We analysed almost 1,000 social media posts about 5 popular medical tests. Most were utterly misleading
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Kim Kardashian posted on Instagram about having had a full-body MRI, she enthused that the test can be “life saving”, detecting diseases in the earliest stages before symptoms arise.
What Kardashian neglected to say was there’s no evidence this expensive scan can bring benefits for healthy people. She also didn’t mention it can carry harms including unnecessary diagnoses and inappropriate treatments.
With this post in mind, we wanted to explore what influencers are telling us about medical tests.
In a new study published today in JAMA Network Open, we analysed nearly 1,000 Instagram and TikTok posts about five popular medical tests which can all do more harm than good to healthy people, including the full-body MRI scan.
We found the overwhelming majority of these posts were utterly misleading.

5 controversial tests
Before we get into the details of what we found, a bit about the five tests included in our study.
While these tests can be valuable to some, all five carry the risk of overdiagnosis for generally healthy people. Overdiagnosis is the diagnosis of a condition which would have never caused symptoms or problems. Overdiagnosis leads to overtreatment, which can cause unnecessary side effects and stress for the person, and wasted resources for the health system.
As an example, estimates suggest 29,000 cancers a year are overdiagnosed in Australia alone.
Overdiagnosis is a global problem, and it’s driven in part by healthy people having tests like these. Often, they’re promoted under the guise of early screening, as a way to “take control” of your health. But most healthy people simply don’t need them.
These are the five tests we looked at:
The full-body MRI scan claims to test for up to 500 conditions, including cancer. Yet there is no proven benefit of the scan for healthy people, and a real risk of unnecessary treatment from “false alarm” diagnoses.
The “egg timer” test (technically known as the AMH, or anti-mullarian hormone test) is often falsely promoted as a fertility test for healthy women. While it may be beneficial for women within a fertility clinic setting, it cannot reliably predict the chance of a woman conceiving, or menopause starting. However, low results can increase fear and anxiety, and lead to unnecessary and expensive fertility treatments.
Multi-cancer early detection blood tests are being heavily marketed as the “holy grail of cancer detection”, with claims they can screen for more than 50 cancers. In reality, clinical trials are still a long way from finished. There’s no good evidence yet that the benefits will outweigh the harms of unnecessary cancer diagnoses.
The gut microbiome test of your stool promises “wellness” via early detection of many conditions, from flatulence to depression, again without good evidence of benefit. There’s also concern that test results can lead to wasted resources.
Testosterone testing in healthy men is not supported by any high-quality evidence, with concerns direct-to-consumer advertising leads men to get tested and take testosterone replacement therapy unnecessarily. Use of testosterone replacement therapy carries its own risk of potential harms with the long-term safety in relation to heart disease and mortality still largely unknown.

What we found
Together with an international group of health researchers, we analysed 982 posts pertaining to the above tests from across Instagram and TikTok. The posts we looked at came from influencers and account holders with at least 1,000 followers, some with a few million followers. In total, the creators of the posts we included had close to 200 million followers.
Even discounting the bots, that’s a massive amount of influence (and likely doesn’t reflect their actual reach to non-followers too).
The vast majority of posts were misleading, failing to even mention the possibility of harm arising from taking one of these tests. We found:
- 87% of posts mentioned test benefits, while only 15% mentioned potential harms
- only 6% of posts mentioned the risk of overdiagnosis
- only 6% of posts discussed any scientific evidence, while 34% of posts used personal stories to promote the test
- 68% of influencers and account holders had financial interests in promoting the test (for example, a partnership, collaboration, sponsorship or selling for their own profit in some way).
Further analysis revealed medical doctors were slightly more balanced in their posts. They were more likely to mention the harms of the test, and less likely to have a strongly promotional tone.

As all studies do, ours had some limitations. For example, we didn’t analyse comments connected to posts. These may give further insights into the information being provided about these tests, and how social media users perceive them.
Nonetheless, our findings add to the growing body of evidence showing misleading medical information is widespread on social media.
What can we do about it?
Experts have proposed a range of solutions including pre-bunking strategies, which means proactively educating the public about common misinformation techniques.
However, solutions like these often place responsibility on the individual. And with all the information on social media to navigate, that’s a big ask, even for people with adequate health literacy.
What’s urgently needed is stronger regulation to prevent misleading information being created and shared in the first place. This is especially important given social media platforms including Instagram are moving away from fact-checking.
In the meantime, remember that if information about medical tests promoted by influencers sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
Brooke Nickel, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, University of Sydney; Joshua Zadro, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, Sydney Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney, and Ray Moynihan, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stop The World…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some news highlights from this week:
“US vs Them”?
With the US now set to lose its WHO membership, what does that mean for Americans? For most, the consequences will be indirect:
- the nation’s scientists and institutions will be somewhat “left out in the cold” when it comes to international scientific collaboration in the field of health
- the US will no longer enjoy a position of influence and power within the WHO, which organization’s reports and position statements have a lot of sway over the world’s health practices
Are there any benefits (of leaving the WHO) for Americans? Yes, there is one: the US will no longer be paying into the WHO’s budget, which means:
- the US will save the 0.006% of the Federal budget that it was paying into the WHO annually
- for the average American’s monthly budget, that means (if the saving is passed on) you’ll have an extra dime
However, since US scientific institutions will still need access to international data, likely that access will need to be paid separately, at a higher rate than US membership in WHO cost.
In short: it seems likely to go the way that Brexit did: “saving” on membership fees and then paying more for access to less.
Why is the US leaving again? The stated reasons were mainly twofold:
- the cost of US membership (the US’s contribution constituted 15% of the the overall WHO budget)
- holding the US’s disproportionately high COVID death rate (especially compared to countries such as China) to be a case of WHO mismanagement
Read in full: What losing WHO membership means for the U.S.
Related: What Would a Second Trump Presidency Look Like for Health Care? ← this was a speculative post by KFF Health News, last year
Halt, You’re Under A Breast
More seriously, this is about halting the metastasis of cancerous tumors in the breast. It is reasonable to expect the same principle and thus treatment may apply to other cancers too, but this is where the research is at for now (breast cancer research gets a lot of funding).
And, what principle and treatment is this, you ask? It’s about the foxglove-derived drug digoxin, and how it stops cancerous cells from forming clusters, and even actively dissolves clusters that have already formed. No clusters means no new tumors, which means no metastasis. No metastasis, in turn, means the cancer becomes much more treatable because it’s no longer a game of whack-a-mole; instead of spreading to other places, it’s a much more manageable case of “here’s the tumor, now let’s kill it with something”.
Note: yes, that does mean the tumor still needs killing by some other means—digoxin won’t do that, it “just” stops it from spreading while treatment is undertaken.
Read in full: Proof-of-concept study dissolves clusters of breast cancer cells to prevent metastases
Related: The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
Force Of Habit
“It takes 21 days to make a habit”, says popular lore. Popular is not, however, evidence-based:
❝This systematic review of 20 studies involving 2601 participants challenges the prevailing notion of rapid habit formation, revealing that health-related habits typically require 2–5 months to develop, with substantial individual variability ranging from 4 to 335 days. The meta-analysis demonstrated significant improvements in habit scores across various health behaviours, with key determinants including morning practices, personal choice, and behavioural characteristics❞
So, this is not a lottery, “maybe it will take until Tuesday, maybe it will take nearly a year”, so much as “there are important factors that seriously change how long a habit takes to become engrained, and here is what those factors are”.
Read in full: Study reveals healthy habits take longer than 21 days to set in
Share This Post
-
Health Tips for Males Too
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Articles are very informative and helpful. Maybe it’s me but things seem to lean more toward females. That being said don’t forget us males❞
Rest assured, we could never forget you! We try to make as much as possible of our content applicable to as many as possible of our readers, but of course not everything can be relevant for everyone.
This is, presumably, in response to our recent feature on menopausal health, because previous to that, our next-most-recent main feature that centred women’s health was a month ago—that was about breast cancer, and did have a section on breast cancer in men too. You might also enjoy the book we reviewed recently about prostate health, or our regular sponsor offering testosterone therapy. Please feel free to check out our articles on saw palmetto against male pattern baldness and BPH, as well as mental health issues that disproportionally affect men.
And of course, if you have specific questions/requests about men’s health (or any other health topic) we’re only ever an email away (or use the handy feedback widget, as you did to make this request)!
Share This Post
-
Kombucha vs Kimchi – Which is Healthier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kombucha to kimchi, we picked the kombucha.
Why?
While both are very respectable gut-healthy fermented products,
• the kombucha contains fermented tea, a little apple cider vinegar, and a little fiber
• the kimchi contains (after the vegetables) 810 mg sodium in that little tin, and despite the vegetables, no fiber.You may reasonably be surprised that they managed to take something that is made of mostly vegetables and ended up with no fiber without juicing it, but they did. Fermented vegetables are great for the healthy bacteria benefits (and are tasty too!), but the osmotic pressure due to the salt destroys the cell walls and thus the fiber.
Thus, we chose the kombucha that does the same job without delivering all that salt.
However! If you are comparing kombucha and kimchi out in the wilds of your local supermarket, do still check individual labels. It’s not uncommon, for example, for stores to sell pre-made kombucha that’s loaded with sugar.
About sugar and kombucha…
Sugar is required to make kombucha, to feed the yeast and helpful bacteria. However, there should be none of that sugar left (or only the tiniest trace amount) in the final product, because the yeast (and friends) consumed and metabolized it.
What some store brands do, however, is add in sugar afterwards, as they believe it improves the taste. This writer cannot imagine how, but that is their rationale in any case. Needless to say, it is not a healthy addition, and specifically, it’s bad for your gut, which (healthwise) is the whole point of drinking kombucha in the first place.
Want some? Here is an example product on Amazon, but feel free to shop around as there are many flavors available!
Read more about gut health: Gut Health 101
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Hack Your Hunger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to dealing with hunger, a common-sense way of dealing with it is “eat something”. However, many people find that they then eat the wrong things, in the wrong quantities, and end up in a cycle of overeating and being hungry.
If this gets to the extreme, it can turn into a full-blown eating disorder:
Eating Disorders: More Varied (And Prevalent) Than People Think
…and even in more moderate presentations, the cycle of hunger and overeating is not great for the health. So, how to avoid that?
Listen to your body (but: actually listen)
Your body says: we’re running a little low on glycogen reserves so our energy’s going to start suffering in a few hours if we don’t eat some fruit, kill something and eat its fatty organs, or perhaps find some oily nuts.
You hear: eat something bright and sugary, shout at the dog, eat some fried food, got it!
Your body says: our water balance is a little off, we could do with some sodium, potassium, and perhaps some phosphorus to correct it.
You hear: eat something salty, got it, potato chips coming right up!
…and so on. Now, we know 10almonds readers are quite a health-conscious readership, so perhaps your responses are not quite like that. But the take-away point is still important: we need to listen to the whole message, and give the body what it actually needs, not what will just shut the message off the most quickly.
Here’s how: Intuitive Eating Might Not Be What You Think
Bonus: Interoception: Improving Our Awareness Of Body Cues
About those cravings…
As illustrated a little above, a lot of cravings might not be what they first appear, and in evolutionary terms, our body is centuries behind industrialization, in terms of adaptations, which means that even if we try to take the above into account, our responses can sometimes be inappropriate in the age of supermarkets.
See also: The Science of Hunger, And How To Sate Cravings
Natural appetite suppressants
Eating more is not always the answer, not even if it’s more healthy food. And hunger pangs can be especially inconvenient if, for example, we are fasting at present, which is by the way a very healthful thing for most people:
Learn more: Intermittent Fasting: What’s the truth?
One way to suppress hunger is simply to trigger the stomach into sending “full” signals, which involves filling it. Since you do not want to overeat, the trick here is imply to use high-volume food.
Consider for example: 30 grapes and 30 raisins have approximately the same calorie count (what with raisins being dried grapes, and the calories didn’t evaporate), but the bowl of fresh fruit is going to physically fill your stomach a lot more quickly than the tiny amount of dried fruit.
More on this: Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
Protein is of course also an appetite suppressant, but it takes about 20 minutes for the signal to kick in. So a “hack” here is to snack on something proteinous at least 15 minutes before your main meal (for example, a portion of nuts while cooking, unless you’re allergic, or some dried fish unless you’re vegetarian/vegan; you get it, pick something high in protein and good for snacking, and have a small portion before your main meal).
Nor is protein the only option!
See also: 3 Natural Appetite Suppressants Better Than Ozempic
Scale it down
Related to the above, there is a feedback loop that occurs here. The more you eat, the more your stomach slowly grows to accommodate it; the less you eat, the more your stomach slowly shrinks because the body tries hard to be an efficient organism, and will not maintain something that isn’t being used.
So, there’s a bit of a catch-22; sate your hunger by filling your stomach with high volume foods, but filling it will cause it to grow?
The trick is: do the “eat until 80% full” thing. That’s full enough that you have had a nice meal and are not suffering, without stretching the stomach.
Enjoy your food
Seriously! Actually enjoy it. Which means paying full attention to it. Eating can and should be a wonderful experience, so it’s best savored rather than inhaling a bowl of something in 30 seconds.
Have you seen those dog bowls that have obstructions to slow down how quickly a dog eats? We can leverage that kind of trick too! While you might not want to eat from a dog bowl, how about having a little bowl of pistachio nuts rather than ready-to-eat peanuts? Or any shelled nuts that we must shell as we go. If you’re allergic to nuts, there are plenty of other foods with a high work-to-food ratio. Take some time and enjoy that pomegranate, for instance!
Not that we necessarily have to make things difficult for ourselves either; we can just take appropriate care to ensure a good dining experience. Life is for living, so why not enjoy it?
See also: Mindful Eating: How To Get More Out Of What’s On Your Plate
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bird Flu Is Bad for Poultry and Dairy Cows. It’s Not a Dire Threat for Most of Us — Yet.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Headlines are flying after the Department of Agriculture confirmed that the H5N1 bird flu virus has infected dairy cows around the country. Tests have detected the virus among cattle in nine states, mainly in Texas and New Mexico, and most recently in Colorado, said Nirav Shah, principal deputy director at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at a May 1 event held by the Council on Foreign Relations.
A menagerie of other animals have been infected by H5N1, and at least one person in Texas. But what scientists fear most is if the virus were to spread efficiently from person to person. That hasn’t happened and might not. Shah said the CDC considers the H5N1 outbreak “a low risk to the general public at this time.”
Viruses evolve and outbreaks can shift quickly. “As with any major outbreak, this is moving at the speed of a bullet train,” Shah said. “What we’ll be talking about is a snapshot of that fast-moving train.” What he means is that what’s known about the H5N1 bird flu today will undoubtedly change.
With that in mind, KFF Health News explains what you need to know now.
Q: Who gets the bird flu?
Mainly birds. Over the past few years, however, the H5N1 bird flu virus has increasingly jumped from birds into mammals around the world. The growing list of more than 50 species includes seals, goats, skunks, cats, and wild bush dogs at a zoo in the United Kingdom. At least 24,000 sea lions died in outbreaks of H5N1 bird flu in South America last year.
What makes the current outbreak in cattle unusual is that it’s spreading rapidly from cow to cow, whereas the other cases — except for the sea lion infections — appear limited. Researchers know this because genetic sequences of the H5N1 viruses drawn from cattle this year were nearly identical to one another.
The cattle outbreak is also concerning because the country has been caught off guard. Researchers examining the virus’s genomes suggest it originally spilled over from birds into cows late last year in Texas, and has since spread among many more cows than have been tested. “Our analyses show this has been circulating in cows for four months or so, under our noses,” said Michael Worobey, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Arizona in Tucson.
Q: Is this the start of the next pandemic?
Not yet. But it’s a thought worth considering because a bird flu pandemic would be a nightmare. More than half of people infected by older strains of H5N1 bird flu viruses from 2003 to 2016 died. Even if death rates turn out to be less severe for the H5N1 strain currently circulating in cattle, repercussions could involve loads of sick people and hospitals too overwhelmed to handle other medical emergencies.
Although at least one person has been infected with H5N1 this year, the virus can’t lead to a pandemic in its current state. To achieve that horrible status, a pathogen needs to sicken many people on multiple continents. And to do that, the H5N1 virus would need to infect a ton of people. That won’t happen through occasional spillovers of the virus from farm animals into people. Rather, the virus must acquire mutations for it to spread from person to person, like the seasonal flu, as a respiratory infection transmitted largely through the air as people cough, sneeze, and breathe. As we learned in the depths of covid-19, airborne viruses are hard to stop.
That hasn’t happened yet. However, H5N1 viruses now have plenty of chances to evolve as they replicate within thousands of cows. Like all viruses, they mutate as they replicate, and mutations that improve the virus’s survival are passed to the next generation. And because cows are mammals, the viruses could be getting better at thriving within cells that are closer to ours than birds’.
The evolution of a pandemic-ready bird flu virus could be aided by a sort of superpower possessed by many viruses. Namely, they sometimes swap their genes with other strains in a process called reassortment. In a study published in 2009, Worobey and other researchers traced the origin of the H1N1 “swine flu” pandemic to events in which different viruses causing the swine flu, bird flu, and human flu mixed and matched their genes within pigs that they were simultaneously infecting. Pigs need not be involved this time around, Worobey warned.
Q: Will a pandemic start if a person drinks virus-contaminated milk?
Not yet. Cow’s milk, as well as powdered milk and infant formula, sold in stores is considered safe because the law requires all milk sold commercially to be pasteurized. That process of heating milk at high temperatures kills bacteria, viruses, and other teeny organisms. Tests have identified fragments of H5N1 viruses in milk from grocery stores but confirm that the virus bits are dead and, therefore, harmless.
Unpasteurized “raw” milk, however, has been shown to contain living H5N1 viruses, which is why the FDA and other health authorities strongly advise people not to drink it. Doing so could cause a person to become seriously ill or worse. But even then, a pandemic is unlikely to be sparked because the virus — in its current form — does not spread efficiently from person to person, as the seasonal flu does.
Q: What should be done?
A lot! Because of a lack of surveillance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and other agencies have allowed the H5N1 bird flu to spread under the radar in cattle. To get a handle on the situation, the USDA recently ordered all lactating dairy cattle to be tested before farmers move them to other states, and the outcomes of the tests to be reported.
But just as restricting covid tests to international travelers in early 2020 allowed the coronavirus to spread undetected, testing only cows that move across state lines would miss plenty of cases.
Such limited testing won’t reveal how the virus is spreading among cattle — information desperately needed so farmers can stop it. A leading hypothesis is that viruses are being transferred from one cow to the next through the machines used to milk them.
To boost testing, Fred Gingrich, executive director of a nonprofit organization for farm veterinarians, the American Association of Bovine Practitioners, said the government should offer funds to cattle farmers who report cases so that they have an incentive to test. Barring that, he said, reporting just adds reputational damage atop financial loss.
“These outbreaks have a significant economic impact,” Gingrich said. “Farmers lose about 20% of their milk production in an outbreak because animals quit eating, produce less milk, and some of that milk is abnormal and then can’t be sold.”
The government has made the H5N1 tests free for farmers, Gingrich added, but they haven’t budgeted money for veterinarians who must sample the cows, transport samples, and file paperwork. “Tests are the least expensive part,” he said.
If testing on farms remains elusive, evolutionary virologists can still learn a lot by analyzing genomic sequences from H5N1 viruses sampled from cattle. The differences between sequences tell a story about where and when the current outbreak began, the path it travels, and whether the viruses are acquiring mutations that pose a threat to people. Yet this vital research has been hampered by the USDA’s slow and incomplete posting of genetic data, Worobey said.
The government should also help poultry farmers prevent H5N1 outbreaks since those kill many birds and pose a constant threat of spillover, said Maurice Pitesky, an avian disease specialist at the University of California-Davis.
Waterfowl like ducks and geese are the usual sources of outbreaks on poultry farms, and researchers can detect their proximity using remote sensing and other technologies. By zeroing in on zones of potential spillover, farmers can target their attention. That can mean routine surveillance to detect early signs of infections in poultry, using water cannons to shoo away migrating flocks, relocating farm animals, or temporarily ushering them into barns. “We should be spending on prevention,” Pitesky said.
Q: OK it’s not a pandemic, but what could happen to people who get this year’s H5N1 bird flu?
No one really knows. Only one person in Texas has been diagnosed with the disease this year, in April. This person worked closely with dairy cows, and had a mild case with an eye infection. The CDC found out about them because of its surveillance process. Clinics are supposed to alert state health departments when they diagnose farmworkers with the flu, using tests that detect influenza viruses, broadly. State health departments then confirm the test, and if it’s positive, they send a person’s sample to a CDC laboratory, where it is checked for the H5N1 virus, specifically. “Thus far we have received 23,” Shah said. “All but one of those was negative.”
State health department officials are also monitoring around 150 people, he said, who have spent time around cattle. They’re checking in with these farmworkers via phone calls, text messages, or in-person visits to see if they develop symptoms. And if that happens, they’ll be tested.
Another way to assess farmworkers would be to check their blood for antibodies against the H5N1 bird flu virus; a positive result would indicate they might have been unknowingly infected. But Shah said health officials are not yet doing this work.
“The fact that we’re four months in and haven’t done this isn’t a good sign,” Worobey said. “I’m not super worried about a pandemic at the moment, but we should start acting like we don’t want it to happen.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Early Bird Or Night Owl? Genes vs Environment
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Sliding Slope?
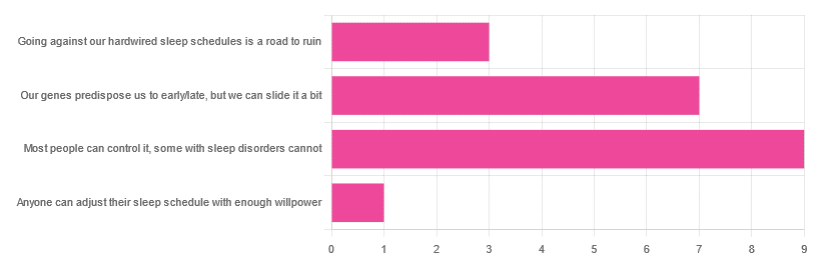
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you how much control you believe we have over our sleep schedule, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- 45% said “most people can control it; some people with sleep disorders cannot
- 35% said “our genes predispose us to early/late, but we can slide it a bit
- 15% said: “going against our hardwired sleep schedules is a road to ruin”
- 5% said “anyone can adjust their sleep schedule with enough willpower”
You may be wondering: what’s with those single-digit numbers in the graph there? And the answer is: Tuesday’s email didn’t go out at the usual time due to a scheduling mistake (sorry!), which is probably what affected the number of responses (poll response levels vary, but are usually a lot higher than this).
Note: yes, this does mean most people who read our newsletter don’t vote. So, not to sound like a politician on the campaign trail, but… Your vote counts! We always love reading your comments when you add those, too—often they provide context that allow us to tailor what we focus on in our articles
However, those are the responses we got, so here we are!
What does the science say?
Anyone can adjust their sleep with enough willpower: True or False?
False, simply. It’s difficult for most people, but for many people with sleep disorders, it is outright impossible.
In a battle of narcolepsy vs willpower, for example, no amount of willpower will stop the brain from switching to sleep mode when it thinks it’s time to sleep:
❝Narcolepsy is the most common neurological cause of chronic sleepiness. The discovery about 20 years ago that narcolepsy is caused by selective loss of the neurons producing orexins sparked great advances in the field
[There is also] developing evidence that narcolepsy is an autoimmune disorder that may be caused by a T cell-mediated attack on the orexin neurons and explain how these new perspectives can inform better therapeutic approaches.❞
~ Dr. Carrie Mahoney et al. (lightly edited for brevity)
Source: The neurobiological basis of narcolepsy
For further reading, especially if this applies to you or a loved one:
Our genes predispose us to early/late, but we can slide it a bit: True or False?
True! First, about our genes predisposing us:
…and also:
Gene distinguishes early birds from night owls and helps predict time of death
Now, as for the “can slide it a bit”, this is really just a function of the general categories of “early bird” and “night owl” spanning periods of time that allow for a few hours’ wiggle-room at either side.
However, it is recommended to make any actual changes more gradually, with the Sleep Foundation going so far as to recommend 30 minutes, or even just 15 minutes, of change per day:
Sleep Foundation | How to Fix Your Sleep Schedule
Going against our hardwired sleep schedule is a road to ruin: True or False?
False, contextually. By this we mean: our “hardwired” sleep schedule is (for most of us), genetically predisposed but not predetermined.
Also, genetic predispositions are not necessarily always good for us; one would not argue, for example, for avoiding going against a genetic predisposition to addiction.
Some genetic predispositions are just plain bad for us, and genes can be a bit of a lottery.
That said, we do recommend getting some insider knowledge (literally), by getting personal genomics tests done, if that’s a viable option for you, so you know what’s really a genetic trait (and what to do with that information) and what’s probably caused by something else (and what to do with that information):
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: