The Polyvagal Theory – by Dr. Stephen Porges
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you ever find that your feelings (or occasionally: lack thereof) sometimes can seem mismatched with the observed facts of your situation? This book unravels that mystery—or rather, that stack of mysteries.
Dr. Porges’ work on this topic is, by the way, the culmination of 40 years of research. While he’s not exactly a household name to the layperson, he’s very respected in his field, and this book is his magnum opus.
Here he explains the disparate roles of the two branches of the vagus nerve (hence: polyvagal theory). At least, the two branches that we mammals have; non-mammalian vertebrates have only one. This makes a big difference, because of the cascade of inhibitions that this allows.
The answer to the very general question “What stops you from…?” is usually found somewhere down this line of cascade of inhibitions.
These range from “what stops you from quitting your job/relationship/etc” to “what stops you from freaking out” to “what stops you from relaxing” to “what stops you from reacting quickly” to “what stop you from giving up” to “what stops you from gnawing your arm off” and many many more.
And because sometimes we wish we could do something that we can’t, or wish we wouldn’t do something that we do, understanding this process can be something of a cheat code to life.
A quick note on style: the book is quite dense and can be quite technical, but should be comprehensible to any layperson who is content to take their time, because everything is explained as we go along.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the mysteries of how you feel vs how you actually are, and what that means for what you can or cannot wilfully do, this is a top-tier book
Click here to check out Polyvagal Theory, and take control of your responses!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Indistractable – by Nir Eyal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever felt that you could accomplish anything you wanted/needed, if only you didn’t get distracted?
This book lays out a series of psychological interventions for precisely that aim, and it goes a lot beyond the usual “download/delete these apps to help you stop checking social media every 47 seconds”.
Some you’ll have heard of before, some you won’t have, and if even one method works for you, it’ll have been well worth your while reading this book. This reviewer, for example, enjoyed the call to identity-based strength, e.g. adopting an “I am indistractable*” perspective going into tasks. This is akin to the strength of, for example, “I don’t drink” over “I am a recovering alcoholic”.
*the usual spelling of this, by the way, is “undistractable”, but we use the author’s version here for consistency. It’s a great marketing gimmick, as all searches for the word “indistractable” will bring up his book.
Nor is the book just about maximizing productivity to the detriment of everything else; this is not about having a 25 hours per day “grindset”. Rather, it even makes sure to cover such things as focusing on one’s loved ones, for instance.
Bottom line: if you’ve tried blocking out the distractions but still find you can’t focus, this book offers next-level solutions
Click here to check out Indistractible, and become indeed indistractable!
Share This Post
-
This Is Your Brain on Food – by Dr. Uma Naidoo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Diet will fix your brain” is a bold claim that often comes from wishful thinking and an optimistic place where anecdote is louder than evidence. But, diet does incontrovertibly also affect brain health. So, what does Dr. Naidoo bring to the table?
The author is a Harvard-trained psychiatrist, a professional chef who graduated with her culinary school’s most coveted award, and a trained-and-certified nutritionist. Between those three qualifications, it’s safe to she knows her stuff when it comes to the niche that is nutritional psychiatry. And it shows.
She takes us through the neurochemistry involved, what chemicals are consumed, made, affected, inhibited, upregulated, etc, what passes through the blood-brain barrier and what doesn’t, what part the gut really plays in its “second brain” role, and how we can leverage that—as well as mythbusting a lot of popular misconceptions about certain foods and moods.
There’s hard science in here, but presented in quite a pop-science way, making for a very light yet informative read.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand what your food is doing to your brain (and what it could be doing instead), then this is a top-tier book for you!
Click here to check out This Is Your Brain On Food, and get to know yours!
Share This Post
-
Pneumonia: Prevention Is Better Than Cure
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pneumonia: What We Can & Can’t Do About It
Pneumonia is a significant killer of persons over the age of 65, with the risk increasing with age after that, rising very sharply around the age of 85:
While pneumonia is treatable, especially in young healthy adults, the risks get more severe in the older age brackets, and it’s often the case that someone goes into hospital with one thing, then develops pneumonia, which the person was already not in good physical shape to fight, because of whatever hospitalized them in the first place:
American Lung Association | Pneumonia Treatment and Recovery
Other risk factors besides age
There are a lot of things that can increase our risk factor for pneumonia; they mainly fall into the following categories:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Other diseases of the immune system (e.g. HIV)
- Medication-mediated immunosuppression (e.g. after an organ transplant)
- Chronic lung diseases (e.g. asthma, COPD, Long Covid, emphysema, etc)
- Other serious health conditions ← we know this one’s broad, but it encompasses such things as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer
See also:
Why Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Is More Likely Than You Think
Things we can do about it
When it comes to risks, we can’t do much about our age and some of the other above factors, but there are other things we can do to reduce our risk, including:
- Get vaccinated against pneumonia if you are over 65 and/or have one of the aforementioned risk factors. This is not perfect (it only reduces the risk for certain kinds of infection) and may not be advisable for everyone (like most vaccines, it can put the body through its paces a bit after taking it), so speak with your own doctor about this, of course.
- See also: Vaccine Mythbusting
- Avoid contagion. While pneumonia itself is not spread person-to-person, it is caused by bacteria or viruses (there are numerous kinds) that are opportunistic and often become a secondary infection when the immune system is already busy with the first one. So, if possible avoid being in confined spaces with many people, and do wash your hands regularly (as a lot of germs are transferred that way and can get into the respiratory tract because you touched your face or such).
- See also: The Truth About Handwashing
- If you have a cold, or flu, or other respiratory infection, take it seriously, rest well, drink fluids, get good immune-boosting nutrients. There’s no such thing as “just a cold”; not anymore.
- Look after your general health too—health doesn’t exist in a vacuum, and nor does disease. Every part of us affects every other part of us, so anything that can be in good order, you want to be in good order.
This last one, by the way? It’s an important reminder that while some diseases (such as some of the respiratory infections that can precede pneumonia) are seasonal, good health isn’t.
We need to take care of our health as best we can every day along the way, because we never know when something could change.
Want to do more?
Check out: Seven Things To Do For Good Lung Health!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Forgotten Exercise That Could Save Your Health After 50
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot depends on this:
Your heart is also a “use it or lose it” muscle
It’s well-known that muscles in general require maintenance (by regular exertion thereof), or they will atrophy and weaken. However, this is not only true of our skeletal muscles (the ones people think about when they say “muscles”), but also muscles like the heart.
Now, of course, we are all using our heart all the time, every day. One might be tempted to think it’ll be fine. It won’t; the body will not maintain anything beyond necessity. Thus, the prescription here is to regularly get our heart out of “zone 1”, its regular resting rate, which is usually about 50% or so of its maximum rate, and into “zone 2”, in which it beats at 60–70% of its maximum rate.
To find your maximum rate: as a general rule of thumb, 220 minus your age will usually give a fairly accurate estimate, unless you are unusually fit or unusually unfit.
Alternatively, if you have a fitness tracker, it can probably give you a number based on actual observation of your heartrate.
The benefits of doing so, as mentioned in this video:
- Improves heart health, circulation, and lowers blood pressure.
- Burns belly fat by using stored fat as energy*
- Boosts aerobic capacity, making daily activities easier.
- Enhances insulin sensitivity, mental health, and sleep.
- Helps manage arthritis, osteoporosis, and high cholesterol.
*note that this won’t happen in zone 1, and if you spend more than a little time in zone 3, it will happen but your body will do a metabolic slump afterwards to compensate, while doing its best to replenish the fat reserves. So, zone 2 is really the goal for this one, unless you want to do HIIT, which is beyond the scope of today’s article.
He recommends activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. You don’t have to become a triathlon competitor if you don’t want to, but just pick what you like and do it at a fair pace. If it’s the brisk walking or cycling*, then (unless it’s very hot/humid where you are), if you break a sweat, you probably broke out of zone 2 and into zone 3. Which is fine, but wasn’t what you were aiming for, so it’s a sign you can go a little easier than that if you want.
*of course the same statement is also true of swimming, but you’ll not notice sweating in a pool 😉
As for how much and how often, averaging 20 minutes per day is good; if you want to condense that into 40 minutes 2–3 times per week, that’s fine too.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less & Move More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Blue Light At Night? Save More Than Just Your Sleep!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Beating The Insomnia Blues
You previously asked us about recipes for insomnia (or rather, recipes/foods to help with easing insomnia). We delivered!
But we also semi-promised we’d cover a bit more of the general management of insomnia, because while diet’s important, it’s not everything.
Sleep Hygiene
Alright, you probably know this first bit, but we’d be remiss if we didn’t cover it before moving on:
- No caffeine or alcohol before bed
- Ideally: none earlier either, but if you enjoy one or the other or both, we realize an article about sleep hygiene isn’t going to be what changes your mind
- Fresh bedding
- At the very least, fresh pillowcase(s). While washing and drying an entire bedding set constantly may be arduous and wasteful of resources, it never hurts to throw your latest pillowcase(s) in with each load of laundry you happen to do.
- Warm bed, cool room = maximum coziness
- Dark room. Speaking of which…
About That Darkness…
When we say the room should be dark, we really mean it:
- Not dark like “evening mood lighting”, but actually dark.
- Not dark like “in the pale moonlight”, but actually dark.
- Not dark like “apart from the light peeking under the doorway”, but actually dark.
- Not dark like “apart from a few LEDs on electronic devices that are on standby or are charging”, but actually dark.
There are many studies about the impact of blue light on sleep, but here’s one as an example.
If blue light with wavelength between 415 nm and 455 nm (in the visible spectrum) hits the retina, melatonin (the sleep hormone) will be suppressed.
The extent of the suppression is proportional to the amount of blue light. This means that there is a difference between starting at an “artificial daylight” lamp, and having the blue LED of your phone charger showing… but the effect is cumulative.
And it gets worse:
❝This high energy blue light passes through the cornea and lens to the retina causing diseases such as dry eye, cataract, age-related macular degeneration, even stimulating the brain, inhibiting melatonin secretion, and enhancing adrenocortical hormone production, which will destroy the hormonal balance and directly affect sleep quality.❞
Read it in full: Research progress about the effect and prevention of blue light on eyes
See also: Age-related maculopathy and the impact of blue light hazard
So, what this means, if we value our health, is:
- Switch off, or if that’s impractical, cover the lights of electronic devices. This might be as simple as placing your phone face-down rather than face-up, for instance.
- Invest in blackout blinds/curtains (per your preference). Serious ones, like these ← see how they don’t have to be black to be blackout! You don’t have to sacrifice style for function
- If you can’t reasonably do the above, consider a sleep mask. Again, a good one. Not the kind you were given on a flight, or got free with some fluffy handcuffs. We mean a full-blackout sleep mask that’s designed to be comfortable enough to sleep in, like this one.
- If you need to get up to pee or whatever, do like a pirate and keep one eye covered/closed. That way, it’ll remain unaffected by the light. Pirates did it to retain their night vision when switching between being on-deck or below, but you can do it to halve the loss of melatonin.
Lights-Out For Your Brain Too
You can have all the darkness in the world and still not sleep if your mind is racing thinking about:
- your recent day
- your next day
- that conversation you wish had gone differently
- what you really should have done when you were 18
- how you would go about fixing your country’s socio-political and economic woes if you were in charge
- Etc.
We wrote about how to hit pause on all that, in a previous edition of 10almonds.
Check it out: The Off-Button For Your Brain—How to “just say no” to your racing mind (this trick really works)
Sweet dreams!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- No caffeine or alcohol before bed
-
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
We’re aware that very many of our readers are women, who do not have a prostate.
However, dear reader: if you do have one, and/or love someone who has one, this is a good thing to know about.
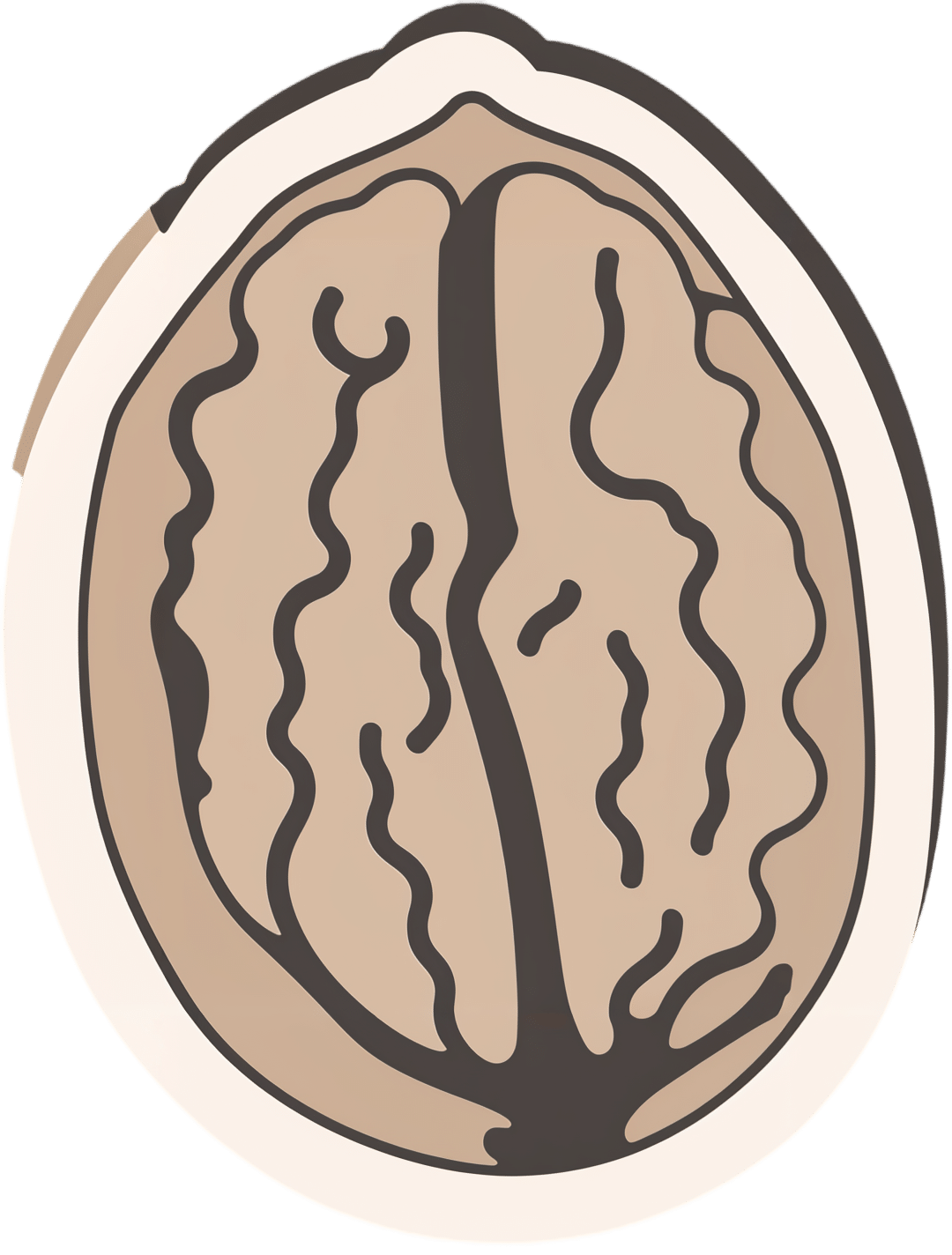
The prostate gland is a (hopefully) walnut-sized gland (it actually looks a bit like a walnut too), that usually sits just under the bladder.
See also: How to Locate Your Prostate*
*The scale is not great in these diagrams, but they’ll get the job done. Besides, everyone is different on the inside, anyway. Not in a “special unique snowflake” way, but in a “you’d be surprised how much people’s insides move around” way.
Fun fact: did you ever feel like your intestines are squirming? That’s because they are.
You can’t feel it most of the time due to the paucity of that kind of nervous sensation down there, but the peristaltic motion that they use to move food along them on the inside, also causes them push against the rest of your guts, on the outside of them. This is the exact same way that many snakes move about.
If someone has to perform an operation in that region, sometimes it will be necessary to hang the intestines on a special rack, to keep them in one place for the surgery.
What can go wrong?
There are two very common things that can go wrong with the prostate:
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH), otherwise known as an enlarged prostate
- Prostate cancer
For most men, the prostate gland continues to grow with age, which is how the former comes about so frequently.
For everyone, due to the nature of the mathematics involved in cellular mutation and replication, we will eventually get cancer if something else doesn’t kill us first.
- Prostate cancer affects 12% of men overall, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing each year thereafter.
- Prostate cancer can look like BPH in the early stages (and/or, an enlarged prostate can turn cancerous) so it’s important to not shrug off the symptoms of BPH.
How can BPH be avoided/managed?
There are prescription medications that can help reduce the size of the prostate, including testosterone blockers (such as spironolactone and bicalutamide) and 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride. Each have their pros and cons:
- Testosterone-blockers are the heavy-hitters, and work very well… but have more potential adverse side effects (your body is used to running on testosterone, after all)
- 5α-reductase inhibitors aren’t as powerful, but they block the conversion of free testosterone to dihydrogen testosterone (DHT), and it’s primarily DHT that causes the problems. By blocking the conversion of T to DHT, you may actually end up with higher serum testosterone levels, but fewer ill-effects. Exact results will vary depending on your personal physiology, and what else you are taking, though.
There are also supplements that can help, including saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil. Here’s a good paper that covers both:
We have recommended saw palmetto before for a variety of uses, including against BPH:
Too much or too little testosterone? This one supplement may fix that
You might want to avoid certain medications that can worsen BPH symptoms (but not actually the size of the prostate itself). They include:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (most modern antidepressants aren’t this kind; ask your pharmacist/doctor if unsure)
You also might want to reduce/skip:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
In all the above cases, it’s because of how they affect the bladder, not the prostate, but given their neighborliness, each thing affects the other.
What if it’s cancer? How do I know and what do I do?
The creator of the Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test has since decried it as “a profit-driven health disaster” that is “no better than a coin toss”, but it remains the first go-to of many medical services.
However, there’s a newer, much more accurate test, called the Prostate Screening Episwitch (PSE) test, which is 94% accurate, so you might consider asking your healthcare provider whether that’s an option:
The new prostate cancer blood test with 94 per cent accuracy
As for where to go from there, we’re out of space for today, but we previously reviewed a very good book about this, Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer, and we highly recommend it—it could easily be a literal lifesaver.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: