomes harder to treat as it goes, and almost impossible to cure if it gets as far as metastasis (i.e., it spread). Like all cancers, it’s better off avoided entirely if possible.
This book covers all the stages:
- How to avoid it
- How to check for it
- How to “nip it in the bud”
- Why some might want to delay treatment (!)
- What options are available afterwards
This latter is quite extensive, and covers not just surgery, but radiation, thermo- or cryoablation, and hormone therapy.
And as for surgery, not just “remove the tumor”, but other options like radical prostatectomy, and even orchiectomy. Not many men will choose to have their testicles removed to stop them from feeding the prostate, but the point is that this book is comprehensive.
It’s asking whenever possible “is there another option?” and exploring all options, with information and without judgment, at each stage.
The writing style (likely co-author Worthington’s influence; she is an award-winning science-writer) is very “for the layman”, and that’s really helpful in demystifying a lot of what can be quite opaque in the field of oncology.
Bottom line: absolutely not an enjoyable read, but a potentially lifesaving one, especially given the odds we mentioned up top.
Click here to check out Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide To Surviving Prostate Cancer, and be prepared!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do We Need Supplements, And Do They Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does our diet need a little help?
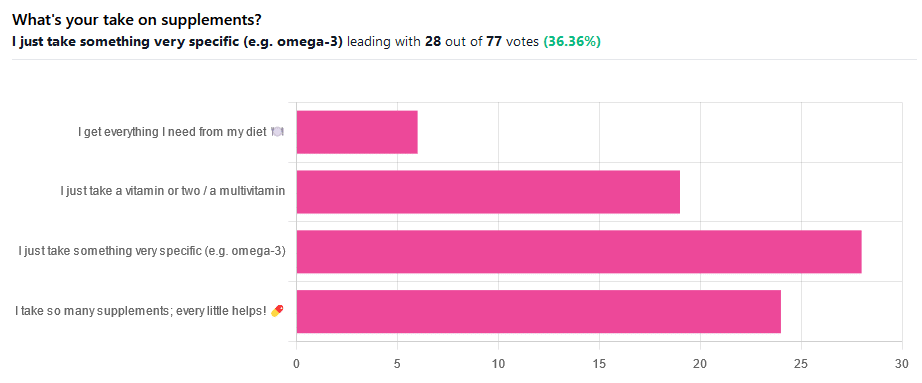
We asked you for your take on supplements, and got the above-illustrated, below-described set of results.
- The largest minority of respondents (a little over a third) voted for “I just take something very specific”
- The next most respondents voted for “I take so many supplements; every little helps!”
- Almost as many voted for “I just take a vitamin or two / a multivitamin”
- Fewest, about 8%, voted for “I get everything I need from my diet”
But what does the science say?
Food is less nutritious now than it used to be: True or False?
True or False depending on how you measure it.
An apple today and an apple from a hundred years ago are likely to contain the same amounts of micronutrients per apple, but a lower percentage of micronutrients per 100g of apple.
The reason for this is that apples (and many other food products; apples are just an arbitrary example) have been selectively bred (and in some cases, modified) for size, and because the soil mineral density has remained the same, the micronutrients per apple have not increased commensurate to the increase in carbohydrate weight and/or water weight. Thus, the resultant percentage will be lower, despite the quantity remaining the same.
We’re going to share some science on this, and/but would like to forewarn readers that the language of this paper is a bit biased, as it looks to “debunk” claims of nutritional values dropping while skimming over “yes, they really have dropped percentage-wise” in favor of “but look, the discrete mass values are still the same, so that’s just a mathematical illusion”.
The reality is, it’s no more a mathematical illusion than is the converse standpoint of saying the nutritional value is the same, despite the per-100g values dropping. After all, sometimes we eat an apple as-is; sometimes we buy a bag of frozen chopped fruit. That 500g bag of chopped fruit is going to contain less copper (for example) than one from decades past.
Here’s the paper, and you’ll see what we mean:
Supplements aren’t absorbed properly and thus are a waste of money: True or False?
True or False depending on the supplement (and your body, and the rest of your diet)
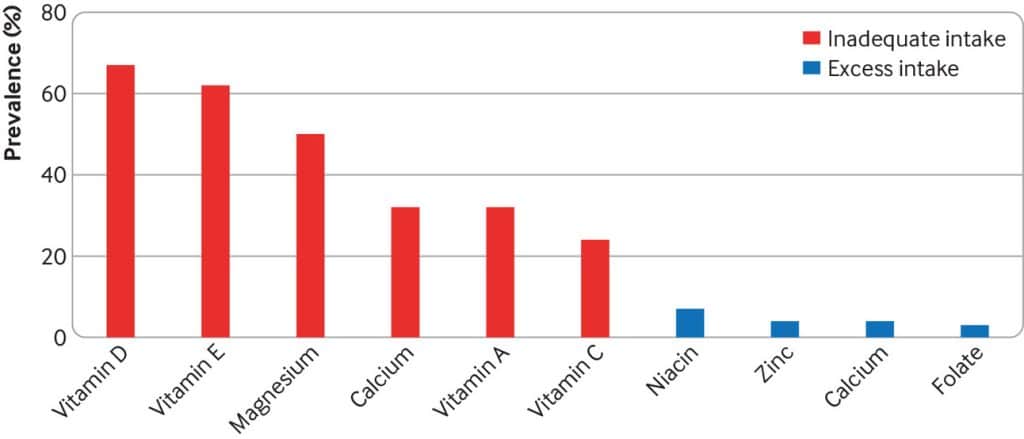
Many people are suffering from dietary deficiencies of vitamins and minerals, that could be easily correctable by supplementation:
However, as this study by Dr. Fang Fang Zhang shows, a lot of vitamin and mineral supplementation does not appear to have much of an effect on actual health outcomes, vis-à-vis specific diseases. She looks at:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Osteoporosis
Her key take-aways from this study were:
- Randomised trial evidence does not support use of vitamin, mineral, and fish oil supplements to reduce the risk of non-communicable diseases
- People using supplements tend to be older, female, and have higher education, income, and healthier lifestyles than people who do not use them
- Use of supplements appreciably reduces the prevalence of inadequate intake for most nutrients but also increases the prevalence of excess intake for some nutrients
- Further research is needed to assess the long term effects of supplements on the health of the general population and in individuals with specific nutritional needs, including those from low and middle income countries
Read her damning report: Health effects of vitamin and mineral supplements
On the other hand…
This is almost entirely about blanket vitamin-and-mineral supplementation. With regard to fish oil supplementation, many commercial fish oil supplements break down in the stomach rather than the intestines, and don’t get absorbed well. Additionally, many people take them in forms that aren’t pleasant, and thus result in low adherence (i.e., they nominally take them, but in fact they just sit on the kitchen counter for a year).
One thing we can conclude from this is that it’s good to check the science for any given supplement before taking it, and know what it will and won’t help for. Our “Monday Research Review” editions of 10almonds do this a lot, although we tend to focus on herbal supplements rather than vitamins and minerals.
We can get everything we need from our diet: True or False?
Contingently True (but here be caveats)
In principle, if we eat the recommended guideline amounts of various macro- and micro-nutrients, we will indeed get all that we are generally considered to need. Obviously.
However, this may come with:
- Make sure to get enough protein… Without too much meat, and also without too much carbohydrate, such as from most plant sources of protein
- Make sure to get enough carbohydrates… But only the right kinds, and not too much, nor at the wrong time, and without eating things in the wrong order
- Make sure to get enough healthy fats… Without too much of the unhealthy fats that often exist in the same foods
- Make sure to get the right amount of vitamins and minerals… We hope you have your calculators out to get the delicate balance of calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, and vitamin D right.
That last one’s a real pain, by the way. Too much or too little of one or another and the whole set start causing problems, and several of them interact with several others, and/or compete for resources, and/or are needed for the others to do their job.
And, that’s hard enough to balance when you’re taking supplements with the mg/µg amount written on them, never mind when you’re juggling cabbages and sardines.
On the topic of those sardines, don’t forget to carefully balance your omega-3, -6, and -9, and even within omega-3, balancing ALA, EPA, and DHA, and we hope you’re juggling those HDL and LDL levels too.
So, when it comes to getting everything we need from our diet, for most of us (who aren’t living in food deserts and/or experiencing food poverty, or having a medical condition that restricts our diet), the biggest task is not “getting enough”, it’s “getting enough of the right things without simultaneously overdoing it on the others”.
With supplements, it’s a lot easier to control what we’re putting in our bodies.
And of course, unless our diet includes things that usually can’t be bought in supermarkets, we’re not going to get the benefits of taking, as a supplement, such things as:
Etc.
So, there definitely are supplements with strong science-backed benefits, that probably can’t be found on your plate!
Share This Post
-
Tourette’s Syndrome Treatment Options
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Is there anything special that might help someone with Tourette’s syndrome?❞
There are of course a lot of different manifestations of Tourette’s syndrome, and some people’s tics may be far more problematic to themselves and/or others, while some may be quite mild and just something to work around.
It’s an interesting topic for sure, so we’ll perhaps do a main feature (probably also covering the related-and-sometimes-overlapping OCD umbrella rather than making it hyperspecific to Tourette’s), but meanwhile, you might consider some of these options:
Share This Post
-
The Many Faces Of Cosmetic Surgery
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cosmetic Surgery: What’s The Truth?
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on elective cosmetic surgeries, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 48% said “Everyone should be able to get what they want, assuming informed consent”
- About 28% said “It can ease discomfort to bring features more in line with normalcy”
- 15% said “They should be available in the case of extreme disfigurement only”
- 10% said “No elective cosmetic surgery should ever be performed; needless danger”
Well, there was a clear gradient of responses there! Not so polarizing as we might have expected, but still enough dissent for discussion
So what does the science say?
The risks of cosmetic surgery outweigh the benefits: True or False?
False, subjectively (but this is important).
You may be wondering: how is science subjective?
And the answer is: the science is not subjective, but people’s cost:worth calculations are. What’s worth it to one person absolutely may not be worth it to another. Which means: for those for whom it wouldn’t be worth it, they are usually the people who will not choose the elective surgery.
Let’s look at some numbers (specifically, regret rates for various surgeries, elective/cosmetic or otherwise):
- Regret rate for elective cosmetic surgery in general: 20%
- Regret rate for knee replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 17.1%
- Regret rate for hip replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 4.8%
- Regret rate for gender-affirming surgeries (for transgender patients): 1%
So we can see, elective surgeries have an 80–99% satisfaction rate, depending on what they are. In comparison, the two joint replacements we mentioned have a 82.9–95.2% satisfaction rate. Not too dissimilar, taken in aggregate!
In other words: if a person has studied the risks and benefits of a surgery and decides to go ahead, they’re probably going to be happy with the results, and for them, the benefits will have outweighed the risks.
Sources for the above numbers, by the way:
- What is the regret rate for plastic surgery?
- Decision regret after primary hip and knee replacement surgery
- A systematic review of patient regret after surgery—a common phenomenon in many specialties but rare within gender-affirmation surgery
But it’s just a vanity; therapy is what’s needed instead: True or False?
False, generally. True, sometimes. Whatever the reasons for why someone feels the way they do about their appearance—whether their face got burned in a fire or they just have triple-J cups that they’d like reduced, it’s generally something they’ve already done a lot of thinking about. Nevertheless, it does also sometimes happen that it’s a case of someone hoping it’ll be the magical solution, when in reality something else is also needed.
How to know the difference? One factor is whether the surgery is “type change” or “restorative”, and both have their pros and cons.
- In “type change” (e.g. rhinoplasty), more psychological adjustment is needed, but when it’s all over, the person has a new nose and, statistically speaking, is usually happy with it.
- In “restorative” (e.g. facelift), less psychological adjustment is needed (as it’s just a return to a previous state), so a person will usually be happy quickly, but ultimately it is merely “kicking the can down the road” if the underlying problem is “fear of aging”, for example. In such a case, likely talking therapy would be beneficial—whether in place of, or alongside, cosmetic surgery.
Here’s an interesting paper on that; the sample sizes are small, but the discussion about the ideas at hand is a worthwhile read:
Does cosmetic surgery improve psychosocial wellbeing?
Some people will never be happy no matter how many surgeries they get: True or False?
True! We’re going to refer to the above paper again for this one. In particular, here’s what it said about one group for whom surgeries will not usually be helpful:
❝There is a particular subgroup of people who appear to respond poorly to cosmetic procedures. These are people with the psychiatric disorder known as “body dysmorphic disorder” (BDD). BDD is characterised by a preoccupation with an objectively absent or minimal deformity that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning.
For several reasons, it is important to recognise BDD in cosmetic surgery settings:
Firstly, it appears that cosmetic procedures are rarely beneficial for these people. Most patients with BDD who have had a cosmetic procedure report that it was unsatisfactory and did not diminish concerns about their appearance.
Secondly, BDD is a treatable disorder. Serotonin-reuptake inhibitors and cognitive behaviour therapy have been shown to be effective in about two-thirds of patients with BDD❞
~ Dr. David Castle et al. (lightly edited for brevity)
Which is a big difference compared to, for example, someone having triple-J breasts that need reducing, or the wrong genitals for their gender, or a face whose features are distinct outliers.
Whether that’s a reason people with BDD shouldn’t be able to get it is an ethical question rather than a scientific one, so we’ll not try to address that with science.
After all, many people (in general) will try to fix their woes with a haircut, a tattoo, or even a new sportscar, and those might sometimes be bad decisions, but they are still the person’s decision to make.
And even so, there can be protectionist laws/regulations that may provide a speed-bump, for example:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Oh She Glows Cookbook – by Angela Liddon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s get the criticism out of the way first: notwithstanding the subtitle promising over 100 recipes, there are about 80-odd here, if we discount recipes that are no-brainer things like smoothies, sides such as for example “roasted garlic”, or meta-ingredients such as oat flour (instructions: blend the oats and you get oat flour).
The other criticism is more subjective: if you are like this reviewer, you will want to add more seasonings than recommended to most of the recipes. But that’s easy enough to do.
As for the rest: this is a very healthy cookbook, and quite wide-ranging and versatile, with recipes that are homely, with a lot of emphasis on comfort foods (but still, healthy), though certainly some are perfectly worthy of entertaining too.
A nice bonus of this book is that it offers a lot of available substitutions (much like we do at 10almonds), and also ways of turning the recipe into something else entirely with just a small change. This trait more than makes up for the slight swindle in terms of number of recipes, since some of the recipes have bonus recipes snuck in.
Bottom line: if you’d like to broaden your plant-based cooking range, this book is a fine option for expanding your repertoire.
Click here to check out The Oh She Glows Cookbook, and indeed glow!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why We’re Called “10almonds”, And Other Questions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Avid coffee drinker so very interested in the results Also question Is there something that you could take or eat that would prevent the caffeine from stimulating the kidneys? I tried to drink decaf from morning to night not a good result! Thanks❞
That is a good question! The simple answer is “no” (but keep reading, because all is not lost)
There’s no way (that we yet know of) to proof the kidneys against the stimulating effect of caffeine. This is especially relevant because part of caffeine’s stimulating effect is noradrenergic, and that “ren” in the middle there? It’s about the kidneys. This is just because the adrenal gland is situated next to them (actually, it’s pretty much sitting on top of them), hence the name, but it does mean that the kidneys are about the hardest thing in the body to have not affected by caffeine.
However! The effects of caffeine in general can be softened a little with l-theanine (found in tea, or it can be taken as a supplement). It doesn’t stop it from working, but it makes the curve of the effect a little gentler, and so it can reduce some unwanted side effects.
You can read more about l-theanine here:
❝How to jump start a inactive metabolism and keep it going? THANKYOU❞
The good news is, if you’re alive, your metabolism is active (it never stops!). So, it may just need perking up a little.
As for keeping it going, well, that’s what we’re here for! We’re all in favor of healthy longevity.
We’ll do a main feature soon on what we can do to influence our metabolism in either direction, but to give some quick notes here:
- A lot of our metabolism is influenced by genes and is unalterable (without modifying our genes, anyway)
- Metabolism isn’t just one thing—it’s many. And sometimes, parts of our metabolism can be much quicker or slower than others.
- When people talk about wanting a “faster metabolism”, they’re usually referring to fat-burning, and that’s just a small part of the picture, but we understand that it’s a focal point for many.
There really is enough material for a whole main feature on metabolic tweaks, though, so watch this space!
❝Why the name “10 Almonds?” Is this recommended by the Doctor? A daily dosage? And, if so, why? Thanks! Please answer me…I truly want to know!❞
Almonds are very nutritionally dense, and for example 20g of almonds (so, about 20 almonds) would give a 100% daily dose of zinc, amongst other nutrients.
We also do like to think that we give our readers an easily digestible dose of condensed “nutrition” in the form of health information.
However! That’s not actually the reason at all. It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was circulating online! So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a nod to that story, but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Increase Your Muscle Mass Boost By 26% (No Extra Effort, No Supplements)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’ve probably seen this technology advertised, but the trick is in how it’s used (which is not how most people use it).
It’s about neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), also called electrical muscle stimulation (EMS); in other words, those squid-like electrode kits that promise “six-pack abs without exercise”, by stimulating the muscles for you—using the exact same tech as for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), for pain relief.
Do they work for pain relief? Yes, for many people in any case. But that’s beyond the scope of today’s article.
Do they work for building muscles as advertised? No. The limiting factor is that they can’t fully exert the muscles in the same way actual exercise can, because of the limitations to how much electrical current can safely be applied.
However…
The cyborgization of your regular workout
A meta-analysis of 13 studies compared two [meta-]groups of exercisers:
- Group 1 doing conventional resistance training
- Group 2 doing the same resistance training, plus NMES at the same time (specifically: NMES of the same muscles being used in the workout)
The analysis had two output variables: strength and muscle mass
What they found: group 2 enjoyed more than 31% greater strength gains, and 26% greater muscle mass gains, from the same training over the same period of time.
Of course, one of the biggest challenges to strength gain and muscle mass gain is hitting a plateau, so it’s worth noting that when they looked at training periods ranging from 2 weeks to 16 weeks, longer durations yielded better results—it is, it seems, the gift that keeps on giving.
You can find the paper here (which also explains how they analysed data from 13 different studies to get one coherent set of results):
How it works and why it matters
While the paper itself does not go into how it works, a reasonable hypothesis is that it works by “confusing” the muscles—because they are receiving mixed signals (one set from your brain, one set from the electrodes), with fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibers both working at the same time.
Another way to “confuse” the muscles is by High Intensity [Interval] Resistance Training (HIRT)—which is basically High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), but for resistance training specifically.
See: How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body) and HIIT, But Make It HIRT
Now, we want to confuse our muscles, not our readers, so if that’s all too much to juggle at once, just pick one and go with it. But today’s article is about the RT+NEMS combination, so perhaps you’ll pick that.
Why it matters: as we get older, sarcopenia (the loss of muscle mass) becomes more of an issue, and even if we’re not inclined to a career in bodybuilding, we do still need to at least maintain a healthy muscle mass because:
- Strong muscles improve our stability and make us less likely to fall
- Strong muscles force the body to build strong bones to hold them on, which means lower risk of fractures or worse
- Muscle mass itself improves the body’s basal metabolic rate, which means systemic benefits to the whole body (including against metabolic diseases especially)
See also: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Want to try it?
If you don’t already have a NMES/EMS/TENS kit lying around the house, here’s an example product on Amazon—remember to use it simultaneously with your regular resistance training workout, on the same muscles at the same time, to get the benefit we talked about! 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: