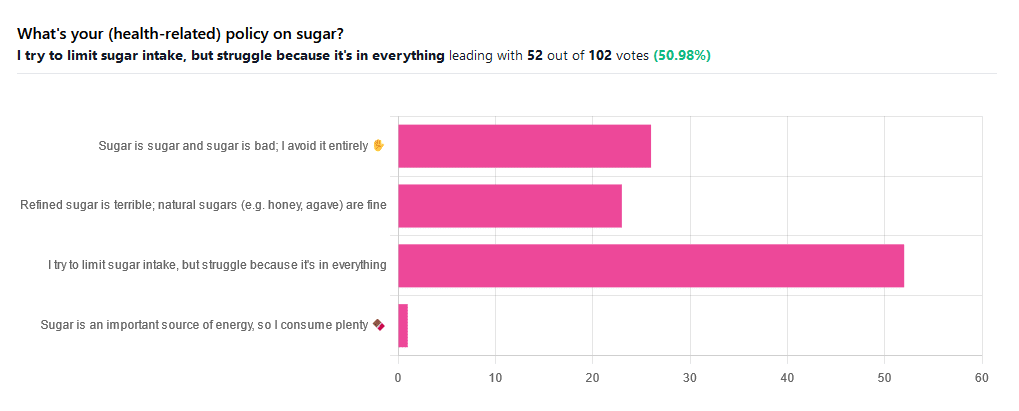Under Pressure: A Guide To Controlling High Blood Pressure – by Dr. Frita Fisher
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hypertension kills a lot of people, and does so with little warning—it can be asymptomatic before it gets severe enough to cause harm, and once it causes harm, well, one heart attack or stroke is already one too many.
Aimed more squarely at people in the 35–45 danger zone (young enough to not be getting regular blood pressure checks, old enough that it may have been building up for decades), this is a very good primer on blood pressure, factors affecting it, what goes wrong, what to do about it, and how to make a good strategy for managing it for life.
The style is easy-reading, making this short (91 pages) book a very quick read, but an informative one.
Bottom line: if you are already quite knowledgeable about blood pressure and blood pressure management, this one’s probably not for you. But if you’re in the category of “what do those numbers mean again?”, then this is a very handy book to have, to get you up to speed so that you can handle things as appropriate.
Click here to check out Under Pressure, and get/keep yours under control!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
25 Healthy Habits That Will Change Your Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cori Lefkowith, of “Redefining Strength” and “Strong At Every Age” fame, has compiled a list of the simple habits that make a big difference, and here they are!
The Tips
Her recommendations include…
- The healthy activities you’re most prone to skipping? Do those first
- Create staple meals… Consciously! This means: instead of getting into a rut of cooking the same few things in rotation because it’s what you have the ingredients in for, consciously and deliberately make a list of at least 7 meals that, between them, constitute a healthy balanced diet, and choose to make them your staples. That doesn’t mean don’t eat anything else (indeed, variety is good!) but having a robust collection of healthy staples to fall back on will help you avoid falling into unhealthy eating traps.
- Schedule time for healthy activities that you love. Instead of thinking “it would be nice to…”, actually figure out a timeslot, plan in advance, making it recurring, and do it!
- Have (healthy!) no-spoil food options always available. No-spoil doesn’t have to mean “won’t spoil ever”, but does mean at least that it has a long shelf-life. Nuts are a good example, assuming you’re not allergic. Sundried fruits are good too; not nearly as good as fresh fruit, but a lot better than some random processed snack because it’s what in. If you eat fish, then see if you can get dried fish in; it’s high in protein and keeps for a very long time indeed.
- Stock up on spices! Not only do they all have great health-giving properties (at least, we can’t think of a refutation by counterexample, Arrakis be damned), but also, they literally spice up our culinary repertoire, and bring joy to cooking and eating healthy food.
If you like these, check out the rest:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Further reading
For more about actually making habits stick quickly and reliably,enjoy:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs
We asked you for your (health-related) policy on sugar. The trends were as follows:
- About half of all respondents voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Refined sugar is terrible; natural sugars (e.g. honey, agave) are fine”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad; I avoid it entirely”
- One (1) respondent voted for “Sugar is an important source of energy, so I consume plenty”
Writer’s note: I always forget to vote in these, but I’d have voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”.
Sometimes I would like to make my own [whatever] to not have the sugar, but it takes so much more time, and often money too.
So while I make most things from scratch (and typically spend about an hour cooking each day), sometimes store-bought is the regretfully practical timesaver/moneysaver (especially when it comes to condiments).
So, where does the science stand?
There has, of course, been a lot of research into the health impact of sugar.
Unfortunately, a lot of it has been funded by sugar companies, which has not helped. Conversely, there are also studies funded by other institutions with other agendas to push, and some of them will seek to make sugar out to be worse than it is.
So for today’s mythbusting overview, we’ve done our best to quality-control studies for not having financial conflicts of interest. And of course, the usual considerations of favoring high quality studies where possible Large sample sizes, good method, human subjects, that sort of thing.
Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
- Sucrose is sucrose, and is generally bad.
- Fructose is fructose, and is worse.
Both ultimately get converted into glycogen (if not used immediately for energy), but for fructose, this happens mostly* in the liver, which a) taxes it b) goes very unregulated by the pancreas, causing potentially dangerous blood sugar spikes.
This has several interesting effects:
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, it doesn’t cause insulin insensitivity (yay)
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, this leaves hyperglycemia untreated (oh dear)
- Because fructose is metabolized by the liver and converted to glycogen which is stored there, it’s one of the main contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (at this point, we’re retracting our “yay”)
Read more: Fructose and sugar: a major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
*”Mostly” in the liver being about 80% in the liver. The remaining 20%ish is processed by the kidneys, where it contributes to kidney stones instead. So, still not fabulous.
Fructose is very bad, so we shouldn’t eat too much fruit: True or False?
False! Fruit is really not the bad guy here. Fruit is good for you!
Fruit does contain fructose yes, but not actually that much in the grand scheme of things, and moreover, fruit contains (unless you have done something unnatural to it) plenty of fiber, which mitigates the impact of the fructose.
- A medium-sized apple (one of the most sugary fruits there is) might contain around 11g of fructose
- A tablespoon of high-fructose corn syrup can have about 27g of fructose (plus about 3g glucose)
Read more about it: Effects of high-fructose (90%) corn syrup on plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and normal subjects
However! The fiber content (in fruit) mitigates the impact of the fructose almost entirely anyway.
And if you take fruits that are high in sugar and/but high in polyphenols, like berries, they now have a considerable net positive impact on glycemic health:
- Polyphenols and Glycemic Control
- Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review
- Dietary polyphenols as antidiabetic agents: Advances and opportunities
You may be wondering: what was that about “unless you have done something unnatural to it”?
That’s mostly about juicing. Juicing removes much (or all) of the fiber, and if you do that, you’re basically back to shooting fructose into your veins:
- Effect of Fruit Juice on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials
- Intake of Fruit, Vegetables, and Fruit Juices and Risk of Diabetes in Women
Natural sugars like honey, agave, and maple syrup, are healthier than refined sugars: True or False?
True… Sometimes, and sometimes marginally.
This is partly because of the glycemic index and glycemic load. The glycemic index scores tail off thus:
- table sugar = 65
- maple syrup = 54
- honey = 46
- agave syrup = 15
So, that’s a big difference there between agave syrup and maple syrup, for example… But it might not matter if you’re using a very small amount, which means it may have a high glycemic index but a low glycemic load.
Note, incidentally, that table sugar, sucrose, is a disaccharide, and is 50% glucose and 50% fructose.
The other more marginal health benefits come from that fact that natural sugars are usually found in foods high in other nutrients. Maple syrup is very high in manganese, for example, and also a fair source of other minerals.
But… Because of its GI, you really don’t want to be relying on it for your nutrients.
Wait, why is sugar bad again?
We’ve been covering mostly the more “mythbusting” aspects of different forms of sugar, rather than the less controversial harms it does, but let’s give at least a cursory nod to the health risks of sugar overall:
- Obesity and associated metabolic risk
- Main contributor to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Insulin resistance and diabetes risk
- Cellular aging (shortened telomeres)
- 95% increased cancer risk
That last one, by the way, was a huge systematic review of 37 large longitudinal cohort studies. Results varied depending on what, specifically, was being examined (e.g. total sugar, fructose content, sugary beverages, etc), and gave up to 200% increased cancer risk in some studies on sugary beverages, but 95% increased risk is a respectable example figure to cite here, pertaining to added sugars in foods.
And finally…
The 56 Most Common Names for Sugar (Some Are Tricky)
How many did you know?
Share This Post
-
Do You Believe In Magic? – by Dr. Paul Offit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Here at 10almonds, we like to examine and present the science wherever it leads, so this book was an interesting read.
Dr. Offit, himself a much-decorated vaccine research scientist, and longtime enemy of the anti-vax crowd, takes aim at alternative therapies in general, looking at what does work (and how), and what doesn’t (and what harm it can cause).
The style of the book is largely polemic in tone, but there’s lots of well-qualified information and stats in here too. And certainly, if there are alternative therapies you’ve left unquestioned, this book will probably prompt questions, at the very least.
And science, of course, is about asking questions, and shouldn’t be afraid of such! Open-minded skepticism is a key starting point, while being unafraid to actually reach a conclusion of “this is probably [not] so”, when and if that’s where the evidence brings us. Then, question again when and if new evidence comes along.
To that end, Dr. Offit does an enthusiastic job of looking for answers, and presenting what he finds.
If the book has downsides, they are primarily twofold:
- He is a little quick to dismiss the benefits of a good healthy diet, supplemented or otherwise.
- His keenness here seems to step from a desire to ensure people don’t skip life-saving medical treatments in the hope that their diet will cure their cancer (or liver disease, or be it what it may), but in doing so, he throws out a lot of actually good science.
- He—strangely—lumps menopausal HRT in with alternative therapies, and does the exact same kind of anti-science scaremongering that he rails against in the rest of the book.
- In his defence, this book was published ten years ago, and he may have been influenced by a stack of headlines at the time, and a popular celebrity endorsement of HRT, which likely put him off it.
Bottom line: there’s something here to annoy everyone—which makes for stimulating reading.
Click here to check out Do You Believe In Magic, and expand your knowledge!
Share This Post
- He is a little quick to dismiss the benefits of a good healthy diet, supplemented or otherwise.
Related Posts
-
Decoding Hormone Balancing in Ads
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Time!
This is the bit whereby each week, we respond to subscriber questions/requests/etc
Have something you’d like to ask us, or ask us to look into? Hit reply to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom, and a Real Human™ will be glad to read it!
Q: As to specific health topics, I would love to see someone address all these Instagram ads targeted to women that claim “You only need to ‘balance your hormones’ to lose weight, get ripped, etc.” What does this mean? Which hormones are they all talking about? They all seem to be selling a workout program and/or supplements or something similar, as they are ads, after all. Is there any science behind this stuff or is it mostly hot air, as I suspect?
Thank you for asking this, as your question prompted yesterday’s main feature, What Does “Balancing Your Hormones” Even Mean?
That’s a great suggestion also about addressing ads (and goes for health-related things in general, not just hormonal stuff) and examining their claims, what they mean, how they work (if they work!), and what’s “technically true but may
be misleading* cause confusion”*We don’t want companies to sue us, of course.
Only, we’re going to need your help for this one, subscribers!
See, here at 10almonds we practice what we preach. We limit screen time, we focus on our work when working, and simply put, we don’t see as many ads as our thousands of subscribers do. Also, ads tend to be targeted to the individual, and often vary from country to country, so chances are good that we’re not seeing the same ads that you’re seeing.
So, how about we pull together as a bit of a 10almonds community project?
- Step 1: add our email address to your contacts list, if you haven’t already
- Step 2: When you see an ad you’re curious about, select “share” (there is usually an option to share ads, but if not, feel free to screenshot or such)
- Step 3: Send the ad to us by email
We’ll do the rest! Whenever we have enough ads to review, we’ll do a special on the topic.
We will categorically not be able to do this without you, so please do join in—Many thanks in advance!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Infections, Heart Failure, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some health news to round off the week:
The Infection That Leads To Heart Failure
It’s long been held that, for example, flossing reduces heart disease risk, with the hypothesis being that if plaque bacteria enter the blood stream, well, that’s an even worse place for plaque bacteria to be. Now, with much more data, attention has turned to
- actual infections, and
- actual heart failure
Way to up the ante! And, it holds true regardless of what kind of infection. So, you might think that a UTI, for example, is surely “downstream” and should not affect the heart, but it does. Because of this, researchers currently believe that it is not the infection itself, so much as the body’s inflammation response to infection, that leads to the heart failure. Which is reasonable, because, for example, atherosclerosis is made mostly not of cholesterol itself, but rather mostly of dead immune cells that got stuck in the cholesterol.
Moreover, it’s not so much about the acute inflammatory response (which is almost always a good thing, circumstantially), but rather that after cases where an infection managed to take hold, the immune system can then often stay on high alert for many years alter. Long COVID is an obvious recent example of this, but it’s hardly a new phenomenon; see for example post-polio syndrome, and consider how many more such post-infection maladies are likely to exist that never got a name because they flew under the radar or got diagnosed as fibromyalgia or something (fibromyalgia is a common diagnosis doctors give when they acknowledge something’s wrong, and it causes pain and exhaustion, but they don’t know what, and it appears to be stable—so while it can be helpful to put a name to the collection of symptoms, it’s a non-diagnosis diagnosis on the doctors’ part. It’s saying “I diagnose you with hurty tiredness”).
The take-away from all this? Avoid infections, for your heart’s sake, and if you do get an infection, take it seriously even if it’s minor. The safe amount of infection is “no infection”.
Read in full: Study uncovers new link between infections and heart failure
Cold Water Immersion: Hot Or Not?
The evidence is clear for some benefits; for others, not so much:
- It’s great (if you’re already in fair health, and definitely not if you have a heart condition) to improve circulation and stress response
- There may be some benefits to immune function, but however reasonable the hypothesis, actual evidence is thin on the ground
- The oft-hyped mood benefits are a) marginal b) short-lived, with benefits fading after 3 months of regular cold baths/showers/etc
Read in full: The big chill: Is cold-water immersion good for our health?
Related: Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
The Unspoken Trials Of Going To The Gym (While Being A Woman)
Public health decision-makers often think that getting people to go to the gym more is a matter of public information, or perhaps branding. Some who have their thinking heads on might even realize that there may be economic factors for many. But for women, there’s an additional factor—or rather, an additionally prominent factor. The study we’ll link started with this observation (please read it in the voice of your favorite nature documentary narrator):
❝Despite an increase in gym memberships, women are less active than men and little is known about the barriers women face when navigating gym spaces.❞
What then, of these shy, elusive creatures that make up a mere 51% of the world’s population?
A medium-sized (n=279) study of women, of whom 84% being current gym-goers, reported often feeling “judged for their appearance or performance, as well as having to fight for space in the gym and to be taken seriously, while navigating harassment and unsolicited comments from men”
Even gym attire becomes an issue:
❝Aligning with previous literature, women often chose attire based on comfort and functionality. However, their choices were also influenced by comparisons with others or fear of judgement for wearing non-branded attire or looking too put together. Many women also chose gym attire to hide perceived problem areas or avoid appearance concerns, including visible sweat stains.❞
…which main seem silly; you’re at the gym, of course you’re going to sweat, but if you’re the only one with visible sweat stains, then there can be social consequences (bad ones).
Similarly, there’s a “damned if you do; damned if you don’t” when it comes to working out while fat—on the one hand, society conflates fatness with laziness; on the other, it can be extra intimidating to be the only fat person in a gym full of people who look like they’re going to audition for a superhero movie.
❝In the gym, just like in other areas of life, women often feel stuck between being seen as ‘too much’ and ‘not enough’, dealing with judgement about how they look, how they perform, and even how much space they take up. Even though the pressure to be super thin is decreasing, the growing focus on being muscular and athletic is creating new challenges. It is pushing unrealistic standards that can negatively affect women’s body image and overall well-being.❞
Writer’s note: I live a few minutes walk from my nearest gym, and I work out at home instead. This way, if I want to do yoga in my pajamas, I can. If I want to use my treadmill naked and watch my T+A bounce in the mirror, I can. If I want to lift weights in the dress I happened to be wearing, I can. Alas that I can’t swim at home!
Read in full: Women face multiple barriers while exercising in gyms
Related: Body Image Dissatisfaction/Appreciation Across The Ages
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
We looked at 700 plant-based foods to see how healthy they really are. Here’s what we found
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re thinking about buying plant-based foods, a trip to the supermarket can leave you bewildered.
There are plant-based burgers, sausages and mince. The fridges are loaded with non-dairy milk, cheese and yoghurt. Then there are the tins of beans and packets of tofu.
But how much is actually healthy?
Our nutritional audit of more than 700 plant-based foods for sale in Australian supermarkets has just been published. We found some products are so high in salt or saturated fat, we’d struggle to call them “healthy”.
We took (several) trips to the supermarket
In 2022, we visited two of each of four major supermarket retailers across Melbourne to collect information on the available range of plant-based alternatives to meat and dairy products.
We took pictures of the products and their nutrition labels.
We then analysed the nutrition information on the packaging of more than 700 of these products. This included 236 meat substitutes, 169 legumes and pulses, 50 baked beans, 157 dairy milk substitutes, 52 cheese substitutes and 40 non-dairy yoghurts.
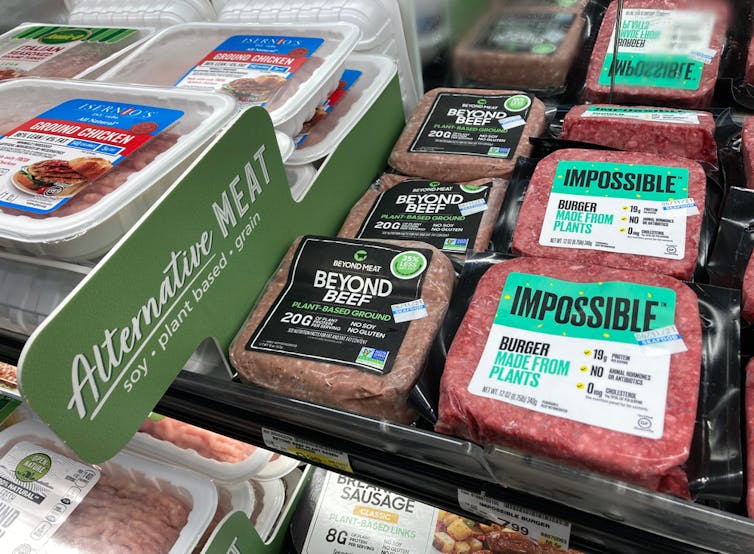
Plant-based meats were surprisingly salty
We found a wide range of plant-based meats for sale. So, it’s not surprising we found large variations in their nutrition content.
Sodium, found in added salt and which contributes to high blood pressure, was our greatest concern.
The sodium content varied from 1 milligram per 100 grams in products such as tofu, to 2,000mg per 100g in items such as plant-based mince products.
This means we could eat our entire daily recommended sodium intake in just one bowl of plant-based mince.
An audit of 66 plant-based meat products in Australian supermarkets conducted in 2014 found sodium ranged from 316mg in legume-based products to 640mg in tofu products, per 100g. In a 2019 audit of 137 products, the range was up to 1,200mg per 100g.
In other words, the results of our audit seems to show a consistent trend of plant-based meats getting saltier.
Looking for plant-based meat? Check the label for the sodium content.
Michael Vi/Shutterstock
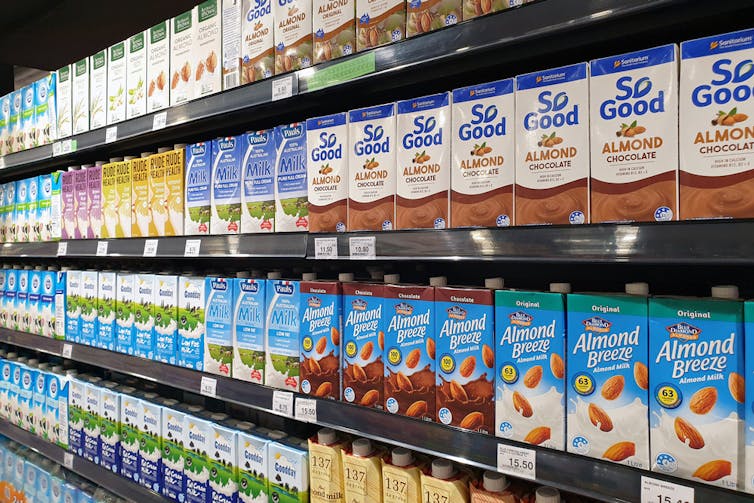
What about plant-based milks?
Some 70% of the plant-based milks we audited were fortified with calcium, a nutrient important for bone health.
This is good news as a 2019-2020 audit of 115 plant-based milks from Melbourne and Sydney found only 43% of plant-based milks were fortified with calcium.
Of the fortified milks in our audit, almost three-quarters (73%) contained the recommended amount of calcium – at least 100mg per 100mL.
We also looked at the saturated fat content of plant-based milks.
Coconut-based milks had on average up to six times higher saturated fat content than almond, oat or soy milks.
Previous audits also found coconut-based milks were much higher in saturated fat than all other categories of milks.
Some plant-based milks were healthier than others.
TY Lim/Shutterstock
A first look at cheese and yoghurt alternatives
Our audit is the first study to identify the range of cheese and yoghurt alternatives available in Australian supermarkets.
Calcium was only labelled on a third of plant-based yoghurts, and only 20% of supermarket options met the recommended 100mg of calcium per 100g.
For plant-based cheeses, most (92%) were not fortified with calcium. Their sodium content varied from 390mg to 1,400mg per 100g, and saturated fat ranged from 0g to 28g per 100g.
So, what should we consider when shopping?
As a general principle, try to choose whole plant foods, such as unprocessed legumes, beans or tofu. These foods are packed with vitamins and minerals. They’re also high in dietary fibre, which is good for your gut health and keeps you fuller for longer.
If opting for a processed plant-based food, here are five tips for choosing a healthier option.
1. Watch the sodium
Plant-based meat alternatives can be high in sodium, so look for products that have around 150-250mg sodium per 100g.
2. Pick canned beans and legumes
Canned chickpeas, lentils and beans can be healthy and low-cost additions to many meals. Where you can, choose canned varieties with no added salt, especially when buying baked beans.
3. Add herbs and spices to your tofu
Tofu can be a great alternative to meat. Check the label and pick the option with the highest calcium content. We found flavoured tofu was higher in salt and sugar content than minimally processed tofu. So it’s best to pick an unflavoured option and add your own flavours with spices and herbs.
4. Check the calcium
When choosing a non-dairy alternative to milk, such as those made from soy, oat, or rice, check it is fortified with calcium. A good alternative to traditional dairy will have at least 100mg of calcium per 100g.
5. Watch for saturated fat
If looking for a lower saturated fat option, almond, soy, rice and oat varieties of milk and yoghurt alternatives have much lower saturated fat content than coconut options. Pick those with less than 3g per 100g.
Laura Marchese, PhD Student at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University and Katherine Livingstone, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow and Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: