The Non-Alcoholic Drinker – by James Ellison
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A mere few decades ago, it was often considered antisocial not to smoke. These days, it’s antisocial if you do. The same social change is starting to happen now with alcohol—Millennials are drinking much less than they did in decades past, and Gen Z are hardly drinking at all.
The author, himself a Baby Boomer, champions the cause of mindful, and/but joyful, abstemiousness. Which latter two words don’t often go together, but in this case, he really has put in a lot of work to make non-alcoholic drinking as exciting, fun, and sophisticated as alcoholic drinking always marketed itself to be.
The mocktail recipes in this book are an order of magnitude better than any others this reviewer has encountered before, and did you know they have non-alcoholic bitters now? As in, the cocktail ingredient. Nor is it the only non-alcoholic botanical used, and the ingredients in general are as varied and flavorful, if not sometimes more so, than many that get used in alcoholic mixes.
This book is a very far cry from “rum and coke without the rum”, and instead will have you excited to go ingredient-shopping, and even more excited when you find out how great non-alcoholic things can taste if given the right attention.
As a convenient extra touch, all the ingredients he mentions are available from Amazon, which takes away the fear of “ok, but where do I get…” when it comes to getting things in.
The book does cover things besides just the recipes themselves though, and also talks the reader through navigating non-alcoholism when friends of your own age (unless you’re one of our younger readers) are probably mostly still partying with alcohol.
Really, the biggest value of this book is the recipes, though.
Bottom line: if you’d like to entertain with sophistication and grace and/but not with alcohol, or even just take up a fun new healthy hobby, this book is by far the best book on non-alcoholic mixology that this reviewer has seen to date.
Click here to check out The Non-Alcoholic Drinker, and get mixing non-alcoholically!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Proteinaholic – by Dr. Garth Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein is important, yes. However, you can have too much of a good thing, and you can also get it from bad sources that do more harm than good.
That’s what this book is about, and how to go about understanding the science in a world where marketing has outstripped the conclusions of research scientists.
Firstly, let’s mention that Dr. Davis’ main issue here is (as the subtitle suggests) about animal proteins, not plant-based proteins. The former are associated with very many health risks that the latter are not. And yes, even just the lean protein, not considering the animal fat.
He does not argue that the reader must, or even necessarily needs to, adopt a vegan diet. However, he does argue for minimizing animal proteins, and getting more plants in.
A lot of the book is about the research to back this approach, and specifically, it’s largely a polemic against animal protein. He also shares anecdotes throughout, about his own health journey—from an overweight cheeseburger-fueled heart attack machine with exciting cholesterol levels, to a healthy, muscular, plant-fueled advocate for healthier eating.
He talks us through the science at hand, including chapters for each of the main health risks associated with meat consumption, as well as how the science got misrepresented by popular marketing for [not necessarily, but usually] meat-heavy diets such as Atkins and Paleo. That yes, they will give short term weight loss, but bring extra health risks in the longer term, and how.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut down your meat consumption but worry “will I get enough protein?”, this book will set your mind at ease with an abundance of science.
Click here to check out Proteinaholic, and give your body better!
Share This Post
-
Simple, 10-Minute Hip Opening Routine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hips Feeling Stiff?
If so, Flow with Adee’s video (below) has just the solution with a quick 10-minute hip-opening routine. Designed for intermediates but open to all, we love Adee’s work and recommend that you reach out to her to tell her what you’d like to see next.
Other Methods
If you’re a book lover, we’ve reviewed a fantastic book on reducing hip pain. Alternatively, learn stretching from a ballerina with Jasmine McDonald’s ballet stretching routine.
Otherwise, enjoy today’s video:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
A new emergency procedure for cardiac arrests aims to save more lives – here’s how it works
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As of January this year, Aotearoa New Zealand became just the second country (after Canada) to adopt a groundbreaking new procedure for patients experiencing cardiac arrest.
Known as “double sequential external defibrillation” (DSED), it will change initial emergency response strategies and potentially improve survival rates for some patients.
Surviving cardiac arrest hinges crucially on effective resuscitation. When the heart is working normally, electrical pulses travel through its muscular walls creating regular, co-ordinated contractions.
But if normal electrical rhythms are disrupted, heartbeats can become unco-ordinated and ineffective, or cease entirely, leading to cardiac arrest.
Defibrillation is a cornerstone resuscitation method. It gives the heart a powerful electric shock to terminate the abnormal electrical activity. This allows the heart to re-establish its regular rhythm.
Its success hinges on the underlying dysfunctional heart rhythm and the proper positioning of the defibrillation pads that deliver the shock. The new procedure will provide a second option when standard positioning is not effective.
Using two defibrillators
During standard defibrillation, one pad is placed on the right side of the chest just below the collarbone. A second pad is placed below the left armpit. Shocks are given every two minutes.
Early defibrillation can dramatically improve the likelihood of surviving a cardiac arrest. However, around 20% of patients whose cardiac arrest is caused by “ventricular fibrillation” or “pulseless ventricular tachycardia” do not respond to the standard defibrillation approach. Both conditions are characterised by abnormal activity in the heart ventricles.
DSED is a novel method that provides rapid sequential shocks to the heart using two defibrillators. The pads are attached in two different locations: one on the front and side of the chest, the other on the front and back.
A single operator activates the defibrillators in sequence, with one hand moving from the first to the second. According to a recent randomised trial in Canada, this approach could more than double the chances of survival for patients with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia who are not responding to standard shocks.
The second shock is thought to improve the chances of eliminating persistent abnormal electrical activity. It delivers more total energy to the heart, travelling along a different pathway closer to the heart’s left ventricle.
Evidence of success
New Zealand ambulance data from 2020 to 2023 identified about 1,390 people who could potentially benefit from novel defibrillation methods. This group has a current survival rate of only 14%.
Recognising the potential for DSED to dramatically improve survival for these patients, the National Ambulance Sector Clinical Working Group updated the clinical procedures and guidelines for emergency medical services personnel.
The guidelines now specify that if ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia persist after two shocks with standard defibrillation, the DSED method should be administered. Two defibrillators need to be available, and staff must be trained in the new approach.
Though the existing evidence for DSED is compelling, until recently it was based on theory and a small number of potentially biased observational studies. The Canadian trial was the first to directly compare DSED to standard treatment.
From a total of 261 patients, 30.4% treated with this strategy survived, compared to 13.3% when standard resuscitation protocols were followed.
The design of the trial minimised the risk of other factors confounding results. It provides confidence that survival improvements were due to the defibrillation approach and not regional differences in resources and training.
The study also corroborates and builds on existing theoretical and clinical scientific evidence. As the trial was stopped early due to the COVID-19 pandemic, however, the researchers could recruit fewer than half of the numbers planned for the study.
Despite these and other limitations, the international group of experts that advises on best practice for resuscitation updated its recommendations in 2023 in response to the trial results. It suggested (with caution) that emergency medical services consider DSED for patients with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia who are not responding to standard treatment.
Training and implementation
Although the evidence is still emerging, implementation of DSED by emergency services in New Zealand has implications beyond the care of patients nationally. It is also a key step in advancing knowledge about optimal resuscitation strategies globally.
There are always concerns when translating an intervention from a controlled research environment to the relative disorder of the real world. But the balance of evidence was carefully considered before making the decision to change procedures for a group of patients who have a low likelihood of survival with current treatment.
Before using DSED, emergency medical personnel undergo mandatory education, simulation and training. Implementation is closely monitored to determine its impact.
Hospitals and emergency departments have been informed of the protocol changes and been given opportunities to ask questions and give feedback. As part of the implementation, the St John ambulance service will perform case reviews in addition to wider monitoring to ensure patient safety is prioritised.
Ultimately, those involved are optimistic this change to cardiac arrest management in New Zealand will have a positive impact on survival for affected patients.
Vinuli Withanarachchie, PhD candidate, College of Health, Massey University; Bridget Dicker, Associate Professor of Paramedicine, Auckland University of Technology, and Sarah Maessen, Research Associate, Auckland University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Entertaining Harissa Traybake
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
No, it’s not entertaining in the sense that it will tell you jokes or perhaps dance for you, but rather: it can be easily prepared in advance, kept in the fridge for up to 3 days, and reheated when needed as part of a spread when entertaining, leaving you more time to spend with your houseguests.
Aside from its convenience, it is of course nutritious and delicious:
You will need
- 14 oz cherry tomatoes
- 2 cans chickpeas, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups cooked chickpeas, drained and rinsed)
- 2 eggplants, cut into ¾” cubes
- 1 red onion, roughly chopped
- 1 bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp harissa paste
- 1 tbsp ras el-hanout
- 1 tsp MSG or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃
2) Mix the onion, eggplant, and garlic (whole cloves; just peel them and put them in) with the olive oil in a mixing bowl, ensuring everything is coated evenly.
3) Add in 1 tbsp of the harissa paste, 1 tbsp of the ras-el hanout, and half of the MSG/salt, and again mix thoroughly to coat evenly.
4) Bake in the oven, in a walled tray, for about 30 minutes, giving things a stir/jiggle halfway through to ensure they cook evenly.
5) Add the cherry tomatoes to the tray, and return to the oven for another 10 minutes.
6) Mix the chickpeas with the other 1 tbsp of the harissa paste, the other 1 tbsp of the ras-el hanout, and the other half of the MSG/salt, and add to the tray, returning it to the oven for a final 10 minutes.
7) Serve hot, or set aside for later, refrigerating once cool enough to do so. When you do serve, we recommend serving with a yogurt, cucumber, and mint dip, and perhaps flatbreads (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe):
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
We’re aware that very many of our readers are women, who do not have a prostate.
However, dear reader: if you do have one, and/or love someone who has one, this is a good thing to know about.
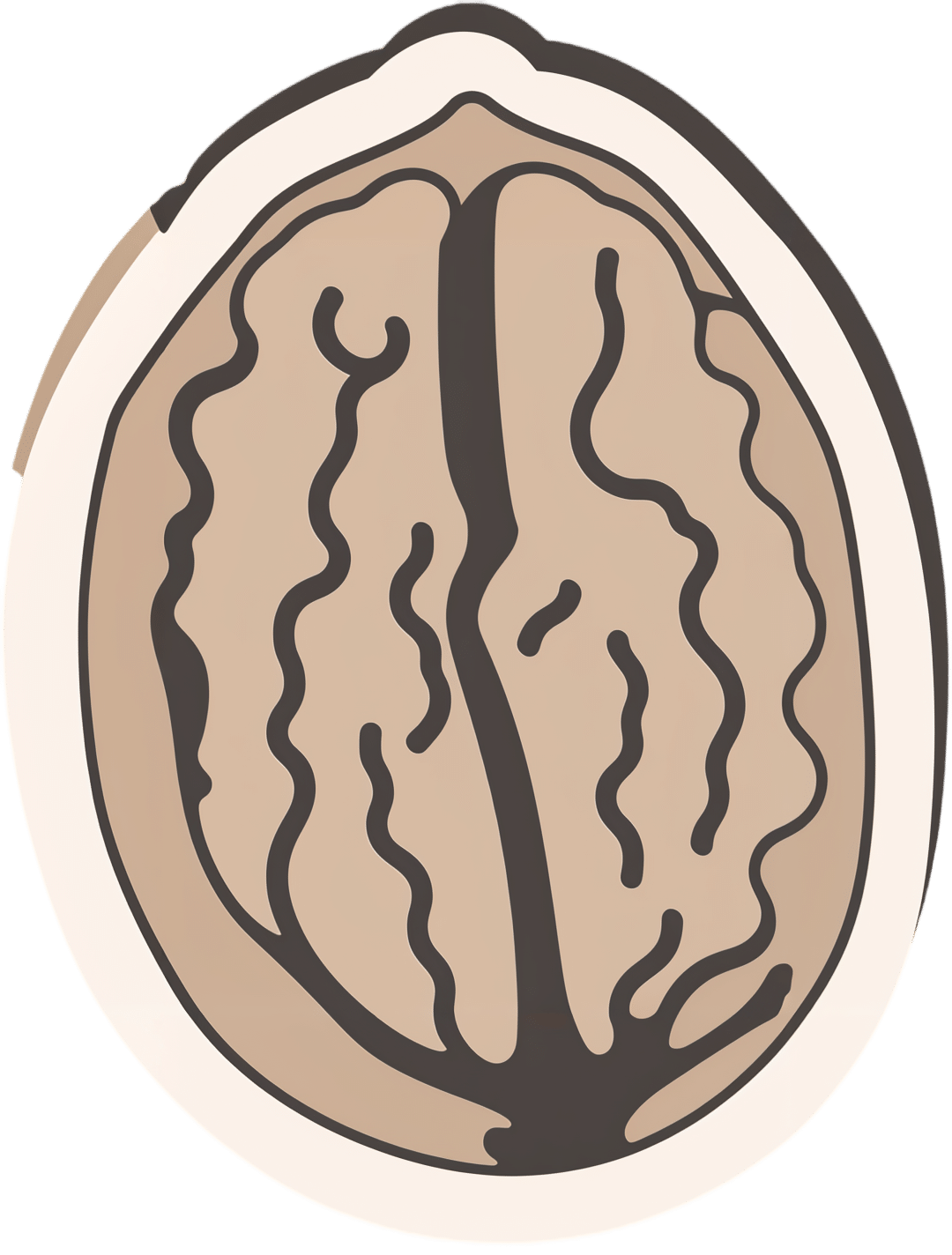
The prostate gland is a (hopefully) walnut-sized gland (it actually looks a bit like a walnut too), that usually sits just under the bladder.
See also: How to Locate Your Prostate*
*The scale is not great in these diagrams, but they’ll get the job done. Besides, everyone is different on the inside, anyway. Not in a “special unique snowflake” way, but in a “you’d be surprised how much people’s insides move around” way.
Fun fact: did you ever feel like your intestines are squirming? That’s because they are.
You can’t feel it most of the time due to the paucity of that kind of nervous sensation down there, but the peristaltic motion that they use to move food along them on the inside, also causes them push against the rest of your guts, on the outside of them. This is the exact same way that many snakes move about.
If someone has to perform an operation in that region, sometimes it will be necessary to hang the intestines on a special rack, to keep them in one place for the surgery.
What can go wrong?
There are two very common things that can go wrong with the prostate:
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH), otherwise known as an enlarged prostate
- Prostate cancer
For most men, the prostate gland continues to grow with age, which is how the former comes about so frequently.
For everyone, due to the nature of the mathematics involved in cellular mutation and replication, we will eventually get cancer if something else doesn’t kill us first.
- Prostate cancer affects 12% of men overall, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing each year thereafter.
- Prostate cancer can look like BPH in the early stages (and/or, an enlarged prostate can turn cancerous) so it’s important to not shrug off the symptoms of BPH.
How can BPH be avoided/managed?
There are prescription medications that can help reduce the size of the prostate, including testosterone blockers (such as spironolactone and bicalutamide) and 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride. Each have their pros and cons:
- Testosterone-blockers are the heavy-hitters, and work very well… but have more potential adverse side effects (your body is used to running on testosterone, after all)
- 5α-reductase inhibitors aren’t as powerful, but they block the conversion of free testosterone to dihydrogen testosterone (DHT), and it’s primarily DHT that causes the problems. By blocking the conversion of T to DHT, you may actually end up with higher serum testosterone levels, but fewer ill-effects. Exact results will vary depending on your personal physiology, and what else you are taking, though.
There are also supplements that can help, including saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil. Here’s a good paper that covers both:
We have recommended saw palmetto before for a variety of uses, including against BPH:
Too much or too little testosterone? This one supplement may fix that
You might want to avoid certain medications that can worsen BPH symptoms (but not actually the size of the prostate itself). They include:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (most modern antidepressants aren’t this kind; ask your pharmacist/doctor if unsure)
You also might want to reduce/skip:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
In all the above cases, it’s because of how they affect the bladder, not the prostate, but given their neighborliness, each thing affects the other.
What if it’s cancer? How do I know and what do I do?
The creator of the Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test has since decried it as “a profit-driven health disaster” that is “no better than a coin toss”, but it remains the first go-to of many medical services.
However, there’s a newer, much more accurate test, called the Prostate Screening Episwitch (PSE) test, which is 94% accurate, so you might consider asking your healthcare provider whether that’s an option:
The new prostate cancer blood test with 94 per cent accuracy
As for where to go from there, we’re out of space for today, but we previously reviewed a very good book about this, Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer, and we highly recommend it—it could easily be a literal lifesaver.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet Slow Cooker Cookbook – by Madeline Given
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a nutritionist, has a strongly reactionary take on what’s inflammatory or not, so we see some interesting choices such as including red meat and excluding soy beans, but for the most part, the recipes are from ingredients generally considered at least non-inflammatory, if not anti-inflammatory (which many are, especially the herbs, spices, berries, and leafy greens).
For those who do wish to avoid specific foods due to allergies or intolerances, they are marked as being, for example, dairy-free, nut-free, nightshade-free, and so forth.
By default, she does give us mostly dairy-free recipes, by the way, usually swapping any unfermented dairy for plant-based alternatives. Of course, not every plant-based alternative will be right for every reader, but a degree of common sense can be assumed with regard to substitutions (e.g. maybe don’t go with the recommendation of a nut milk if you have a nut allergy, etc).
The recipes themselves, of which there are 90, are pleasant and clearly described, and (consistent with what one would expect from a book of slow cooker recipes) involve an absolute minimum of preparation time.
Bottom line: this one will go best if you are already aware of what’s inflammatory or not for you personally; aside from that, it’s a mostly very respectable book of tasty slow cooker recipes.
Click here to check out The Anti-Inflammatory Diet Slow Cooker Cookbook, and go slow!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: