5 Ways To Naturally Boost The “Ozempic Effect”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Jason Fung is perhaps most well-known for his work in functional medicine for reversing diabetes, and he’s once again giving us sound advice about metabolic hormone-hacking with dietary tweaks:
All about incretin
As you may gather from the thumbnail, this video is about incretin, a hormone group (the most well-known of which is GLP-1, as in GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide drugs such as Ozempic, Wegovy, etc) that slows down stomach emptying, which means a gentler blood sugar curve and feeling fuller for longer. It also acts on the hypothalmus, controlling appetite via the brain too (signalling fullness and reducing hunger).
Dr. Fung recommends 5 ways to increase incretin levels:
- Enjoy dietary fat: healthy kinds, please (e.g. nuts, seeds, eggs, etc—not fried foods), but this increases incretin levels more than carbs
- Enjoy protein: again, prompts higher incretin levels of promotes satiety
- Enjoy fiber: this is more about slowing digestion, but when it’s fermented in the gut into short-chain fatty acids, those too increase incretin secretion
- Enjoy bitter foods: these don’t actually affect incretin levels, but they can bind to incretin receptors, making the body “believe” that you got more incretin (think of it like a skeleton key that fits the lock that was designed to be opened by a different key)
- Enjoy turmeric: for its curcumin content, which increases GLP-1 levels specifically
For more information on each of these, here’s Dr. Fung himself:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Semaglutide for Weight Loss?
- Ozempic vs Five Natural Supplements
- How To Prevent And Reverse Type 2 Diabetes ← this was our “Expert Insights” feature on Dr. Fung’s work
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Problem With Sweeteners
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The WHO’s view on sugar-free sweeteners
The WHO has released a report offering guidance regards the use of sugar-free sweeteners as part of a weight-loss effort.
In a nutshell, the guidance is: don’t
- Here’s the report itself: Use of non-sugar sweeteners: WHO guideline
- Here’s the WHO’s own press release about it: WHO advises not to use non-sugar sweeteners for weight control in newly released guideline
- And it was based on this huge systematic review: Health effects of the use of non-sugar sweeteners: a systematic review and meta-analysis
They make for interesting reading, so if you don’t have time now, you might want to just quickly open and bookmark them for later!
Some salient bits and pieces:
Besides that some sweeteners can cause gastro-intestinal problems, a big problem is desensitization:
Because many sugar substitutes are many times (in some cases, hundreds of times) sweeter than sugar, this leads to other sweet foods tasting more bland, causing people to crave sweeter and sweeter foods for the same satisfaction level.
You can imagine how that’s not a spiral that’s good for the health!
The WHO recommendation applies to artificial and naturally-occurring non-sugar sweeteners, including:
- Acesulfame K
- Advantame
- Aspartame
- Cyclamates
- Neotame
- Saccharin
- Stevia
Sucralose and erythritol, by the way, technically are sugars, just not “that kind of sugar” so they didn’t make the list of non-sugar sweeteners.
That said, a recent study did find that erythritol was linked to a higher risk of heart attack, stroke, and early death, so it may not be an amazing sweetener either:
Read: The artificial sweetener erythritol and cardiovascular event risk
Want to know a good way of staying healthy in the context of sweeteners?
Just get used to using less. Your taste buds will adapt, and you’ll get just as much pleasure as before, from progressively less sweetening agent.
Share This Post
-
AI: The Doctor That Never Tires?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
AI: The Doctor That Never Tires?
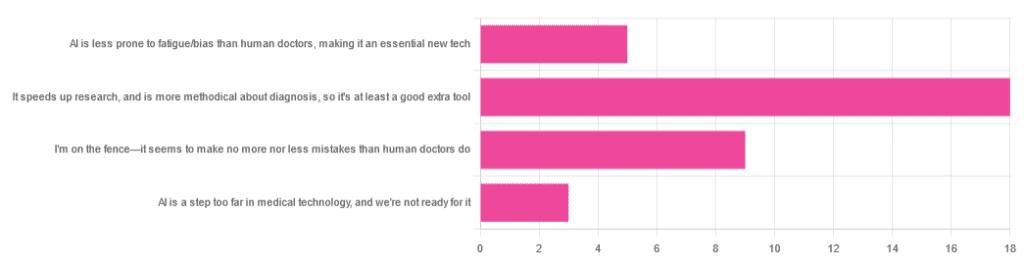
We asked you for your opinion on the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- A little over half of respondents to the poll voted for “It speeds up research, and is more methodical about diagnosis, so it’s at least a good extra tool”
- A quarter of respondents voted for “I’m on the fence—it seems to make no more nor less mistakes than human doctors do”
- A little under a fifth of respondents voted for “AI is less prone to fatigue/bias than human doctors, making it an essential new tech”
- Three respondents voted for “AI is a step too far in medical technology, and we’re not ready for it”
Writer’s note: I’m a professional writer (you’d never have guessed, right?) and, apparently, I really did write “no more nor less mistakes”, despite the correct grammar being “no more nor fewer mistakes”. Now, I know this, and in fact, people getting less/fewer wrong is a pet hate of mine. Nevertheless, I erred.
Yet, now that I’m writing this out in my usual software, and not directly into the poll-generation software, my (AI!) grammar/style-checker is highlighting the error for me.
Now, an AI could not do my job. ChatGPT would try, and fail miserably. But can technology help me do mine better? Absolutely!
And still, I dismiss a lot of the AI’s suggestions, because I know my field and can make informed choices. I don’t follow it blindly, and I think that’s key.
AI is less prone to fatigue/bias than human doctors, making it an essential new tech: True or False?
True—with one caveat.
First, a quick anecdote from a subscriber who selected this option in the poll:
❝As long as it receives the same data inputs as my doctor (ie my entire medical history), I can see it providing a much more personalised service than my human doctor who is always forgetting what I have told him. I’m also concerned that my doctor may be depressed – not an ailment that ought to affect AI! I recently asked my newly qualified doctor goddaughter whether she would prefer to be treated by a human or AI doctor. No contest, she said – she’d go with AI. Her argument was that human doctors leap to conclusions, rather than properly weighing all the evidence – meaning AI, as long as it receives the same inputs, will be much more reliable❞
Now, an anecdote is not data, so what does the science say?
Well… It says the same:
❝Of 6695 responding physicians in active practice, 6586 provided information on the areas of interest: 3574 (54.3%) reported symptoms of burnout, 2163 (32.8%) reported excessive fatigue, and 427 (6.5%) reported recent suicidal ideation, with 255 of 6563 (3.9%) reporting a poor or failing patient safety grade in their primary work area and 691 of 6586 (10.5%) reporting a major medical error in the prior 3 months. Physicians reporting errors were more likely to have symptoms of burnout (77.6% vs 51.5%; P<.001), fatigue (46.6% vs 31.2%; P<.001), and recent suicidal ideation (12.7% vs 5.8%; P<.001).❞
See the damning report for yourself: Physician Burnout, Well-being, and Work Unit Safety Grades in Relationship to Reported Medical Errors
AI, of course, does not suffer from burnout, fatigue, or suicidal ideation.
So, what was the caveat?
The caveat is about bias. Humans are biased, and that goes for medical practitioners just the same. AI’s machine learning is based on source data, and the source data comes from humans, who are biased.
See: Bias and Discrimination in AI: A Cross-Disciplinary Perspective
So, AI can perpetuate human biases and doesn’t have a special extra strength in this regard.
The lack of burnout, fatigue, and suicidal ideation, however, make a big difference.
AI speeds up research, and is more methodical about diagnosis: True or False?
True! AI is getting more and more efficient at this, and as has been pointed out, doesn’t make errors due to fatigue, and often comes to accurate conclusions near-instantaneously. To give just one example:
❝Deep learning algorithms achieved better diagnostic performance than a panel of 11 pathologists participating in a simulation exercise designed to mimic routine pathology workflow; algorithm performance was comparable with an expert pathologist interpreting whole-slide images without time constraints. The area under the curve was 0.994 (best algorithm) vs 0.884 (best pathologist).❞
About that “getting more and more efficient at this”; it’s in the nature of machine learning that every new piece of data improves the neural net being used. So long as it is getting fed new data, which it can process at rate far exceeding humans’ abilities, it will always be constantly improving.
AI makes no more nor
lessfewer mistakes than humans do: True or False?False! AI makes fewer, now. This study is from 2021, and it’s only improved since then:
❝Professionals only came to the same conclusions [as each other] approximately 75 per cent of the time. More importantly, machine learning produced fewer decision-making errors than did all the professionals❞
See: AI can make better clinical decisions than humans: study
All that said, we’re not quite at Star Trek levels of “AI can do a human’s job entirely” just yet:
BMJ | Artificial intelligence versus clinicians: pros and cons
To summarize: medical AI is a powerful tool that:
- Makes healthcare more accessible
- Speeds up diagnosis
- Reduces human error
…and yet, for now at least, still requires human oversights, checks and balances.
Essentially: it’s not really about humans vs machines at all. It’s about humans and machines giving each other information, and catching any mistakes made by the other. That way, humans can make more informed decisions, and still keep a “hand on the wheel”.
Share This Post
-
Strawberries vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing strawberries to cherries, we picked the cherries.
Why?
Both are great, and an argument could be made for either! But here’s our rationale:
In terms of macros, as with most fruits they are both mostly water, and have similar carbs and fiber. Nominally, cherries have the lower glycemic index, so we could call this category nominally a win for cherries, but honestly, they’re both low-GI foods and nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating strawberries, so it’s fairer to consider this category a tie.
Looking at the vitamins, strawberries have more of vitamins C, B9, E, and K, while cherries have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, and choline. Thus, a modest win for cherries here.
When it comes to minerals, strawberries see their day: strawberries have more iron, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus, while cherries have more calcium, copper, and potassium. By the numbers, a win for strawberries.
So far, so tied!
What swings it into cherries’ favor is cherries’ slew of specific phytochemical benefits, including cherry-specific anti-inflammatory properties, sleep-improving abilities, and post-exercise recovery boosts, as well as anti-diabetic benefits above and beyond the normal “this is a fruit” level.
In short, both are very respectable fruits, but cherries have some extra qualities that are just special.
Of course, as ever, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Cherries’ Health Benefits Simply Pop
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Do CBD Gummies Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I take CBD gummies. I don’t know if they are worth buying. Can you find a study on the effectiveness of gummies❞
If you take them, and you’re not sure whether they’re worth it, then it sounds like you’re not getting any observable benefit from them?
If so, that would seem to answer your question, since presumably the reason that you are taking them is for relaxation and/or pain relief, so if you’re not getting the results you want, then no, they are not worth it.
However! CBD gummies are an incredibly diverse and not-well-studied product, so far, given the relative novelty of their legality. By diverse we mean, they’re not well-standardized.
In other words: the CBD gummies you get could be completely unlike CBD gummies from a different source.
CBD itself (i.e. in forms other than just gummies, and mostly as oil) has been studied somewhat better, and we did a main feature on it here:
And while we’re at it:
Cannabis Myths vs Reality ← This one is about cannabis products in general, and includes discussion of THC content and effects, which might not be so relevant to you, but may to some readers.
Companies selling CBD and CBD gummies may make bold claims that are not yet backed by science, so if you are buying them for those reasons, you might want to be aware:
Selling cannabidiol products in Canada: a framing analysis of advertising claims by online retailers
One thing that we would add is that even though CBD is generally recognized as safe, it is possible to overdose on CBD gummies, so do watch your limits:
A Case of Toxicity from Cannabidiol Gummy Ingestion
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Doctor’s Kitchen – by Dr. Rupy Aujla
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve featured Dr. Aujla before as an expert-of-the-week, and now it’s time to review a book by him. What’s his deal, and what should you expect?
Dr. Aujla first outlines the case for food as medicine. Not just “eat nutritionally balanced meals”, but literally, “here are the medicinal properties of these plants”. Think of some of the herbs and spices we’ve featured in our Monday Research Reviews, and add in medicinal properties of cancer-fighting cruciferous vegetables, bananas with dopamine and dopamine precursors, berries full of polyphenols, hemp seeds that fight cognitive decline, and so forth.
Most of the book is given over to recipes. They’re plant-centric, but mostly not vegan. They’re consistent with the Mediterranean diet, but mostly Indian. They’re economically mindful (favoring cheap ingredients where reasonable) while giving a nod to where an extra dollar will elevate the meal. They don’t give calorie values etc—this is a feature not a bug, as Dr. Aujla is of the “positive dieting” camp that advocates for us to “count colors, not calories”. Which, we have to admit, makes for very stress-free cooking, too.
Dr. Aujla is himself an Indian Brit, by the way, which gives him two intersecting factors for having a taste for spices. If you don’t share that taste, just go easier on the pepper etc.
As for the medicinal properties we mentioned up top? Four pages of references at the back, for any who are curious to look up the science of them. We at 10almonds do love references!
Bottom line: if you like tasty food and you’re looking for a one-stop, well-rounded, food-as-medicine cookbook, this one is a top-tier choice.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why ’10almonds’? Newsletter Name Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: Why is your newsletter called 10almonds? Maybe I missed it in the intro email, but my curiosity wants to know the significance. Thanks!”
It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was online… So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a tongue-in-cheek reference to that story… but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: