Want to sleep longer? Adding mini-bursts of exercise to your evening routine can help – new study
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Exercising before bed has long been discouraged as the body doesn’t have time to wind down before the lights go out.
But new research has found breaking up a quiet, sedentary evening of watching television with short bursts of resistance exercise can lead to longer periods of sleep.
Adults spend almost one third of the 24-hour day sleeping. But the quality and length of sleep can affect long-term health. Sleeping too little or waking often in the night is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Physical activity during the day can help improve sleep. However, current recommendations discourage intense exercise before going to bed as it can increase a person’s heart rate and core temperature, which can ultimately disrupt sleep.
Nighttime habits
For many, the longest period of uninterrupted sitting happens at home in the evening. People also usually consume their largest meal during this time (or snack throughout the evening).
Insulin (the hormone that helps to remove sugar from the blood stream) tends to be at a lower level in the evening than in the morning.
Together these factors promote elevated blood sugar levels, which over the long term can be bad for a person’s health.
Our previous research found interrupting evening sitting every 30 minutes with three minutes of resistance exercise reduces the amount of sugar in the bloodstream after eating a meal.
But because sleep guidelines currently discourage exercising in the hours before going to sleep, we wanted to know if frequently performing these short bursts of light activity in the evening would affect sleep.
Activity breaks for better sleep
In our latest research, we asked 30 adults to complete two sessions based in a laboratory.
During one session the adults sat continuously for a four-hour period while watching streaming services. During the other session, they interrupted sitting by performing three minutes of body-weight resistance exercises (squats, calf raises and hip extensions) every 30 minutes.
After these sessions, participants went home to their normal life routines. Their sleep that evening was measured using a wrist monitor.
Our research found the quality of sleep (measured by how many times they woke in the night and the length of these awakenings) was the same after the two sessions. But the night after the participants did the exercise “activity breaks” they slept for almost 30 minutes longer.
Identifying the biological reasons for the extended sleep in our study requires further research.
But regardless of the reason, if activity breaks can extend sleep duration, then getting up and moving at regular intervals in the evening is likely to have clear health benefits.
Time to revisit guidelines
These results add to earlier work suggesting current sleep guidelines, which discourage evening exercise before bed, may need to be reviewed.
As the activity breaks were performed in a highly controlled laboratory environment, future research should explore how activity breaks performed in real life affect peoples sleep.
We selected simple, body-weight exercises to use in this study as they don’t require people to interrupt the show they may be watching, and don’t require a large space or equipment.
If people wanted to incorporate activity breaks in their own evening routines, they could probably get the same benefit from other types of exercise. For example, marching on the spot, walking up and down stairs, or even dancing in the living room.
The key is to frequently interrupt evening sitting time, with a little bit of whole-body movement at regular intervals.
In the long run, performing activity breaks may improve health by improving sleep and post-meal blood sugar levels. The most important thing is to get up frequently and move the body, in a way the works best for a person’s individual household.
Jennifer Gale, PhD candidate, Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago and Meredith Peddie, Senior Lecturer, Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which B Vitamins? It Makes A Difference
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everyone knows “B vitamins are for energy!” and that is definitely a theme, but there’s a lot more to it than that, and in some cases, there are big mistakes that people make when it comes to supplementing their diet.
First, let’s do a quick overview of what each of the B vitamins do, by number, and putting names to them:
B1 (Thiamine)
- Function: helps convert carbohydrates into energy, supports nerve function
- Forms: thiamine hydrochloride, thiamine mononitrate, benfotiamine (fat-soluble form)
- Example foods: lentils, sunflower seeds
B2 (Riboflavin)
- Function: supports energy production, skin health, and eye function, turns your pee fluorescent yellow (the latter is really only if you consume exciting amounts of it; this will usually occur from supplementation, not from normal diet)
- Forms: riboflavin, riboflavin-5’-phosphate
- Example foods: almonds, mushrooms
B3 (Niacin)
- Function: aids metabolism, supports skin, nerves, and cholesterol levels
- Forms: niacin (nicotinic acid), niacinamide (nicotinamide), inositol hexanicotinate (flush-free niacin)
- Example foods: whole grains, peanuts (literally the best nut for this)
B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Function: essential for fatty acid metabolism and hormone production
- Forms: pantothenic acid, calcium pantothenate, panthenol (alcohol form!)
- Example foods: it’s in pretty much everything (hence the name); it’s almost impossible to be deficient in this vitamin unless you are literally starving
B6 (Pyridoxine)
- Function: needed for red blood cell production, supports brain function, as well as specifically being a part of neurotransmitter production (including dopamine and serotonin, despite them being made in different places—the brain and the gut, respectively),
- Forms: pyridoxine hydrochloride, pyridoxal-5’-phosphate (active form)
- Example foods: bananas, potatoes
B7 (Biotin)
- Function: helps with fatty acid synthesis, skin, hair, and nail health
- Forms: d-biotin, biotinylated compounds of various kinds
- Example foods: fava beans, walnuts
B9 (Folate/Folic Acid)
- Function: crucial for DNA synthesis, cell division, and fetal development
- Forms: folic acid, folinic acid, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF, active form)
- Example foods: chickpeas, spinach ← we only mentioned one leafy green here for fairness, but leafy greens in general are great sources of vitamin B9, hence the name, from the Latin “folium”, meaning leaf.
B12 (Cobalamin)
- Function: supports red blood cell formation, nerve function, and DNA synthesis
- Forms: cyanocobalamin, methylcobalamin (active), hydroxocobalamin (active), adenosylcobalamin (active)
- Example foods: nutritional yeast, nori
You may be wondering: what about vitamins B4, B8, B10, and B11? Those are now vacant spots, that once contained things that are no longer considered vitamins.
Three Critical Vitamin B Mistakes That May Be Sabotaging Your Health
Some mistakes that people make include:
Not supplementing when necessary
This occurs most often after midlife, especially in women, and the most common deficiencies are B1, B9, and B12.
See also: These Signs Often Mean These Nutrient Deficiencies (Do You Have Any?)
While it’s tempting to think “if I have a good balanced diet, I won’t need…” but the fact is sometimes our diet isn’t as nutrient dense as we hope—often through no fault of our own! But many modern farming methods prioritize yield over nutritional value, and that can result in plants and animals that do not have the nutritional qualities they “should”.
We wrote about this a while back, weighing up the “supplementation vs diet alone” dilemma:
Does Our Diet Need A Little Help? ← this also has a very useful chart of which vitamins people usually get too little or too much of. Note however that the statement of marginally excessive folate is slightly misleading, as the data pool contains men and women aged 18–65, while B9 is mostly needed more by women, and especially around childbirth or menopause, so B9 is actually a very common deficiency, but here it’s being balanced out lots of men getting too much (because every multivitamin has it).
Supplementing to excess
Most B vitamins have a very high maximum tolerable dose, because (with the exception of where we marked otherwise) they are water-soluble, which means that if you take more than you need, you’ll just pee it out later. Hence the famous fluorescence, for example.
However, the fat soluble form of vitamin B1 is harder to get in and harder to get out.
As for the others, problems usually only occur if you take enough to cause toxicity, faster than you pee it out. In other words, go easy on those Berocca drinks!
Nevertheless, there are other problems that can arise:
Vitamin B6 is essential—but too much can be toxic. Here’s what to know to stay safe ← tl;dr: there are issues with it causing peripheral neuropathy at doses over 10mg (the safe dose is disputed, so we’re mentioning the lowest safe dose here, but you can read about the others in the article)
Getting forms that don’t work so well
Those different forms we listed? They are not all created equal! For example:
- Folic acid is cheap; unfortunately, it’s not absorbed or used well
- Cyanocobalamin is cheap; unfortunately, it’s not absorbed or used well
Let us quote a recent book review of ours:
❝Rather, the most common forms of vitamins B9 and B12 provided in supplements are folic acid and cyanocobalamin, respectively, which as he demonstrates with extensive research to back up his claims, cannot be easily absorbed or used especially well.
About those vitamers: a vitamer is simply a form of a vitamin—most vitamins we need can arrive in a variety of forms. In the case of vitamins B9 and B12, he advocates for ditching vitamers folic acid and cyanocobalamin, cheap as they are, and springing for bioactive vitamers L-methylfolate, methylcobalamin, and adenosylcobalamin.
He also discusses (again, just as well-evidenced as the above things) why we might struggle to get enough from our diet after a certain age. For example, if trying to get these vitamins from meat, 50% of people over 50 cannot manufacture enough stomach acid to break down that protein to release the vitamins.
And as for methyl-B12 vitamers, you might expect you can get those from meat, and technically you can, but they don’t occur in all animals, just in one kind of animal. Specifically, the kind that has the largest brain-to-body ratio. However, eating the meat of this animal can result in protein folding errors in general and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease in particular, so the author does not recommend eating humans, however nutritionally convenient that would be.
All this means that supplementation after a certain age really can be a sensible way to do it—but do it wisely, and pick the right vitamers.❞
You can read that review in full here: Your Vitamins are Obsolete: The Vitamer Revolution – by Dr. Sheldon Zablow
Want to try those latter two?
We don’t sell them, but here for your convenience are example products on Amazon:
L-methylfolate (active form of vitamin B9)
Methylcobalamin, adenosylcobalamin, & hydroxocobalamin (active forms of vitamin B12)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Health Tips for Males Too
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Articles are very informative and helpful. Maybe it’s me but things seem to lean more toward females. That being said don’t forget us males❞
Rest assured, we could never forget you! We try to make as much as possible of our content applicable to as many as possible of our readers, but of course not everything can be relevant for everyone.
This is, presumably, in response to our recent feature on menopausal health, because previous to that, our next-most-recent main feature that centred women’s health was a month ago—that was about breast cancer, and did have a section on breast cancer in men too. You might also enjoy the book we reviewed recently about prostate health, or our regular sponsor offering testosterone therapy. Please feel free to check out our articles on saw palmetto against male pattern baldness and BPH, as well as mental health issues that disproportionally affect men.
And of course, if you have specific questions/requests about men’s health (or any other health topic) we’re only ever an email away (or use the handy feedback widget, as you did to make this request)!
Share This Post
-
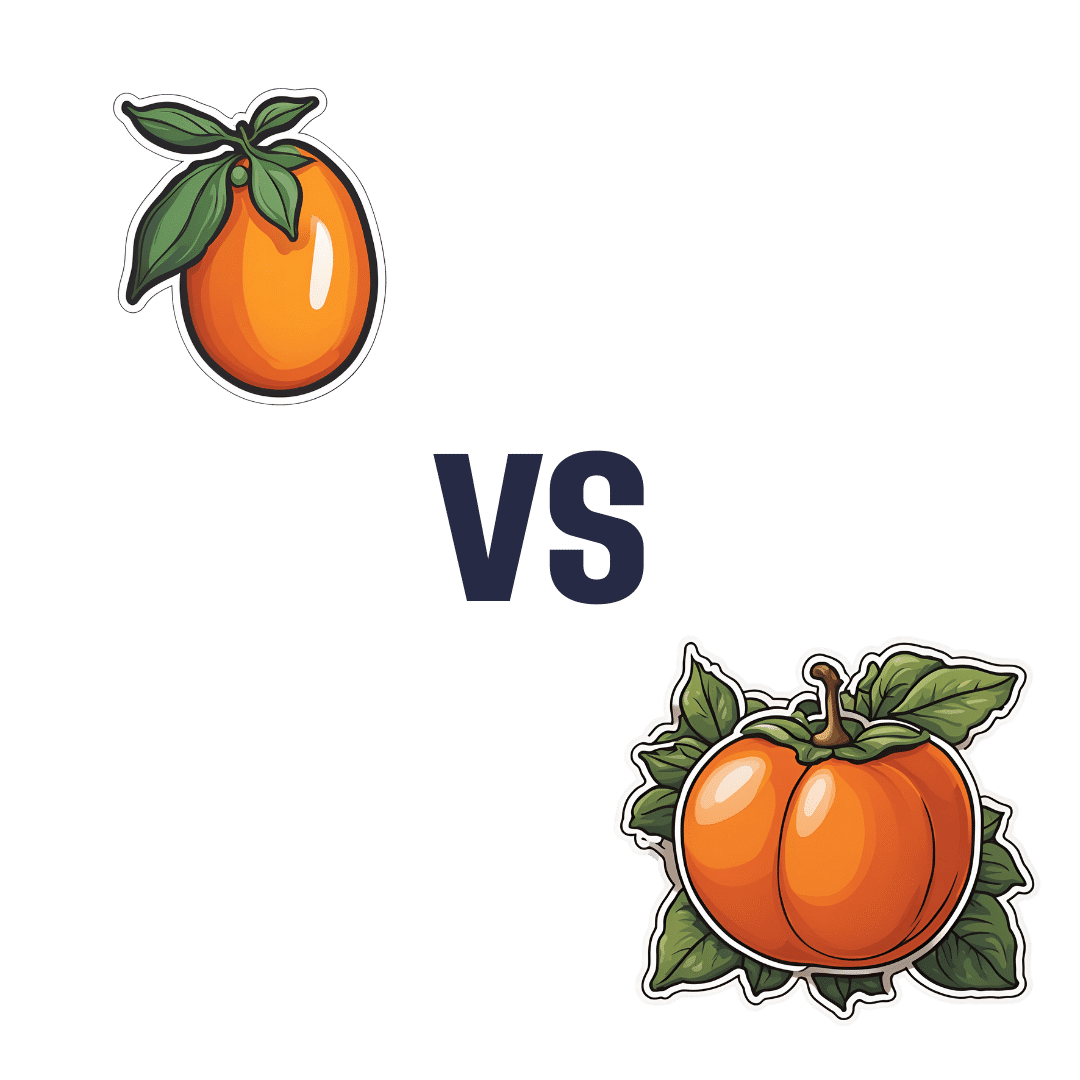
Kumquat vs Persimmon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kumquat to persimmon, we picked the kumquat.
Why?
In terms of macros, kumquats have more protein, though like most fruits, it’s unlike anybody’s eating them for the protein content. More importantly, they have a lot more fiber, for less than half the carbs. It bears mentioning though that (again, like most fruits) persimmon isn’t bad for this either, and both fruits are low glycemic index foods.
When it comes to vitamins, it’s not close: kumquats have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, E, and choline, while persimmon has more vitamin C. It’s worth noting that kumquats are already a very good source of vitamin C though; persimmon just has more.
In the category of minerals, kumquats again lead with more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while persimmon has more iron, phosphorus, and potassium.
In short, enjoy both, and/or whatever fruit you enjoy the most, but if looking for nutritional density, kumquats are bringing it.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Fixing Fascia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fascia: Why (And How) You Should Take Care Of Yours
Fascia is the web-like layer of connective tissue that divides your muscles and organs from each other. It simultaneously holds some stuff in place, and allows other parts to glide over each other with minimal friction.
At least, that’s what it’s supposed to do.
Like any body part, it can go wrong. More on this later. But first…
A quick note on terms
It may seem like sometimes people say “myofascial” because it sounds fancier, but it does actually have a specific meaning too:
- “Fascia” is what we just described above
- “Myofascial” means “of or relating to muscles and fascia”
For example, “myofascial release” means “stopping the fascia from sticking to the muscle where it shouldn’t” and “myofascial pain” means “pain that has to do with the muscles and fascia”. See also:
Myofascial vs Fascia: When To Use Each One? What To Consider
Why fascia is so ignored
For millennia, it was mostly disregarded as a “neither this nor that” tissue that just happens to be in the body. We didn’t pay attention to it, just like we mostly don’t pay attention to the air around us.
But, much like the air around us, we sure pay attention when something goes wrong with it!
However, even in more recent years, we’ve been held back until quite new developments like musculoskeletal ultrasound that could show us problems with the fascia.
What can go wrong
It’s supposed to be strong, thin, supple, and slippery. It holds on in the necessary places like a spiderweb, but for the most part, it is evolved for minimum friction.
Some things can cause it to thicken and become sticky in the wrong places. Things such as:
- Physical trauma, e.g. an injury or surgery—but we repeat ourselves, because a surgery is an injury! It’s a (usually) necessary injury, but an injury nonetheless.
- Compensation for pain. If a body part hurts for some reason, and your posture changes to accommodate that, doing so can mess up your fascia, and cause you different problems somewhere else entirely.
- This is not witchcraft; think of how, when using a corded vacuum cleaner, sometimes the cord can get snagged on something in the next room and we nearly break something because we expected it to just come with us and it didn’t? It’s like that.
- Repetitive movements (repetitive strain injury is partly a myofascial issue)
- Not enough movement: when it comes to range of motion, it’s “use it or lose it”.
- The human body tries its best to be as efficient as possible for us! So eventually it will go “Hey, I notice you never move more than 30º in this direction, so I’m going to stop making fascia that allows you to go past that point, and I’ll just dump the materials here instead”
“I’ll just dump the materials here instead” is also part of the problem—it creates what we colloquially call “knots”, which are not so much part of the muscle as the fascia that covers it. That’s an actual physical sticky lumpy bit.
What to do about it
Firstly, avoid the above things! But, if for whatever reason something has gone wrong and you now have sticky lumpy fascia that doesn’t let you move the way you’d like (if you have any mobility/flexibility issues that aren’t for another known reason, then this is usually it), there are things can be done:
- Heat—is definitely not a cure-all, but it’s a good first step before doing the other things. A heating pad or a warm bath are great.
- Here’s an example of a neck+back+shoulders heating pad; you can get them for different body parts, or just use an electric blanket!
- Massage—ideally, by someone else who knows what they are doing. Self-massage is possible, as is teaching oneself (there are plenty of video tutorials available), but skilled professional therapeutic myofascial release massage is the gold standard.
- Foam rollers are a great no-skill way to get going with self-massage, whether because that’s what’s available to you, or because you just want something you can do between sessions. Here’s an example of the kind we mean.
- Acupuncture—triggering localized muscular relaxation, an important part of myofascial release, is something acupuncture is good at.
- See also: Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture ← noteworthily, the strongest criticism of acupuncture for pain relief is that it performs only slightly better than sham acupuncture, but taken in practical terms, all that really means is “sticking little needles in does work, even if not necessarily by the mechanism acupuncturists believe”
- Calisthenics—Pilates, yoga, and other forms of body movement training can help gradually get one’s fascia to where and how it’s supposed to be.
- This is that “use it or lose it” bodily efficiency we talked about!
Remember, the body is always rebuilding itself. It never stops, until you die. So on any given day, you get to choose whether it rebuilds itself a little bit worse or a little bit better.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
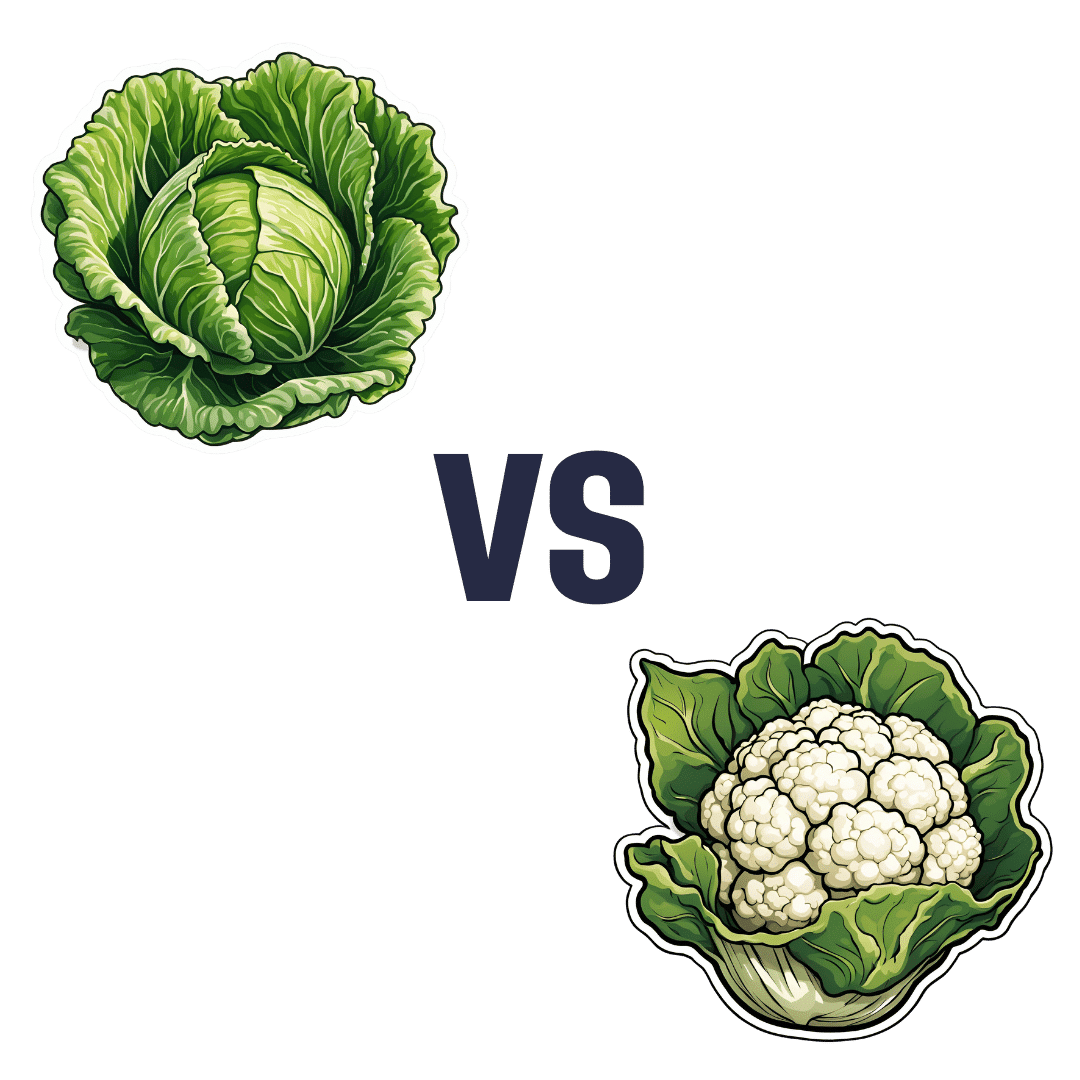
Cabbage vs Cauliflower – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cabbage to cauliflower, we picked the cauliflower.
Why?
First, let’s note: these are two different cultivars of the same species (Brassica oleracea) and/but as usual (we say, as there are a lot of cultivars of Brassica oleracea, and we’ve done a fair few pairings of them before) there are still nutritional differences to consider, such as…
In terms of macros, cabbage has very slightly more carbs and fiber, while cauliflower has very slightly more protein. However, the numbers are all so close (and the glycemic index equal), such that we’re going to call the macros category a tie.
In the category of vitamins, cabbage has more of vitamins A, B1, E, and K, while cauliflower has more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline. Superficially, this is a clear 8:4 win for cauliflower; it’s worth noting though that the differences in amounts are mostly small, so this isn’t as big a win as it looks like. Still a win for cauliflower, though.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a similar story: cabbage has a little more calcium, iron, and manganese, while cauliflower has a little more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. This time a 6:3 win for cauliflower, and again, the margins are small so there’s really not as much between them as it looks like. Still a win for cauliflower, though.
In short: enjoy either or both (diversity is good), but the most nutritionally dense is cauliflower, even if cabbage isn’t far behind it.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pine Nuts vs Macadamia Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pine nuts to macadamias, we picked the pine nuts.
Why?
In terms of macros, it’s subjective depending on what you want to prioritize; the two nuts are equal in carbs, but pine nuts have more protein and macadamias have more fiber. We’d generally prioritize the fiber, which so far would give macadamias a win in this category, but if you prefer the protein, then consider it pine nuts. Next, we must consider fats; macadamias have slightly more fat, and of which, proportionally more saturated fat, resulting in 3x the total saturated fat compared to pine nuts, gram for gram. With this in mind, we consider this category a tie or a marginal nominal win for pine nuts.
In the category of vitamins, pine nuts have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, E, K, and choline, while macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, and C. A clear win for pine nuts this time, especially with pine nuts having more than 17x the vitamin E of macadamias.
When it comes to minerals, pine nuts have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while macadamias have more calcium and selenium. Another easy win for pine nuts.
In short, enjoy either or both (diversity is good), but pine nuts are the healthier by most metrics.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: