Is Your Gut Leading You Into Osteoporosis?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bacterioides Vulgatus & Bone Health
We’ve talked before about the importance of gut health:
And we’ve shared quite some information and resources on osteoporosis:
- The Bare-bones Truth: Osteoporosis Mythbusting
- Osteoporosis Exercises (What To Do, And What To Avoid)
- Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
- Collagen For Bones: We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Which Osteoporosis Medication, If Any, Is Right For You?
How the two are connected
A recent study looked at Bacterioides vulgatus, a very common gut bacterium, and found that it suppresses the gut’s production of valeric acid, a short-chain fatty acid that enhances bone density:
❝For the study, researchers analyzed the gut bacteria of more than 500 peri- and post-menopausal women in China and further confirmed the link between B. vulgatus and a loss of bone density in a smaller cohort of non-Hispanic White women in the United States.❞
Pop-sci source: Does gut bacteria cause osteoporosis?
The study didn’t stop there, though. They proceeded to test, with a rodent model, the effect of giving them either:
- more B. vulgatus, or
- valeric acid supplements
The results of this were as expected:
- Those who were given more B. vulgatus got worse bone microstructure
- Those who were given valeric acid supplements got stronger bones overall
Study source: Gut microbiota impacts bone via Bacteroides vulgatus-valeric acid-related pathways
Where can I get valeric acid?
We couldn’t find a handy supplement for this, but it is in many foods, including avocados, blueberries, cocoa beans, and an assortment of birds.
Click here to see a more extensive food list (you’ll need to scroll down a little)
Bonus: if you happen to be on HRT in the form of Estradiol valerate (e.g: Progynova), then that “valerate” is an ester of valeric acid, that your body can metabolize and use as such.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Resistance band Training – by James Atkinson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those who’d like a full gym workout at home, without splashing out thousands on a home gym, resistance bands provide a lot of value. But how much value, really?
As James Atkinson demonstrates, there’s more exercise available than one might think.
Did you know that you can use the same band to strengthen your triceps as well as your biceps, for instance? and the same goes for your quadriceps and biceps femoris. And core strength? You bet.
The style here is not a sales pitch (though he does, at the end, offer extra resources if desired), but rather, instructional, and this book is in and of itself already a complete guide. With clear instructions and equally clear illustrations, you don’t need to spend a dime more (unless you don’t own a resistance band, in which case then yes, you will need one of those).
Bottom line: if you’d like to give your body the workout it deserves, this book is a potent resource.
Click here to check out Resistance Band Training, and get training!
Share This Post
-
Staying Sane In A Hyper-Connected World
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Staying Sane In A Hyper-Connected World
There’s a war over there, a genocide in progress somewhere else, and another disease is ravaging the population of somewhere most Americans would struggle to point out on the map. Not only that, but that one politician is at it again, and sweeping wildfires are not doing climate change any favors.
To borrow an expression from Gen-Z…
“Oof”.
A Very Modern Mental Health Menace
For thousands of years, we have had wars and genocides and plagues and corrupt politicians and assorted major disasters. Dire circumstances are not new to us as a species. So what is new?
As some reactionary said during the dot-com boom, “the Internet doesn’t make people stupid; it just makes their stupidity more accessible”.
The same is true now of The Horrors™.
The Internet doesn’t, by and large, make the world worse. But what it does do is make the bad things much, much more accessible.
Understanding and empathy are not bad things, but watch out…
- When soldiers came home from the First World War, those who hadn’t been there had no conception of the horrors that had been endured. That made it harder for the survivors to get support. That was bad.
- Nowadays, while mass media covering horrors certainly doesn’t convey the half of it, even the half it does convey can be overwhelming. This is also bad.
The insidious part is: while people are subjectively reporting good physical/mental health, the reports of the symptoms of poor physical/mental health from the same population do not agree:
Stress in America 2023: A nation grappling with psychological impacts of collective trauma
Should we just not watch the news?
In principle that’s an option, but it’s difficult to avoid, unless you truly live under a rock, and also do not frequent any social media at all. And besides, isn’t it our duty as citizens of this world to stay informed? How else can we make informed choices?
Staying informed, mindfully
There are steps that can be taken to keep ourselves informed, while protecting our mental health:
- Choose your sources wisely. Primary sources (e.g. tweets and videos from people who are there) will usually be most authentic, but also most traumatizing. Dispassionate broadsheets may gloss over or misrepresent things more (something that can be countered a bit by reading an opposing view from a publication you hate on principle), but will offer more of an emotional buffer.
- Boundary your consumption of the news. Set a timer and avoid doomscrolling. Your phone (or other device) may help with this if you set a screentime limit per app where you consume that kind of media.
- Take (again, boundaried) time to reflect. If you don’t, your brain will keep grinding at it “like a fork in the garbage disposal”. Talking about your feelings on the topic with a trusted person is great; journaling is also a top-tier more private option.
- If you feel helpless, help. Taking even small actions to help in the face of suffering somewhere else (e.g. donating to relief funds, engaging in advocacy / hounding your government about it), can help alleviate feelings of anguish and helplessness. And of course, as a bonus, it actually helps in the real world too.
- When you relax, relax fully. Even critical care doctors need downtime, nobody can be “always on” without burning out. So whatever distracts and relaxes you completely, make sure to make time for that too.
Want to know more?
That’s all we have room for today, but you might like to check out:
- Distressing images and videos can take a toll on our mental health. How can we stay informed without being traumatised?
- PTSD expert on how to protect yourself and your kids from overexposure to war images from the Mideast
You also might like our previous main features:
- C-PTSD, And What To Do When Life Genuinely Sucks
- A Surprisingly Powerful Tool: Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What Menopause Does To The Heart
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
World Menopause Day: Menopause & Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Today, the 18th of October, is World Menopause Day.
The theme for this year is cardiovascular disease (CVD), and if your first reaction is to wonder what that has to do with the menopause, then this is the reason why it’s being featured. Much of the menopause and its effects are shrouded in mystery; not because of a lack of science (though sometimes a bit of that too), but rather, because it is popularly considered an unimportant, semi-taboo topic.
So, let’s be the change we want to see, and try to fix that!
What does CVD have to do with the menopause?
To quote Dr. Anjana Nair:
❝The metabolic and clinical factors secondary to menopause, such as dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, fat redistribution and systemic hypertension, contribute to the accelerated risk for cardiovascular aging and disease.
Atherosclerosis appears to be the end result of the interaction between cardiovascular risk factors and their accentuation during the perimenopausal period.
The increased cardiovascular risk in menopause stems from the exaggerated effects of changing physiology on the cardiovascular system.❞
Source: Cardiovascular Changes in Menopause
See also: Menopause-associated risk of cardiovascular disease
Can we do anything about it?
Yes, we can! Here be science:
- Menopause Transition and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Implications for Timing of Early Prevention: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
- Cardiovascular risk in menopausal women and our evolving understanding of menopausal hormone therapy: risks, benefits, and current guidelines for use
This (in few words: get your hormone levels checked, and consider HRT if appropriate) is consistent with the advice from gynecologist Dr. Jen Gunter, whom we featured back in August:
What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
What about lifestyle changes?
We definitely can do some good things; here’s what the science has to say:
- Mediterranean diet: yes, evidence-based
- High soy consumption: mixed evidence, unclear. So, eat it if you want, don’t if you don’t.
- Supplements e.g. vitamins and minerals: yes, evidence-based.
- Supplements e.g. herbal preparations: many may help, but watch out for adverse interactions with meds. Check with your pharmacist or doctor.
- Supplements; specifically CBD: not enough evidence yet
- Exercise: yes, evidence-based—especially low-impact high-resistance training, for bone strength, as well as regular moderate-intensity exercise and/or High-Intensity Interval Training, to guard against CVD.
For a full low-down on all of these:
Revealing the evidence-based lifestyle solutions to managing your menopause symptoms
Want to know more?
You can get the International Menopause Society’s free downloadable booklet here:
Menopause & Cardiovascular Disease: What Women Need To Know
You may also like our previous main feature:
What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Self-Compassion In A Relationship (Positives & Pitfalls)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Practise Self-Compassion In Your Relationship (But Watch Out!)
Let’s make clear up-front: this is not about “…but not too much”.
With that in mind…
Now let’s set the scene: you, a happily-partnered person, have inadvertently erred and upset your partner. They may or may not have already forgiven you, but you are still angry at yourself.
Likely next steps include all or any of:
- continuing to apologise and try to explain
- self-deprecatory diatribes
- self-flagellation, probably not literally but in the sense of “I don’t deserve…” and acting on that feeling
- self-removal, because you don’t want to further inflict your bad self on your partner
As you might guess, these are quite varied in their degree of healthiness:
- apologising is good, as even is explaining, but once it’s done, it’s done; let it go
- self-deprecation is pretty much never useful, let alone healthy
- self-flagellation likewise; it is not only inherently self-destructive, but will likely create an additional problem for your partner too
- self-removal can be good or bad depending on the manner of that removal: there’s a difference between just going cold and distant on your partner, and saying “I’m sorry; this is my fault not yours, I don’t want to take it out on you, so please give me half an hour by myself to regain my composure, and I will come back with love then if that’s ok with you”
About that last: mentioning the specific timeframe e.g. “half an hour” is critical, by the way—don’t leave your partner hanging! And then do also follow through on that; come back with love after the half-hour elapses. We suggest mindfulness meditation in the interim (here’s our guide to how), if you’re not sure what to do to get you there.
To Err Is Human; To Forgive, Healthy (Here’s How To Do It) ← this goes for when the forgiveness in question is for yourself, too—and we do write about that there (and how)!
This is important, by the way; not forgiving yourself can cause more serious issues down the line:
If, by the way, you’re hand-wringing over “but was my apology good enough really, or should I…” then here is how to do it. Basically, do this, and then draw a line under it and consider it done:
The Apology Checklist ← you’ll want to keep a copy of this, perhaps in the notes app on your phone, or a screenshot if you prefer
(the checklist is at the bottom of that page)
The catch
It’s you, you’re the catch 👈👈😎
Ok, that being said, there is actually a catch in the less cheery sense of the word, and it is:
“It is important to be compassionate about one’s occasional failings in a relationship” does not mean “It is healthy to be neglectful of one’s partner’s emotional needs; that’s self-care, looking after #1; let them take care of themself too”
…because that’s simply not being a couple at all.
Think about it this way: the famous airline advice,
“Put on your own oxygen mask before helping others with theirs”
…does not mean “Put on your own oxygen mask and then watch those kids suffocate; it’s everyone for themself”
So, the same goes in relationships too. And, as ever, we have science for this. There was a recent (2024) study, involving hundreds of heterosexual couples aged 18–73, which looked at two things, each measured with a scaled questionnaire:
- Subjective levels of self-compassion
- Subjective levels of relationship satisfaction
For example, questions included asking participants to rate, from 1–5 depending on how much they felt the statements described them, e.g:
In my relationship with my partner, I:
- treat myself kindly when I experience sorrow and suffering.
- accept my faults and weaknesses.
- try to see my mistakes as part of human nature.
- see difficulties as part of every relationship that everyone goes through once.
- try to get a balanced view of the situation when something unpleasant happens.
- try to keep my feelings in balance when something upsets me.
Note: that’s not multiple choice! It’s asking participants to rate each response as applicable or not to them, on a scale of 1–5.
And…
❝Women’s self-compassion was also positively linked with men’s total relationship satisfaction. Thus, men seem to experience overall satisfaction with the relationship when their female partner is self-kind and self-caring in difficult situations.
Unexpectedly, however, we found that men’s relationship-specific self-compassion was negatively associated with women’s fulfillment.
Baker and McNulty (2011) reported that, only for men, a Self-Compassion x Conscientiousness interaction explained whether the positive effects of self-compassion on the relationship emerged, but such an interaction was not found for women.
Highly self-compassionate men who were low in conscientiousness were less motivated than others to remedy interpersonal mistakes in their romantic relationships, and this tendency was in turn related to lower relationship satisfaction❞
~ Dr. Astrid Schütz et al. (2024)
And if you’d like to read the cited older paper from 2011, here it is:
Read in full: Self-compassion and relationship maintenance: the moderating roles of conscientiousness and gender
The take-away here is not: “men should not practice self-compassion”
(rather, they absolutely should)
The take-away is: we must each take responsibility for managing our own mood as best we are able; practice self-forgiveness where applicable and forgive our partner where applicable (and communicate that!)…. And then go consciously back to the mutual care on which the relationship is hopefully founded.
Which doesn’t just mean love-bombing, by the way, it also means listening:
The Problem With Active Listening (And How To Do Better)
To close… We say this often, but we mean it every time: take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Studies of Parkinson’s disease have long overlooked Pacific populations – our work shows why that must change
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A form of Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in a gene known as PINK1 has long been labelled rare. But our research shows it’s anything but – at least for some populations.
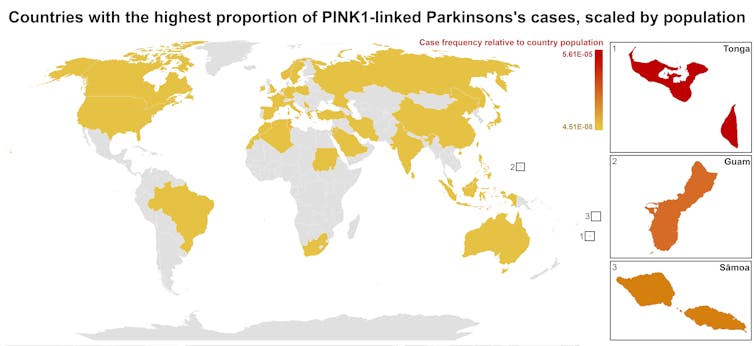
Our meta-analysis revealed that people in specific Polynesian communities have a much higher rate of PINK1-linked Parkinson’s than expected. This finding reshapes not only our understanding of who is most at risk, but also how soon symptoms may appear and what that might mean for treatment and testing.
Parkinson’s disease is often thought of as a single condition. In reality, it is better understood as a group of syndromes caused by different factors – genetic, environmental or a combination of both.
These varying causes lead to differences in disease patterns, progression and subsequent diagnosis. Recognising this distinction is crucial as it paves the way for targeted interventions and may even help prevent the disease altogether.
Shutterstock/sfam_photo Why we focus on PINK1-linked Parkinson’s
We became interested in this gene after a 2021 study highlighted five people of Samoan and Tongan descent living in New Zealand who shared the same PINK1 mutation.
Previously, this mutation had been spotted only in a few more distant places –Malaysia, Guam and the Philippines. The fact it appeared in people from Samoan and Tongan backgrounds suggested a historical connection dating back to early Polynesian migrations.
One person in 1,300 West Polynesians carries this mutation. This is a frequency well above what scientists usually classify as rare (below one in 2,200). This discovery means we may be overlooking entire communities in Parkinson’s research if we continue to assume PINK1-linked cases are uncommon.
This world map shows people in some Polynesian communities have a much higher rate of PINK1-linked Parkinson’s than the global population. Eden Yin, CC BY-SA Traditional understanding says PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is both rare and typically strikes younger people, mostly in their 30s or 40s, if they inherit two faulty copies of the gene. In other words, it’s considered a recessive condition, needing two matching puzzle pieces before the disease can unfold.
Our work challenges this view. We show that even one defective PINK1 gene can cause Parkinson’s at an average age of 43, much earlier than the typical onset after 65. That’s a significant departure from the standard belief that only people with two defective gene copies are at risk.
Why this matters for people with the disease
It’s not just genetics that challenge long-held views. Historically, PINK1-linked Parkinson’s was thought to lack some of the classic features of the disease, such as toxic clumps of alpha-synuclein protein.
In typical Parkinson’s, alpha-synuclein builds up in the brain, forming sticky clumps known as Lewy bodies. Our results, contrary to prior beliefs, show that alpha-synuclein pathology is present in 87.5% of PINK1 cases. This finding opens up a promising new avenue for future treatment development.
The biggest concern is early onset. PINK1-linked Parkinson’s can begin as early as 11 years old, although a more common starting point is around the mid-30s. This early onset means living longer with the disease, which can profoundly affect education, work opportunities and family life.
Current treatments (such as levodopa, a precursor of dopamine) help manage symptoms, but they’re not designed to address the root cause. If we know someone has a PINK1 mutation, scientists and clinicians can explore therapies for specific genetic pathways, potentially delivering relief beyond symptom management.
Sex differences add a layer of complexity
In Parkinson’s, generally, men are at higher risk and tend to develop symptoms earlier. However, our findings suggest the opposite pattern for PINK1-linked cases. Particularly, women with two defective copies of the gene experience onset earlier than men.
This highlights the need to consider sex-related factors in Parkinson’s research. Overlooking them risks missing key elements of the disease.
Genetic testing could be a game-changer for PINK1-linked Parkinson’s. Because it often appears earlier, doctors may not recognise it immediately, especially if they are more familiar with the common, later-onset form of Parkinson’s.
Early genetic testing could lead to a faster, more accurate diagnosis, allowing treatment to begin when interventions are most effective. It would help families understand how the disease is inherited, enabling relatives to get tested.
In some cases, where appropriate and culturally acceptable, embryo screening may be considered to prevent the passing of the faulty gene.
Knowing you have a PINK1 mutation could also make finding the right treatment more efficient. Instead of a lengthy trial-and-error process with different medications, doctors could use emerging therapies designed to target the underlying PINK1 mutation rather than relying on general Parkinson’s treatments meant for the broader population.
Addressing research gaps
These findings underscore how crucial it is to include diverse populations in health research.
Many communities, such as those in Samoa, Tonga and other Pacific nations, have had little to no involvement in global Parkinson’s genetics studies. This has created gaps in knowledge and real-world consequences for people who may not receive timely or accurate diagnoses.
Researchers, funding bodies and policymakers must prioritise projects beyond the usual focus on European or industrialised countries to ensure research findings and treatments are relevant to all affected populations.
To better diagnose and treat Parkinson’s, we need a more inclusive approach. Recognising that PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is not as rare as previously thought – and that genetics, sex differences and cultural factors all play a role – allows us to improve care for everyone.
By expanding genetic testing, refining treatments and ensuring research reflects the full spectrum of Parkinson’s, we can move closer to more precise diagnoses, targeted therapies and better support systems for all.
Victor Dieriks, Research Fellow in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau and Eden Paige Yin, PhD candidate in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Quit Drinking – by Rebecca Dolton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many “quit drinking” books focus on tips you’ve heard already—cut down like this, rearrange your habits like that, make yourself accountable like so, add a reward element this way, etc.
Dolton takes a different approach.
She focuses instead on the underlying processes of addiction, so as to not merely understand them to fight them, but also to use them against the addiction itself.
This is not just a social or behavioral analysis, by the way, and goes into some detail into the physiological factors of the addiction—including such things as the little-talked about relationship between addiction and gut flora. Candida albans, found in most if not all humans to some extent, gets really out of control when given certain kinds of sugars (including those from alcohol); it grows, eventually puts roots through the intestinal walls (ouch!) and the more it grows, the more it demands the sugars it craves, so the more you feed it.
Quite a motivator to not listen to such cravings! It’s not even you that wants it, it’s the Candida!
Anyway, that’s just one example; there are many. The point here is that this is a well-researched, well-written book that sets itself apart from many of its genre.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: