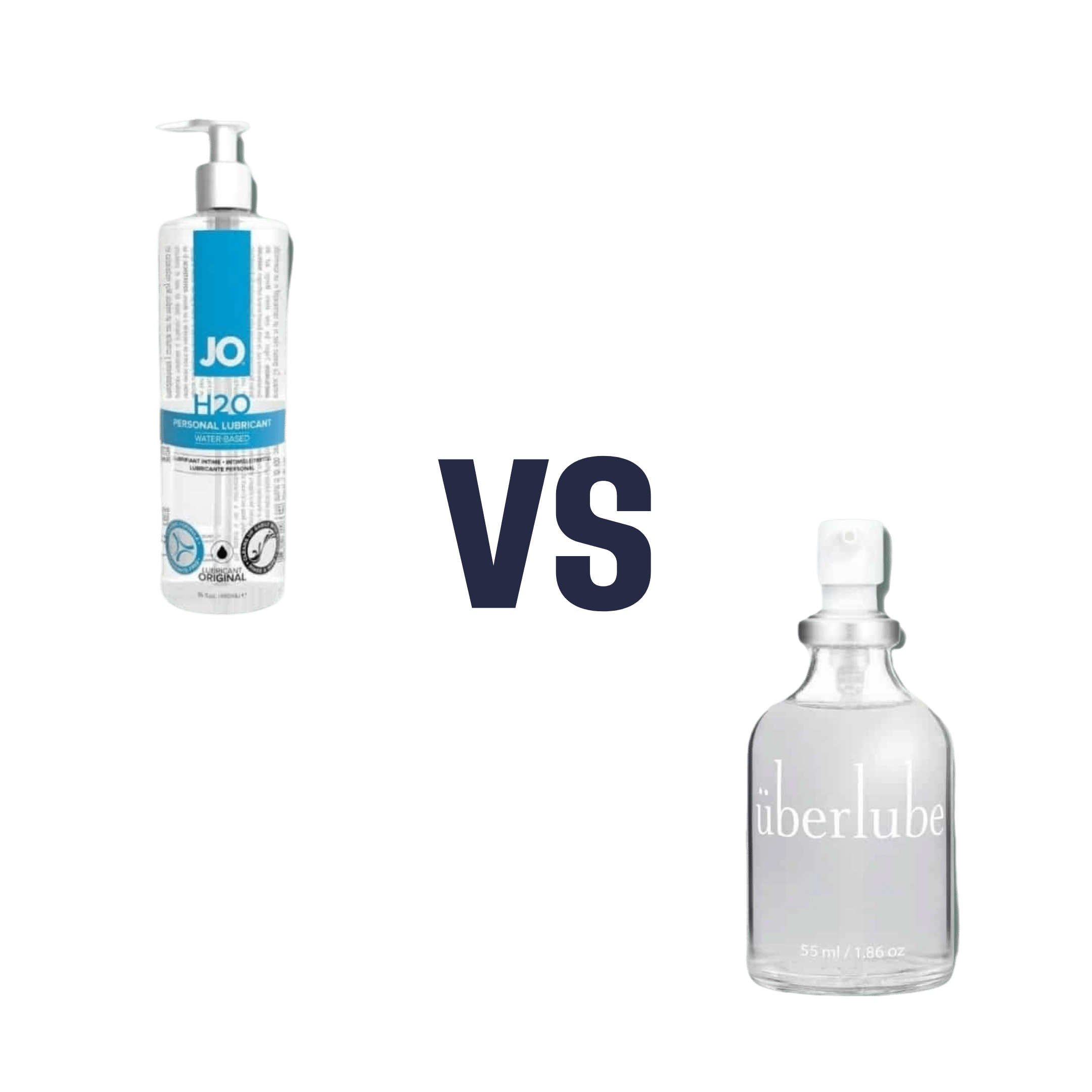
Water-based Lubricant vs Silicon-based Lubricant – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing water-based lubricant to silicon-based lubricant, we picked the silicon-based.
Why?
First, some real talk about vaginas, because this is something not everyone knows, so let’s briefly cover this before moving onto the differences:
Yes, vaginas are self-lubricating, but a) not always and b) not always sufficiently, especially as we get older. Much like with penile hardness (or lack thereof), there’s a lot of stigma associated with vaginal dryness, and there really needn’t be, because the simple reality is that we don’t live in the fictitious world of porn, and here in the real world, anatomy and physiology can be quite arbitrary at times.
It is this writer’s firm opinion that everyone (or: everyone who is sexual, anyway) should have good quality lube at home—regardless of one’s gender, relationship status, or anything else.
Ok, with that in mind, onwards:
The water-based lube has nine ingredients: water, glycerin, cytopentasioxane, propylene glycol, xantham gum, phenoxyethanol, dimethiconol, triethanolamine, and ethylhexylglycerine.
All of these ingredients are considered body-safe in the doses present, and/but most of them will be absorbed into the skin, especially via the relatively permeable membrane that is the inside of the vagina (or anus—while the microbiome is very different, tissue-wise these are very similar).
While this is not meaningfully toxic, there’s a delicate balance going on in there, and this can upset that balance a little.
Also, because the lube is absorbed into the skin, you’ll then need more, which means either a moment’s inconvenience to add more, or else the risk of chafing, which isn’t fun.
The silicon lube has four ingredients: dimethicone, dimethiconol, cyclomethicone, and tocopheryl acetate.
Note: “tocopheryl acetate” is vitamin E
…which reminds us: just because something is hard to spell, doesn’t mean it’s necessarily bad for us.
What are the other three ingredients, though? They are all silicon compounds, all inert, and all with molecules too big to be absorbed into our skin. Basically they all slide right off, which is entirely the point of lube, after all.
It not being absorbed into our skin is good for our health; it’s also convenient as it means a tiny bit of lube goes a long way.
Any downsides to silicon-based lube?
There are two, and neither are health-related:
- It can damage silicon toys if not cleaned quickly and thoroughly, the silicon of the lube may bond with the silicon of the toy after a while.
- Because it doesn’t just disappear like water-based lube, you might want to put a towel down if you don’t want your bed to be slippy afterwards! The towel can then be put in the laundry as normal.
Want to try it out? Here it is on Amazon
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Nature Provides Us With A Surprisingly Powerful Painkiller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-known (at least to regular 10almonds-readers) that seeing nature, ideally green leaves and blue sky, improves our mood by stimulating production of serotonin.
See also: Neurotransmitter Cheatsheet
But it does a lot more.
Reducing the actual signals of pain
Researchers at the University of Vienna have discovered that viewing nature scenes (even if just on video) alleviates physical pain—not just in self-reported subjective assessments, but also by a reduction of the neural activity that signals pain:
❝Pain is like a puzzle, made up of different pieces that are processed differently in the brain. Some pieces of the puzzle relate to our emotional response to pain, such as how unpleasant we find it. Other pieces correspond to the physical signals underlying the painful experience, such as its location in the body and its intensity.
Unlike placebos, which usually change our emotional response to pain, viewing nature changed how the brain processed early, raw sensory signals of pain.
Thus, the effect appears to be less influenced by participants’ expectations, and more by changes in the underlying pain signals❞
This was tested against, varyingly, viewing an urban environment or viewing an indoor environment, neither of which gave the same benefits.
The setup of the experiment is relevant, so…
Matching soundscape accompanied each visual stimulus. The three pain runs had a total duration of 9 min each, during which one environment was accompanied by 16 painful and 16 non-painful shocks. Neuroimaging was used for all parts, and participants were exposed to all environments:
- First, a cue indicating the intensity of the next shock (red = painful, yellow = not painful) was presented for 2000 milliseconds (ms).
- Second, a variable interval of 3500 ± 1500 ms was shown.
- Third, a cue indicating the intensity of the shock was presented for 1000 ms, accompanied by an electrical shock with a duration of 500 ms.
- Fourth, a variable interval of 3500 ± 1500 ms followed.
- Fifth, after each third trial, participants rated the shock’s intensity and unpleasantness at 6000 ms each.
- Sixth, each trial ended with an intertrial interval (ITI) presented for 2000 ms.
They found that as well as the self-assessment reports being as expected (nature scenes reduced subjective experience of pain),
❝In summary, the multivoxel and region of interest analyses converged in showing that pain responses when exposed to nature as compared to urban or indoor stimuli were associated with a decrease in neural processes related to lower-level nociception-related features (NPS, thalamus), as well as in regions of descending modulatory circuitry associated with attentional alterations of pain that also encode sensory-discriminative aspects (S2, pINS).❞
In other words—to the extent that pain can be quantified objectively by neural imaging—the pain was also objectively reduced, much like with a chemical painkiller.
You can read the paper in full, here:
Nature exposure induces analgesic effects by acting on nociception-related neural processing
How to benefit from this
Well, first there is the obvious, “view nature“.
However, note the timescales involved in the testing periods: 2000 milliseconds is two seconds, and that was the intertrial interval used—the equivalent of a washout phase in an interventional trial (but a drug/supplement/diet washout is usually a number of weeks).
The fact that the test periods were a matter of seconds, and the intertrial period was also literally two seconds, this means:
It works quickly, and the effect disappears quickly, too.
In other words: if you want pain relief from nature, the good news is you can get it immediately while viewing nature, and the bad news is that you have to keep viewing nature to continue enjoying the painkilling effect.
So that’s a limitation, but it’s still clearly a very worthy option for a little respite from chronic pain now and again, for example.
Want to learn more?
We’ve written quite a bit about pain management, including:
- Before You Reach For That Tylenol…
- How To Stop Pain Spreading
- How To Dial Down Your Pain
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- Get The Right Help For Your Pain
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief (When Painkillers Aren’t Helping, These Things Might)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
More Than One Way To Kill Pain
This is Dr. Deepak Ravindran (MD, FRCA. FFPMRCA, EDRA. FIPP, DMSMed). He has decades of experience and is a specialist in acute and chronic pain management, anesthesia, musculoskeletal medicine, and lifestyle medicine.
A quick catch-up, first:
We’ve written about chronic pain management before:
Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
As well as:
Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
Dr. Ravindran’s approach
Dr. Ravindran takes a “trauma-informed care” approach to his professional practice, and recommends the same for others.
In a nutshell, this means starting from a position of not “what’s wrong with you?”, but rather “what happened to you?”.
This seemingly subtle shift is important, because it means actually dealing with a person’s issues, instead of “take one of these and call my secretary next month”. Read more:
Pain itself can be something of a many-headed hydra. Dr. Ravindran’s approach is equally many-headed; specifically, he has a 7-point plan:
Medications
Dr. Ravindran sees painkillers (and a collection of other drugs, like antidepressants and muscle relaxants) as a potential means to an end worth exploring, but he doesn’t expect them to be the best choice for everyone, and nor does he expect them to be a cure-all. Neither should we. He also advises being mindful of the drawbacks and potential complications of these drugs, too.
Interventions
Sometimes, surgery is the right choice. Sometimes it isn’t. Often, it will change a life—one way or the other. Similar to with medications, Dr. Ravindran is very averse to a “one size fits all” approach here. See also:
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
Neuroscience and stress management
Often a lot of the distress of pain is not just the pain itself, but the fear associated with it. Will it get worse if I move wrong or eat the wrong thing? How long will it last? Will it ever get better? Will it get worse if I do nothing?. Dr. Ravindran advises tackling this, with the same level of importance as the pain itself. Here’s a good start:
Stress, And Building Psychological Resilience
Diet and the microbiome
Many chronic illnesses are heavily influenced by this, and Dr. Ravindran’s respect for lifestyle medicine comes into play here. While diet might not fix all our ills, it certainly can stop things from being a lot worse. Beyond the obvious “eat healthily” (Mediterranean diet being a good starting point for most people), he also advises doing elimination tests where appropriate, to screen out potential flare-up triggers. You also might consider:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
Sleep
“Get good sleep” is easy advice for those who are not in agonizing pain that sometimes gets worse from staying in the same position for too long. Nevertheless, it is important, and foundational to good health. So it’s important to explore—whatever limitations one might realistically have—what can be done to improve it.
If you can only sleep for a short while at a time, you may get benefit from this previous main feature of ours:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
Exercise and movement
The trick here is to move little and often; without overdoing it, but without permitting loss of mobility either. See also:
The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Therapies of the mind and body
This is about taking a holistic approach to one’s wellness. In Dr. Ravindran’s words:
❝Mind-body therapies are often an extremely sensitive topic about which people hold very strong opinions and sometimes irrational beliefs.
Some, like reiki and spiritual therapy and homeopathy, have hardly any scientific evidence to back them up, while others like yoga, hypnosis, and meditation/mindfulness are mainstream techniques with many studies showing the benefits, but they all work for certain patients.❞
In other words: evidence-based is surely the best starting point, but if you feel inclined to try something else and it works for you, then it works for you. And that’s a win.
Want to know more?
You might like his book…
The Pain-Free Mindset: 7 Steps to Taking Control and Overcoming Chronic Pain
He also has a blog and a podcast.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Nasal Hair; How Far To Go?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
t’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝As a man in his sixties I find I need to trim my nasal hair quite frequently, otherwise it sticks out in an unsightly manner. But I’m never sure how severely I should cut the hairs back, or even how best to do it. Please advise.❞
As you might know, those hairs are really important for our health, so let’s start by mentioning that yes, trimming is the way, not plucking!
In an ideal world, we’d not trim them further back than the entrance to our nostrils, but given the constant nature of hair-growing, that could become a Sisyphean task.
A good compromise, if you’re not up for trimming when you get up and having visible hairs by evening, is to put the scissors away (if you haven’t already) and use a nasal hair trimmer; these are good at a) trimming nasal hairs b) abstaining from trimming them too far back.
By all means shop around, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience!
- Note 1: despite the product description, please do not stick this in your ear (or any other orifice that’s not your nose, for the love of all that is holey)
- Note 2: we chose that one for a reason; the shape of the head prevents overtrimming.
- In contrast, we do not recommend this cheaper one that has a different shape head for a closer trim, which in this case, is not what we want.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Carrot vs Kale – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing carrot to kale, we picked the kale.
Why?
These are both known as carotene-containing heavyweights, but kale emerges victorious:
In terms of macros, carrot has more carbs while kale has more protein and fiber. An easy win there for kale.
When it comes to vitamins, both are great! But, carrots contain more of vitamins A, B5, and choline, whereas kale contains more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, and K. And while carrot’s strongest point is vitamin A, a cup of carrots contains around 10x the recommended daily dose of vitamin A, whereas a cup of kale contains “only” 6x the recommended daily dose of vitamin A. So, did we really need the extra in carrots? Probably not. In any case, kale already won on overall vitamin coverage, by a long way.
In the category of minerals, kale again sweeps. On the one hand, carrots contain more sodium. On the other hand, kale contains a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. Not a tricky choice!
But don’t be fooled: carrots really are a nutritional powerhouse and a great food. Kale is just better—nutritionally speaking, in any case. If you’re making a carrot cake, please don’t try substituting kale; it will not work 😉
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
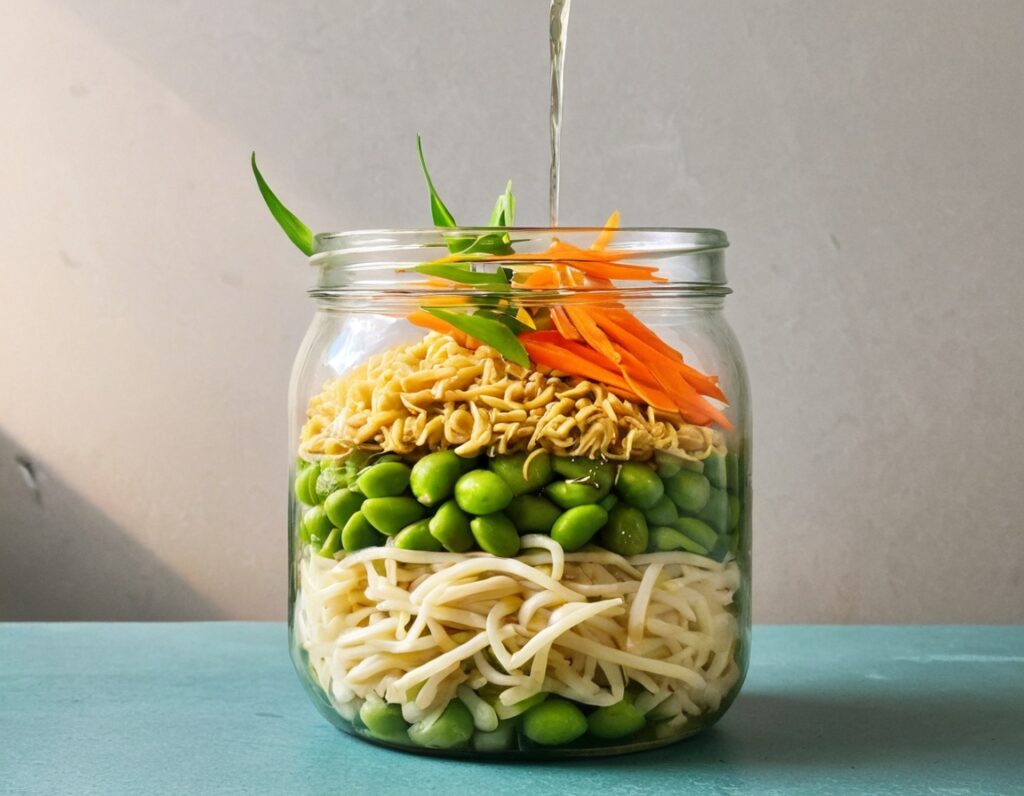
Gut-Positive Pot Noodles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everything we consume either improves our health a little or worsens it. Pot noodles aren’t generally the healthiest foods, but these ones sure are! There’s quite a range of fiber in this, including the soluble fiber of the noodles themselves (which are, in fact, mostly fiber and water). As a bonus, the glucomannan in the noodles promotes feelings of fullness, notwithstanding its negligible carb count. Of course, the protein in the edamame beans also counts for satiety!
You will need
- ½ cup konjac noodles (also called shirataki), tossed in 1 tsp avocado oil (or sesame oil, if you don’t have avocado)
- 2 oz mangetout, thinly sliced
- 1 oz edamame beans
- ¼ carrot, grated
- 2 baby sweetcorn, cut in half lengthways
- 1 scallion, finely diced
- 1 heaped tsp crunchy peanut butter (omit if allergic)
- 1 tsp miso paste
- 1 tsp chili oil
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp peeled-and-grated ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Layer a heat-resistant jar (mason jars are usually quite resistant to temperature changes) with the noodles and vegetables.
2) Combine the peanut butter, miso paste, and chili oil, black pepper, and ginger in a small bowl. Pour this dressing over the layered vegetables and noodles, and screw the lid on. Refrigerate until needed.
3) Add hot water to the jar and stir, to serve. If you prefer the vegetables to be more cooked, you can microwave (without the lid!) for a minute or two.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars ← today’s recipe makes a perfect high-fiber, low-carb starter, per the hacks here
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Codependent No More – by Melody Beattie
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a book review, not a book summary, but first let’s quickly cover a common misconception, because the word “codependent” gets misused a lot in popular parlance:
- What codependence isn’t: “we depend on each other and must do everything together”
- What codependence is:“person 1 has a dependency on a substance (or perhaps a behavior, such as gambling); person 2 is trying to look after person 1, and so has developed a secondary relationship with the substance/behavior. Person 2 is now said to be codependent, because it becomes all-consuming for them too, even if they’re not using the substance/behavior directly”
Funny how often it happens that the reality is more complex than the perception, isn’t it?
Melody Beattie unravels all this for us. We get a compassionate and insightful look at how we can look after ourselves, while looking after another. Perhaps most importantly: how and where to draw a line of what we can and cannot do/change for them.
Because when we love someone, of course we want to fight their battles with them, if not for them. But if we want to be their rock of strength, we can’t get lost in it too, and of course that hurts.
Beatty takes us through these ideas and more, for example:
- How to examine our own feelings even when it’s scary
- How to practice self-love and regain self-worth, while still caring for them
- How to stop being reactionary, step back, and act with purpose
If the book has any weak point, it’s that it repeatedly recommends 12-step programs, when in reality that’s just one option. But for those who wish to take another approach, this book does not require involvement in a 12-step program, so it’s not a barrier to usefulness.
Click here to check out Codependent No More and take care of yourself, too
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: