Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Amy Dee, pharmacist and cancer survivor herself, lays out the best options for anticancer fruits:
The fruits
Without further ado, they are:
- Kiwi: promotes cancer cell death while sparing healthy cells
- Plums & peaches: an interesting choice to list these similar fruits together as one item, but they both also induce cell death in cancer cells while sparing healthy ones
- Dragon fruit: this does the same, while also inhibiting cancer cell growth
- Figs: these have antitumor effects specifically, while removing carcinogens too, and additionally sensitizing cancer cells to light therapy
- Cranberries: disrupt cancer cell adhesion, breaking down tumors, while protecting non-cancerous cells against DNA damage
- Citrus fruits: inhibit tumor growth and kill cancer cells; regular consumption is also associated with a lower cancer risk (be warned though, grapefruit interacts with some medications)
- Cherries: induce cancer cell death; protect healthy cells against DNA damage
- Tomatoes: don’t often make it into lists of fruits, but lycopene reduces cancer risk, and slows the growth of cancer cells (10almonds note: watermelon has more lycopene than tomatoes, and is more traditionally considered a fruit in all respects, so could have taken the spot here).
We would also argue that apricots could have had a spot on the list, both for their lycopene content (comparable to tomatoes) and their botanical (and thus phytochemical) similarities to peaches and plums.
For more information on each of these (she also talks about the different polyphenols and other nutrients that constitute the active compounds delivering these anticancer effects), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Food Choice & Cancer Risk: Eat To Beat Cancer
- Beat Cancer Kitchen: Deliciously Simple Plant-Based Anticancer Recipes (book)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Time to go nuts for nuts!
Nuts, in popular perception, range from “basically the healthiest food anyone can eat” to “basically high calorie salty snacks”. And, they can be either!
Some notes, then:
- Raw is generally better that not
- Dry roasted is generally better than the kind with added oils
- Added salt is neither necessary nor good
Quick tip: if “roasted salted” are the cheapest or most convenient to buy, you can at least mitigate that by soaking them in warm water for 5 minutes, before rinsing and (if you don’t want wet nuts) drying.
You may be wondering: who does want wet nuts? And the answer is, if for example you’re making a delicious cashew and chickpea balti, the fact you didn’t dry them before throwing them in won’t make a difference.
Now, let’s do a quick run-down; we don’t usually do “listicles” but it seemed a good format here, so we’ve picked a top 5 for nutritional potency:
Almonds
We may have a bias. We accept it. But almonds are also one of the healthiest nuts around, and generally considered by most popular metrics the healthiest.
Not only are they high in protein, healthy fat, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, but they’re even a natural prebiotic that increases the populations of healthy gut bacteria, while simultaneously keeping down the populations of gut pathogens—what more can we ask of a nut?
Read more: Prebiotic effects of almonds and almond skins on intestinal microbiota in healthy adult humans
Pistachios
Not only are these super tasty and fun to eat (and mindful eating is all but guaranteed, as shelling them by hand slows us down and makes us more likely to eat them one at a time rather than by the handful), but also they contain lots of nutrients and are lower in calories than most nuts, so they’re a great option for anyone who’d like to eat more nuts but is doing a calorie-controlled diet and doesn’t want to have half a day’s calories in a tiny dish of nuts.
Walnuts
Popularly associated with brain health (perhaps easy to remember because of their appearance), they really are good for the brain:
Check it out: Beneficial Effects of Walnuts on Cognition and Brain Health
Cashews
A personal favorite of this writer for their versatility in cooking, food prep, or just as a snack, they also do wonders for metabolic health:
Brazil nuts
The most exciting thing about these nuts is that they’re an incredibly potent source of selenium, which is important not just for hair/skin/nails as popularly marketed, but also for thyroid hormone production and DNA synthesis.
But don’t eat too many, because selenium is definitely one of those “you can have too much of a good thing” nutrients, and selenium poisoning can make your hair (however beautiful and shiny it got because of the selenium) fall out if you take too much.
Know the numbers: Brazil nuts and selenium—health benefits and risks
Bottom line on nuts:
- Nuts are a great and healthful part of almost anyone’s diet
- Obviously, if you have a nut allergy, then we’re sorry; this one won’t have helped you so much
- Almonds are one of the most healthful nuts out there
- Brazil nuts are incredibly potent, to the point where moderation is recommended
- A handful of mixed nuts per day is a very respectable option—when it comes to food and health, diversity is almost always good!
Share This Post
-
Stop Using The Wrong Hairbrush For Your Hair Type
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When you brush your hair, you’re either making it healthier or damaging it, depending on what you’re using and how. To avoid pulling your hair out, and to enjoy healthy hair of whatever kind you have and whatever length suits you, it pays to know a little about different brushes, and the different techniques involved.
Head-to-head
Brush shapes and sizes are designed to achieve different effects in hair, not just for decoration. For example:
- Rat tail combs are excellent for parting and sectioning hair with clean lines. The rat tail part is actually more important than the comb part.
- Regular combs are multipurpose but best for use with flat irons, ensuring straighter hair for a longer time.
- Wide-tooth combs should not be used for detangling as they can cause breakage; instead, use a proper detangling brush. Speaking of detangling…
- Detangling brushes are essential for daily use. Whichever you use, start brushing from the bottom to prevent tangles from stacking and worsening. As for kinds of detangling brush:
- The “Tangle Teaser” is a good beginner option, but it may not detangle well for thicker hair.
- Wet Brush (this is a brand name, and is not about any inherent wetness) is the recommended detangling brush for most people. It can be used on wet or dry hair.
- Mason Pearson brush is a luxury detangling brush (see it here on Amazon) that works slightly more quickly and efficiently, but is expensive and not necessary for most people.
- Teasing brushes are for adding volume by backcombing—but require skill to prevent visible tangles. Best avoided for most people.
- Ceramic round brushes are the best for blow-drying, because they hold tension and help hair dry smoother and shinier.
- Blow-dryer brushes are great for easy blow-drying but should not be used on dry hair, to avoid damage.
- Denman brushes are for people with natural curls, enhancing curls without straightening them like a Wet brush would.
For more on all of these brushes, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Felt Time – by Dr. Marc Wittmann
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book goes far beyond the obvious “time flies when you’re having fun / passes slowly when bored”, or “time seems quicker as we get older”. It does address those topics too, but even in doing so, unravels deeper intricacies within.
The author, a research psychologist, includes plenty of reference to actual hard science here, and even beyond subjective self-reports. For example, you know how time seems to slow down upon immediate apparent threat of violent death (e.g. while crashing, while falling, or other more “violent human” options)? We learn of an experiment conducted in an amusement park, where during a fear-inducing (but actually safe) plummet, subjective time slows down yes, but measures of objective perception and cognition remained the same. So much for adrenal superpowers when it comes to the brain!
We also learn about what we can change, to change our perception of time—in either direction, which is a neat collection of tricks to know.
The style is on the dryer end of pop-sci; we suspect that being translated from German didn’t help its levity. That said, it’s not scientifically dense either (i.e. not a lot of jargon), though it does have many references (which we like to see).
Bottom line: if you’ve ever wished time could go more quickly or more slowly, this book can help with that.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
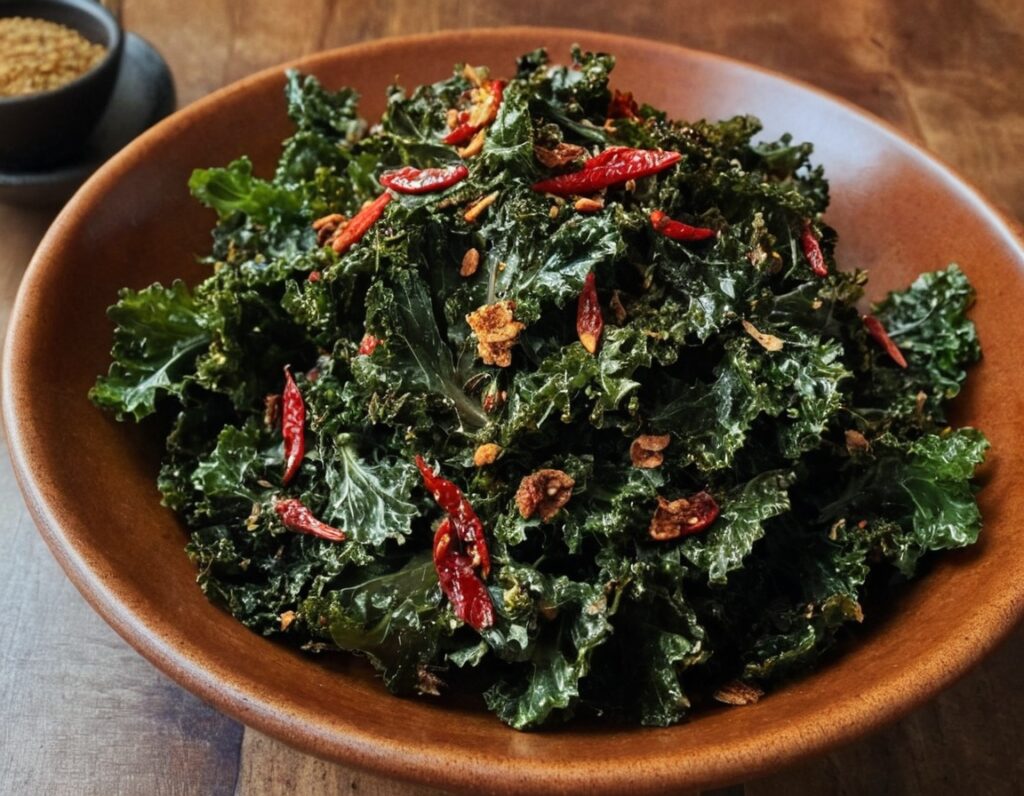
Thai-Style Kale Chips
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
…that are actually crispy, tasty, and packed with nutrients! Lots of magnesium and calcium, and array of health-giving spices too.
You will need
- 7 oz raw curly kale, stalks removed
- extra virgin olive oil, for drizzling
- 3 cloves garlic, crushed
- 2 tsp red chili flakes (or crushed dried red chilis)
- 2 tsp light soy sauce
- 2 tsp water
- 1 tbsp crunchy peanut butter (pick one with no added sugar, salt, etc)
- 1 tsp honey
- 1 tsp Thai seven-spice powder
- 1 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Pre-heat the oven to 180℃ / 350℉ / Gas mark 4.
2) Put the kale in a bowl and drizzle a little olive oil over it. Work the oil in gently with your fingertips so that the kale is coated; the leaves will also soften while you do this; that’s expected, so don’t worry.
3) Mix the rest of the ingredients to make a sauce; coat the kale leaves with the sauce.
4) Place on a baking tray, as spread-out as there’s room for, and bake on a middle shelf for 15–20 minutes. If your oven has a fierce heat source at the top, it can be good to place an empty baking tray on a shelf above the kale chips, to baffle the heat and prevent them from cooking unevenly—especially if it’s not a fan oven.
5) Remove and let cool, and then serve! They can also be stored in an airtight container if desired.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- What’s The Truth About MSG?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Relationships: When To Stick It Out & When To Call It Quits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Like A Ship Loves An Anchor?
Today’s article may seem a little bit of a downer to start with, but don’t worry, it picks up again too. Simply put, we’ve written before about many of the good parts of relationships, e.g:
Only One Kind Of Relationship Promotes Longevity This Much!
…but what if that’s not what we have?
Note: if you have a very happy, secure, fulfilling, joyous relationship, then, great! Or if you’re single and happy, then, also great! Hopefully you will still find today’s feature of use if you find yourself advising a friend or family member one day. So without further ado, let’s get to it…
You may be familiar with the “sunk cost fallacy”; if not: it’s what happens when a person or group has already invested into a given thing, such that even though the thing is not going at all the way they hoped, they now want to continue trying to make that thing work, lest their previous investment be lost. But the truth is: if it’s not going to work, then the initial investment is already lost, and pouring out extra won’t help—it’ll just lose more.
That “investment” in a given thing could be money, time, energy, or (often the case) a combination of the above.
In the field of romance, the “sunk cost fallacy” keeps a lot of bad relationships going for longer than perhaps they should, and looking back (perhaps after a short adjustment period), the newly-single person says “why did I let that go on?” and vows to not make the same mistake again.
But that prompts the question: how can we know when it’s right to “keep working on it, because relationships do involve work”, as perfectly reasonable relationship advice often goes, and when it’s right to call it quits?
Should I stay or should I go?
Some questions for you (or perhaps a friend you might find yourself advising) to consider:
- What qualities do you consider the most important for a partner to have—and does your partner have them?
- If you described the worst of your relationship to a close friend, would that friend feel bad for you?
- Do you miss your partner when they’re away, or are you glad of the break? When they return, are they still glad to see you?
- If you weren’t already in this relationship, would you seek to enter it now? (This takes away sunk cost and allows a more neutral assessment)
- Do you feel completely safe with your partner (emotionally as well as physically), or must you tread carefully to avoid conflict?
- If your partner decided tomorrow that they didn’t want to be with you anymore and left, would that be just a heartbreak, or an exciting beginning of a new chapter in your life?
- What things would you generally consider dealbreakers in a relationship—and has your partner done any of them?
The last one can be surprising, by the way. We often see or hear of other people’s adverse relationship situations and think “I would never allow…” yet when we are in a relationship and in love, there’s a good chance that we might indeed allow—or rather, excuse, overlook, and forgive.
And, patience and forgiveness certainly aren’t inherently bad traits to have—it’s just good to deploy them consciously, and not merely be a doormat.
Either way, reflect (or advise your friend/family member to reflect, as applicable) on the “score” from the above questions.
- If the score is good, then maybe it really is just a rough patch, and the tools we link at the top and bottom of this article might help.
- If the score is bad, the relationship is bad, and no amount of historic love or miles clocked up together will change that. Sometimes it’s not even anyone’s fault; sometimes a relationship just ran its course, and now it’s time to accept that and turn to a new chapter.
“At my age…”
As we get older, it’s easy for that sunk cost fallacy to loom large. Inertia is heavy, the mutual entanglement of lives is far-reaching, and we might not feel we have the same energy for dating that we did when we were younger.
And there may sometimes be a statistical argument for “sticking it out” at least for a while, depending on where we are in the relationship, per this study (with 165,039 participants aged 20–76), which found:
❝Results on mean levels indicated that relationship satisfaction decreased from age 20 to 40, reached a low point at age 40, then increased until age 65, and plateaued in late adulthood.
As regards the metric of relationship duration, relationship satisfaction decreased during the first 10 years of the relationship, reached a low point at 10 years, increased until 20 years, and then decreased again.❞
Source: Development of Relationship Satisfaction Across the Life Span: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
And yet, when it comes to prospects for a new relationship…
- If our remaining life is growing shorter, then it’s definitely too short to spend in an unhappy relationship
- Maybe we really won’t find romance again… And maybe that’s ok, if w’re comfortable making our peace with that and finding joy in the rest of life (this widowed writer (hi, it’s me) plans to remain single now by preference, and her life is very full of purpose and beauty and joy and yes, even love—for family, friends, etc, plus the memory of my wonderful late beloved)
- Nevertheless, the simple fact is: many people do find what they go on to describe as their best relationship yet, late in life ← this study is with a small sample size, but in this case, even anecdotal evidence seems sufficient to make the claim reasonable; probably you personally know someone who has done so. If they can, so can you, if you so wish.
- Adding on to that last point… Later life relationships can also offer numerous significant advantages unique to such (albeit some different challenges too—but with the right person, those challenges are just a fun thing to tackle together). See for example:
An exploratory investigation into dating among later‐life women
And about those later-life relationships that do work? They look like this:
this one looks like the title says it all, but it really doesn’t, and it’s very much worth at least reading the abstract, if not the entire paper—because it talks a lot about the characteristics that make for happy or unhappy relationships, and the effect that those things have on people. It really is very good, and quite an easy read.
See again: Healthy Relationship, Healthy Life
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Does Your Butt…Wink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What is a Butt Wink?
A “butt wink” is a common issue that occurs during squatting exercises.
Now, we’ve talked about the benefits of squatting countless times (see here or here for just a few examples). As with all exercises, using the correct technique is imperative, helping to both reduce injury and maximize gain.
Given butt winks are a common issue when squatting, we thought it natural to devote an article to it.
So, a butt wink happens when, at the bottom of your squat position, your pelvis tucks rotates backward (otherwise known as a “posterior pelvic tilt”) and the lower back rounds. This motion looks like a slight ‘wink’, hence the name.
How to Avoid Butt Winking
When the pelvis tucks under and the spine rounds, it can put undue pressure on the lumbar discs. This is especially risky when squatting with weights, as it can exacerbate the stress on the spine.
To avoid a butt wink, it’s important to maintain a neutral spine throughout the squat and to work on flexibility and strength in the hips, glutes, and hamstrings. Adjusting the stance width or foot angle during squats can also help in maintaining proper form.
A visual representation would likely work better than our attempt at describing what to do, so without further ado, here’s today’s video:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: