Slowing the Progression of Cataracts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Understanding Cataracts
Cataracts are natural and impact everyone.
That’s a bit of a daunting opening line, but as Dr. Michele Lee, a board-certified ophthalmologist, explains, cataracts naturally develop with age, and can be accelerated by factors such as trauma, certain medications, and specific eye conditions.
We know how important your vision is to you (we’ve had great feedback about the book Vision for Life) as well as our articles on how glasses impact your eyesight and the effects of using eye drops.
While complete prevention isn’t possible, steps such as those mentioned below can be taken to slow their progression.
Here is an overview of the video’s first 3 takeaways. You can watch the whole video below.
Protect Your Eyes from Sunlight
Simply put, UV light damages lens proteins, which (significantly) contributes to cataracts. Wearing sunglasses can supposedly prevent up to 20% of cataracts caused by UV exposure.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption
We all, at some level, know that alcohol consumption doesn’t do us any good. Your eye health isn’t an exception to the rule; alcohol has been shown to contribute to cataract development.
If you’re looking at reducing your alcohol use, try reading this guide on lowering, or eradicating, alcohol consumption.
Avoid Smoking
Smokers are 2-3 times more likely to develop cataracts. Additionally, ensure good ventilation while cooking to avoid exposure to harmful indoor smoke.
See all 5 steps in the below video:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Soy Beans vs Kidney Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing soy beans to kidney beans, we picked the soy.
Why?
In terms of macros, soy has 2x the protein, while kidney beans have nearly 3x the carbs and very slightly more fiber. Ratio-wise, the “very slightly more fiber” does not offset the “nearly 3x the carbs” when it comes to glycemic index (though both are still good, really, but this is a head-to-head so the comparison is relevant), and 2x the protein is also quite a bonus, so this category’s an easy win for soy.
In the category of vitamins, soy beans have more of vitamins A, B2, B6, C, E, K, and choline, while kidney beans have more of vitamins B3, B5, and B9, thus making for a 7:3 win for soy.
When it comes to minerals, soy beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while kidney beans are not higher in any mineral. Another clear win for soy.
Adding up the three strong wins for soy, makes for an overall easy win for soy. Still, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Each Monday, we’re going to be bringing you cutting-edge research reviews to not only make your health and productivity crazy simple, but also, constantly up-to-date.
But today, in this special edition, we want to lay out plain and simple how to see through a lot of the tricks used not just by popular news outlets, but even sometimes the research publications themselves.
That way, when we give you health-related science news, you won’t have to take our word for it, because you’ll be able to see whether the studies we cite really support the claims we make.
Of course, we’ll always give you the best, most honest information we have… But the point is that you shouldn’t have to trust us! So, buckle in for today’s special edition, and never have to blindly believe sci-hub (or Snopes!) again.
The above now-famous Tumblr post that became a meme is a popular and obvious example of how statistics can be misleading, either by error or by deliberate spin.
But what sort of mistakes and misrepresentations are we most likely to find in real research?
Spin Bias
Perhaps most common in popular media reporting of science, the Spin Bias hinges on the fact that most people perceive numbers in a very “fuzzy logic” sort of way. Do you?
Try this:
- A million seconds is 11.5 days
- A billion seconds is not weeks, but 13.2 months!
…just kidding, it’s actually nearly thirty-two years.
Did the months figure seem reasonable to you, though? If so, this is the same kind of “human brains don’t do large numbers” problem that occurs when looking at statistics.
Let’s have a look at reporting on statistically unlikely side effects for vaccines, as an example:
- “966 people in the US died after receiving this vaccine!” (So many! So risky!)
- “Fewer than 3 people per million died after receiving this vaccine!” (Hmm, I wonder if it is worth it?)
- “Half of unvaccinated people with this disease die of it” (Oh)
How to check for this: ask yourself “is what’s being described as very common really very common?”. To keep with the spiders theme, there are many (usually outright made-up) stats thrown around on social media about how near the nearest spider is at any given time. Apply this kind of thinking to medical conditions.. If something affects only 1% of the population (So few! What a tiny number!), how far would you have to go to find someone with that condition? The end of your street, perhaps?
Selection/Sampling Bias
Diabetes disproportionately affects black people, but diabetes research disproportionately focuses on white people with diabetes. There are many possible reasons for this, the most obvious being systemic/institutional racism. For example, advertisements for clinical trial volunteer opportunities might appear more frequently amongst a convenient, nearby, mostly-white student body. The selection bias, therefore, made the study much less reliable.
Alternatively: a researcher is conducting a study on depression, and advertises for research subjects. He struggles to get a large enough sample size, because depressed people are less likely to respond, but eventually gets enough. Little does he know, even the most depressed of his subjects are relatively happy and healthy compared with the silent majority of depressed people who didn’t respond.
See This And Many More Educational Cartoons At Sketchplanations.com!
How to check for this: Does the “method” section of the scientific article describe how they took pains to make sure their sample was representative of the relevant population, and how did they decide what the relevant population was?
Publication Bias
Scientific publications will tend to prioritise statistical significance. Which seems great, right? We want statistically significant studies… don’t we?
We do, but: usually, in science, we consider something “statistically significant” when it hits the magical marker of p=0.05 (in other words, the probability of getting that result is 1/20, and the results are reliably coming back on the right side of that marker).
However, this can result in the clinic stopping testing once p=0.05 is reached, because they want to have their paper published. (“Yay, we’ve reached out magical marker and now our paper will be published”)
So, you can think of publication bias as the tendency for researchers to publish ‘positive’ results.
If it weren’t for publication bias, we would have a lot more studies that say “we tested this, and here are our results, which didn’t help answer our question at all”—which would be bad for the publication, but good for science, because data is data.
To put it in non-numerical terms: this is the same misrepresentation as the technically true phrase “when I misplace something, it’s always in the last place I look for it”—obviously it is, because that’s when you stop looking.
There’s not a good way to check for this, but be sure to check out sample sizes and see that they’re reassuringly large.
Reporting/Detection/Survivorship Bias
There’s a famous example of the rise in “popularity” of left-handedness. Whilst Americans born in ~1910 had a bit under a 3.5% chance of being left handed, those born in ~1950 had a bit under a 12% change.
Why did left-handedness become so much more prevalent all of a sudden, and then plateau at 12%?
Simple, that’s when schools stopped forcing left-handed children to use their right hands instead.
In a similar fashion, countries have generally found that homosexuality became a lot more common once decriminalized. Of course the real incidence almost certainly did not change—it just became more visible to research.
So, these biases are caused when the method of data collection and/or measurement leads to a systematic error in results.
How to check for this: you’ll need to think this through logically, on a case by case basis. Is there a reason that we might not be seeing or hearing from a certain demographic?
And perhaps most common of all…
Confounding Bias
This is the bias that relates to the well-known idea “correlation ≠ causation”.
Everyone has heard the funny examples, such as “ice cream sales cause shark attacks” (in reality, both are more likely to happen in similar places and times; when many people are at the beach, for instance).
How can any research paper possibly screw this one up?
Often they don’t and it’s a case of Spin Bias (see above), but examples that are not so obviously wrong “by common sense” often fly under the radar:
“Horse-riding found to be the sport that most extends longevity”
Should we all take up horse-riding to increase our lifespans? Probably not; the reality is that people who can afford horses can probably afford better than average healthcare, and lead easier, less stressful lives overall. The fact that people with horses typically have wealthier lifestyles than those without, is the confounding variable here.
See This And Many More Educational Cartoons on XKCD.com!
In short, when you look at the scientific research papers cited in the articles you read (you do look at the studies, yes?), watch out for these biases that found their way into the research, and you’ll be able to draw your own conclusions, with well-informed confidence, about what the study actually tells us.
Science shouldn’t be gatekept, and definitely shouldn’t be abused, so the more people who know about these things, the better!
So…would one of your friends benefit from this knowledge? Forward it to them!
Share This Post
-
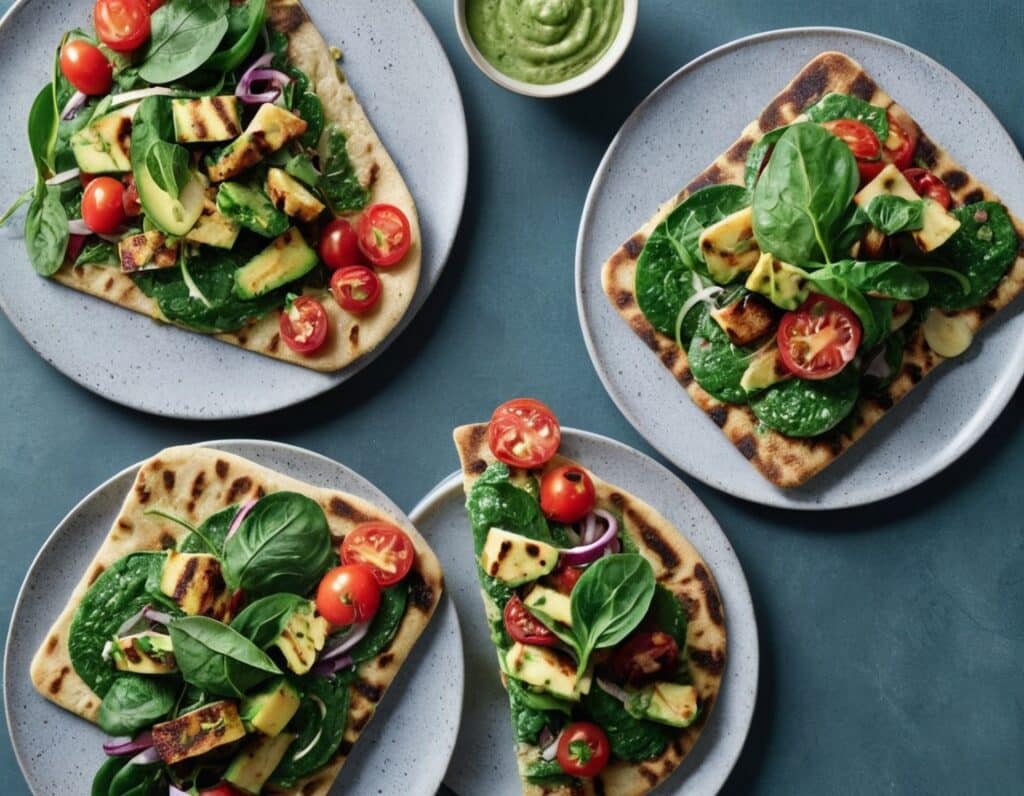
Green Paneer Flatbreads
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These are versatile little snacks that can be eaten alone or served as part of a buffet; great for warm summer nights!
You will need
- 1 lb block of paneer (you can also use our plant-based high-protein paneer recipe)
- 7 oz unsweetened yogurt (your choice what kind; plant-based is fine; live cultured is best)
- 1 tomato, thinly sliced
- ½ red onion, thinly sliced
- 2 oz spinach leaves
- 1 tbsp lime juice
- 1 tsp red chili powder
- 4 wholewheat flatbreads
And then the marinade:
- 3 oz spinach
- ½ bulb garlic
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp coriander seeds
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt (MSG being the preferable and healthier option)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- Juice of ½ lime
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the marinade ingredients in a blender.
2) Cut the paneer into long cuboid chapes (similar to fish fingers) and put them in a bowl. Pour ⅔ of the marinade over them, and gently mix to coat evenly.
3) Heat a ridged griddle pan, and when hot, add the paneer and cook for 1–2 minutes each side without stirring, jiggling, or doing anything other than turning once per uncooked side.
4) Combine the onion, tomato, spinach leaves, lime choice, and chili powder to make the salad.
5) Add the remaining marinade to the yogurt to make a green dip.
6) Toast your flatbreads under the grill.
5) Assemble, putting the paneer and salad with a spoonful of the dip on the flatbread, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- High-Protein Plant-Based Paneer
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Don’t Do *This* If You’re Over 50 (And Want Better Sleep)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michael Breus, sleep specialist, explains:
Don’t make these mistakes
Dr. Breus recommends avoiding…
- Misusing magnesium: magnesium is a helpful sleep aid but must be carefully monitored. Recommended doses are 250mg for women and 300–350 mg for men, with slight adjustments for hot climates or active lifestyles. Overdosing can cause stomach issues, diarrhea, and dehydration, disrupting sleep. He recommends starting with magnesium glycinate for fewer stomach issues, and later mix with magnesium citrate. Always check supplements to avoid excessive magnesium intake.
- Misusing melatonin: melatonin production declines after age 55–60, making low-dose supplementation (0.5–1 mg) beneficial. He recommends, however, avoiding high doses (3–10mg), and he recommends to take it 90 minutes before bedtime. Melatonin interacts with some medications (including some meds for blood pressure or depression), so consult a pharmacist before use to avoid risks like serotonin syndrome.
- Going to bed too early: going to bed too early disrupts circadian rhythms and reduces sleep drive, causing earlier waking. Now, being an “early bird” is a generally healthy thing, but if you’re already getting up at 5am, say, you probably want your schedule to not continue to creep further forwards until you become nocturnal. Set a consistent wake-up time and count 7.5 hours backward (plus a set time to fall asleep, e.g. 20 minutes, but you’ll know what it is for you) to determine bedtime.
- Excessive caffeine consumption: from the heading, it may seem like a no-brainer, but older adults metabolize caffeine 33% slower on average, prolonging its effects. Dr. Breus recommends to reduce intake with “caffeine fading,” switching to half-caffeinated coffee for a while and then considering transitioning to decaf. He also suggests enjoying increasingly lower-caffeine teas, like black tea in the morning, matcha in the afternoon, and herbal tea at night to reduce caffeine’s impact on sleep.
- Falling foul of serotonin: avoid taking 5-HTP supplements with SSRI antidepressants like Prozac or Zoloft due to the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- Consider checking for physical problems: if you regularly wake up tired and/or groggy (despite having ostensibly had enough sleep, and there not being a pharmaceutical explanation for your grogginess), consider screening for sleep apnea. Home sleep tests are a convenient way to identify and treat this common but often undiagnosed condition.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
How to Fall Asleep Faster: CBT-Insomnia Treatment
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Good Energy – by Dr. Casey Means
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For a book with a title like “Good Energy” and chapters such as “Bad Energy Is the Root of Disease”, this is actually a very science-based book (and there are a flock of well-known doctors saying so in the “praise for” section, too).
The premise is simple: most of our health is a matter of what our metabolism is (or isn’t) doing, and it’s not just a case of “doing more” or “doing less”. Indeed, a lot of “our” energy is expended doing bad things (such as chronic inflammation, to give an obvious example).
Dr. Means outlines about a dozen things many people do wrong, and about a dozen things we can do right, to get our body’s energy system working for us, rather than against us.
The style here is pop-science throughout, and in the category of criticism, the bibliography is offloaded to her website (we prefer to have things in our hands). However, the information here is good, clearly-presented, and usefully actionable.
Bottom line: if you ever find yourself feeling run-down and like your body is using your resources against you rather than for you, this is the book to get you out of that slump!
Click here to check out Good Energy, and get your metabolism working for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tourette’s Syndrome Treatment Options
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Is there anything special that might help someone with Tourette’s syndrome?❞
There are of course a lot of different manifestations of Tourette’s syndrome, and some people’s tics may be far more problematic to themselves and/or others, while some may be quite mild and just something to work around.
It’s an interesting topic for sure, so we’ll perhaps do a main feature (probably also covering the related-and-sometimes-overlapping OCD umbrella rather than making it hyperspecific to Tourette’s), but meanwhile, you might consider some of these options:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: