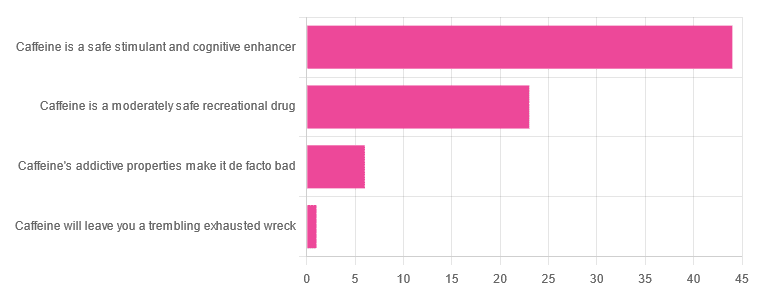The Worst Cookware Lurking In Your Kitchen (Toxicologist Explains)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Yvonne Burkart gives us a rundown of the worst offenders, and what to use instead:
Hot mess
The very worst offender is non-stick cookware, the kind with materials such as Teflon. These are the most toxic, due to PFAS chemicals.
Non-stick pans release toxic gases, leach chemicals into food, and release microplastic particles, which can accumulate in the body.
One that a lot of people don’t think about, in that category, is the humble air-fryer, which often as not has a non-stick cooking “basket”. These she describes as highly toxic, as they combine plastic, non-stick coatings, and high heat, which can release fumes and other potentially dangerous chemicals into the air and food.
You may be wondering: how bad is it? And the answer is, quite bad. PFAS chemicals are linked to infertility, hypertension in pregnancy, developmental issues in children, cancer, weakened immune systems, hormonal disruption, obesity, and intestinal inflammation.
Dr. Burkart’s top picks for doing better:
- Pure ceramic cookware: top choice for safety, particularly brands like Xtrema, which are tested for heavy metal leaching.
- Carbon steel & cast iron: durable and safe; can leach iron in acidic foods (for most people, this is a plus, but some may need to be aware of it)
- Stainless steel: lightweight and affordable but can leach nickel and chromium in acidic foods at high temperatures. Use only if nothing better is available.
And specifically as alternatives to air-fryers: glass convection ovens or stainless steel ovens are safer than conventional air fryers. The old “combination oven” can often be a good choice here.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
- It’s Not Fantastic To Be Plastic ← for the closely related topic of microplastics and nanoplastics
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fast Like A Girl – by Dr. Mindy Pelz
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of information out there when it comes to intermittent fasting is very much centered on men in the 25–35 years age range. What about the rest of us?
Our physiological needs are not the same, and it’d be foolhardy to ignore that. But what things do still stand the same, and what things would benefit from a different approach in our cases?
Dr. Pelz has our back with this book packed with information based on the best science currently out there. She gives a general overview of fasting with full consideration to the fact that we the reader may well be female or over a certain age or both. In addition, the book offers:
- Metabolic switching (the “missing key to weight loss”)
- Building a fasting lifestyle (that works with your actual life, not just on paper)
- How to time fasting according to your menstrual cycle (if you don’t have a cycle, she has you covered too)
- How to break a fast—properly (and many other hacks/tips/tricks to make fasting so much easier)
Bottom line: if you want to do intermittent fasting and want to work with rather than against your body, then this book is a fine option.
Share This Post
-
Feeding your baby butter won’t help them sleep through the night, whatever TikTok says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleep is the holy grail for new parents. So no wonder many tired parents are looking for something to help their babies sleep.
A TikTok trend claims giving your baby a tablespoon or two of butter in the evening will help them sleep more at night.
As we’ll see, butter is just the latest food that promises to help babies sleep at night. But no single food can do this.
So if you’re a new parent and desperate for a good night’s sleep, here’s what to try instead.
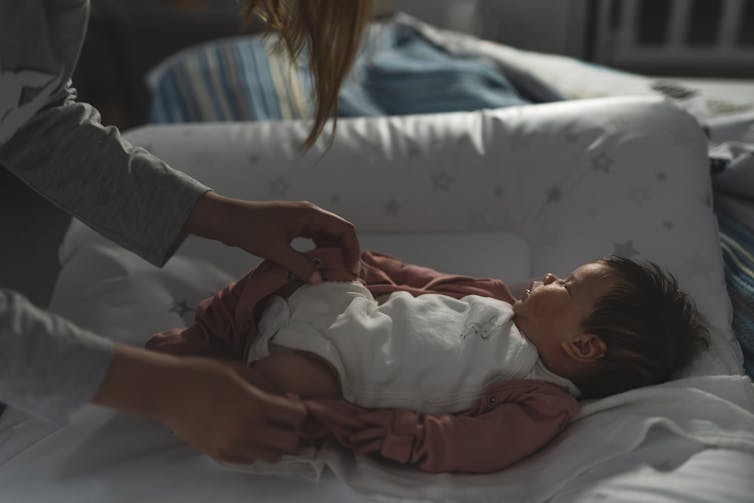
BaLL LunLa/Shutterstock Is my baby’s sleep normal?
Babies need help to fall asleep, through feeding, movement (like rocking) or touch (like a cuddle or massage).
Newborn babies also do not know night from day. Melatonin in breastmilk helps babies sleep more at night until they start to make this sleep-inducing hormone themselves. Bottlefed newborn babies do not have access to this melatonin. Regardless of how you feed your baby, it can take several months for them to develop a sleep pattern with longer stretches at night.
Babies also sleep lighter than older children and adults. Light sleep helps ensure they continue breathing, protecting them from SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome). It also means they wake easily and often.
The idea that babies should sleep deeply, alone and for long stretches, goes against their physiology. So “sleeping like a baby” usually means waking quite a lot at night.
Yet, many parents have been asked whether their baby is sleeping through the night and is a “good baby”. The perception is that if a baby doesn’t sleep for long stretches at night, it must be “bad”.
This may lead parents to say their babies sleep longer than they really do, setting unrealistic expectations for other new parents.
Could feeding butter do any harm?
The social pressure around baby sleep can add stress and anxiety for new parents. So the Tiktok trend about feeding babies butter may seem tempting.
But giving babies any solid food before they are around six months old is not recommended. Babies’ digestive systems are not ready for solid food until they are around six months and feeding them before this can cause constipation or make them more likely to catch an illness. For this reason alone, you should not give your young baby butter.
From about six months old, babies should be offered nutritious, iron-rich solid foods. Butter doesn’t fit this bill because it is almost all saturated fat. If butter replaces more nutritious foods, babies may not get the vitamins and minerals they need.
Butter is just the latest food claimed to help babies sleep better at night. Pixel-Shot/Shutterstock Butter is the latest in a long line of beliefs about certain foods making babies sleep longer at night. It was once thought that adding cereal or crushed arrowroot biscuits in bottle of milk before bedtime would make them sleep longer. Research found this did not increase sleep at all.
Similarly, there is no evidence that giving babies butter before bed makes them sleep longer.
In fact, research shows the foods babies eat make no difference to night waking.
What else can I try?
Waking overnight doesn’t necessarily mean a baby is hungry. And stopping breastfeeds or bottle feeds overnight doesn’t necessarily reduce night waking.
Your baby could be too hot or cold, or need a nappy change. But some babies continue to wake at night even without an obvious problem.
The good news is, sleeping is a skill babies develop naturally as they grow.
Behavioural sleep interventions, known as “sleep training”, are not very effective in increasing overnight sleep. In one study, sleep training did not reduce the number of night wakes and only increased the length of the longest sleep by about 16 minutes. Sleep training is especially not recommended for babies under six months.
The good news is that babies do eventually get the hang of sleeping at night. Miljan Zivkovic/Shutterstock Look after yourself
If you’re missing out on sleep at night, try to have small naps during the day while your baby sleeps. Ask friends and family to do some chores to allow you to nap.
If your baby is crying and you find yourself getting overwhelmed it is OK to put your baby down somewhere safe (like a cot or baby mat) and take some time to settle yourself.
If your baby’s sleep pattern changes significantly or they haven’t slept at all for more than a day, or if your baby seems to have pain or a fever see your doctor, or family and child health nurse, as soon as possible.
Some helpful resources
If you think your baby is not sleeping well because of a breastfeeding problem, the Australian Breastfeeding Association has a national helpline. The association can also advise on co-sleeping.
The charity Little Sparklers provides peer support for parents, including someone to chat to, about baby sleep. It also has helpful resources.
UNICEF has resources about caring for your baby at night. And the UK-based Baby Sleep Info Source (Basis) provides evidence-based information about babies and sleep.
Karleen Gribble, Adjunct Professor, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Western Sydney University; Naomi Hull, PhD candidate, Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney, and Nina Jane Chad, Research Fellow, University of Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Two Sides Of Caffeine
We asked you for your health-related opinions on caffeine itself, not necessarily the coffee, tea, energy drinks, etc that might contain it.
We have, by the way previously written about the health effects of coffee and tea specifically:
As for our question about caffeine itself, though, we got the above-depicted, below-described, set of results:
- About 59% said “caffeine is a safe stimulant and cognitive enhancer”
- About 31% said “caffeine is a moderately safe recreational drug”
- About 8% said “caffeine’s addictive properties make it de facto bad”
- One (1) person said “caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck”
But what does the science say?
Caffeine is addictive: True or False?
True, though one will find occasional academics quibbling the definition. Most of the studies into the mechanisms of caffeine addiction have been conducted on rats, but human studies exist too and caffeine is generally considered addictive for humans, for example:
See also:
Notwithstanding its addictive status, caffeine is otherwise safe: True or False?
True-ish, for most people. Some people with heart conditions or a hypersensitivity to caffeine may find it is not safe for them at all, and for the rest of us, the dose makes the poison. For example:
❝Can too much caffeine kill you? Although quite rare, caffeine can be fatal in cases of overdose; such circumstances are generally not applicable to healthy individuals who typically consume caffeine via beverages such as tea or coffee.❞
this paper, by the way, also includes a good example of academics quibbling the definition of addiction!
Caffeine is a cognitive enhancer: True or False?
True, but only in the case of occasional use. If you are using it all the time, your physiology will normalize it and you will require caffeine in order to function at your normal level. To attain higher than that, once addicted to caffeine, would now require something else.
Read more: Caffeine: benefits and drawbacks for technical performance
Caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck: True or False?
True or False depending on usage:
- The famously moderate 3–5 cups per day will not, for most people, cause any such problems.
- Using/abusing it to make up for lost sleep (or some other source of fatigue, such as physical exhaustion from exertion), however, is much more likely to run into problems.
In the latter case, caffeine really is the “payday loan” of energy! It’ll give you an adrenal boost now (in return, you must suffer the adrenal dumping later, along with lost energy expended in the adrenaline surge), and also, the tiredness that you thought was gone, was just caffeine’s adenosine-blocking activities temporarily preventing you from being able to perceive the tiredness. So you’ll have to pay that back later, with interest, because of the extra time/exertion too.
Want to make caffeine a little more gentle on your system?
Taking l-theanine alongside caffeine can ameliorate some of caffeine’s less wonderful effects—and as a bonus, l-theanine has some nifty benefits of its own, too:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Gut Renovation – by Dr. Roshini Raj, with Sheila Buff
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Unless we actually feel something going on down there, gut health is an oft-neglected part of overall health—which is unfortunate, because invisible as it may often be, it affects so much.
Gastroenterologist Dr. Roshini Raj gives us all the need-to-know information, explanations of why things happen the way they do with regard to the gut, and tips, tricks, and hacks to improve matters.
She also does some mythbusting along the way, and advises about what things don’t make a huge difference, including what medications don’t have a lot of evidence for their usefulness.
The style is easy-reading pop-science, with plenty of high-quality medical content.
Reading between the lines, a lot of the book as it stands was probably written by the co-author, Sheila Buff, who is a professional ghostwriter and specializes in working closely with doctors to produce works that are readable and informative to the layperson while still being full of the doctor’s knowledge and expertise. So a reasonable scenario is that Dr. Raj gave her extensive notes, she took it from there, passed it back to her for medical corrections, and they had a little back and forth until it was done. Whatever their setup, the end result was definitely good!
Bottom line: if you’d like a guide to gut health that’s practical and easy to read, while being quite comprehensive and certainly a lot more than “eat probiotics and fiber”, then this book is a fine choice.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
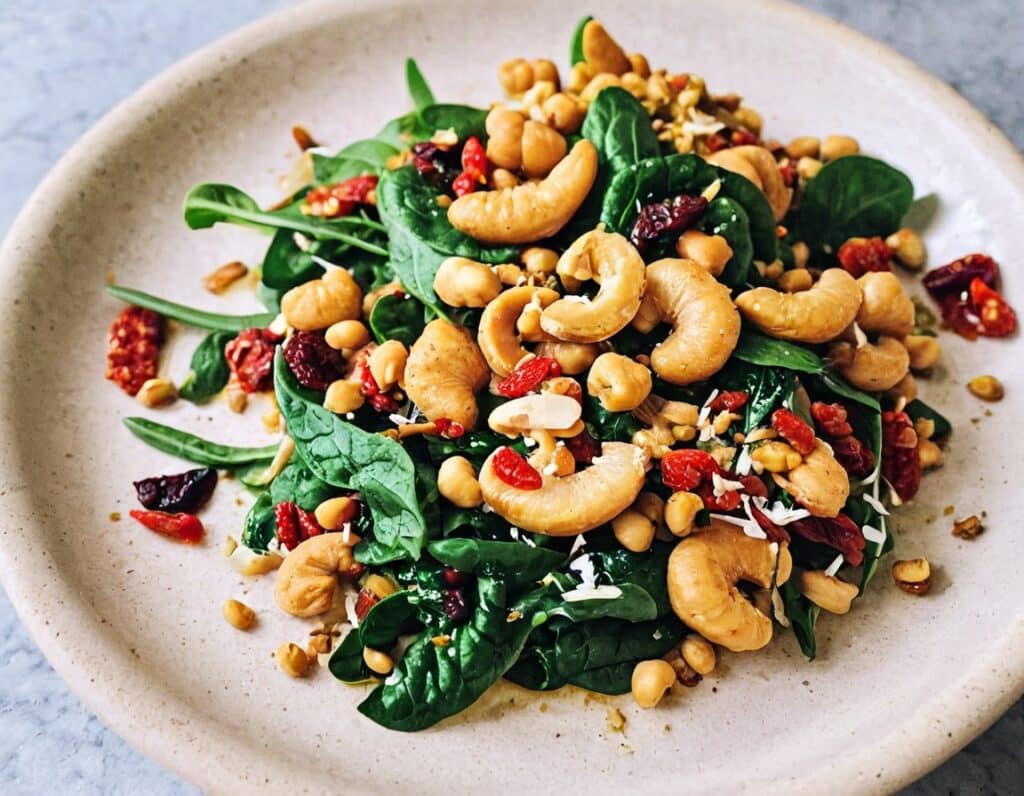
Protein Immune Support Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to get enough protein from a salad, without adding meat? Cashews and chickpeas have you more than covered! Along with the leafy greens and an impressive array of minor ingredients full of healthy phytochemicals, this one’s good for your muscles, bones, skin, immune health, and more.
You will need
- 1½ cups raw cashews (if allergic, omit; the chickpeas and coconut will still carry the dish for protein and healthy fats)
- 2 cans (2x 14oz) chickpeas, drained
- 1½ lbs baby spinach leaves
- 2 large onions, finely chopped
- 3 oz goji berries
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp dessicated coconut
- 1 tbsp dried cumin
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a pan; add the onions and cook for about 3 minutes.
2) Add the garlic and cook for a further 2 minutes.
3) Add the spinach, and cook until it wilts.
4) Add the remaining ingredients except the coconut, and cook for another three minutes.
5) Heat another pan (dry); add the coconut and toast for 1–2 minutes, until lightly golden. Add it to the main pan.
6) Serve hot as a main, or an attention-grabbing side:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Lower Your Blood Pressure (Cardiologists Explain)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today we enjoy the benefit of input from Dr. Zalzal, Dr. Weeing, and Dr. Hefferman!
If the thought of being in an operating room with three cardiologists in scrubs doesn’t raise your blood pressure too much, the doctors in question have a lot to offer for bringing those numbers down and keeping them down! They recommend…
150 mins of Exercise
This isn’t exactly controversial, but: move your body!
See also: Exercise Less; Move More
Reduce salt
Most people eating the Standard American Diet (SAD) are getting far too much—mostly because it’s in so many processed foods already.
See also: How Too Much Salt May Lead To Organ Failure
Eating habits
There’s a lot more to eating healthily for the heart than just reducing salt, and over all, the Mediterranean diet comes out scoring highest:
- What Is The Mediterranean Diet Anyway? ← a primer for the uncertain
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean ← includes a heart-specialized version!
Reduce alcohol
According to the WHO, the only healthy amount of alcohol is zero. According to these cardiologists: at the very least cut down. However much or little you’re drinking right now, less is better.
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
Maintain healthy weight
While the doctors agree that BMI isn’t a great method of measuring metabolic health, it is clear that carrying excessive weight isn’t good for the heart.
See also: Lose Weight (Healthily!)
No smoking
This one’s pretty straight forward: just don’t.
See also: Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
Reduce stress
Chronic stress has a big impact on chronic health in general and that includes its effect on blood pressure. So, improving one improves the other.
See also: Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
Good sleep
Quality matters as much as quantity, and that goes for its effect on your blood pressure too, so take the time to invest in your good health!
See also: The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: