The Dirt Cure – by Dr. Maya Shetreat-Klein
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we discussed in our article “Stop Sabotaging Your Gut”, there is indeed merit to living a little dirty, in particular when it comes to what we put in our mouths. Having the space of an entire book rather than a small article, Dr. Shetreat-Klein expands on this in great detail.
The subtitle mentions “growing healthy kids with food straight from the soil”; it’s worth noting that all the information here (with the exception of concerning breastfeeding etc) is equally applicable to adults too—so if it’s your own health you’re focused on rather than that of kids or grandkids, then that’s fine too.
You may be wondering: what more is there to say than “don’t scrub your vegetables as though you’re about to perform surgery with them”?
There’s a lot of background information on what things help or harm our bodies in the first place, most notably via our gut, and as an important extra consideration, the gut-brain axis. Incidentally, the author is a neurologist by professional background.
Then she gets more specific, into “include and exclude” recommendations. In this matter we have one criticism: she does recommend raw milk over pasteurized, and that is, by overwhelming scientific consensus, a terrible idea. Raw milk is an abundant source of pathogens and a breeding ground for even more. There is “living dirty” and there is “living dangerously”, and drinking raw milk is the latter. See also: Pasteurization: What It Does And Doesn’t Do
However, for the most part, the rest of her advice is sound, and there’s even a recipes section too.
The style is something of a polemic throughout, but the extensive venting does not take away from there being a lot of genuine information in here too.
Bottom line: please skip the raw milk, but aside from that, if you’d like to improve your diet to improve your gut and immune health, then this book can help with that.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
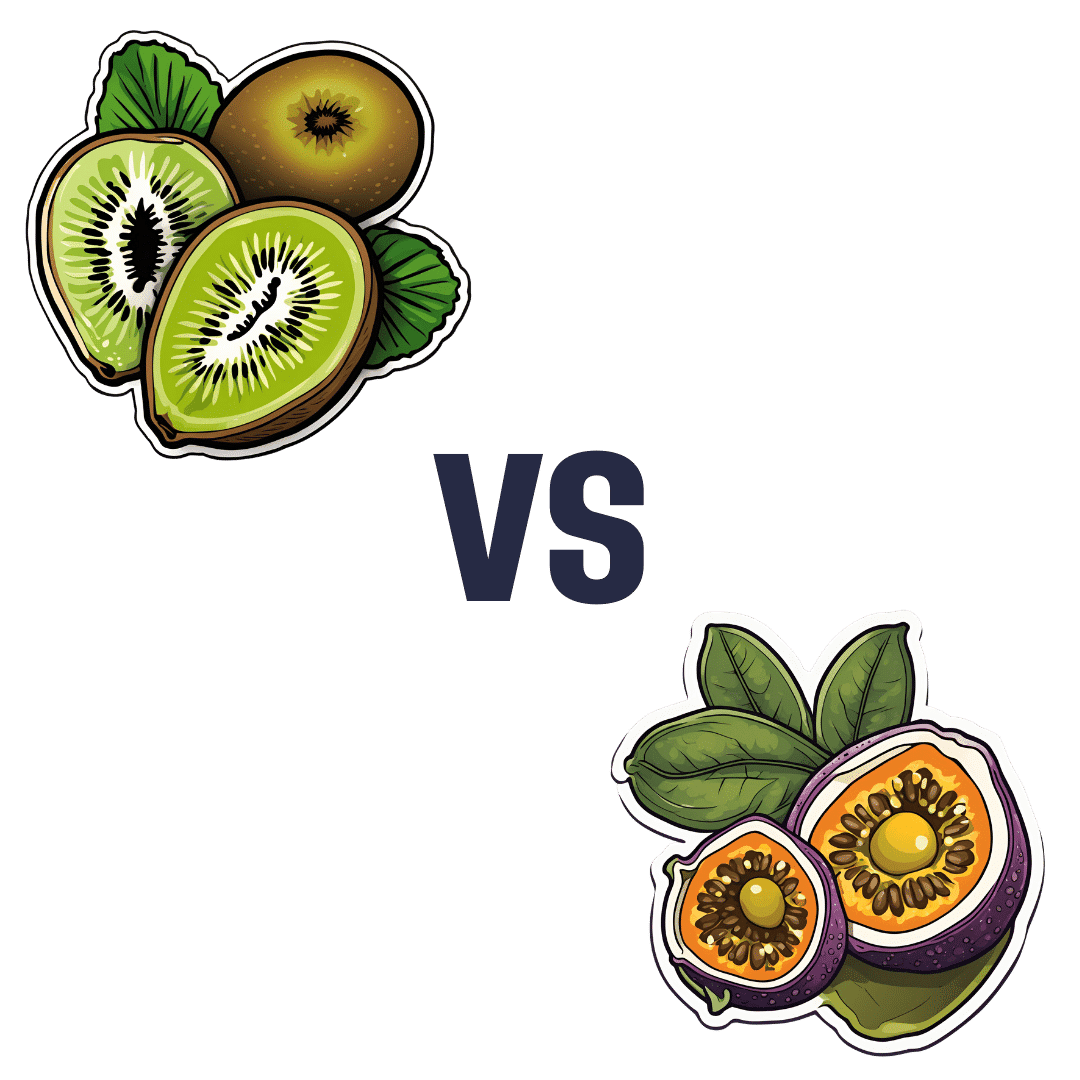
Kiwi vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi to passion fruit, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
This fruit is so passionate about delivery nutrient-dense goodness, that at time of writing, nothing has beaten it yet!
In terms of macros, passion fruit has a little more protein, as well as 50% more carbs, and/but more than 3x the fiber. That last stat is particularly impressive, and also results in passion fruit having a much lower glycemic index, too. In short, a clear win for passion fruit in the macros category.
In the category of vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins B9, C, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and B6, making for a tie this time.
As for minerals, kiwi has more calcium, copper, manganese, and zinc, while passion fruit has more iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, resulting in a modest, marginal win for passion fruit in this category.
Adding up the categories gives a convincing win for passion fruit, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good! And kiwi has its merits too (for example, it’s particularly high in vitamin K, appropriately enough).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
How To Lower Your Blood Pressure (Cardiologists Explain)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today we enjoy the benefit of input from Dr. Zalzal, Dr. Weeing, and Dr. Hefferman!
If the thought of being in an operating room with three cardiologists in scrubs doesn’t raise your blood pressure too much, the doctors in question have a lot to offer for bringing those numbers down and keeping them down! They recommend…
150 mins of Exercise
This isn’t exactly controversial, but: move your body!
See also: Exercise Less; Move More
Reduce salt
Most people eating the Standard American Diet (SAD) are getting far too much—mostly because it’s in so many processed foods already.
See also: How Too Much Salt May Lead To Organ Failure
Eating habits
There’s a lot more to eating healthily for the heart than just reducing salt, and over all, the Mediterranean diet comes out scoring highest:
- What Is The Mediterranean Diet Anyway? ← a primer for the uncertain
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean ← includes a heart-specialized version!
Reduce alcohol
According to the WHO, the only healthy amount of alcohol is zero. According to these cardiologists: at the very least cut down. However much or little you’re drinking right now, less is better.
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
Maintain healthy weight
While the doctors agree that BMI isn’t a great method of measuring metabolic health, it is clear that carrying excessive weight isn’t good for the heart.
See also: Lose Weight (Healthily!)
No smoking
This one’s pretty straight forward: just don’t.
See also: Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
Reduce stress
Chronic stress has a big impact on chronic health in general and that includes its effect on blood pressure. So, improving one improves the other.
See also: Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
Good sleep
Quality matters as much as quantity, and that goes for its effect on your blood pressure too, so take the time to invest in your good health!
See also: The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
Inhaled Eucalyptus’s Immunomodulatory and Antimicrobial Effects
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝At the first hint of a cough or a cold, I resort to steam inhalation. Some people add herbs or aromatic oils to the boiling water. What do you recommend?❞
First of all, please do be careful:
Western science’s view is predominantly “this is popular and/but evidence for its usefulness is lacking”:
But! Traditional Chinese Medicine indicates shuanghuanglian, yuxingcao and qingkailing, which the China Food and Drug Administration has also approved:
Chinese Medicine in Inhalation Therapy: A Review of Clinical Application and Formulation Development
Indian scientists are also looking at modern scientific applications of certain Ayurvedic herbs:
Promising phytochemicals of traditional Indian herbal steam inhalation therapy to combat COVID-19
In terms of what is likely more available to you, there are several reasons to choose eucalyptus over popular alternatives:
Immune-modifying and antimicrobial effects of Eucalyptus oil and simple inhalation devices
For the sake of being methodical, here’s an example product on Amazon, though we’re sure you’d have no trouble finding this in your local pharmacy if you prefer.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Lower Cholesterol Naturally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lower Cholesterol, Without Statins
We’ll start this off by saying that lowering cholesterol might not, in fact, be critical or even especially helpful for everyone, especially in the case of women. We covered this more in our article about statins:
…which was largely informed by the wealth of data in this book:
The Truth About Statins – by Dr. Barbara H. Roberts
…which in turn, may in fact put a lot of people off statins. We’re not here to tell you don’t use them—they may indeed be useful or even critical for some people, as Dr. Roberts herself also makes makes clear. But rather, we always recommend learning as much as possible about what’s going on, to be able to make the most informed choices when it comes to what often might be literally life-and-death decisions.
On which note, if anyone would like a quick refresher on cholesterol, what it actually is (in its various forms) and what it does, why we need it, the problems it can cause anyway, then here you go:
Now, with all that in mind, we’re going to assume that you, dear reader, would like to know:
- how to lower your LDL cholesterol, and/or
- how to maintain a safe LDL cholesterol level
Because, while the jury’s out on the dangers of high LDL levels for women in particular, it’s clear that for pretty much everyone, maintaining them within well-established safe zones won’t hurt.
Here’s how:
Relax
Or rather, manage your stress. This doesn’t just reduce your acute risk of a heart attack, it also improves your blood metrics along the way, and yes, that includes not just blood pressure and blood sugars, but even triglycerides! Here’s the science for that, complete with numbers:
What are the effects of psychological stress and physical work on blood lipid profiles?
With that in mind, here’s…
How To Manage Chronic Stress (Even While Chronically Stressed)
Not chemically “relaxed”, though
While relaxing is important, drinking alcohol and smoking are unequivocally bad for pretty much everything, and this includes cholesterol levels:
Can We Drink To Good Health? ← this also covers popular beliefs about red wine and heart health, and the answer is no, we cannot
As for smoking, it is good to quit as soon as possible, unless your doctor specifically advises you otherwise (there are occasional situations where something else needs to be dealt with first, but not as many some might like to believe):
Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
If you’re wondering about cannabis (CBD and/or THC), then we’d love to tell you about the effect these things have on heart health in general and cholesterol levels in particular, but the science is far too young (mostly because of the historic, and in some places contemporary, illegality cramping the research), and we could only find small, dubious, mutually contradictory studies so far. So the honest answer is: science doesn’t know this one, yet.
Exercise… But don’t worry, you can still stay relaxed
When it comes to heart health, the most important thing is keeping moving, so getting in those famous 150 minutes per week of moderate exercise is critical, and getting more is ideal.
240 minutes per week is a neat 40 minutes per day, by the way and is very attainable (this writer lives a 20-minute walk away from where she does her daily grocery shopping, thus making for a daily 40-minute round trip, not counting the actual shopping).
See: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
If walking is for some reason not practical for you, here’s a whole list of fun options that don’t feel like exercise but are:
Manage your hormones
This one is mostly for menopausal women, though some people with atypical hormonal situations may find it applicable too.
Estrogen protects the heart… Until it doesn’t:
See also: World Menopause Day: Menopause & Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Here’s a great introduction to sorting it out, if necessary:
Dr. Jen Gunter: What You Should Have Been Told About Menopause Beforehand
Eat a heart-healthy diet
Shocking nobody, but it has to be said, for the sake of being methodical. So, what does that look like?
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
(it’s fiber in the #1 spot, but there’s a list of most important things there, that’s worth checking out and comparing it to what you habitually eat)
You can also check out the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) edition of the Mediterranean diet, here:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
As for saturated fat (and especially trans-fats), the basic answer is to keep them to minimal, but there is room for nuance with saturated fats at least:
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
And lastly, do make sure to get enough omega 3 fatty-acids:
What Omega-3s Really Do For Us
And enjoy plant sterols and stanols! This would need a whole list of their own, so here you go:
Take These To Lower Cholesterol! (Statin Alternatives)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Salt Sugar Fat – by Michael Moss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You are probably already aware that food giants put unhealthy ingredients in processed food. So what does this book offer of value?
Sometimes, better understanding leads to better movation. In this case, while a common (reasonable) view has been:
“The food giants fill their food with salt, sugar, and fat, because it makes that food irresistibly delicious”
…but that doesn’t exactly put us off the food, does it? It just makes it a guilty pleasure. Ah yes, the irresistible McDouble Dopamineburger. The time-honored tradition of Pizza Night; a happy glow; a special treat.
What Pulitzer-winning author Michael Moss brings to us is different.
He examines not just how they hooked us, but why. And the answer is not merely the obvious “profit and greed”, but also “survival, under capitalism”. That without regulation forcing companies to keep salt/sugar/fat levels down, companies that have tried to do so voluntarily have quickly had to u-turn to regain any hope of competitiveness.
He also looks at how the salt/sugar/fat components are needed to mask the foul taste of the substandard ingredients they use to maintain lower costs… Processed food, without the heavy doses of salt/sugar/fat, is not anywhere close to what you might make at home. Industry will cut costs where it can.
Bottom line: if you need a push to kick the processed food habit, this is the book that will do it.
Click here to check out Salt Sugar Fat, and reclaim your health!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What To Do If Having A Stroke Alone?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Thank you for the video about what to do if you have a heart attack alone, what about what to do if you have a stroke alone?❞
(for anyone who missed that video, here it is)
That’s a good question, especially as stroke risk is rising in the industrialized world in general, and the US in particular.
However, let’s start with the caveat that if you are having a stroke, there’s a good chance you will forget what we are about to say, what with the immediate effects it has on the brain. That said…
The general advice when it comes to looking after someone else who is experiencing a stroke, is, “don’t”.
In other words, call emergency services, and don’t do anything else, e.g:
- don’t give them anything to eat or drink
- don’t give them any medications
- don’t let them go to sleep
- don’t let them talk you out of calling emergency services
- don’t let them drive themselves to hospital
- don’t drive them to hospital yourself either*
*This is for two reasons:
- an ambulance crew has skills and resources that you don’t, and can begin treatment en-route, and also,
- not all hospitals have appropriate resources to treat stroke, so the ambulance crew will know to drive to one that does, instead of driving to a random hospital and hoping for the best
So, flipping this for if it’s you having the stroke, and you’re cognizant enough to remember this:
- do call an ambulance; stay on the line and don’t do anything else unless instructed by the emergency services.
In order to do that, of course it’s important to recognize the symptoms; you probably know these but just in case, the mnemonic is “FAST”:
- Face: is there weakness on one side of their face?
- Arms: if they raise both arms, does one drift downwards?
- Speech: if they speak, is their speech slurred or otherwise unusual?
- Time: to call emergency services
It’s great to not get caught out by surprise, so you might also want to check out:
6 Signs Of Stroke (One Month In Advance)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: