Top 10 Early Warning Signs Of Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s a harmless momentary mind-blank, and what’s a potential warning sign of dementia? Dementia Careblazers, a dementia care organization, has input:
The signs
With the caveat that this is a list of potential warning signs, not a diagnostic tool, the 10 signs are:
- Memory loss: e.g. forgetting important or well-learned information, such as one’s home address
- Challenges in planning or solving problems: e.g. difficulty with tasks such as paying bills (for organizational rather than financial reasons), following recipes, or managing medications
- Difficulty completing familiar tasks: e.g. trouble remembering rules of a familiar game, or directions to a familiar place
- Confusion with place or time: e.g. forgetting where one is, or making mistakes with the date, season, or other time-related details. Note that anyone can be momentarily unsure of today’s date, but if someone thinks it’s 1995, probably something wrong is not quite right. Similarly, being wrong about who is the current national leader is often used as a test, too—assuming countries with enough political stability to not have five different national leaders in the past four years, including one who did not outlast a lettuce *side-eyeing the UK*
- Trouble understanding visual images and spatial relationships: e.g. increased clumsiness, difficulty parking, or bumping into objects
- New problems with speaking or writing: e.g. losing track in conversations, or struggling to find the right words
- Misplacing things: e.g. losing items and being unable to retrace one’s steps to find them
- Decreased or poor judgment: e.g. falling for scams, giving out too much information or money without investigating appropriately first
- Withdrawal from social activities or hobbies: e.g. losing interest in activities one used to enjoy or avoiding social interactions
- Changes in mood and personality: e.g. increased irritability, anxiety, or other noticeable changes in behavior and personality
For more information on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Dementia: Spot The Signs (Because None Of Us Are Immune)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between a psychopath and a sociopath? Less than you might think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Articles about badly behaved people and how to spot them are common. You don’t have to Google or scroll too much to find headlines such as 7 signs your boss is a psychopath or How to avoid the sociopath next door.
You’ll often see the terms psychopath and sociopath used somewhat interchangeably. That applies to perhaps the most famous badly behaved fictional character of all – Hannibal Lecter, the cannibal serial killer from The Silence of the Lambs.
In the book on which the movie is based, Lecter is described as a “pure sociopath”. But in the movie, he’s described as a “pure psychopath”. Psychiatrists have diagnosed him with something else entirely.
So what’s the difference between a psychopath and a sociopath? As we’ll see, these terms have been used at different times in history, and relate to some overlapping concepts.
Benoit Daoust/Shutterstock What’s a psychopath?
Psychopathy has been mentioned in the psychiatric literature since the 1800s. But the latest edition of the Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (known colloquially as the DSM) doesn’t list it as a recognised clinical disorder.
Since the 1950s, labels have changed and terms such as “sociopathic personality disturbance” have been replaced with antisocial personality disorder, which is what we have today.
Was Hannibal Lecter from The Silence of the Lambs a psychopath, a sociopath or something else entirely? Ralf Liebhold/Shutterstock Someone with antisocial personality disorder has a persistent disregard for the rights of others. This includes breaking the law, repeated lying, impulsive behaviour, getting into fights, disregarding safety, irresponsible behaviours, and indifference to the consequences of their actions.
To add to the confusion, the section in the DSM on antisocial personality disorder mentions psychopathy (and sociopathy) traits. In other words, according to the DSM the traits are part of antisocial personality disorder but are not mental disorders themselves.
US psychiatrist Hervey Cleckley provided the first formal description of psychopathy traits in his 1941 book The Mask of Sanity. He based his description on his clinical observations of nine male patients in a psychiatric hospital. He identified several key characteristics, including superficial charm, unreliability and a lack of remorse or shame.
Canadian psychologist Professor Robert Hare refined these characteristics by emphasising interpersonal, emotional and lifestyle characteristics, in addition to the antisocial behaviours listed in the DSM.
When we draw together all these strands of evidence, we can say a psychopath manipulates others, shows superficial charm, is grandiose and is persistently deceptive. Emotional traits include a lack of emotion and empathy, indifference to the suffering of others, and not accepting responsibility for how their behaviour impacts others.
Finally, a psychopath is easily bored, sponges off others, lacks goals, and is persistently irresponsible in their actions.
So how about a sociopath?
The term sociopath first appeared in the 1930s, and was attributed to US psychologist George Partridge. He emphasised the societal consequences of behaviour that habitually violates the rights of others.
Academics and clinicians often used the terms sociopath and psychopath interchangeably. But some preferred the term sociopath because they said the public sometimes confused the word psychopath with psychosis.
“Sociopathic personality disturbance” was the term used in the first edition of the DSM in 1952. This aligned with the prevailing views at the time that antisocial behaviours were largely the product of the social environment, and that behaviours were only judged as deviant if they broke social, legal, and/or cultural rules.
Some of these early descriptions of sociopathy are more aligned with what we now call antisocial personality disorder. Others relate to emotional characteristics similar to Cleckley’s 1941 definition of a psychopath.
In short, different people had different ideas about sociopathy and, even today, sociopathy is less-well defined than psychopathy. So there is no single definition of sociopathy we can give you, even today. But in general, its antisocial behaviours can be similar to ones we see with psychopathy.
Over the decades, the term sociopathy fell out of favour. From the late 60s, psychiatrists used the term antisocial personality disorder instead.
Born or made?
Both “sociopathy” (what we now call antisocial personality disorder) and psychopathy have been associated with a wide range of developmental, biological and psychological causes.
For example, people with psychopathic traits have certain brain differences especially in regions associated with emotions, inhibition of behaviour and problem solving. They also appear to have differences associated with their nervous system, including a reduced heart rate.
However, sociopathy and its antisocial behaviours are a product of someone’s social environment, and tends to run in families. These behaviours has been associated with physical abuse and parental conflict.
What are the consequences?
Despite their fictional portrayals – such as Hannibal Lecter in Silence of the Lambs or Villanelle in the TV series Killing Eve – not all people with psychopathy or sociopathy traits are serial killers or are physically violent.
But psychopathy predicts a wide range of harmful behaviours. In the criminal justice system, psychopathy is strongly linked with re-offending, particularly of a violent nature.
In the general population, psychopathy is associated with drug dependence, homelessness, and other personality disorders. Some research even showed psychopathy predicted failure to follow COVID restrictions.
But sociopathy is less established as a key risk factor in identifying people at heightened risk of harm to others. And sociopathy is not a reliable indicator of future antisocial behaviour.
In a nutshell
Neither psychopathy nor sociopathy are classed as mental disorders in formal psychiatric diagnostic manuals. They are both personality traits that relate to antisocial behaviours and are associated with certain interpersonal, emotional and lifestyle characteristics.
Psychopathy is thought to have genetic, biological and psychological bases that places someone at greater risk of violating other people’s rights. But sociopathy is less clearly defined and its antisocial behaviours are the product of someone’s social environment.
Of the two, psychopathy has the greatest use in identifying someone who is most likely to cause damage to others.
Bruce Watt, Associate Professor in Psychology, Bond University and Katarina Fritzon, Associate Professor of Psychology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
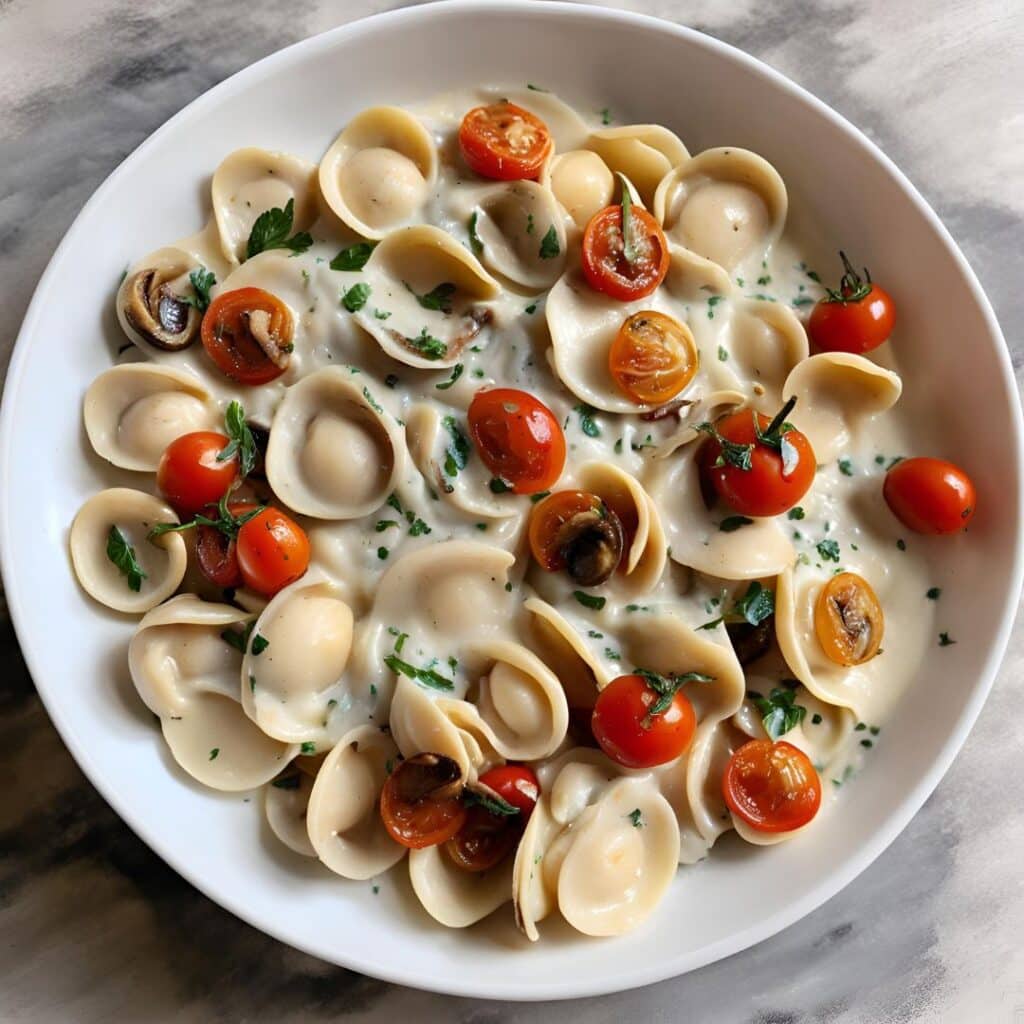
Gut-Healthy Labneh Orecchiette
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Labneh (a sort of yogurt-cheese made from strained yogurt) is a great probiotic, and there’s plenty of resistant starch in this dish too, from how we cook, cool, and reheat the pasta. Add to this the lycopene from the tomatoes, the ergothioneine from the mushrooms, and the healthful properties of the garlic, black pepper, and red chili, and we have a very healthy dish!
You will need
- 10 oz labneh (if you can’t buy it locally, you can make your own by straining Greek yogurt through a muslin cloth, suspended over a bowl to catch the water that drips out, overnight—and yes, plant-based is also fine if you are vegan, and the gut benefits are similar because unlike vegan cheese, vegan yogurt is still fermented)
- 6 oz wholegrain orecchiette (or other pasta, but this shape works well for this sauce)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated
- Juice of ½ lemon
- Large handful chopped parsley
- Large handful chopped dill
- 9 oz cherry tomatoes, halved
- 9 oz mushrooms (your choice what kind), sliced (unless you went for shiitake or similar, which don’t need it due to already being very thin)
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the pasta as you normally would. Drain, and rinse with cold water. Set aside.
2) Combine the labneh with the garlic, black pepper, dill, parsley, and lemon juice, in a large bowl. Set aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil in a skillet; add the chili flakes, followed by the mushrooms. Cook until soft and browned, then add the tomatoes and fry for a further 1 minute—we want the tomatoes to be blistered, but not broken down. Stir in the MSG/salt, and take off the heat.
4) Refresh the pasta by passing a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander, then add the hot pasta to the bowl of labneh sauce, stirring to coat thoroughly.
5) Serve, spooning the mushrooms and tomatoes over the labneh pasta.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Anti-Aging Myths This Dermatologist Wants You To Stop Believing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dermatologist Dr. Sam Ellis lays all bare:
Bare-faced lies?
Obviously, we are hearing from a dermatologist here, so the focus is on skin aging specifically. We may well also not want to age our brain, joints, etc, but that’s not what this one is about.
So, without further ado, here are the myths she wants to bust:
- “Medical grade skincare”: the term “medical grade” is a marketing term and does not indicate superior efficacy or better ingredients.
- “Expensive skincare is more effective”: price does not always correlate with effectiveness; some high-end products justify their cost, but many do not.
- “More products = better results”: using too many products can reduce effectiveness and cause irritation; a simple routine with sunscreen and a retinoid is key.
- “Drink more water for better skin”: if you’re dehydrated, then yes, hydrate—but drinking excessive water does not improve skin appearance beyond normal hydration levels.
- “You don’t need anti-aging products until you see signs of aging”: starting skincare early, especially sun protection, helps maintain youthful skin longer.
- “Wrinkles are the first signs of aging”: hyperpigmentation and sagging are often more significant early indicators of aging than wrinkles.
- “Skincare is all you need for anti-aging”: by “skincare” here she means creams, lotions, tonics, etc, and recommends other treatments such as laser treatment and even Botox*.
- “Non-prescription retinoids are a waste of time”: over-the-counter retinoids like retinol and retinal can still be effective alternatives to prescription retinoids.
- “You must use retinoids every night”: retinoids are effective even when used a few times per week, depending on individual tolerance.
*We’re not convinced about the Botox; we’ll have to do a deep-dive research review one of these days!
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Retinoids: Retinol vs Retinal vs Retinoic Acid vs..?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Chorus or Cacophony? Cicada Song Hits Some Ears Harder Than Others
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ST. LOUIS — Shhhooo. Wee-uuu. Chick, chick, chick. That’s the sound of three different cicada species. For some people, those sounds are the song of the summer. Others wish the insects would turn it down. The cacophony can be especially irritating for people on the autism spectrum who have hearing sensitivity.
Warren Rickly, 14, lives in suburban south St. Louis County, Missouri. Warren, who has autism, was at the bus stop recently waiting for his younger brother when the sound of cicadas became too much to bear.
“He said it sounds like there’s always a train running next to him,” his mother, Jamie Reed, said.
Warren told her the noise hurt.
Starting this spring, trillions of the red-eyed insects crawled their way out of the ground across the Midwest and Southeast. It’s part of a rare simultaneous emergence of two broods — one that appears every 13 years, the other every 17.
The noisy insects can be stressful. People with autism can have a sensitivity to texture, brightness, and sound.
“I think the difference for individuals with autism is the level of intensity or how upsetting some of these sensory differences are,” said Rachel Follmer, a developmental and behavioral pediatrician at Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago.
“It can get to the extreme where it can cause physical discomfort,” she said.
When a large group of cicadas starts to sing, the chorus can be as loud as a motorcycle. Researchers at the University of Missouri-St. Louis this year crowdsourced cicada noise levels as high as 86 decibels, about as loud as a food blender.
That can be stressful, not melodic, Follmer said.
To help children cope, she suggests giving them a primer before they encounter a noisy situation. For cicadas, that could mean explaining what they are, that they don’t bite or sting, and that they’ll be here for just a short time.
“When something is uncomfortable, not having power in that situation can be very scary for a lot of individuals, whether you’re on the spectrum or not,” Follmer said.
Jamie Reed’s family has been using this and other strategies to help her son. Warren wears noise-canceling headphones, listens to music, and has been teaching himself about cicadas.
“For him, researching it and looking into it I think grounds him a little bit,” Reed said.
Fatima Husain is a professor and neuroscientist at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and studies how the brain processes sound. She said people with tinnitus may also struggle with cicada song.
Tinnitus, a ringing or other noise in the ears, is a person’s perception of sound without an external source.
“Some people say it sounds like buzzing, like wind blowing through trees, and ironically, quite a few people say it sounds like cicadas,” Husain said.
For most people with tinnitus the cicada’s song is harmless background noise, according to Husain, but for others the ringing can prevent easy conversation or sleep. Those with tinnitus are also more likely to have anxiety or depression. A loud persistent sound, like singing cicadas, can make someone’s tinnitus worse, Husain said.
It’s not always bad, though. The cicada’s song can also be a relief.
For some, tinnitus gets worse in a quiet environment. Husain said she’s seen reports this year of patients saying the cicadas’ song has been like soothing white noise.
“The sound is loud enough that in some ways it’s drowning their internal tinnitus,” Husain said.
As loud as the cicadas can be, they won’t necessarily damage anyone’s hearing, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hearing loss builds up over time from repeated exposure to loud sounds. Cicadas aren’t loud enough for long enough to do lasting damage, Husain said.
Everyday sources of noise come with a higher risk. Husain said constant exposure to loud highways, an airport, industrial sites, or household appliances like blenders and hair dryers can be a concern. And they can take a toll on someone’s emotional well-being.
“If you are being exposed to very loud sounds for a part of your school day or your working day, it may make you more stressed out; it may make you more angry about things,” she said.
Unlike the highway or an airport, cicadas won’t be around long. Most of the current brood will be gone in the next few weeks. Just in time for another noisy summer event: the Fourth of July.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is considered by many to be the current “gold standard” of healthy eating, and with good reason. With 10,000+ studies underpinning it and counting, it has a pretty hefty weight of evidence.
(For contrast, the Ketogenic Diet for example has under 5,000 studies at time of writing, and many of those include mentioning the problems with it. That’s not to say the Keto is without its merits! It certainly can help achieve some short term goals, but that’s a topic for another day)
Wondering what the Mediterranean Diet consists of? We outlined it in a previous main feature, so here it is for your convenience 😎
To get us started today, we’ll quickly drop some links to a few of those Mediterranean Diet studies from the top:
- Definition of the Mediterranean Diet; a Literature Review
- Mediterranean Diet In Healthy Aging
- Cancer and Mediterranean Diet: A Review
- Impact of Mediterranean Diet on Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases and Longevity
- Mediterranean diet and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: meta-analysis
The short version is: it glows, in a good way.
The anti-inflammatory upgrade
One thing about the traditional Mediterranean Diet is… where are the spices?!
A diet focusing on fruits and non-starchy vegetables, healthy oils and minimal refined carbs, can be boosted by adding uses of spices such as chili, turmeric, cumin, fenugreek, and coriander:
The gut-healthy upgrade:
The Mediterranean Diet already gives for having a small amount of dairy, mostly in the form of cheeses, but this can be tweaked:
Mediterranean diet with extra dairy could be a gut gamechanger
The heart-healthy upgrade
The Mediterranean Diet is already highly recommended for heart health, and it offers different benefits to different parts of cardiovascular health:
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet can boost it further, specifically in the category of, as the name suggests, lowering blood pressure.
It’s basically the Mediterranean Diet with a few tweaks. Most notably, red meat no longer features (the Mediterranean Diet allows for a small amount of red meat), and fish has gone up in the list:
Description of the DASH Eating Plan
The brain-healthy upgrade:
The MIND (Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay) diet combines several elements from the above, as the name suggests. It also adds extra portions of specific brain-foods, that already exist in the above diets, but get a more substantial weighting in this one:
MIND and Mediterranean diets linked to fewer signs of Alzheimer’s brain pathology
See also: The cognitive effects of the MIND diet
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How anti-vaccine figures abuse data to trick you
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The anti-vaccine movement is nearly as old as vaccines themselves. For as long as humans have sought to harness our immune system’s incredible ability to recognize and fight infectious invaders, critics and conspiracy theorists have opposed these efforts.
Anti-vaccine tactics have advanced since the early days of protesting “unnatural” smallpox inoculation, and the rampant abuse of scientific data may be the most effective strategy yet.
Here’s how vaccine opponents misuse data to deceive people, plus how you can avoid being manipulated.
Misappropriating raw and unverified safety data
Perhaps the oldest and most well-established anti-vaccine tactic is the abuse of data from the federal Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration maintain VAERS as a tool for researchers to detect early warning signs of potential vaccine side effects.
Anyone can submit a VAERS report about any symptom experienced at any point after vaccination. That does not mean that these symptoms are vaccine side effects.
VAERS was not designed to determine if a specific vaccine caused a specific adverse event. But for decades, vaccine opponents have misinterpreted, misrepresented, and manipulated VAERS data to convince people that vaccines are dangerous.
Anyone relying on VAERS to draw conclusions about vaccine safety is probably trying to trick you. It isn’t possible to determine from VAERS data alone if a vaccine caused a specific health condition.
VAERS isn’t the only federal data that vaccine opponents abuse. Originally created for COVID-19 vaccines, V-safe is a vaccine safety monitoring system that allows users to report—via text message surveys—how they feel and any health issues they experience up to a year after vaccination. Anti-vaccine groups have misrepresented data in the system, which tracks all health experiences, whether or not they are vaccine-related.
The U.S. Department of Defense’s Defense Medical Epidemiology Database (DMED) has also become a target of anti-vaccine misinformation. Vaccine opponents have falsely claimed that DMED data reveals massive spikes in strokes, heart attacks, HIV, cancer, and blood clots among military service members since the COVID-19 vaccine rollout. The spike was due to an updated policy that corrected underreporting in the previous years
Misrepresenting legitimate studies
A common tactic vaccine opponents use is misrepresenting data from legitimate sources such as national health databases and peer-reviewed studies. For example, COVID-19 vaccines have repeatedly been blamed for rising cancer and heart attack rates, based on data that predates the pandemic by decades.
A prime example of this strategy is a preliminary FDA study that detected a slight increase in stroke risk in older adults after a high-dose flu vaccine alone or in combination with the bivalent COVID-19 vaccine. The study found no “increased risk of stroke following administration of the COVID-19 bivalent vaccines.”
Yet vaccine opponents used the study to falsely claim that COVID-19 vaccines were uniquely harmful, despite the data indicating that the increased risk was almost certainly driven by the high-dose flu vaccine. The final peer-reviewed study confirmed that there was no elevated stroke risk following COVID-19 vaccination. But the false narrative that COVID-19 vaccines cause strokes persists.
Similarly, the largest COVID-19 vaccine safety study to date confirmed the extreme rarity of a few previously identified risks. For weeks, vaccine opponents overstated these rare risks and falsely claimed that the study proves that COVID-19 vaccines are unsafe.
Citing preprint and retracted studies
When a study has been retracted, it is no longer considered a credible source. A study’s retraction doesn’t deter vaccine opponents from promoting it—it may even be an incentive because retracted papers can be held up as examples of the medical establishment censoring so-called “truthtellers.” For example, anti-vaccine groups still herald Andrew Wakefield nearly 15 years after his study falsely linking the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine to autism was retracted for data fraud.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought the lasting impact of retracted studies into sharp focus. The rush to understand a novel disease that was infecting millions brought a wave of scientific publications, some more legitimate than others.
Over time, the weaker studies were reassessed and retracted, but their damage lingers. A 2023 study found that retracted and withdrawn COVID-19 studies were cited significantly more frequently than valid published COVID-19 studies in the same journals.
In one example, a widely cited abstract that found that ivermectin—an antiparasitic drug proven to not treat COVID-19—dramatically reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients exemplifies this phenomenon. The abstract, which was never peer reviewed, was retracted at the request of its authors, who felt the study’s evidence was weak and was being misrepresented.
Despite this, the study—along with the many other retracted ivermectin studies—remains a touchstone for proponents of the drug that has shown no effectiveness against COVID-19.
In a more recent example, a group of COVID-19 vaccine opponents uploaded a paper to The Lancet’s preprint server, a repository for papers that have not yet been peer reviewed or published by the prestigious journal. The paper claimed to have analyzed 325 deaths after COVID-19 vaccination, finding COVID-19 vaccines were linked to 74 percent of the deaths.
The paper was promptly removed because its conclusions were unsupported, leading vaccine opponents to cry censorship.
Applying animal research to humans
Animals are vital to medical research, allowing scientists to better understand diseases that affect humans and develop and screen potential treatments before they are tested in humans. Animal research is a starting point that should never be generalized to humans, but vaccine opponents do just that.
Several animal studies are frequently cited to support the claim that mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are dangerous during pregnancy. These studies found that pregnant rats had adverse reactions to the COVID-19 vaccines. The results are unsurprising given that they were injected with doses equal to or many times larger than the dose given to humans rather than a dose that is proportional to the animal’s size.
Similarly, a German study on rat heart cells found abnormalities after exposure to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine opponents falsely insinuated that this study proves COVID-19 vaccines cause heart damage in humans and was so universally misrepresented that the study’s author felt compelled to dispute the claims.
The author noted that the study used vaccine doses significantly higher than those administered to humans and was conducted in cultured rat cells, a dramatically different environment than a functioning human heart.
How to avoid being misled
The internet has empowered vaccine opponents to spread false information with an efficiency and expediency that was previously impossible. Anti-vaccine narratives have advanced rapidly due to the rampant exploitation of valid sources and the promotion of unvetted, non-credible sources.
You can avoid being tricked by using multiple trusted sources to verify claims that you encounter online. Some examples of credible sources are reputable public health entities like the CDC and World Health Organization, personal health care providers, and peer-reviewed research from experts in fields relevant to COVID-19 and the pandemic.
Read more about anti-vaccine tactics:
- How vaccine opponents spread misinformation
- How misinformation tricks our brains
- How vaccine opponents use kids to spread misinformation
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: