3 Appetite Suppressants Better Than Ozempic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Annette Bosworth gives her recommendations, and explains why:
What and how
We’ll get straight to it; the recommendations are:
- Coffee, black, unsweetened: not only suppresses the appetite but also boosts the metabolism, increasing fat burn.
- Salt: especially for when fasting (as under such circumstances we may lose salts without replenishing them), a small taste of this can help satisfy taste buds while replenishing sodium and—depending on the salt—other minerals. For example, if you buy “low-sodium salt” in the supermarket, this is generally sodium chloride cut with potassium chloride and/or occasionally magnesium sulfate.
- Ketones (MCT oil): ketones can suppress hunger, particularly when fasting causes blood sugar levels to drop. Supplementing with MCT oil promotes ketone production in the liver, training the body to produce more ketones naturally, thus curbing appetite.
For more on these including the science of them, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Ozempic vs Five Natural Supplements
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
- The Fruit That Can Specifically Reduce Belly Fat
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Lies That Depression Tells Us
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In this short (6:42) video, psychiatrist Dr. Tracey Marks talks about 8 commonly-believed lies that depression often tells us. They are:
- “I don’t measure up”
- “No one cares about me”
- “I’m better off alone”
- “No one understands”
- “It’s all my fault”
- “I have no reason to be depressed”
- “Nothing matters”
- “I’ll never get better”
Some of these can be reinforced by people around us; it’s easy to believe that “no one understands” if for example the few people we interact with the most don’t understand, or that “I have no reason to be depressed” if people try to cheer you up by pointing out your many good fortunes.
The reality, of course, is that depression is a large, complex, and many-headed beast, with firm roots in neurobiology.
There are things we can do that may ameliorate it… But they also may not, and sometimes life is just going to suck for a while. That doesn’t mean we should give up (that, too, is depression lying to us, per “I’ll never get better”), but it does mean that we should not be so hard on ourselves for not having “walked it off” the way one might “just walk off” a broken leg.
Oh, you can’t “just walk off” a broken leg? Well then, perhaps it’s not surprising if we don’t “just think off” a broken brain, either. The brain can rebuild itself, but that’s a slow process, so buckle in:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to know more?
You might like these previous articles of ours about depression (managing it, and overcoming it):
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
- Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
- The Easiest Way To Take Up Journaling
- Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Anise vs Diabetes & Menopause
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What A Daily Gram Of Anise Can Do
Anise, specifically the seed of the plant, also called aniseed, is enjoyed for its licorice taste—as well as its medicinal properties.
Let’s see how well the science lives up to the folk medicine…
What medicinal properties does it claim?
The main contenders are:
- Reduces menopause symptoms
- Reduces blood sugar levels
- Reduces inflammation
Does it reduce menopause symptoms?
At least some of them! Including hot flashes and bone density loss. This seems to be due to the estrogenic-like activity of anethole, the active compound in anise that gives it these effects:
Estrogenic activity of isolated compounds and essential oils of Pimpinella species
1g of anise/day yielded a huge reduction in frequency and severity of hot flashes, compared to placebo*:
*you may be wondering what the placebo is for 1g of a substance that has a very distinctive taste. The researchers used capsules, with 3x330g as the dose, either anise seed or potato starch.
❝In the experimental group, the frequency and severity of hot flashes before the treatment were 4.21% and 56.21% and, after that, were 1.06% and 14.44% at the end of the fourth week respectively. No change was found in the frequency and severity of hot flashes in the control group. The frequency and severity of hot flashes was decreased during 4 weeks of follow up period. P. anisum is effective on the frequency and severity of hot flashes in postmenopausal women. ❞
See for yourself: The Study on the Effects of Pimpinella anisum on Relief and Recurrence of Menopausal Hot Flashes
As for bone mineral density, we couldn’t find a good study for anise, but we did find this one for fennel, which is a plant of the same family and also with the primary active compound anethole:
The Prophylactic Effect of Fennel Essential Oil on Experimental Osteoporosis
That was a rat study, though, so we’d like to see studies done with humans.
Summary on this one: it clearly helps against hot flashes (per the very convincing human study we listed above); it probably helps against bone mineral density loss.
Does it reduce blood sugar levels?
This one got a flurry of attention all so recently, on account of this research review:
Review on Anti-diabetic Research on Two Important Spices: Trachyspermum ammi and Pimpinella anisum
If you read this (and we do recommend reading it! It has a lot more information than we can squeeze in here!) one of the most interesting things about the in vivo anti-diabetic activity of anise was that while it did lower the fasting blood glucose levels, that wasn’t the only effect:
❝Over a course of 60 days, study participants were administered seed powders (5 g/d), which resulted in significant antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and hypolipidemic effects.
Notably, significant reductions in fasting blood glucose levels were observed. This intervention also elicited alterations in the lipid profile, LPO, lipoprotein levels, and the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level.
Moreover, the serum levels of essential antioxidants, such as beta carotene, vitamin C, vitamin A, and vitamin E, which are typically decreased in diabetic patients, underwent a reversal.❞
That’s just one of the studies cited in that review (the comments lightly edited here for brevity), but it stands out, and you can read that study in its entirety (it’s well worth reading).
Rajeshwari et al, bless them, added a “tl;dr” at the top of their already concise abstract; their “tl;dr” reads:
❝Both the seeds significantly influenced almost all the parameters without any detrimental effects by virtue of a number of phytochemicals, vitamins and minerals present in the seeds having therapeutic effects.❞
Shortest answer: yes, yes it does
Does it fight inflammation?
This one’s quick and simple enough: yes it does; it’s full of antioxidants which thus also have an anti-inflammatory effect:
Review of Pharmacological Properties and Chemical Constituents of Pimpinella anisum
…which can also be used an essential oil, applied topically, to fight both pain and the inflammation that causes it—at least in rats and mice:
❝Indomethacin and etodolac were treated reference drugs for the anti-inflammatory activity. Aspirin and morphine hydrochloride were treated reference drugs for the analgesic activity. The results showed that fixed oil of P. anisum has an anti-inflammatory action more than etodolac and this effect was as strong as indomethacin. P. anisum induces analgesic effect comparable to that of 100 mg/kg Aspirin and 10 mg/kg morphine at 30 th min. of the study❞
Summary of this section:
- Aniseeds are a potent source of antioxidants, which fight inflammation.
- Anise essential oil is probably also useful as a topical anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, but we’d like to see human tests to know for sure.
Is it safe?
For most people, enjoyed in moderation (e.g., within the dosage parameters described in the above studies), anise is safe. However:
- If you’re allergic to it, it won’t be safe
- Its estrogen-mimicking effects could cause problems if you have (or have a higher risk factor for) breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or endometriosis.
- For most men, the main concern is that it may lower sperm count.
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, you can buy the seeds in bulk on Amazon, or in case you prefer it, here’s an example of it available as an essential oil.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Brussels Sprouts vs Broccoli – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sprouts to broccoli, we picked the sprouts.
Why?
First let’s note that we have an interesting comparison today, because these two plants are the exact same species (and indeed, also the exact same species as cabbage, cauliflower. and kale)—just a different cultivar. All of these plants and more are simply cultivars of Brassica oleracea.
Them being the same species notwithstanding, there are nutritional differences:
In terms of macros, sprouts have slightly more protein, carbohydrates, and fiber, whereas broccoli has slightly more water weight. An easy win for sprouts here.
In the category of vitamins, sprouts have more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B6, C, E, and K, while broccoli has more of vitamins B2 and B5. Another easy win for sprouts.
When it comes to minerals, sprouts again lead with more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while broccoli has more calcium and selenium.
A note on oxalates: while oxalates are not a problem for most people, it is important to be mindful of them if one has kidney problems. You may know that spinach (a fellow green vegetable high in vitamins and minerals, as well as being a fellow oleracea, albeit of a different genus, so not the same species for once) is high in oxalates, but these two Brassica oleracea we compared today are amongst the lowest in oxalates (source 1 | source 2), making them an ideal way to get vitamins, minerals, and fiber on an oxalate-controlled diet.
Since both are also high in polyphenols, especially kaempferol and quercetin, we’ll mention that sprouts have more lignans while broccoli has more flavonoids. In short: they’re both very good, just different.
As ever, enjoy both! But if you’re going to pick one for total best nutritional density, it’s sprouts.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc ← sprout your Brassica oleracea, too!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Power of Hormones – by Dr. Max Nieuwdorp
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First a quick note on the author: he’s an MD & PhD, internist, endocrinologist, and professor. He knows his stuff.
There are a lot of books with “the new science of” in the title, and they don’t often pertain to science that is actually new, and in this case, for the most part the science contained within this book is quite well-established.
A strength of this book is that it’s not talking about hormones in just one specific aspect (e.g. menopause, pregnancy, etc) but rather, in the full span of human health, across the spectra of ages and sexes—and yes, also covering hormones that are not sex hormones, so for example also demystifying the different happiness-related neurotransmitters, as well as the hormones responsible for hunger and satiety, weight loss and gain, sleep and wakefulness, etc.
Which is all very good, because there’s a lot of overlap and several hormones fall into several categories there.
Moreover, the book covers how your personal cocktail of hormones impacts how you look, feel, behave, and more—there’s a lot about chronic health issues here too, and how to use the information in this book to if not outright cure, then at least ameliorate, many conditions.
Bottom line: this is an information-dense book with a lot of details great and small; if you read this, you’ll come away with a much better understanding of hormones than you had previously!
Click here to check out The Power of Hormones, and harness that power for yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Drug & Supplement Combo That Reverses Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So far, its effects have been dramatic (in a good way) in mice; human trials are now underway.
How does it work?
It builds from previous work, in which a Japanese research team created an “anti-aging vaccine”, that responded to a problem more specific than aging as a whole, namely atherosclerosis.
They found that a certain* protein was upregulated (i.e., it was made at a greater rate resulting in greater quantities) in patients (mouse and human alike) with atherosclerosis. So, they immunized the mice against that protein, and long story short, everything improved for them, from their atherosclerosis to general markers of aging—including growing back fur that had been lost due to age-related balding (just like in humans). They also lived longer, as is to be expected of a mouse who is now biologically younger.
*To avoid being mysterious: it was glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma protein B, known to its friends as GPNMB.
You may be wondering: how can one be immunized against a protein? If so, do bear in mind, a virus is also a protein. In this case, they developed an RNA vaccine, that works in a similar way to the COVID vaccines we all know and love (albeit with a different target).
You can read about this in abundant detail here: Senolytic vaccination improves normal and pathological age-related phenotypes and increases lifespan in progeroid mice
Hot on the heels of that, new approaches were found, including…
The combination
We’ll not keep you waiting; the combination is dasatinib plus quercetin, or else fisetin alone.
It’s about killing senescent (aging) “zombie cells” while sparing healthy cells, which that drug (dasatinib) and those supplements (quercetin and fisetin) do.
The researchers noted:
❝Senescent cells are resistant to apoptosis, which is governed through the upregulation of senescent cell anti-apoptotic pathways (SCAPs). Compounds were subsequently identified that disrupted the SCAPs, inducing death of senescent cells while leaving healthy cells unaffected. Forty-six potential senolytic agents were discovered through this process. To advance translational efforts, the majority of research has focused on agents with known safety profiles and limited off-target effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
The best characterized senolytic agents are dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for use in humans for cancer treatment, and quercetin, a naturally occurring plant flavonoid. The agents have a synergistic effect, making their combination more potent for senescent cell clearance (Zhu et al., 2015). As senescent cells do not divide and accumulate over a period of weeks, they can be administered using an intermittent approach, which further serves to reduce the risk of side effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
In preclinical trials, the combination of dasatinib and quercetin (D + Q) have been found to alleviate numerous chronic medical conditions including vascular stiffness, osteoporosis, frailty, and hepatic stenosis❞
Source: A geroscience motivated approach to treat Alzheimer’s disease: Senolytics move to clinical trials
As to how they expanded on this research:
❝In our study, oral D + Q were intermittently administered to tau transgenic mice with late-stage pathology (approximated to a 70-year-old human with advanced AD) (Musi et al., 2018). The treatment effectively reduced cellular senescence and associated senescence-associated secretory phenotype incidence. The 35 % reduction in neurofibrillary tangles was accompanied by enhanced neuron density, decreased ventricular enlargement, diminished tau accumulation, and restoration of aberrant cerebral blood flow. A subsequent preclinical study validated the findings, reporting that intermittently administered D + Q cleared senescent cells in the central nervous system, reduced amyloid-β plaques, attenuated neuroinflammation, and enhanced cognition❞
Source: Ibid.
And now taking it to humans:
❝The first clinical trial of D + Q for early-stage Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) has completed enrollment (Gonzales et al., 2021). The primary aim of the open-label pilot study was to examine the central nervous system penetrance of D and Q in a small sample of older adults with early-stage AD (NCT04063124). In addition, two placebo-controlled trials of D + Q for neurodegenerative disease are underway (NCT04685590 and NCT04785300).
One of the trials in development is a multi-site, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of senolytic therapy in older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or early-stage dementia (Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) Global 0.5–1) due to AD (elevated CSF total tau/Aβ42 ratio).
The treatment regimen will consist of 12-weeks of intermittently administered oral D + Q.❞
Source: Ibid.
The study is actually completed now, but its results are not yet published (again, at time of writing). Which means: they have the data, and now they’re writing the paper.
We look forward to providing an update about that, when the paper is published!
In the meantime…
Dasatinib is a drug usually prescribed to people with certain kinds of leukemia, and suffice it to say, it’s prescription-only. And unlike drugs that are often prescribed off-label (such as metformin for weight loss), getting your doctor to prescribe you an anticancer drug is unlikely unless you have the cancer in question.
You may be wondering: how is an anticancer drug helpful against aging? And the answer is that cancer and aging are very interrelated, and both have to do with “these old cells just won’t die, and are using the resources needed for young healthy cells”. So in both cases, killing those “zombie cells” while sparing healthy ones, is what’s needed. However, your doctor will probably not buy that as a reason to prescribe you a drug that is technically chemotherapy.
Quercetin, on the other hand, is a readily-available supplement, as is fisetin, and both have glowing (in a good way) safety profiles.
Want to know more?
You can read more about each of quercetin and fisetin (including how to get them), here:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
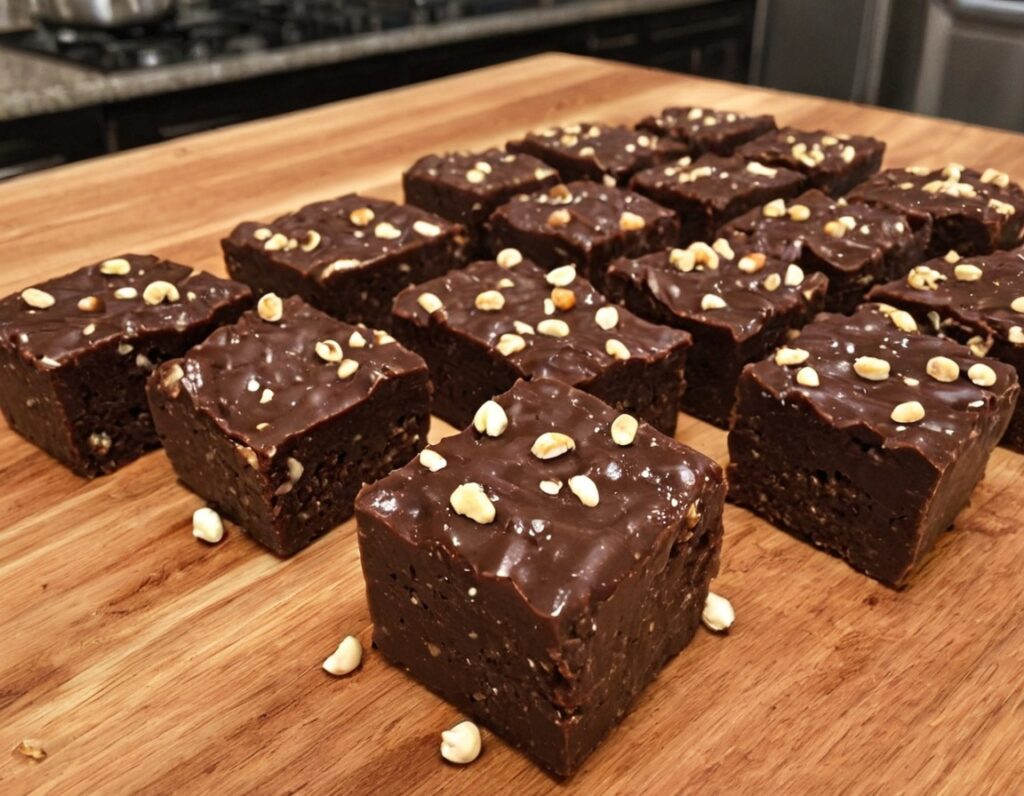
Healthy Chocolate Fudge Energy Bites
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While these are quite high-calorie, they’re also high in protein, and the fiber and healthy fats flatten the blood sugar curve:
You will need
- 1 cup peanut butter
- 4 oz dark chocolate, melted (try to get dark chocolate with >80% cocoa, if you can; 85% is very respectable and 90% is perfect)
- ⅓ cup maple syrup (you can safely reduce this, or even omit it, if you prefer less sweetness)
- ¼ cup hazelnuts
- ¼ cup almond milk (or your preferred milk, but we recommend almond for taste and health)
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- Topping: ¼ cup hazelnuts, roughly chopped
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine all the ingredients (except the topping) in a food processor, and blend until smooth.
2) Line a container (5″x7″ is a good size) with baking paper and spread the mixture evenly into it, pressing down gently.
3) Sprinkle the topping onto it, press that even more gently into it.
4) Refrigerate overnight (or chill it for 2hrs in the freezer).
5) Cut into cubes to serve; they can be served frozen or thawed, per your preference:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eating For Energy (In Ways That Actually Work)
- “Let Them Eat Cake”, She Said…
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Plant-Based Milks—What’s Best?
- Chocolate & Health: Fact or Fiction?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: