Whole – by Dr. T. Colin Campbell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us have at least a broad idea of what we’re supposed to be eating, what nutrients we should be getting. Many of us look at labels, and try to get our daily dose of this and that and the other.
And what we don’t get from food? There are supplements.
Dr. Campbell thinks we can do better:
Perhaps most critical in this book, where it stands out from others (we may already know, for example, that we should try to eat diverse plants and whole foods) is its treatment of why many supplements aren’t helpful.
We tend to hear “supplements are a waste of money” and sometimes they are, sometimes they aren’t. How to know the difference?
Key: things directly made from whole food sources will tend to be better. Seems reasonable, but… why? The answer lies in what else those foods contain. An apple may contain a small amount of vitamin C, less than a vitamin C tablet, but also contains a whole host of other things—tiny phytonutrients, whose machinations are mostly still mysteries to us—that go with that vitamin C and help it work much better. Lab-made supplements won’t have those.
There’s a lot more to the book… A chunk of which is a damning critique of the US healthcare system (the author argues it would be better named a sicknesscare system). We also learn about getting a good balance of macro- and micronutrients from our diet rather than having to supplement so much.
The style is conversational, while not skimping on the science. The author has had more than 150 papers published in peer-reviewed journals, and is no stranger to the relevant academia. Here, however, he focuses on making things easily comprehensible to the lay reader.
In short: if you’ve ever wondered how you’re doing at getting a good nutritional profile, and how you could do better, this is definitely the book for you.
Click here to check out “Whole” on Amazon today, and level up your daily diet!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
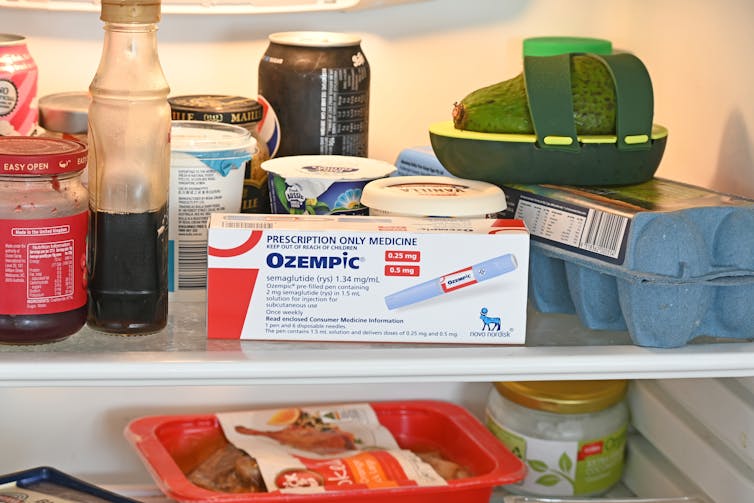
People on Ozempic may have fewer heart attacks, strokes and addictions – but more nausea, vomiting and stomach pain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ozempic and Wegovy are increasingly available in Australia and worldwide to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity.
The dramatic effects of these drugs, known as GLP-1s, on weight loss have sparked huge public interest in this new treatment option.
However, the risks and benefits are still being actively studied.
In a new study in Nature Medicine, researchers from the United States reviewed health data from about 2.4 million people who have type 2 diabetes, including around 216,000 people who used a GLP-1 drug, between 2017 and 2023.
The researchers compared a range of health outcomes when GLP-1s were added to a person’s treatment plan, versus managing their diabetes in other ways, often using glucose-lowering medications.
Overall, they found people who used GLP-1s were less likely to experience 42 health conditions or adverse health events – but more likely to face 19 others.
myskin/Shutterstock What conditions were less common?
Cardiometabolic conditions
GLP-1 use was associated with fewer serious cardiovascular and coagulation disorders. This includes deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, stroke, cardiac arrest, heart failure and myocardial infarction.
Neurological and psychiatric conditions
GLP-1 use was associated with fewer reported substance use disorders or addictions, psychotic disorders and seizures.
Infectious conditions
GLP-1 use was associated with fewer bacterial infections and pneumonia.
What conditions were more common?
Gastrointestinal conditions
Consistent with prior studies, GLP-1 use was associated with gastrointestinal conditions such as nausea, vomiting, gastritis, diverticulitis and abdominal pain.
Other adverse effects
Increased risks were seen for conditions such as low blood pressure, syncope (fainting) and arthritis.
People who took Ozempic were more likely to experience stomach upsets than those who used other type 2 diabetes treatments. Douglas Cliff/Shutterstock How robust is this study?
The study used a large and reputable dataset from the US Department of Veterans Affairs. It’s an observational study, meaning the researchers tracked health outcomes over time without changing anyone’s treatment plan.
A strength of the study is it captures data from more than 2.4 million people across more than six years. This is much longer than what is typically feasible in an intervention study.
Observational studies like this are also thought to be more reflective of the “real world”, because participants aren’t asked to follow instructions to change their behaviour in unnatural or forced ways, as they are in intervention studies.
However, this study cannot say for sure that GLP-1 use was the cause of the change in risk of different health outcomes. Such conclusions can only be confidently made from tightly controlled intervention studies, where researchers actively change or control the treatment or behaviour.
The authors note the data used in this study comes from predominantly older, white men so the findings may not apply to other groups.
Also, the large number of participants means that even very small effects can be detected, but they might not actually make a real difference in overall population health.
Observational studies track outcomes over time, but can’t say what caused the changes. Jacob Lund/Shutterstock Other possible reasons for these links
Beyond the effect of GLP-1 in the body, other factors may explain some of the findings in this study. For example, it’s possible that:
- people who used GLP-1 could be more informed about treatment options and more motivated to manage their own health
- people who used GLP-1 may have received it because their health-care team were motivated to offer the latest treatment options, which could lead to better care in other areas that impact the risk of various health outcomes
- people who used GLP-1 may have been able to do so because they lived in metropolitan centres and could afford the medication, as well as other health-promoting services and products, such as gyms, mental health care, or healthy food delivery services.
Did the authors have any conflicts of interest?
Two of the study’s authors declared they were “uncompensated consultants” for Pfizer, a global pharmaceutical company known for developing a wide range of medicines and vaccines. While Pfizer does not currently make readily available GLP-1s such as Ozempic or Wegovy, they are attempting to develop their own GLP-1s, so may benefit from greater demand for these drugs.
This research was funded by the US Department of Veterans Affairs, a government agency that provides a wide range of services to military veterans.
No other competing interests were reported.
Diabetes vs weight-loss treatments
Overall, this study shows people with type 2 diabetes using GLP-1 medication generally have more positive health outcomes than negative health outcomes.
However, the study didn’t include people without type 2 diabetes. More research is needed to understand the effects of these medications in people without diabetes who are using them for other reasons, including weight loss.
While the findings highlight the therapeutic benefits of GLP-1 medications, they also raise important questions about how to manage the potential risks for those who choose to use this medication.
The findings of this study can help many people, including:
- policymakers looking at ways to make GLP-1 medications more widely available for people with various health conditions
- health professionals who have regular discussions with patients considering GLP-1 use
- individuals considering whether a GLP-1 medication is right for them.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Shoulders Range – by Elia Bartolini
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Shoulder flexibility and mobility can be a big deal, especially when it starts to decline—more so than other kinds of flexibility. Most seniors can get through the day without doing the splits against a wall, for example, but shoulder tightness can be more of a problem if you can’t easily get into or out of your clothes.
If you think it couldn’t happen to you: the great Jane Fonda has a now-famous photoset of her looking glamorous in a dress at a red carpet event, and then looking frazzled making breakfast in the same dress in her kitchen the next morning, because, as she wrote, “I couldn’t get my dress unzipped so I slept in it”.
Now, “to avoid ending up like Jane Fonda” is not a series of words that usually precedes advice, but in this case: this book delves into the science of one of the most quirky joints of the human body, and how to leverage this to maximize shoulder mobility, while maintaining adequate strength (because flexibility without strength is just asking for a dislocation) without doing anything that would actually bulk up our shoulders, because it’s just about progressing through passive, active, and tensed stretching, static, dynamic, and loaded stretching, as well as PNF stretching and antagonist stretching.
If that seems like a lot of stretching, don’t worry; the author presents a series of workouts that will take us through these stretches in a very small amount of time each day.
The style is instructional like a textbook, with clear diagrams where appropriate, and lots of callout boxes, bullet points, emboldening for key points, etc. It all makes for every easy learning.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve and maintain your shoulder mobility, this is an excellent book for that.
Click here to check out Shoulders Range, and perfect your shoulders and upper body flexibility!
Share This Post
-
Does PRP Work For Hair Loss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Ankit Gupta takes us through the details of this hair loss remedy for androgenic alopecia.
The bald truth
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is a controversial treatment for androgenic hair loss.
What it involves: blood is drawn and separated using a centrifuge. PRP—including growth proteins and hormones—is extracted from the blood; about 30 ml of blood is needed to produce 5 ml of PRP. This is then injected directly into the scalp. As this can be painful, local anaesthetic is sometimes used first. This usually involves monthly sessions for the first 3 months, then booster sessions every 3–6 months thereafter.
Does it work? Research is young; so far 60% of trials have found it worked; 40% found it didn’t. When it works, effectiveness (in terms of hair restoration) is considered to be between 25–43%. Results are inconsistent and seem to vary from person to person.
In short, this doctor’s recommendation is to consider it after already having tried standard treatments such as finasteride and/or minoxidil, as they are more likely to work and don’t involve such exciting procedures as injecting your own blood extracts back into your head.
For more on all of this, plus links to the 13 papers cited, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Hair-Loss Remedies, By Science
- Hair Growth: Caffeine and Minoxidil Strategies
- Gentler Hair Health Options
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Get Better Sleep: Beyond The Basics
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First though, for the sake of being methodical, let’s quickly note the basics:
- Aim for 7–9 hours per night
- Set a regular bedtime and (equally important!) regular getting-up time
- Have a 2-hour wind-down period before bed, to decompress from any stresses of the day
- Minimal device/screen usage before bed
- Abstain from stimulants for as long before bed as reasonably possible (caffeine elimination halflife is 4–8 hours depending on your genes, call it 6 hours average to eliminate half (not the whole lot), and you’ll see it’s probably best to put a cap on it earlier rather than later).
- Abstain from alcohol, ideally entirely, but allow at least 1hr/unit before bed. So for example, 1hr for a 1oz single shot of spirits, or 2–3 hours for a glass of wine (depending on size), or 3–4 hours for a martini (depending on recipe). Not that that is not the elimination time, nor even the elimination halflife of alcohol, it’s just a “give your body a chance at least” calculation. If you like to have a drink to relax before bed, then well, only you can decide what you like more: that or actually getting restorative sleep.
- Consider a warm bath/shower before bed, if that suits your schedule.
- Wash and change your bedsheets more often than seems necessary. Or if that’s too onerous, at least change the pillowcases more often, which makes quite a difference already.
- Lower the temperature of your bedroom shortly before bedtime; this will help cue the body to produce melatonin
- Make your bedroom as dark as reasonably possible. Invest in blackout blinds/curtains, and remove any pesky electronics, or at least cover their little LEDs if it’s something that reasonably needs to remain on.
Ok, now, onwards…
Those 7–9 hours? Yes, it goes for you too.
A lot of people mistake getting 6 hours sleep per night for only needing 6 hours sleep per night. Sure, you may still be alive after regularly getting 6 hours, but (unless you have a rare mutation of the ADRB1 gene) it will be causing harm, and yes, that includes later in life; we don’t stop needing so much sleep, even stop getting it:
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
With this in mind, it becomes important to…
Prioritize your sleep—which means planning for it!
When does your bedtime routine start? According to sleep scientist Dr. Lisa Matricciani, it starts before breakfast. This is because the things we do earlier in the day can greatly affect the amount (and quality) of sleep we get later. For example, a morning moderate-to-intense exercise session greatly improves sleep at night:
Planning Ahead For Better Sleep
As for quality, that is as important as quantity, and it’s not just about “soundness” of sleep:
The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
“What gets measured, gets done” goes for sleep too
Sleep-deprived people usually underestimate how sleep-deprived they are. This is for the same reason as why drunk people usually underestimate how drunk they are—to put it in words that go for both situations: a cognitively impaired person lacks the cognitive function to realize how cognitively impaired they are.
Here’s the science on that, by the way:
How Sleep-Deprived Are You, Really?
For that reason, we recommend using sleep-tracking software (there are many apps for that) on your phone or, ideally, a wearable device (such as a smartwatch or similar).
A benefit of doing so is that we don’t think “well, I slept from 10pm to 6am, so that’s 8 hours”, if our device tells us we slept between 10:43pm and 5:56 am with 74% sleep efficiency because we woke up many times.
As an aside, sleep efficiency should be about 85%, by the way. Why not 100%, you ask? It’s because if your body is truly out like a light for the entire night, something is wrong (either you were very sleep-deprived, or you have been drugged, that kind of thing). See also:
An unbroken night’s sleep is a myth. Here’s what good sleep looks like.
So waking up during the night is normal, and nothing to worry about per se. If you do find trouble getting back to sleep, though:
How to Fall Back Asleep After Waking Up in the Middle of the Night
Be careful about how you try to supplement sleep
This goes both for taking substances of various kinds, and napping. Some sleep aids can help, but many are harmful and/or do not really work as such; here’s a rundown of examples of those:
Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors?
And when it comes to napping, timing is everything:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
Want to know a lot more?
This is the book on sleep:
Why We Sleep – by Dr. Matthew Walker
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between vegan and vegetarian?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
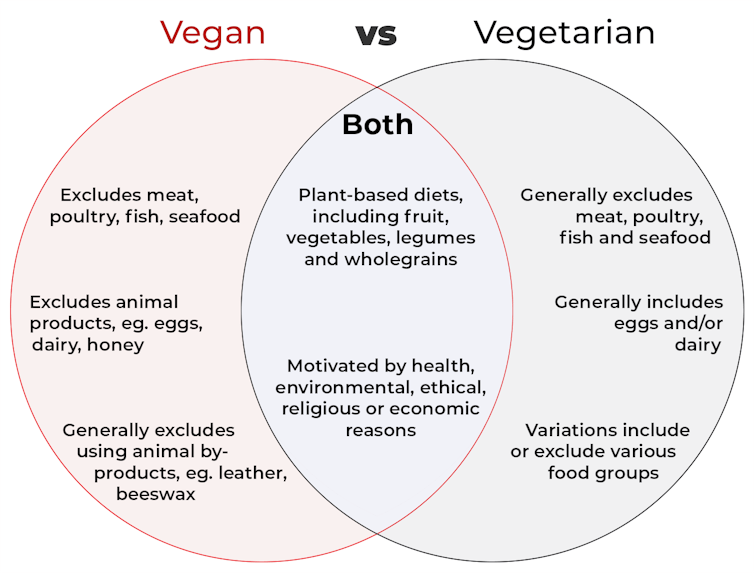
Vegan and vegetarian diets are plant-based diets. Both include plant foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains.
But there are important differences, and knowing what you can and can’t eat when it comes to a vegan and vegetarian diet can be confusing.
So, what’s the main difference?
Creative Cat Studio/Shutterstock What’s a vegan diet?
A vegan diet is an entirely plant-based diet. It doesn’t include any meat and animal products. So, no meat, poultry, fish, seafood, eggs, dairy or honey.
What’s a vegetarian diet?
A vegetarian diet is a plant-based diet that generally excludes meat, poultry, fish and seafood, but can include animal products. So, unlike a vegan diet, a vegetarian diet can include eggs, dairy and honey.
But you may be wondering why you’ve heard of vegetarians who eat fish, vegetarians who don’t eat eggs, vegetarians who don’t eat dairy, and even vegetarians who eat some meat. Well, it’s because there are variations on a vegetarian diet:
- a lacto-ovo vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, fish and seafood, but includes eggs, dairy and honey
- an ovo-vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, fish, seafood and dairy, but includes eggs and honey
- a lacto-vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, fish, seafood and eggs, but includes dairy and honey
- a pescatarian diet excludes meat and poultry, but includes eggs, dairy, honey, fish and seafood
- a flexitarian, or semi-vegetarian diet, includes eggs, dairy and honey and may include small amounts of meat, poultry, fish and seafood.
Are these diets healthy?
A 2023 review looked at the health effects of vegetarian and vegan diets from two types of study.
Observational studies followed people over the years to see how their diets were linked to their health. In these studies, eating a vegetarian diet was associated with a lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or a stroke), diabetes, hypertension (high blood pressure), dementia and cancer.
For example, in a study of 44,561 participants, the risk of heart disease was 32% lower in vegetarians than non-vegetarians after an average follow-up of nearly 12 years.
Further evidence came from randomised controlled trials. These instruct study participants to eat a specific diet for a specific period of time and monitor their health throughout. These studies showed eating a vegetarian or vegan diet led to reductions in weight, blood pressure, and levels of unhealthy cholesterol.
For example, one analysis combined data from seven randomised controlled trials. This so-called meta-analysis included data from 311 participants. It showed eating a vegetarian diet was associated with a systolic blood pressure (the first number in your blood pressure reading) an average 5 mmHg lower compared with non-vegetarian diets.
It seems vegetarian diets are more likely to be healthier, across a number of measures.
For example, a 2022 meta-analysis combined the results of several observational studies. It concluded a vegetarian diet, rather than vegan diet, was recommended to prevent heart disease.
There is also evidence vegans are more likely to have bone fractures than vegetarians. This could be partly due to a lower body-mass index and a lower intake of nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D and protein.
But it can be about more than just food
Many vegans, where possible, do not use products that directly or indirectly involve using animals.
So vegans would not wear leather, wool or silk clothing, for example. And they would not use soaps or candles made from beeswax, or use products tested on animals.
The motivation for following a vegan or vegetarian diet can vary from person to person. Common motivations include health, environmental, ethical, religious or economic reasons.
And for many people who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet, this forms a central part of their identity.
More than a diet: veganism can form part of someone’s identity. Shutterstock So, should I adopt a vegan or vegetarian diet?
If you are thinking about a vegan or vegetarian diet, here are some things to consider:
- eating more plant foods does not automatically mean you are eating a healthier diet. Hot chips, biscuits and soft drinks can all be vegan or vegetarian foods. And many plant-based alternatives, such as plant-based sausages, can be high in added salt
- meeting the nutrient intake targets for vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and iodine requires more careful planning while on a vegan or vegetarian diet. This is because meat, seafood and animal products are good sources of these vitamins and minerals
- eating a plant-based diet doesn’t necessarily mean excluding all meat and animal products. A healthy flexitarian diet prioritises eating more whole plant-foods, such as vegetables and beans, and less processed meat, such as bacon and sausages
- the Australian Dietary Guidelines recommend eating a wide variety of foods from the five food groups (fruit, vegetables, cereals, lean meat and/or their alternatives and reduced-fat dairy products and/or their alternatives). So if you are eating animal products, choose lean, reduced-fat meats and dairy products and limit processed meats.
Katherine Livingstone, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow and Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does This Practice Really Hold A Candle To Evidence-Based Medicine?
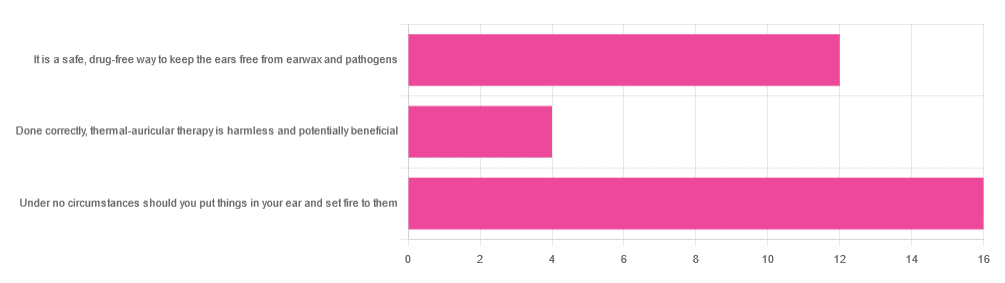
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion of ear candling, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- Exactly 50% said “Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them”
- About 38% said “It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens”
- About 13% said “Done correctly, thermal-auricular therapy is harmless and potentially beneficial”
This means that if we add the two positive-to-candling answers together, it’s a perfect 50:50 split between “do it” and “don’t do it”.
(Yes, 38%+13%=51%, but that’s because we round to the nearest integer in these reports, and more precisely it was 37.5% and 12.5%)
So, with the vote split, what does the science say?
First, a quick bit of background: nobody seems keen to admit to having invented this. One of the major manufacturers of ear candles refers to them as “Hopi” candles, which the actual Hopi tribe has spent a long time asking them not to do, as it is not and never has been used by the Hopi people. Other proposed origins offered by advocates of ear candling include Traditional Chinese Medicine (not used), Ancient Egypt (no evidence of such whatsoever), and Atlantis:
Quackwatch | Why Ear Candling Is Not A Good Idea
It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens: True or False?
False! In a lot of cases of alternative therapy claims, there’s an absence of evidence that doesn’t necessarily disprove the treatment. In this case, however, it’s not even an open matter; its claims have been actively disproven by experimentation:
- It doesn’t remove earwax; on the contrary, experimentation “showed no removal of cerumen from the external auditory canal. Candle wax was actually deposited in some“
- It doesn’t remove pathogens, and the proposed mechanism of action for removing pathogens, that of the “chimney effect”: the idea that the burning candle creates a vacuum that draws wax out of the ear along with debris and bacteria, simply does not work; on the contrary, “Tympanometric measurements in an ear canal model demonstrated that ear candles do not produce negative pressure”.
- It isn’t safe; on the contrary, “Ear candles have no benefit in the management of cerumen and may result in serious injury”
In a medium-sized survey (n=122), the following injuries were reported:
- 13 x burns
- 7 x occlusion of the ear canal
- 6 x temporary hearing loss
- 3 x otitis externa (this also called “swimmer’s ear”, and is an inflammation of the ear, accompanied by pain and swelling)
- 1 x tympanic membrane perforation
Indeed, authors of one paper concluded:
❝Ear candling appears to be popular and is heavily advertised with claims that could seem scientific to lay people. However, its claimed mechanism of action has not been verified, no positive clinical effect has been reliably recorded, and it is associated with considerable risk.
No evidence suggests that ear candling is an effective treatment for any condition. On this basis, we believe it can do more harm than good and we recommend that GPs discourage its use❞
Source: Canadian Family Physician | Ear Candling
Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them: True or False?
True! It’s generally considered good advice to not put objects in general in your ears.
Inserting flaming objects is a definite no-no. Please leave that for the Cirque du Soleil.
You may be thinking, “but I have done this and suffered no ill effects”, which seems reasonable, but is an example of survivorship bias in action—it doesn’t make the thing in question any safer, it just means you were one of the one of the ones who got away unscathed.
If you’re wondering what to do instead… Ear oils can help with the removal of earwax (if you don’t want to go get it sucked out at a clinic—the industry standard is to use a suction device, which actually does what ear candles claim to do). For information on safely getting rid of earwax, see our previous article:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: