Which gut drugs might end up in a lawsuit? Are there really links with cancer and kidney disease? Should I stop taking them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Common medicines used to treat conditions including heartburn, reflux, indigestion and stomach ulcers may be the subject of a class action lawsuit in Australia.
Lawyers are exploring whether long-term use of these over-the-counter and prescription drugs are linked to stomach cancer or kidney disease.
The potential class action follows the settlement of a related multi-million dollar lawsuit in the United States. Last year, international pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca settled for US$425 million (A$637 million) after patients made the case that two of its drugs caused significant and potentially life-threatening side effects.
Specifically, patients claimed the company’s drugs Nexium (esomeprazole) and Prilosec (omeprazole) increased the risk of kidney damage.

Which drugs are involved in Australia?
The class of drugs we’re talking about are “proton pump inhibitors” (sometimes called PPIs). In the case of the Australian potential class action, lawyers are investigating:
- Nexium (esomeprazole)
- Losec, Asimax (omeprazole)
- Somac (pantoprazole)
- Pariet (rabeprazole)
- Zoton (lansoprazole).
Depending on their strength and quantity, these medicines are available over-the-counter in pharmacies or by prescription.
They have been available in Australia for more than 20 years and are in the top ten medicines dispensed through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme.
They are used to treat conditions exacerbated by stomach acid. These include heartburn, gastric reflux and indigestion. They work by blocking the protein responsible for pumping acid into the stomach.
These drugs are also prescribed with antibiotics to treat the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which causes stomach ulcers and stomach cancer.
What do we know about the risks?
Appropriate use of proton pump inhibitors plays an important role in treating several serious digestive problems. Like all medicines, there are risks associated with their use depending on how much and how long they are used.
When proton pump inhibitors are used appropriately for the short-term treatment of stomach problems, they are generally well tolerated, safe and effective.
Their risks are mostly associated with long-term use (using them for more than a year) due to the negative effects from having reduced levels of stomach acid. In elderly people, these include an increased risk of gut and respiratory tract infections, nutrient deficiencies and fractures. Long-term use of these drugs in elderly people has also been associated with an increased risk of dementia.
In children, there is an increased risk of serious infection associated with using these drugs, regardless of how long they are used.
How about the cancer and kidney risk?
Currently, the Australian consumer medicine information sheets that come with the medicines, like this one for esomeprazole, do not list stomach cancer or kidney injury as a risk associated with using proton pump inhibitors.
So what does the evidence say about the risk?
Over the past few years, there have been large studies based on observing people in the general population who have used proton pump inhibitors. These studies have found people who take them are almost two times more likely to develop stomach cancer and 1.7 times more likely to develop chronic kidney disease when compared with people who are not taking them.
In particular, these studies report that users of the drugs lansoprazole and pantoprazole have about a three to four times higher risk than non-users of developing chronic kidney disease.
While these observational studies show a link between using the drugs and these outcomes, we cannot say from this evidence that one causes the other.
What can I do if I’m worried?
Several digestive conditions, especially reflux and heartburn, may benefit from simple dietary and lifestyle changes. But the overall evidence for these is not strong and how well they work varies between individuals.
But it may help to avoid large meals within two to three hours before bed, and reduce your intake of fatty food, alcohol and coffee. Eating slowly and getting your weight down if you are overweight may also help your symptoms.
There are also medications other than proton pump inhibitors that can be used for heartburn, reflux and stomach ulcers.
These include over-the-counter antacids (such as Gaviscon and Mylanta), which work by neutralising the acidic environment of the stomach.
Alternatives for prescription drugs include nizatidine and famotidine. These work by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach, which decreases stomach acid production.
If you are concerned about your use of proton pump inhibitors it is important to speak with your doctor or pharmacist before you stop using them. That’s because when you have been using them for a while, stopping them may result in increased or “rebound” acid production.
Nial Wheate, Professor and Director – Academic Excellence, Macquarie University; Joanna Harnett, Senior Lecturer – Sydney Pharmacy School, Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Sydney, and Wai-Jo Jocelin Chan, Pharmacist and Associate Lecturer, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Teas To Drink Before Bed (By Science!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Which Sleepy Tea?
Herbal “tea” preparations (henceforth we will write it without the quotation marks, although these are not true teas) are popular for winding down at the end of a long day ready for a relaxing sleep.
Today we’ll look at the science for them! We’ll be brief for each, because we’ve selected five and have only so much room, but here goes:
Camomile
Simply put, it works and has plenty of good science for it. Here’s just one example:
❝Noteworthy, our meta-analysis showed a significant improvement in sleep quality after chamomile administration❞
Also this writer’s favourite relaxation drink!
(example on Amazon if you want some)
Lavender
We didn’t find robust science for its popularly-claimed sedative properties, but it does appear to be anxiolytic, and anxiety gets in the way of sleep, so while lavender may not be a sedative, it may calm a racing mind all the same, thus facilitating better sleep:
(example on Amazon if you want some)
Magnolia
Animal study for the mechanism:
Human study for “it is observed to help humans sleep better”:
As you can see from the title, its sedative properties weren’t the point of the study, but if you click through to read it, you can see that they found (and recorded) this benefit anyway
(example on Amazon if you want some)
Passionflower
There’s not a lot of evidence for this one, but there is some. Here’s a small study (n=41) that found:
❝Of six sleep-diary measures analysed, sleep quality showed a significantly better rating for passionflower compared with placebo (t(40) = 2.70, p < 0.01). These initial findings suggest that the consumption of a low dose of Passiflora incarnata, in the form of tea, yields short-term subjective sleep benefits for healthy adults with mild fluctuations in sleep quality.❞
So, that’s not exactly a huge body of evidence, but it is promising.
(example on Amazon if you want some)
Valerian
We’ll be honest, the science for this one is sloppy. It’s very rare to find Valerian tested by itself (or sold by itself; we had to dig a bit to find one for the Amazon link below), and that skews the results of science and renders any conclusions questionable.
And the studies that were done? Dubious methods, and inconclusive results:
Nevertheless, if you want to try it for yourself, you can do a case study (i.e., n=1 sample) if not a randomized controlled trial, and let us know how it goes 🙂
(example on Amazon if you want some)
Summary
- Valerian we really don’t have the science to say anything about it
- Passionflower has some nascent science for it, but not much
- Lavender is probably not soporific, but it is anxiolytic
- Magnolia almost certainly helps, but isn’t nearly so well-backed as…
- Camomile comes out on top, easily—by both sheer weight of evidence, and by clear conclusive uncontroversial results.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Alzheimer’s Gut-Brain Connection—Caught On X-Ray!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about Alzheimer’s disease (a lot), and if you’re just joining us, then a great place to start is here:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
We’ve also written about gut health (a lot), and if you’re just joining us, then a great place to start is here:
Make Friends With Your Gut! (Here’s Why & How)
And as a hat trick, yes, we’ve also written (admittedly not as much) about the gut-brain connection; here’s a primer:
The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
Because of how gut microbes influence brain function, behavior, and cognition, scientists wondered whether one’s microbiome might play a role in Alzheimer’s development. Recently, scientists from Italy’s Institute of Nanotechnology, working with the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF), found some concrete answers:
How gut health affects Alzheimer’s
When the gut loses its healthy balance of bacteria, harmful bacteria (and fungi, like C. albicans, also popularly called by its first name, “Candida”) take the wheel. This problem (called “dysbiosis”) allows harmful microbes to produce toxic substances, leading to inflammation and weakening the protective barriers between the gut and brain.
In some cases, like the aforementioned C. albicans, they’ll even put roots through your gut wall (and interact with your nervous system, and they are a common reason for sugar and alcohol cravings—your CNS has literally been hacked by a fungal colony that wants sugar (including the sugar that occurs when alcohol is broken down—and that’s without considering the fact that alcohol also kills several of C. albicans competitors that rank amongst the “good bacteria”). Suffice it to say, the holes it puts in your gut wall aren’t great for the health either.
In any case, once the gut barrier is breached, it’s been hypothesized that harmful bacteria may even travel to the brain, triggering Alzheimer’s.
How the x-rays helped
To better understand gut changes in Alzheimer’s, scientists used a technique called nano- and micro- x-ray phase-contrast tomography (XPCT) at the aforementioned ESRF. That very fancy string of words refers to a commensurately powerful imaging method, which allows researchers to see detailed structures inside the gut without damaging tissue, or even adding contrast agents (like those unpleasant drinks that are sometimes required to be taken before soft-tissue x-rays).
The study examined gut samples from mice with Alzheimer’s (so yes, this does need to be repeated with humans, but in this case there’s no obvious reason why it shouldn’t be the same).
The scans revealed important changes in gut structures, including:
- The tiny finger-like villi and corresponding crypts in the gut lining
- Important cells* that help with digestion and protection
- Neurons involved in gut function
*e.g. Paneth cells, goblet cells, telocytes, and erythrocytes, all of whom would take more explanation than we have room for here, but suffice it to say they’re important to both digestion and correct mucus production (bearing in mind, mucus membranes are one of the main physical barriers to harmful bacteria—as humans, our conscious interactions with mucus are usually only the nuisance that occurs when we get a cold or something, but rest assured, mucus keeps us alive).
In short, all these findings suggest (we’d say “show”, but technically cause and effect have not been proven) gut health indeed plays a crucial role in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and pathology (i.e., how the disease begins and progresses, respectively).
Why it matters
To quote Dr. Alessia Cedola,
❝This technique represents a real breakthrough for the thorough analysis of the gut, and it could be pivotal in early detection and prognosis of the disease.
By gaining a deeper understanding of these processes, we hope to identify new therapeutic targets and develop innovative treatments for this devastating disease.❞
In short: the technology can be used as a super-early diagnostic tool, and ultimately, improve prevention (by encouraging people to focus on gut health) as well as, hopefully, leading to new treatments, too.
Want to see it?
Here’s the paper itself, where there are also abundant very clear images:
Are you on top of your gut health already?
If not, do refer back to that first link we dropped about gut health, up top!
If you are already sure you’re looking after your gut and want to do something else to avoid Alzheimer’s coming to call, you might want to consider:
How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer) ← your glymphatic system, something many people neglect, is the brain’s cleanup crew, and removes things like the beta-amyloid proteins that are implicated in Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. So, it’s worth knowing how to keep it in working order!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
10 Healthiest Foods You Should Eat In The Morning
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For many of us, our creative minds aren’t their absolute best first thing in the morning, and it’s easy to reach for what’s available, if we haven’t planned ahead.
So here’s some inspiration for the coming week! If you’re a regular coffee-and-toast person, at least consider alternating some of these with that:
- Oatmeal with fresh fruit: fiber, energy, protein, vitamins and minerals (10almonds tip: we recommend making it as overnight oats! Same nutrients, lower glycemic index)
- Greek yogurt parfait: probiotic gut benefits, along with all the goodness of fruit
- Avocado toast: so many nutrients; most famous for the healthy fats, but there’s lots more in there too!
- Egg + vegetable scramble: protein, healthy fats, vitamins and minerals, fiber
- Smoothie bowl: many nutrients—But be aware that blending will reduce fiber and make the sugar quicker to enter your bloodstream. Still not bad as an occasional feature for the sake of variety, though!
- Wholegrain pancakes: energy, fiber, and whatever your toppings! Fresh fruit is a top-tier choice; the video suggests maple syrup; we however invite you to try aged balsamic vinegar instead (sounds unlikely, we know, but try it and you’ll see; it is so delicious and your blood sugars will thank you too!)
- Chia pudding: so many nutrients in this one; chia seeds are incredible!
- Quinoa breakfast bowl: the healthy grains are a great start to the day, and contain a fair bit of protein too, and served with nuts, seeds, and diced fruit, many more nutrients get added to the mix. Unclear why the video-makers want to put honey or maple syrup on everything.
- Berries: lots of vitamins, fiber, hydration, and very many polyphenols
For a quick visual overview, and a quick-start preparation guide for the ones that aren’t just “berries” or similar, enjoy this short (3:11) video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
PS: They said 10, and we only counted 9. Where is the tenth one? Who would say “10 things” and then ostensibly only have 9? Who would do such a thing?!
About that chia pudding…
It’s a great way to get a healthy dose of protein, healthy fats, antioxidants, and a lot of other benefits for the heart and brain:
The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
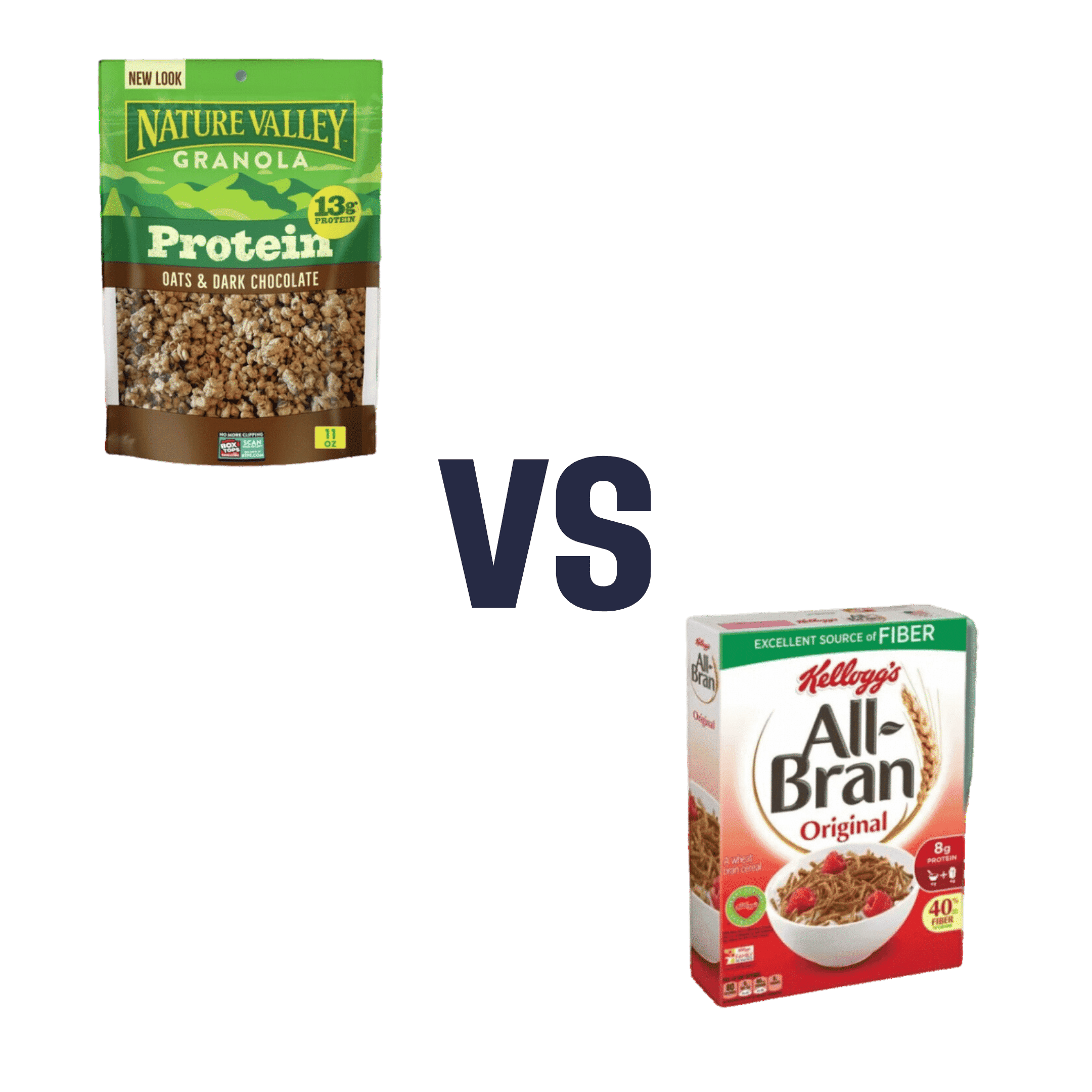
Nature Valley Protein Granola vs Kellog’s All-Bran – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Nature Valley Protein Granola to Kellog’s All-Bran, we picked the All-Bran.
Why?
While the Protein Granola indeed contains more protein (13g/cup, compared to 5g/cup), it also contains three times as much sugar (18g/cup, compared to 9g/cup) and only ⅓ as much fiber (4g/cup, compared to 12g/cup)
Given that fiber is what helps our bodies to absorb sugar more gently (resulting in fewer spikes), this is extremely important, especially since 18g of sugar in one cup of Protein Granola is already most of the recommended daily allowance, all at once!
For reference: the AHA recommends no more than 25g added sugar for women, or 32g for men
Hence, we went for the option with 3x as much fiber and ⅓ of the sugar, the All-Bran.
For more about keeping blood sugars stable, see:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
- Myth: you can’t get too much calcium!
- Myth: you must get as much vitamin D as possible!
Let’s tackle calcium first:
❝Calcium is good for you! You need more calcium for your bones! Be careful you don’t get calcium-deficient!❞
Contingently, those comments seem reasonable. Contingently on you not already having the right amount of calcium. Most people know what happens in the case of too little calcium: brittle bones, osteoporosis, and so forth.
But what about too much?
Hypercalcemia
Having too much calcium—or “hypercalcemia”— can lead to problems with…
- Groans: gastrointestinal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis.
- Bones: bone-related pains. Osteoporosis, osteomalacia, arthritis and pathological fractures.
- Stones: kidney stones causing pain.
- Moans: refers to fatigue and malaise.
- Thrones: polyuria, polydipsia, and constipation
- Psychic overtones: lethargy, confusion, depression, and memory loss.
(mnemonic courtesy of Sadiq et al, 2022)
What causes this, and how do we avoid it? Is it just dietary?
It’s mostly not dietary!
Overconsumption of calcium is certainly possible, but not common unless one has an extreme diet and/or over-supplementation. However…
Too much vitamin D
Again with “too much of a good thing”! While keeping good levels of vitamin D is, obviously, good, overdoing it (including commonly prescribed super-therapeutic doses of vitamin D) can lead to hypercalcemia.
This happens because vitamin D triggers calcium absorption into the gut, and acts as gatekeeper to the bloodstream.
Normally, the body only absorbs 10–20% of the calcium we consume, and that’s all well and good. But with overly high vitamin D levels, the other 80–90% can be waved on through, and that is very much Not Good™.
See for yourself:
- Hypercalcemia of Malignancy: An Update on Pathogenesis and Management
- Vitamin D-Mediated Hypercalcemia: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
How much is too much?
The United States’ Office of Dietary Supplements defines 4000 IU (100μg) as a high daily dose of vitamin D, and recommends 600 IU (15μg) as a daily dose, or 800 IU (20μg) if aged over 70.
See for yourself: Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Health Professionals ← there’s quite a bit of extra info there too
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
3 Day Juice Fasting? Not So Fast!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Juice fasts are trending… Again. They have been before, and this will probably not be the last time either.
The rationale is that by having nothing but fruit and/or vegetable juice for a few days, the body can clear itself of toxins while it’s not being preoccupied by dealing with what you’re eating on a daily basis.
This is not bad in theory, and in fact is a sort of parallel to the actually good advice to help the liver regenerate—by abstaining from things that the liver has to do hard work about, it has more internal resources to devote to taking care of itself.
Learn more about this: How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Just one problem
By having only juice for a few days, you are doing the opposite of what the liver needs.
In fact, by giving it what’s basically straight sugars in water with no fiber and not even any fats to slow it down, you are making your liver work overtime to deal with the flood of sugars, and it will not cope well.
Indeed, processed carbs without sufficient fiber are one of the main drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
And yes, that’s what juice is: processed carbs without fiber
(juicing is a process!)
You can read more about the science of that, here:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same? ← we get into quite some detail about how, exactly, such a harmless-seeming thing as fruit juice messes up the liver so badly
Here be (more) science
A three-day interventional study was performed on juicing and microbiome health, with three groups:
- Juice only
- Juice with whole foods
- Only whole plant-based foods
The results?
- Juice only: biggest growth in bacteria that cause inflammation and gut permeability (that’s bad; very bad)
- Juice with whole foods: the same bad effects, but much less pronounced than the juice-only group
- Only whole plant-based food: notable improvements in the microbiome
That’s what the changes were immediately post-intervention; what’s interesting to note is that the bad effects of the juice-only group also lingered longer, whereas the juice+food group enjoyed a relatively quicker recovery in the two weeks after the intervention.
Here’s the paper itself; be warned, you’ll be reading a lot about feces and saliva alongside eating and drinking:
Effects of Vegetable and Fruit Juicing on Gut and Oral Microbiome Composition
Ok, what can I do to detox?
Well, the advice we gave up top in the linked article about liver health is very sound, and also you might like to check out:
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
Want to learn more?
Here’s a video explainer from the ever-charming French biochemist Jessie Inchauspé (and our own text overview, for those who prefer reading):
Fruit Is Healthy; Juice Isn’t (Here’s Why)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: