Walking… Better.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Walking… Better.
We recently reviewed “52 Ways To Walk” by Annabel Streets. You asked us to share some more of our learnings from that book, and… Obviously we can’t do all 52, nor go into such detail, but here are three top tips inspired by that book…
Walk in the cold!
While cold weather is often seen as a reason to not walk, in fact, it has numerous health benefits, the most exciting of which might be:
Walking in the cold causes us to convert white and yellow fat into the healthier brown fat. If you didn’t know about this, neither did scientists until about 15 years ago.
In fact, scientists didn’t even know that adult humans could even have brown adipose tissue! It was really quite groundbreaking.
In case you missed it: The Changed Metabolic World with Human Brown Adipose Tissue: Therapeutic Visions
Work while you walk!
Obviously this is only appropriate for some kinds of work… but if in your life you have any kind of work that is chiefly thinking, a bunch of it can be done while walking.
Open your phone’s note-taking app, lock the screen and pocket your phone, and think on some problem that you need to solve. Whenever you have an “aha” moment, take out your phone and make a quick note on the go.
For that matter, if you have the money and space (or are fortunate to have an employer disposed towards facilitating such), you could even set up a treadmill desk… At worst, it wouldn’t harm your work (and it’ll be a LOT better than sitting for so long).
Walk within an hour of waking!
No, this doesn’t mean that if you don’t get out of the house within 60 minutes you say “Oh no, missed the window, guess it’s a day in today”
But it does mean: in the evening, make preparations to head out first thing in the morning. Set out your clothes and appropriate footwear, find your flask to fill with the beverage of your choice in the morning and set that with them.
Then, when morning arrives… do your morning necessaries (e.g. some manner of morning ablutions and perhaps a light breakfast), make that drink for your flask, and hit the road.
Why? We’ll tell you a secret:
You ever wondered why some people seem to be more able to keep a daylight-regulated circadian rhythm than others? It’s not just about smartphones and coffees…
This study found that getting sunlight (not electric light, not artificial sunlight, but actual sunlight, from the sun, even if filtered through partial cloud) between 08:30—09:00 resulted in higher levels of a protein called PER2. PER2 is critical for setting circadian rhythms, improving metabolism, and fortifying blood vessels.
Besides, on a more simplistic level, it’s also a wonderful and energizing start to a healthy and productive day!
Read: Beneficial effects of daytime light exposure on daily rhythms, metabolic state and affect
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Healers Heal – by Dr. Shilpi Pradhan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First note: the listed author here is in fact the compiler, with the authors being a collection of no fewer than 33 board-certified lifestyle medicine physicians. So, we’re not getting just a single person’s opinions/bias here!
But what is lifestyle medicine? This book holds the six pillars of lifestyle medicine to be:
- Nutrition
- Physical activity
- Stress management
- Restorative sleep
- Social connections
- Avoidance of risky substances
…and those things are what we read about throughout the book, both in highly educational mini-lecture form, and sometimes highly personal storytelling.
It’s not just a “do these things” book, though yes, there’s a large part of that. It also covers wide topics, from COVID to alopecia, burnout to grief, immune disorders to mysterious chest pains (and how such mysteries are unravelled, when taken seriously).
One of the greatest strengths of this book is that it’s very much “medicine, as it should be”, so that the reader knows how to recognize the difference.
Bottom line: this book doesn’t fit into a very neat category, but it’s a very worthwhile book to read, and one that could help inform a decision that changes the entire path of your life or that of a loved one.
Click here to check out How Healers Heal, and learn to recognize the healthcare you deserve!
Share This Post
-
Statins: Study Insights
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Q: Can you let us know about more studies that have been done on statins? Are they really worth taking?
That is a great question! We imagine it might have been our recent book recommendation that prompted it? It’s quite a broad question though, so we’ll do that as a main feature in the near future!
Share This Post
-
How To Actually Get Abs (10 Annoying Tips That Work!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cori Lefkowitz, of “Strong At Any Age”, advises…
The method
It may not be fun, but here’s what she finds works:
- Be boring: stick to a simple, repetitive diet to track progress easily, and make hitting macros simpler.
- Cut back on protein bars: processed protein bars are calorie-dense but not filling (due to their small volume), so limit them, especially when trying to get lean.
- Stop daily fluctuations: she advises to be precise with macros and calories daily, not just weekly, to see consistent results.
- Focus on fiber: aim for 25–30g of fiber daily to improve gut health, reduce cravings, and maintain health while cutting fat.
- Get 30–40g of protein per meal: ensure each meal has enough protein to fuel muscle growth and support overall body function.
- Prioritize carbs around workouts: eat carbs before and after training to fuel performance, aid muscle repair, and maintain lean mass.
- Take diet breaks: incorporate 1–2 week maintenance phases to prevent metabolic adaptation, maintain muscle, and thus stay consistent in the long-term.
- Be careful with fat burners & preworkout: these can harm sleep, recovery, and long-term fat loss; opt for natural dietary energy sources instead.
- Don’t set-and-forget: regularly assess and adjust your diet and macros as your body and lifestyle change.
- “Suck it up, buttercup”: fat loss requires persistence, discipline, and pushing through tough moments when you feel like quitting.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Is A Visible Six-Pack Obtainable Regardless Of Genetic Predisposition?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Rest For The Restless (Legs)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Any tips for dealing with restless legs syndrome?❞
As a neurological disorder (Willis-Ekbom Disease, as it is also called
by almost nobody outside of academia), there’s a lot that’s not known about its pathology, but we do know that looking after one’s nerves can help a lot.This means:
- Avoid alcohol, as this is bad for everything, including nerves
- See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
- Don’t smoke, as this is bad for everything, including nerves
- Do exercise those restless legs! It may sound funny, but in seriousness, movement promotes nerve health
- See also: Walking… Better.
- Take care of your blood sugars, because diabetic neuropathy can also cause this
- See also: 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- Massage your legs, and enjoy a hot bath/shower
You can also take into account the measures recommended for dealing with peripheral neuropathy, e.g:
Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
There are also medication options for RLS; most of them are dopamine agonists, so if you want to try something yourself before going the pharmaceutical route, then things that improve your dopamine levels will probably be a worth checking out. In the category of supplements, you might enjoy:
NALT: The Dopamine Precursor And More
Take care! And… Want something answered here? Send us your questions!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Avoid alcohol, as this is bad for everything, including nerves
-
Foot Drop!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Interesting about DVT after surgery. A friend recently got diagnosed with foot drop. Could you explain that? Thank you.❞
First, for reference, the article about DVT after surgery was:
DVT Risk Management Beyond The Socks
As for foot drop…
Foot drop is descriptive of the main symptom: the inability to raise the front part of the foot due to localized weakness/paralysis. Hence, if a person with foot drop dangles their feet over the edge of the bed, for example, the affected foot will simply flop down, while the other (if unaffected) can remain in place under its own power. The condition is usually neurological in origin, though there are various more specific causes:
When walking unassisted, this will typically result in a distinctive “steppage gait”, as it’s necessary to lift the foot higher to compensate, or else the toes will scuff along the ground.
There are mobility aids that can return one’s walking to more or less normal, like this example product on Amazon.
Incidentally, the above product will slightly shorten the lifespan of shoes, as it will necessarily pull a little at the front.
There are alternatives that won’t like this example product on Amazon, but this comes with the different problem that it limits the user to stepping flat-footedly, which is not only also not an ideal gait, but also, will serve to allow any muscles down there that were still (partially or fully) functional to atrophy. For this reason, we’d recommend the first product we mentioned over the second one, unless your personal physiotherapist or similar advises otherwise (because they know your situation and we don’t).
Both have their merits, though:
Trends and Technologies in Rehabilitation of Foot Drop: A Systematic Review
Of course, prevention is better than cure, so while some things are unavoidable (especially when it comes to neurological conditions), we can all look after our nerve health as well as possible along the way:
Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
…as well as the very useful:
What Does Lion’s Mane Actually Do, Anyway?
…which this writer personally takes daily and swears by (went from frequent pins-and-needles to no symptoms and have stayed that way, and that’s after many injuries over the years).
If you’d like a more general and less supplements-based approach though, check out:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caloric Restriction with Optimal Nutrition
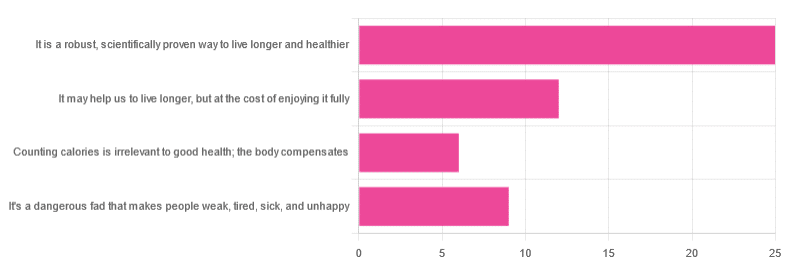
Yesterday, we asked you “What is your opinion of caloric restriction as a health practice?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- 48% said “It is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier”
- 23% said “It may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully”
- 17% said “It’s a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy”
- 12% said “Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates”
So… What does the science say?
A note on terms, first
“Caloric restriction” (henceforth: CR), as a term, sees scientific use to mean anything from a 25% reduction to a 50% reduction, compared to metabolic base rate.
This can also be expressed the other way around, “dropping to 60% of the metabolic base rate” (i.e., a 40% reduction).
Here we don’t have the space to go into much depth, so our policy will be: if research papers consider it CR, then so will we.
A quick spoiler, first
The above statements about CR are all to at least some degree True in one way or another.
However, there are very important distinctions, so let’s press on…
CR is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier: True or False?
True! This has been well-studied and well-documented. There’s more science for this than we could possibly list here, but here’s a good starting point:
❝Calorie restriction (CR), a nutritional intervention of reduced energy intake but with adequate nutrition, has been shown to extend healthspan and lifespan in rodent and primate models.
Accumulating data from observational and randomized clinical trials indicate that CR in humans results in some of the same metabolic and molecular adaptations that have been shown to improve health and retard the accumulation of molecular damage in animal models of longevity.
In particular, moderate CR in humans ameliorates multiple metabolic and hormonal factors that are implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, the leading causes of morbidity, disability and mortality❞
Source: Ageing Research Reviews | Calorie restriction in humans: an update
See also: Caloric restriction in humans reveals immunometabolic regulators of health span
We could devote a whole article (or a whole book, really) to this, but the super-short version is that it lowers the metabolic “tax” on the body and allows the body to function better for longer.
CR may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully: True or False?
True or False, contingently, depending on what’s important to you. And that depends on psychology as much as physiology, but it’s worth noting that there is often a selection bias in the research papers; people ill-suited to CR drop out of the studies and are not counted in the final data.
Also, relevant for a lot of our readers, most (human-based) studies recruit people over 18 and under 60. So while it is reasonable to assume the same benefits will be carried over that age, there is not nearly as much data for it.
Studies into CR and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) have been promising, and/but have caveats:
❝In non-obese adults, CR had some positive effects and no negative effects on HRQoL.❞
❝We do not know what degree of CR is needed to achieve improvements in HRQoL, but we do know it requires an extraordinary amount of support.
Therefore, the incentive to offer this intervention to a low-risk, normal or overweight individual is lacking and likely not sustainable in practice.❞
CR a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy: True or False?
True if it is undertaken improperly, and/or without sufficient support. Many people will try CR and forget that the idea is to reduce metabolic load while still getting good nutrition, and focus solely on the calorie-counting.
So for example, if a person “saves” their calories for the day to have a night out in a bar where they drink their calories as alcohol, then this is going to be abysmal for their health.
That’s an extreme example, but lesser versions are seen a lot. If you save your calories for a pizza instead of a night of alcoholic drinks, then it’s not quite so woeful, but for example the nutrition-to-calorie ratio of pizza is typically not great. Multiply that by doing it as often as not, and yes, someone’s health is going to be in ruins quite soon.
Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates: True or False?
True if by “good health” you mean weight loss—which is rarely, if ever, what we mean by “good health” here at 10almonds (unless we clarify such), but it’s a very common association and indeed, for some people it’s a health goal. You cannot sustainably and healthily lose weight by CR alone, especially if you’re not getting optimal nutrition.
Your body will notice that you are starving, and try to save you by storing as much fat as it can, amongst other measures that will similarly backfire (cortisol running high, energy running low, etc).
For short term weight loss though, yes, it’ll work. At a cost. That we don’t recommend.
❝By itself, decreasing calorie intake will have a limited short-term influence.❞
Source: Reducing Calorie Intake May Not Help You Lose Body Weight
See also…
❝Caloric restriction is a commonly recommended weight-loss method, yet it may result in short-term weight loss and subsequent weight regain, known as “weight cycling”, which has recently been shown to be associated with both poor sleep and worse cardiovascular health❞
Source: Dieting Behavior Characterized by Caloric Restriction
In summary…
Caloric restriction is a well-studied area of health science. We know:
- Practised well, it can extend not only lifespan, but also healthspan
- Practised well, it can improve mood, energy, sexual function, and the other things people fear losing
- Practised badly, it can be ruinous to the health—it is critical to practise caloric restriction with optimal nutrition.
- Practised badly, it can lead to unhealthy weight loss and weight regain
One final note…
If you’ve tried CR and hated it, and you practised it well (e.g., with optimal nutrition), then we recommend just not doing it.
You could also try intermittent fasting instead, for similar potential benefits. If that doesn’t work out either, then don’t do that either!
Sometimes, we’re just weird. It can often be because of a genetic or epigenetic quirk. There are usually workarounds, and/but not everything that’s right for most people will be right for all of us.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: