The Menopause Risk That Nobody Talks About
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In this week’s health news round up, we cover menopausal disordered eating, air pollution & Alzheimer’s, and cold sore comebacks:
When the body starts changing…
Eating disorders are often thought of as a “teenage girl thing”. But in fact, eating disorders in girls/women mostly occur along with “the three Ps”:
- Puberty
- Pregnancy
- Perimenopause & menopause
In very many cases, it’s likely “my body is changing and I have strong opinions on how it should be”. Those opinions are often reflective of societal norms and pressures, but still, they are earnestly felt also. In the case of pregnancy, the societal pressures and standards are generally lifted while pregnant, but come back immediately postpartum, with an expectation to rebound quickly into the same shape one was in beforehand. And in the case of menopause, this is often concurrent with a sense of loss of identity, and can be quite reactionary against what is generally considered to be the ravages of time.
Of course, looking after one’s health is great at any age, and certainly there is no reason not to pursue health goals and try to get one’s body the way one wants it. However, it is all-too-easy for people to fall into the trap of taking drastic steps that are not actually that healthy, in the hopes of quick results.
Further, 13% of women over 50 report current core eating disorder symptoms, and that is almost certain vastly underreported.
Read in full: Eating disorders don’t just affect teen girls—the risk may also go up around pregnancy and menopause
Related: Body Image Dissatisfaction/Appreciation Across The Ages From Age 16 To Age 88
Where there’s smoke…
It’s been known for a while that air pollution is strongly associated with Alzheimer’s disease incidence, but exactly how this happens has not been entirely clear, beyond that it involves S-nitrosylation, in which NO-related particles bind to sulfur (S) atoms, forming SNO (and scientists being how they are, the term for the resultant brain effect has been called a SNO-STORM).
However, researchers have now found that it has to do with how certain toxins in the air (notwithstanding our heading here, they don’t have to be smoke—it can be household chemicals or other things too) cause this resultant SNO to interfere with protein CRTC1, which is critical for forming/maintaining connections between brain cells.
This is important, because it means that if a drug can be made that selectively blocks S-nitrosylatoin actions affecting CRTC1, it can reverse a lot of Alzheimer’s brain damage (as was found in the laboratory, when testing the theory with CRTC1 proteins that had been genetically engineered to resist S-nitrosylation, which is not something we can do with living human brains yet, but it is “proof of principle” and means funding will likely be forthcoming to find drugs to do the same thing).
Read in full: Study reveals how air pollution contributes to Alzheimer’s disease
Related: 14 Powerful Strategies To Prevent Dementia
The virus that comes back from the cold
Cold sores are created by the Herpes simplex virus (yes, the same one as for the genital variety), and by adulthood, most of us are either infected (and periodically get cold sores), or else infected (as an asymptomatic carrier). A noteworthy minority, but a minority nevertheless, are immune. Unless you’ve never had physical contact with other humans, it’s highly unlikely you’re not in one of the above three categories.
For those who do get cold sores, they can seem random in their reoccurrence, but in reality the virus never went away; it was just dormant for a while.
This much was known already, but scientists have now identified the trigger protein (known as “UL 12.5” to its friends) that acts as an alarm clock for the virus—which may pave the way to a greatly-improved treatment, if a way can be found to safely interfere with that wake-up call:
Read in full: Cold sore discovery identifies unknown trigger for those annoying flare-ups
Related: Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs
We asked you for your (health-related) policy on sugar. The trends were as follows:
- About half of all respondents voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Refined sugar is terrible; natural sugars (e.g. honey, agave) are fine”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad; I avoid it entirely”
- One (1) respondent voted for “Sugar is an important source of energy, so I consume plenty”
Writer’s note: I always forget to vote in these, but I’d have voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”.
Sometimes I would like to make my own [whatever] to not have the sugar, but it takes so much more time, and often money too.
So while I make most things from scratch (and typically spend about an hour cooking each day), sometimes store-bought is the regretfully practical timesaver/moneysaver (especially when it comes to condiments).
So, where does the science stand?
There has, of course, been a lot of research into the health impact of sugar.
Unfortunately, a lot of it has been funded by sugar companies, which has not helped. Conversely, there are also studies funded by other institutions with other agendas to push, and some of them will seek to make sugar out to be worse than it is.
So for today’s mythbusting overview, we’ve done our best to quality-control studies for not having financial conflicts of interest. And of course, the usual considerations of favoring high quality studies where possible Large sample sizes, good method, human subjects, that sort of thing.
Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
- Sucrose is sucrose, and is generally bad.
- Fructose is fructose, and is worse.
Both ultimately get converted into glycogen (if not used immediately for energy), but for fructose, this happens mostly* in the liver, which a) taxes it b) goes very unregulated by the pancreas, causing potentially dangerous blood sugar spikes.
This has several interesting effects:
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, it doesn’t cause insulin insensitivity (yay)
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, this leaves hyperglycemia untreated (oh dear)
- Because fructose is metabolized by the liver and converted to glycogen which is stored there, it’s one of the main contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (at this point, we’re retracting our “yay”)
Read more: Fructose and sugar: a major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
*”Mostly” in the liver being about 80% in the liver. The remaining 20%ish is processed by the kidneys, where it contributes to kidney stones instead. So, still not fabulous.
Fructose is very bad, so we shouldn’t eat too much fruit: True or False?
False! Fruit is really not the bad guy here. Fruit is good for you!
Fruit does contain fructose yes, but not actually that much in the grand scheme of things, and moreover, fruit contains (unless you have done something unnatural to it) plenty of fiber, which mitigates the impact of the fructose.
- A medium-sized apple (one of the most sugary fruits there is) might contain around 11g of fructose
- A tablespoon of high-fructose corn syrup can have about 27g of fructose (plus about 3g glucose)
Read more about it: Effects of high-fructose (90%) corn syrup on plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and normal subjects
However! The fiber content (in fruit) mitigates the impact of the fructose almost entirely anyway.
And if you take fruits that are high in sugar and/but high in polyphenols, like berries, they now have a considerable net positive impact on glycemic health:
- Polyphenols and Glycemic Control
- Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review
- Dietary polyphenols as antidiabetic agents: Advances and opportunities
You may be wondering: what was that about “unless you have done something unnatural to it”?
That’s mostly about juicing. Juicing removes much (or all) of the fiber, and if you do that, you’re basically back to shooting fructose into your veins:
- Effect of Fruit Juice on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials
- Intake of Fruit, Vegetables, and Fruit Juices and Risk of Diabetes in Women
Natural sugars like honey, agave, and maple syrup, are healthier than refined sugars: True or False?
True… Sometimes, and sometimes marginally.
This is partly because of the glycemic index and glycemic load. The glycemic index scores tail off thus:
- table sugar = 65
- maple syrup = 54
- honey = 46
- agave syrup = 15
So, that’s a big difference there between agave syrup and maple syrup, for example… But it might not matter if you’re using a very small amount, which means it may have a high glycemic index but a low glycemic load.
Note, incidentally, that table sugar, sucrose, is a disaccharide, and is 50% glucose and 50% fructose.
The other more marginal health benefits come from that fact that natural sugars are usually found in foods high in other nutrients. Maple syrup is very high in manganese, for example, and also a fair source of other minerals.
But… Because of its GI, you really don’t want to be relying on it for your nutrients.
Wait, why is sugar bad again?
We’ve been covering mostly the more “mythbusting” aspects of different forms of sugar, rather than the less controversial harms it does, but let’s give at least a cursory nod to the health risks of sugar overall:
- Obesity and associated metabolic risk
- Main contributor to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Insulin resistance and diabetes risk
- Cellular aging (shortened telomeres)
- 95% increased cancer risk
That last one, by the way, was a huge systematic review of 37 large longitudinal cohort studies. Results varied depending on what, specifically, was being examined (e.g. total sugar, fructose content, sugary beverages, etc), and gave up to 200% increased cancer risk in some studies on sugary beverages, but 95% increased risk is a respectable example figure to cite here, pertaining to added sugars in foods.
And finally…
The 56 Most Common Names for Sugar (Some Are Tricky)
How many did you know?
Share This Post
-
16 Overlooked Autistic Traits In Women
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We hear a lot about “autism moms”, but Taylor Heaton is an autistic mom, diagnosed as an adult, and she has insights to share about overlooked autistic traits in women.
The Traits
- Difficulty navigating romantic relationships: often due to misreading signs
- Difficulty understanding things: including the above, but mostly: difficulty understanding subtext, when people leave things as “surely obvious”. Autistic women are likely to be aware of the possible meanings, but unsure which it might be, and may well guess wrongly.
- Masking: one of the reasons for the gender disparity in diagnosis is that autistic women are often better at “masking”, that is to say, making a conscious effort to blend in to allistic society—often as a result of being more societally pressured to do so.
- Honesty: often to a fault
- Copy and paste: related to masking, this is about consciously mirroring others in an effort to put them at ease and be accepted
- Being labelled sensitive and/or gifted: usually this comes at a young age, but the resultant different treatment can have a lifetime effect
- Secret stims: again related to masking, and again for the same reasons that displaying autistic symptoms is often treated worse in women, autistic women’s stims tend to be more subtle.
- Written communication: autistic women are often more comfortable with the written word than the spoken
- Leadership: autistic women will often gravitate to leadership roles, partly as a survival mechanism
- Gaslighting: oneself, e.g. “If this person did this without that, then I can to” (without taking into account that maybe the circumstances are different, or maybe they actually did lean on crutches that you didn’t know were there, etc).
- Inner dialogue: rich inner dialogue, but unable to express it outwardly—often because of the sheer volume of thoughts per second.
- Fewer female friends: often few friends overall, for that matter, but there’s often a gender imbalance towards male friends, or where there isn’t, towards more masculine friends at least.
- Feeling different: often a matter of feeling one does not meet standard expectations in some fashion
- School: autistic women are often academically successful
- Special interests: often more “socially accepted” interests than autistic men’s.
- Flirting: autistic women are often unsure how to flirt or what to do about it, which can result in simple directness instead
For more details on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Related reading:
You might like a main feature of ours from not long back:
Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Parents are increasingly saying their child is ‘dysregulated’. What does that actually mean?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Welcome aboard the roller coaster of parenthood, where emotions run wild, tantrums reign supreme and love flows deep.
As children reach toddlerhood and beyond, parents adapt to manage their child’s big emotions and meltdowns. Parenting terminology has adapted too, with more parents describing their child as “dysregulated”.
But what does this actually mean?
ShUStudio/Shutterstock More than an emotion
Emotional dysregulation refers to challenges a child faces in recognising and expressing emotions, and managing emotional reactions in social settings.
This may involve either suppressing emotions or displaying exaggerated and intense emotional responses that get in the way of the child doing what they want or need to do.
“Dysregulation” is more than just feeling an emotion. An emotion is a signal, or cue, that can give us important insights to ourselves and our preferences, desires and goals.
An emotionally dysregulated brain is overwhelmed and overloaded (often, with distressing emotions like frustration, disappointment and fear) and is ready to fight, flight or freeze.
Developing emotional regulation
Emotion regulation is a skill that develops across childhood and is influenced by factors such as the child’s temperament and the emotional environment in which they are raised.
In the stage of emotional development where emotion regulation is a primary goal (around 3–5 years old), children begin exploring their surroundings and asserting their desires more actively.
A child’s temperament and upbringing affect how they regulate emotions. bluedog studio/Shutterstock It’s typical for them to experience emotional dysregulation when their initiatives are thwarted or criticised, leading to occasional tantrums or outbursts.
A typically developing child will see these types of outbursts reduce as their cognitive abilities become more sophisticated, usually around the age they start school.
Express, don’t suppress
Expressing emotions in childhood is crucial for social and emotional development. It involves the ability to convey feelings verbally and through facial expressions and body language.
When children struggle with emotional expression, it can manifest in various ways, such as difficulty in being understood, flat facial expressions even in emotionally charged situations, challenges in forming close relationships, and indecisiveness.
Several factors, including anxiety, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, giftedness, rigidity and both mild and significant trauma experiences, can contribute to these issues.
Common mistakes parents can make is dismissing emotions, or distracting children away from how they feel.
These strategies don’t work and increase feelings of overwhelm. In the long term, they fail to equip children with the skills to identify, express and communicate their emotions, making them vulnerable to future emotional difficulties.
We need to help children move compassionately towards their difficulties, rather than away from them. Parents need to do this for themselves too.
Caregiving and skill modelling
Parents are responsible for creating an emotional climate that facilitates the development of emotion regulation skills.
Parents’ own modelling of emotion regulation when they feel distressed. The way they respond to the expression of emotions in their children, contributes to how children understand and regulate their own emotions.
Children are hardwired to be attuned to their caregivers’ emotions, moods, and coping as this is integral to their survival. In fact, their biggest threat to a child is their caregiver not being OK.
Unsafe, unpredictable, or chaotic home environments rarely give children exposure to healthy emotion expression and regulation. Children who go through maltreatment have a harder time controlling their emotions, needing more brainpower for tasks that involve managing feelings. This struggle could lead to more problems with emotions later on, like feeling anxious and hypervigilant to potential threats.
Recognising and addressing these challenges early on is essential for supporting children’s emotional wellbeing and development.
A dysregulated brain and body
When kids enter “fight or flight” mode, they often struggle to cope or listen to reason. When children experience acute stress, they may respond instinctively without pausing to consider strategies or logic.
If your child is in fight mode, you might observe behaviours such as crying , clenching fists or jaw, kicking, punching, biting, swearing, spitting or screaming.
In flight mode, they may appear restless, have darting eyes, exhibit excessive fidgeting, breathe rapidly, or try to run away.
A shut-down response may look like fainting or a panic attack.
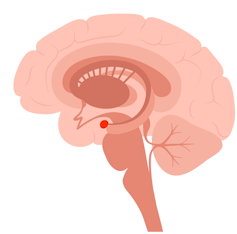
When a child feels threatened, their brain’s frontal lobe, responsible for rational thinking and problem-solving, essentially goes offline.
The amygdala, shown here in red, triggers survival mode. pikovit/Shutterstock This happens when the amygdala, the brain’s alarm system, sends out a false alarm, triggering the survival instinct.
In this state, a child may not be able to access higher functions like reasoning or decision-making.
While our instinct might be to immediately fix the problem, staying present with our child during these moments is more effective. It’s about providing support and understanding until they feel safe enough to engage their higher brain functions again.
Reframe your thinking so you see your child as having a problem – not being the problem.
Tips for parents
Take turns discussing the highs and lows of the day at meal times. This is a chance for you to be curious, acknowledge and label feelings, and model that you, too, experience a range of emotions that require you to put into practice skills to cope and has shown evidence in numerous physical, social-emotional, academic and behavioural benefits.
Talk about your day over dinner. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Spending even small amounts (five minutes a day!) of quality one-on-one time with your child is an investment in your child’s emotional wellbeing. Let them pick the activity, do your best to follow their lead, and try to notice and comment on the things they do well, like creative ideas, persevering when things are difficult, and being gentle or kind.
Take a tip from parents of children with neurodiversity: learn about your unique child. Approaching your child’s emotions, temperament, and behaviours with curiosity can help you to help them develop emotion regulation skills.
When to get help
If emotion dysregulation is a persistent issue that is getting in the way of your child feeling happy, calm, or confident – or interfering with learning or important relationships with family members or peers – talk to their GP about engaging with a mental health professional.
Many families have found parenting programs helpful in creating a climate where emotions can be safely expressed and shared.
Remember, you can’t pour from an empty cup. Parenting requires you to be your best self and tend to your needs first to see your child flourish.
Cher McGillivray, Assistant Professor Psychology Department, Bond University and Shawna Mastro Campbell, Assistant Professor Psychology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Healthy Made Simple – by Ella Mills
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Often, cookbooks leave a gap between “add the beans to the rice, then microwave” and “delicately embarrass the green-shooted scallions with assiduous garlic before adding to the matelote of orrazata flamed in Sapient Pear Brandy”. This book fills that gap:
It has dishes good for entertaining, and dishes good for eating on a Tuesday night after a long day. Sometimes, they’re even the same dishes.
It has a focus on what’s pleasing, easy, healthy, and consistent with being cooked in a real home kitchen for real people.
The book offers 75 recipes that:
- Take under 30 minutes to make*
- Contain 10 ingredients or fewer
- Have no more than 5 steps
- Are healthy and packed with goodness
- Are delicious and flavorful
*With a selection for under 15 minutes, too!
A strength of the book is that it’s based on practical, real-world cooking, and as such, there are sections such as “Prep-ahead [meals]”, and “cook once, eat twice”, etc.
Just because one is cooking with simple fresh ingredients doesn’t mean that everything bought today must be used today!
Bottom line: if you’d like simple, healthy recipe ideas that lend themselves well to home-cooking and prepping ahead / enjoying leftovers the next day, this is an excellent book for you.
Click here to check out Healthy Made Simple, enjoy the benefits to your health, the easy way!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Beating Toxic Positivity
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
There have been many studies done regards optimism and health, and they generally come to the same conclusion: optimism is simply good for the health.
Here’s an example we’ve mentioned before, but it’s a good introduction to today’s main feature. It’s a longitudinal study, and it followed 121,700 women (what a sample size!) for eight years. It controlled for all kinds of other lifestyle factors (especially smoking, drinking, diet, and exercise habits, as well as pre-existing medical conditions), so this wasn’t a case of “people who are healthy are more optimistic as results. And, in the researchers’ own words…
❝We found strong and statistically significant associations of increasing levels of optimism with decreasing risks of mortality, including mortality due each major cause of death, such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, respiratory disease, and infection. Importantly, findings were maintained after close control for potential confounding factors, including sociodemographic characteristics and depression❞
Read: Optimism and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study
And yet, toxic positivity can cause as many problems as it tries to fix.
What is toxic positivity?
- Toxic positivity is the well-meaning friend who says “I’m sure it’ll be ok” when you know full well it definitely will not.
- Toxic positivity is the allegorical frog-in-a-pan saying that the temperature rises due to climate change are gradual, so they’re nothing to worry about
- Toxic positivity is thinking that “good vibes” will outperform chemotherapy
Sometimes, a dose of realism is needed. So, can we do that and maintain a positive attitude?
The answer is: somewhat, yes! But first, a quick check-in:
❝I’m not a pessimist; I’m a realist!❞
~ every pessimist ever
To believe self-reports, the world is divided between optimists and realists. But how does your outlook measure up, really?
While like most free online tests, this is offered “as-is” with the usual caveats about not being a clinical diagnostic tool, this one actually has a fair amount of scientific weight behind it:
❝Empirical testing has indicated the validity of the Optimism Pessimism Instrument as published in the scientific journal Current Psychology: Research and Reviews.
The IDRlabs Optimism/Pessimism Test (IDR-OPT) was developed by IDRlabs. The IDR-OPT is based on the Optimism/Pessimism Instrument (OPI) developed by Dr. William Dember, Dr. Stephanie Martin, Dr. Mary Hummer, Dr. Steven Howe, and Dr. Richard Melton, at the University of Cincinnati.❞
Take This Short (1–2 mins) Test
How did you score? And what could you do to improve on that score?
First, it’s said that with a big enough “why”, one can overcome any “how”. So…
An attitude of gratitude
We know, we know, it’s very Oprah Winfrey. But also, it works. Take the time, ideally daily, to quickly list 3–5 things for which you feel grateful. Great or small, it can be anything from your spouse to your cup of coffee, provided you feel fortunate to have it.
How this works: our brains easily get stuck in loops, so it can help to nudge them into a more positive loop.
What about when we are treated unfairly? Are we supposed to be grateful?
Sometimes, our less positive emotions are necessary, to protect us and/or those around us, and to provide a motivational force. We can still maintain a positive attitude by noting the bad thing and some good, but watch out! Notice the difference:
- “How dare they take our healthcare away, but at least I’m not sick right now” (lasting impression: no action required)
- “At least I’m not sick right now, but how dare they take our healthcare away!” (lasting impression: action required)
It’s a well-known idea in neurolinguistic programming, that “but” negates whatever goes before it (think of “I’m sorry but”, or “I’m not racist but”, etc), so use it consciously and wisely, or else simply use “and” instead.
Cognitive reframing: problem, or opportunity?
Most problems can be opportunities, even if the problems themselves genuinely suck and are not intrinsically positive. A way of leveraging this can be replacing “I have to…” with “I get to…”.
This not only can reframe problems as opportunities, but also calls back to the gratitude idea.
- Instead of “I have to get my mammogram / prostate exam” (not generally considered fun activities), “I get to have the peace of mind of being free from cancer / I get to have the forewarning that will keep me safe”.
- Instead of “I have to go to work”, “I get to go to work” (many wish they were in your shoes!)
- Instead of “I have to rest”, “I get to rest”
When things are truly not great
Whether due to internal or external factors, whether you can control something or not, sometimes things are truly not great. The trick here is that in most contexts, one can replace negative talk, with verbally positive talk, no matter how dripping with scathing irony. You’ll still get to express the idea you wanted, but your brain will feel more positive and you’ll be in a positive loop rather than a negative one.
This, by the way, is the inverse of talking to a dog with a tone of voice that is completely the opposite of the meaning of the words. Whereas the dog will interpret the tone only, your brain will interpret the words only.
- You just spilled your drink over yourself at a social function? “Aren’t I the very model of grace and charm?”
- You made a costly mistake in your business dealings? “I am such a genius”
- You just got a diagnosis of a terrible disease? “Well, this is fabulous”
None of these things involve burying your head in the sand, in the manner of toxic positivity. You’ll still learn from your business mistake and correct it as best you can, or take appropriate action regards the disease, for example.
You’ll just feel better while you do it, and not get caught into a negative spiral that ruins your day, or even your next few months.
Sympathetic/Somatic Therapy:
Lastly, an easy one, leveraging the body’s tendency to get in sync with things around us:
For when you do just need a mood change, have an uplifting playlist available at the touch of a button. It’s hard to be consumed with counterproductive feelings to the tune of “Walking on Sunshine”!
Bonus tip: consider having the playlist start with something that is lyrically negative while musically upbeat. That way, your brain won’t resist it as antithetical to your mood, and by the second track, you’ll already be on your way to a better mood.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
You’ve Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Cucumbers To Kindles
Q: Where do I get cucumber extract?
A: You can buy it from BulkSupplements.com (who, despite their name, start at 100g packs)
Alternatively: you want it as a topical ointment (for skin health) rather than as a dietary supplement (for bone and joint health), you can extract it yourself! No, it’s not “just juice cucumbers”, but it’s also not too tricky.
Click Here For A Quick How-To Guide!
Q: Tips for reading more and managing time for it?
A: We talked about this a little bit in yesterday’s edition, so you may have seen that, but aside from that:
- If you don’t already have one, consider getting a Kindle or similar e-reader. They’re very convenient, and also very light and ergonomic—no more wrist strain as can occur with physical books. No more eye-strain, either!
- Consider making reading a specific part of your daily routine. A chapter before bed can be a nice wind-down, for instance! What’s important is it’s a part of your day that’ll always, or at least almost always, allow you to do a little reading.
- If you drive, walk, run, or similar each day, a lot of people find that’s a great time to listen to an audiobook. Please be safe, though!
- If your lifestyle permits such, a “reading retreat” can be a wonderful vacation! Even if you only “retreat” to your bedroom, the point is that it’s a weekend (or more!) that you block off from all other commitments, and curl up with the book(s) of your choice.
Q: Any study tips as we approach exam season? A lot of the productivity stuff is based on working life, but I can’t be the only student!
A: We’ve got you covered:
- Be passionate about your subject! We know of no greater study tip than that.
- Find a willing person and lecture them on your subject. When one teaches, two learn!
- Your mileage may vary depending on your subject, but, find a way of studying that’s fun to you!
- If you can get past papers, get as many as you can, and use those as your “last minute” studying in the week before your exam(s). This will prime you for answering exam-style questions (and leverage state-dependent memory). As a bonus, it’ll also help ease any anxiety, because by the time of your exam it’ll be “same old, same old”!
Q: Energy drinks for biohacking, yea or nay?
A: This is definitely one of those “the dose makes the poison” things!
- Caffeine, in and of itself, can be healthy in moderation for most people.
- Taurine has assorted benefits at safe dosages:
- Other ingredients often have health benefits too.
But… The generally agreed safe dose of taurine is around 3g/day for most people; a standard Red Bull contains 1g.
That math would be simple, but… if you eat meat (including poultry or fish), that can also contain 10–950mg per 100g. For example, tuna is at the high end of that scale, with a standard 12oz (340g) tin already containing up to 3.23g of taurine!
And sweetened carbonated beverages in general have so many health issues that it’d take us a full article to cover them.
Short version? Enjoy in moderation if you must, but there are definitely better ways of getting the benefits they may offer.
Q: Best morning routine?
A: The best morning routine is whatever makes you feel most ready to take on your day!
This one’s going to vary a lot—one person’s morning run could be another person’s morning coffee and newspaper, for example.
In a nutshell, though, ask yourself these questions:
- How long does it take me to fully wake up in the morning, and what helps or hinders that?
- When I get out of bed, what do I really need before I can take on my day?
- If I could have the perfect morning, what would it look like?
- What can evening me do, to look after morning me’s best interests? (Semi-prepare breakfast ready? Lay out clothes ready? Running shoes? To-Do list?)
Q: I’m curious how much of these things you actually use yourselves, and are there any disagreements in the team? In a lot of places things can get pretty heated when it’s paleo vs vegan / health benefits of tea/coffee vs caffeine-abstainers / you need this much sleep vs rise and grinders, etc?
A: We are indeed genuinely enthusiastic about health and productivity, and that definitely includes our own! We may or may not all do everything, but between us, we probably have it all covered. As for disagreements, we’ve not done a survey, but if you take an evidence-based approach, any conflict will tend to be minimized. Plus, sometimes you can have the best of both!
- You could have a vegan paleo diet (you’d better love coconut if you do, though!
- There is decaffeinated coffee and tea (your taste may vary)
- You can get plenty of sleep and rise early (so long as an “early to bed, early to rise” schedule suits you!)
Interesting note: humans are social creatures on an evolutionary level. Evolution has resulted in half of us being “night owls” and the other half “morning larks”, the better to keep each other safe while sleeping. Alas, modern life doesn’t always allow us to have the sleep schedule that’d suit each of us best individually!
Have a question you’d like answered? Reply to this email, or use the feedback widget at the bottom! We always love to hear from you
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: