Superfood Broccoli Pesto
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cruciferous vegetables have many health benefits of their own (especially: a lot of anticancer benefits). But, it can be hard to include them in every day’s menu, so this is just one more way that’ll broaden your options! It’s delicious mixed into pasta, or served as a dip, or even on toast.
You will need
- 4 cups small broccoli florets
- 1 cup fresh basil leaves
- ½ cup pine nuts
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 3 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Steam the broccoli for 3–5 minutes. Allow to cool.
2) Blend the pine nuts, garlic, lemon juice, and nutritional yeast.
3) Add the broccoli, basil, olive oil, black pepper, red pepper, and MSG or salt, and blend in the food processor again until well-combined.
4) Serve:
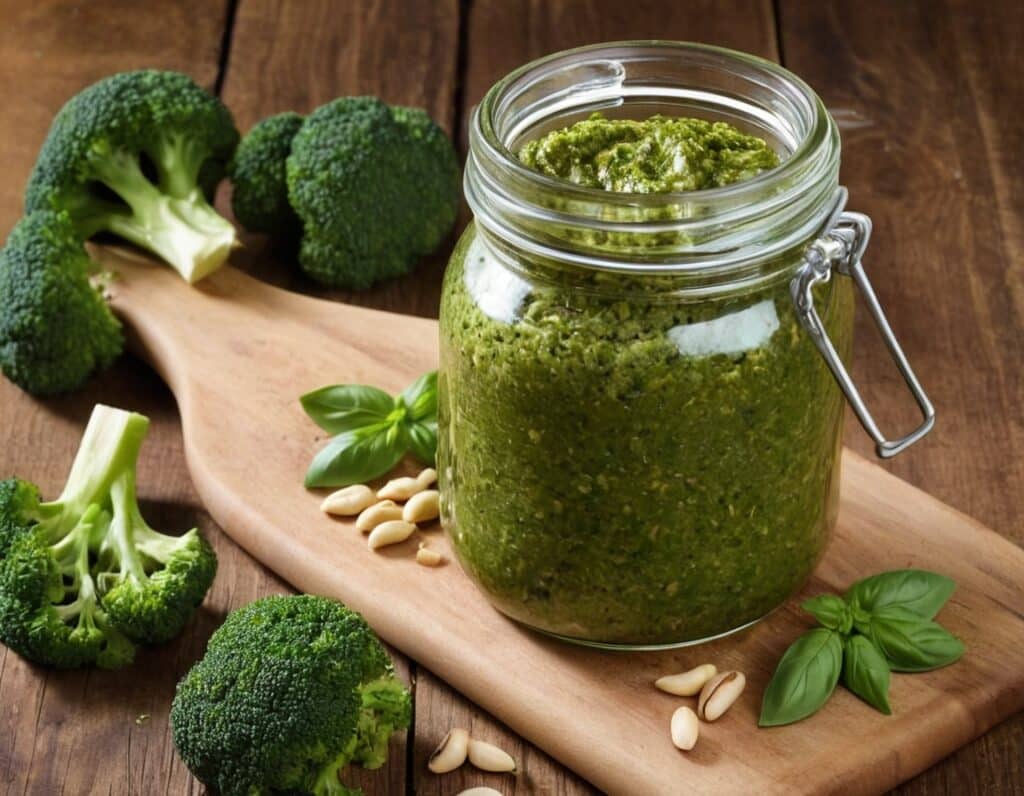

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Broccoli vs Cauliflower – Which is Healthier?
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Herbs for (Evidence-Based) Health & Healing ← Basil features here! It’s easy to think that medicinal herbs have to be some kind of arcane obscurity, but it’s often not so.
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← Black pepper, red pepper, and garlic all feature here
- All About Olive Oil: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Heal Your Stressed Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Rochelle Walsh, therapist, explains the problem and how to fix it:
Not all brain damage is from the outside
Long-term stress and burnout cause brain damage; it’s not just a mindset issue—it impacts the brain physiologically. To compound matters, it also increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. While the brain can indeed grow new neurons and regenerate itself, chronic stress damages specific regions, and inhibits that.
There are some effects of chronic stress that can seem positive—the amygdalae and hypothalamus are seen to grow larger and stronger, for instance—but this is, unfortunately, “all the better to stress you with”. In compensation for this, chronic stress deprioritizes the pre-frontal cortex and hippocampi, so there goes your reasoning and memory.
This often results in people not managing chronic stress well. Just like a weak heart and lungs might impede the exercise that could make them stronger, the stressed brain is not good at permitting you to do the things that would heal it—preferring to keep you on edge all day, worrying and twitchy, mind racing and body tense. It also tends to lead to autoimmune diseases, due to the increased inflammation (because the body’s threat-detection system as at “jumping at own shadow” levels so it’s deploying every defense it has, including completely inappropriate ones).
Notwithstanding the “Heal Your Stressed Brain” thumbnail, she doesn’t actually go into this in detail and bids us sign up for her masterclass. We at 10almonds however like to deliver, so you can find useful advice and free resources in our links-drop at the bottom of this article.
Meanwhile, if you’d like to hear more about the neurological woes described above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
- How To Manage/Reduce Chronic Stress
- Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
- How Healthy People Regulate Their Emotions
- Sleep: Yes, You Really Do Still Need It!
- Give Your Adrenal Glands A Chance
- The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Figs vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing figs to passion fruit, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
Both are top-tier fruits! But the passion fruit is just that bit more passionate about delivering healthy nutrients:
In terms of macros, passion fruit has slightly more carbs, notably more protein, and a lot more fiber, giving it the win in this category.
In the category of vitamins, figs have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, C, and choline, making for a marginal win by the numbers for passion fruit here.
When it comes to minerals, figs have more calcium, manganese, and zinc, while passion fruit has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. A clearer win for passion fruit this time.
Adding up the sections makes for an easy overall win for passion fruit, but again, figs are really a top-tier fruit too; passion fruit just beats them! By all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← figs have antitumor effects specifically, while removing carcinogens too, and additionally sensitizing cancer cells to light therapy
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Too Much Or Too Little Testosterone?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One Man’s Saw Palmetto Is Another Woman’s Serenoa Repens…
Today we’re going to look at saw palmetto. So, first:
What is it?
Saw palmetto is a type of palm native to the southeastern United States. Its scientific name is “Serenoa repens”, so if that name appears in studies we cite, it’s the same thing. By whichever name, it’s widely enjoyed as a herbal supplement.
Why do people take it?
Here’s where it gets interesting, because people take it for some completely opposite reasons…
Indeed, searching for it on the Internet will cause Google to suggest “…for men” and “…for women” as the top suggestions.
That’s because it works on testosterone, and testosterone can be a bit of a double-edged sword, so some people want to increase or decrease certain testosterone-related effects on their body.
And it works for both! Here be science:
- Testosterone (henceforth, “T”) is produced in the human body.
- Yes, all human bodies, to some extent.
- An enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase converts T in to DHT (dihydrogen testosterone)
- DHT is a much more potent androgen (masculinizing agent) than T alone, such that its effects are often unwanted, including:
- Enlarged prostate (if you have one)
- Hair loss (especially in men)
- New facial hair growth (usually unwanted by women)
- Women are more likely to get this due to PCOS and/or the menopause
To avoid those effects, you really want less of your T to be converted into DHT.
Saw palmetto is a 5α-reductase inhibitor, so if you take it, you’ll have less DHT, and you’ll consequently lose less hair, have fewer prostate problems, etc.
^The above study showed that saw palmetto extract performed comparably to finasteride. Finasteride is the world’s main go-to prescription drug for treating enlarged prostate and/or hair loss.
See also: Natural Hair Supplement: Friend or Foe? Saw Palmetto, a Systematic Review in Alopecia
Hair today… Growing tomorrow!
So, what was that about increasing T levels?
Men usually suffer declining T levels as they get older, with a marked drop around the age of 45. With lower T comes lower energy, lower mood, lower libido, erectile dysfunction, etc.
Guess what… It’s T that’s needed for those things, not DHT. So if you block the conversion of T to DHT, you’ll have higher blood serum T levels, higher energy, higher mood, higher libido, and all that.
(the above assumes you have testicles, without which, your T levels will certainly not increase)
Saw Palmetto Against Enlarged Prostate?
With higher DHT levels in mid-late life, prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperlasia) can become a problem for many men. The size of that problem ranges from urinary inconvenience (common, when the prostate presses against the bladder) to prostate cancer (less common, much more serious). Saw palmetto, like other 5α-reductase inhibitors such as finasteride, may be used to prevent or treat this.
Wondering how safe/reliable it is? We found a very high-quality fifteen-year longitudinal observational study of the use of saw palmetto, and it found:
❝The 15 years’ study results suggest that taking S. repens plant extract continuously at a daily dose of 320 mg is an effective and safe way to prevent the progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia.❞
Want a second opinion? We also found a 10-year study (by different researchers with different people taking it), which reached the same conclusion:
❝The results of study showed the absence of progression, both on subjective criteria (IPSS, and QoL scores), and objective criteria (prostate volume, the rate of urination, residual urine volume). Furthermore, patients had no undesirable effects directly related to the use of this drug.❞
- IPSS = International Prostate Symptom Score
- QoL = Quality of Life
❝But wait a minute; I, a man over the age of 45 with potentially declining T levels but a fabulous beard, remember that you said just a minute ago that saw palmetto is used by women to avoid having facial hair; I don’t want to lose mine!❞
You won’t. Once your facial hair follicles were fully developed and activated during puberty, they’ll carry on doing what they do for life. That’s no longer regulated by hormones once they’re up and running.
The use of saw palmetto can only be used to limit facial hair if caught early—so it’s more useful at the onset of menopause, for those who have (or will have) such, or else upon the arrival of PCOS symptoms or hirsuitism from some other cause.
Take The Test!
Do you have a prostate, and would like to know your IPSS score, and what that means for your prostate health?
(takes 1 minute, no need to pee or go probing for anything)
Bottom Line on Saw Palmetto
- It blocks the conversion of T into DHT
- It will increase blood serum T levels, thus boosting mood, energy, libido, etc in men (who typically have more T, but whose T levels decline with age)
- It will decrease DHT levels, thus limiting hair loss (especially in men) and later-life new facial hair growth (especially in women).
- It can be used to prevent or treat prostate enlargement
- Bonus: it’s a potent antioxidant and thus reduces general inflammation (in everyone)
Want To Try Saw Palmetto?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience…
Share This Post
- Testosterone (henceforth, “T”) is produced in the human body.
Related Posts
-
From Dr. Oz to Heart Valves: A Tiny Device Charted a Contentious Path Through the FDA
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In 2013, the FDA approved an implantable device to treat leaky heart valves. Among its inventors was Mehmet Oz, the former television personality and former U.S. Senate candidate widely known as “Dr. Oz.”
In online videos, Oz has called the process that brought the MitraClip device to market an example of American medicine firing “on all cylinders,” and he has compared it to “landing a man on the moon.”
MitraClip was designed to spare patients from open-heart surgery by snaking hardware into the heart through a major vein. Its manufacturer, Abbott, said it offered new hope for people severely ill with a condition called mitral regurgitation and too frail to undergo surgery.
“It changed the face of cardiac medicine,” Oz said in a video.
But since MitraClip won FDA approval, versions of the device have been the subject of thousands of reports to the agency about malfunctions or patient injuries, as well as more than 1,100 reports of patient deaths, FDA records show. Products in the MitraClip line have been the subject of three recalls. A former employee has alleged in a federal lawsuit that Abbott promoted the device through illegal inducements to doctors and hospitals. The case is pending, and Abbott has denied illegally marketing the device.
The MitraClip story is, in many ways, a cautionary tale about the science, business, and regulation of medical devices.
Manufacturer-sponsored research on the device has long been questioned. In 2013, an outside adviser to the FDA compared some of the data marshaled in support of its approval to “poop.”
The FDA expanded its approval of MitraClip to a wider set of patients in 2019, based on a clinical trial in which Abbott was deeply involved and despite conflicting findings from another study.
In the three recalls, the first of which warned of potentially deadly consequences, neither the manufacturer nor the FDA withdrew inventory from the market. The company told doctors it was OK for them to continue using the recalled products.
In response to questions for this article, both Abbott and the FDA described MitraClip as safe and effective.
“With MitraClip, we’re addressing the needs of people with MR who often have no other options,” Abbott spokesperson Brent Tippen said. “Patients suffering from mitral regurgitation have severely limited quality of life. MitraClip can significantly improve survival, freedom for hospitalization and quality of life via a minimally invasive, now common procedure.”
An FDA spokesperson, Audra Harrison, said patient safety “is the FDA’s highest priority and at the forefront of our work in medical device regulation.”
She said reports to the FDA about malfunctions, injuries, and deaths that the device may have caused or contributed to are “consistent” with study results the FDA reviewed for its 2013 and 2019 approvals.
In other words: They were expected.
Inspiration in Italy
When a person has mitral regurgitation, blood flows backward through the mitral valve. Severe cases can lead to heart failure.
With MitraClip, flaps of the valve — known as “leaflets” — are clipped together at one or more points to achieve a tighter seal when they close. The clips are deployed via a catheter threaded through a major vein, typically from an incision in the groin. The procedure offers an alternative to connecting the patient to a heart-lung machine and repairing or replacing the mitral valve in open-heart surgery.
Oz has said in online videos that he got the idea after hearing a doctor describe a surgical technique for the mitral valve at a conference in Italy. “And on the way home that night, on a plane heading back to Columbia University, where I was on the faculty, I wrote the patent,” he told KFF Health News.
A patent obtained by Columbia in 2001, one of several associated with MitraClip, lists Oz first among the inventors.
But a Silicon Valley-based startup, Evalve, would develop the device. Evalve was later acquired by Abbott for about $400 million.
“I think the engineers and people at Evalve always cringe a little bit when they see Mehmet taking a lot of, you know, basically claiming responsibility for what was a really extraordinary team effort, and he was a small to almost no player in that team,” one of the company’s founders, cardiologist Fred St. Goar, told KFF Health News.
Oz did not respond to a request for comment on that statement.
As of 2019, the MitraClip device cost $30,000 per procedure, according to an article in a medical journal. According to the Abbott website, more than 200,000 people around the world have been treated with MitraClip.
Oz filed a financial disclosure during his unsuccessful run for the U.S. Senate in 2022 that showed him receiving hundreds of thousands of dollars in annual MitraClip royalties.
Abbott recently received FDA approval for TriClip, a variation of the MitraClip system for the heart’s tricuspid valve.
Endorsed ‘With Trepidation’
Before the FDA said yes to MitraClip in 2013, agency staffers pushed back.
Abbott had originally wanted the device approved for “patients with significant mitral regurgitation,” a relatively broad term. After the FDA objected, the company narrowed its proposal to patients at too-high risk for open-heart surgery.
Even then, in an analysis, the FDA identified “fundamental” flaws in Abbott’s data.
One example: The data compared MitraClip patients with patients who underwent open-heart surgery for valve repair — but the comparison might have been biased by differences in the expertise of doctors treating the two groups, the FDA analysis said. While MitraClip was implanted by a highly select, experienced group of interventional cardiologists, many of the doctors doing the open-heart surgeries had performed only a “very low volume” of such operations.
FDA “approval is not appropriate at this time as major questions of safety and effectiveness, as well as the overall benefit-risk profile for this device, remain unanswered,” the FDA said in a review prepared for a March 2013 meeting of a committee of outside advisers to the agency.
Some committee members expressed misgivings. “If your right shoe goes into horse poop and your left shoe goes into dog poop, it’s still poop,” cardiothoracic surgeon Craig Selzman said, according to a transcript.
The committee voted 5-4 against MitraClip on the question of whether it proved effective. But members voted 8-0 that they considered the device safe and 5-3 that the benefits of the device outweighed its risks.
Selzman voted yes on the last question “with trepidation,” he said at the time.
In October 2013, the FDA approved the MitraClip Clip Delivery System for a narrower group of patients: those with a particular type of mitral regurgitation who were considered a surgery risk.
“The reality is, there is no perfect procedure,” said Jason Rogers, an interventional cardiologist and University of California-Davis professor who is an Abbott consultant. The company referred KFF Health News to Rogers as an authority on MitraClip. He called MitraClip “extremely safe” and said some patients treated with it are “on death’s door to begin with.”
“At least you’re trying to do something for them,” he said.
Conflicting Studies
In 2019, the FDA expanded its approval of MitraClip to a wider set of patients.
The agency based that decision on a clinical trial in the United States and Canada that Abbott not only sponsored but also helped design and manage. It participated in site selection and data analysis, according to a September 2018 New England Journal of Medicine paper reporting the trial results. Some of the authors received consulting fees from Abbott, the paper disclosed.
A separate study in France reached a different conclusion. It found that, for some patients who fit the expanded profile, the device did not significantly reduce deaths or hospitalizations for heart failure over a year.
The French study, which appeared in the New England Journal of Medicine in August 2018, was funded by the government of France and Abbott. As with the North American study, some of the researchers disclosed they had received money from Abbott. However, the write-up in the journal said Abbott played no role in the design of the French trial, the selection of sites, or in data analysis.
Gregg Stone, one of the leaders of the North American study, said there were differences between patients enrolled in the two studies and how they were medicated. In addition, outcomes were better in the North American study in part because doctors in the U.S. and Canada had more MitraClip experience than their counterparts in France, Stone said.
Stone, a clinical trial specialist with a background in interventional cardiology, acknowledged skepticism toward studies sponsored by manufacturers.
“There are some people who say, ‘Oh, well, you know, these results may have been manipulated,’” he said. “But I can guarantee you that’s not the truth.”
‘Nationwide Scheme’
A former Abbott employee alleges in a lawsuit that after MitraClip won approval, the company promoted the device to doctors and hospitals using inducements such as free marketing support, the chance to participate in Abbott clinical trials, and payments for participating in “sham speaker programs.”
The former employee alleges that she was instructed to tell referring physicians that if they observed mitral regurgitation in their patients to “just send it” for a MitraClip procedure because “everything can be clipped.” She also alleges that, using a script, she was told to promote the device to hospital administrators based on financial advantages such as “growth opportunities through profitable procedures, ancillary tests, and referral streams.”
The inducements were part of a “nationwide scheme” of illegal kickbacks that defrauded government health insurance programs including Medicare and Medicaid, the lawsuit claims.
The company denied doing anything illegal and said in a court filing that “to help its groundbreaking therapy reach patients, Abbott needed to educate cardiologists and other healthcare providers.”
Those efforts are “not only routine, they are laudable — as physicians cannot use, or refer a patient to another doctor who can use, a device that they do not understand or in some cases even know about,” the company said in the filing.
Under federal law, the person who filed the suit can receive a share of any money the government recoups from Abbott. The suit was filed by a company associated with a former employee in Abbott’s Structural Heart Division, Lisa Knott. An attorney for the company declined to comment and said Knott had no comment.
Reports to the FDA
As doctors started using MitraClip, the FDA began receiving reports about malfunctions and cases in which the product might have caused or contributed to a death or an injury.
According to some reports, clips detached from valve flaps. Flaps became damaged. Procedures were aborted. Mitral leakage worsened. Doctors struggled to control the device. Clips became “entangled in chordae” — cord-like structures also known as heartstrings that connect the valve flaps to the heart muscle. Patients treated with MitraClip underwent corrective operations.
As of March 2024, the FDA had received more than 17,000 reports documenting more than 22,000 “events” involving mitral valve repair devices, FDA data shows. All but about 200 of those reports mention one iteration of MitraClip or another, a KFF Health News review of FDA data found.
Almost all the reports came from Abbott. The FDA requires manufacturers to submit reports when they learn of mishaps potentially related to their devices.
The reports are not proof that devices caused problems, and the same event might be reported multiple times. Other events may go unreported.
Despite the reports’ limitations, the FDA provides an analysis of them for the public on its website.
MitraClip’s risks weren’t a surprise.
Like the rapid-fire fine print in television ads for prescription drugs, the original product label for the device listed more than 60 types of potential complications.
Indeed, during clinical research on the device, about 6% of patients implanted with MitraClip died within 30 days, according to the label. Almost 1 in 4 — 23.6% – were dead within a year.
The FDA spokesperson, Harrison, pointed to a study originally published in 2021 in The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, based on a central registry of mitral valve procedures, that found lower rates of death after MitraClip went on the market.
“These data confirmed that the MitraClip device remains safe and effective in the real-world setting,” Harrison said.
But the study’s authors, several of whom disclosed financial or other connections to Abbott, said data was missing for more than a quarter of patients one year after the procedure.
A major measure of success would be the proportion of MitraClip patients who are alive “with an acceptable quality of life” a year after undergoing the procedure, the study said. Because such information was available for fewer than half of the living patients, “we have omitted those outcomes from this report,” the authors wrote.
If you’ve had an experience with MitraClip or another medical device and would like to tell KFF Health News about it, click here to share your story with us.
KFF Health News audience engagement producer Tarena Lofton contributed to this report.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Junk Food Turns Public Villain as Power Shifts in Washington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The new Trump administration could be coming for your snacks.
For years, the federal government has steered clear of regulating junk food, fast food, and ultra-processed food.
Now attitudes are changing. Some members of President-elect Donald Trump’s inner circle are gearing up to battle “Big Food,” or the companies that make most of the food and beverages consumed in the United States. Nominees for top health agencies are taking aim at ultra-processed foods that account for an estimated 70% of the nation’s food supply. Based on recent statements, a variety of potential politically charged policy options to regulate ultra-processed food may land on the Trump team menu, including warning labels, changes to agribusiness subsidies, and limits on which products consumers can buy with government food aid.
The push to reform the American diet is being driven largely by conservatives who have taken up the cause that has long been a darling of the left. Trump supporters such as Robert F. Kennedy Jr., whose controversial nomination to lead the Department of Health and Human Services still faces Senate confirmation, are embracing a concept that champions natural foods and alternative medicine. It’s a movement they’ve dubbed “MAHA,” or Make America Healthy Again. Their interest has created momentum because their goals have fairly broad bipartisan support even amid a bitterly divided Congress in which lawmakers from both sides of the aisle focused on the issue last year.
It’s likely to be a pitched battle because the food industry wields immense political influence and has successfully thwarted previous efforts to regulate its products or marketing. The category of “food processing and sales companies,” which includes Tyson Foods and Nestle SA, tallied $26.7 million in spending on lobbying in 2024, according to OpenSecrets. That’s up from almost $10 million in 1998.
“They have been absolutely instrumental and highly, highly successful at delaying any regulatory effectiveness in America,” said Laura Schmidt, a health policy professor at the University of California-San Francisco. “It really does feel like there needs to be a moment of reckoning here where people start asking the question, ‘Why do we have to live like this?’”
“Ultra-processed food” is a widely used term that means different things to different people and is used to describe items ranging from sodas to many frozen meals. These products often contain added fats, starches, and sugars, among other things. Researchers say consumption of ultra-processed foods is linked — in varying levels of intensity — to chronic conditions like diabetes, cancer, mental health problems, and early death.
Nutrition and health leaders are optimistic that a reckoning is already underway. Kennedy has pledged to remove processed foods from school lunches, restrict certain food additives such as dyes in cereal, and shift federal agricultural subsidies away from commodity crops widely used in ultra-processed foods.
The intensifying focus in Washington has triggered a new level of interest on the legal front as lawyers explore cases to take on major foodmakers for selling products they say result in chronic disease.
Bryce Martinez, now 18, filed a lawsuit in December against almost a dozen foodmakers such as Kraft Heinz, The Coca-Cola Co., and Nestle USA. He developed diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by age 16, and is seeking to hold them accountable for his illnesses. According to the suit, filed in the Philadelphia Court of Common Pleas, the companies knew or should have known ultra-processed foods were harmful and addictive.
The lawsuit noted that Martinez grew up eating heavily advertised, brand-name foods that are staples of the American diet — sugary soft drinks, Cheerios and Lucky Charms, Skittles and Snickers, frozen and packaged dinners, just to name a few.
Nestle, Coca-Cola, and Kraft Heinz didn’t return emails seeking comment for this article. The Consumer Brands Association, a trade association for makers of consumer packaged goods, disputed the allegations.
“Attempting to classify foods as unhealthy simply because they are processed, or demonizing food by ignoring its full nutrient content, misleads consumers and exacerbates health disparities,” said Sarah Gallo, senior vice president of product policy, in a statement.
Other law firms are on the hunt for children or adults who believe they were harmed by consuming ultra-processed foods, increasing the likelihood of lawsuits.
One Indiana personal injury firm says on its website that “we are actively investigating ultra processed food (UPF) cases.” Trial attorneys in Texas also are looking into possible legal action against the federal regulators they say have failed to police ultra-processed foods.
“If you or your child have suffered health problems that your doctor has linked directly to the consumption of ultra-processed foods, we want to hear your story,” they say on their website.
Meanwhile, the FDA on Jan. 14 announced it is proposing to require a front-of-package label to appear on most packaged foods to make information about a food’s saturated fat, sodium, and added sugar content easily visible to consumers.
And on Capitol Hill, Sens. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), Ron Johnson (R-Wis.), and Cory Booker (D-N.J.) are sounding the alarm over ultra-processed food. Sanders introduced legislation in 2024 that could lead to a federal ban on junk food advertising to children, a national education campaign, and labels on ultra-processed foods that say the products aren’t recommended for children. Booker cosigned the legislation along with Sens. Peter Welch (D-Vt.) and John Hickenlooper (D-Colo.).
The Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions held a December hearing examining links between ultra-processed food and chronic disease during which FDA Commissioner Robert Califf called for more funding for research.
Food companies have tapped into “the same neural circuits that are involved in opioid addiction,” Califf said at the hearing.
Sanders, who presided over the hearing, said there’s “growing evidence” that “these foods are deliberately designed to be addictive,” and he asserted that ultra-processed foods have driven epidemics of diabetes and obesity, and hundreds of billions of dollars in medical expenses.
Research on food and addiction “has accumulated to the point where it’s reached a critical mass,” said Kelly Brownell, an emeritus professor at Stanford who is one of the editors of a scholarly handbook on the subject.
Attacks from three sides — lawyers, Congress, and the incoming Trump administration, all seemingly interested in taking up the fight — could lead to enough pressure to challenge Big Food and possibly spur better health outcomes in the U.S., which has the lowest life expectancy among high-income countries.
“Maybe getting rid of highly processed foods in some things could actually flip the switch pretty quickly in changing the percentage of the American public that are obese,” said Robert Redfield, a virologist who led the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention during the previous Trump administration, in remarks at a December event hosted by the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank.
Claims that Big Food knowingly manufactured and sold addictive and harmful products resemble the claims leveled against Big Tobacco before the landmark $206 billion settlement was reached in 1998.
“These companies allegedly use the tobacco industry’s playbook to target children, especially Black and Hispanic children, with integrated marketing tie-ins with cartoons, toys, and games, along with social media advertising,” Rene Rocha, one of the lawyers at Morgan & Morgan representing Martinez, told KFF Health News.
The 148-page Martinez lawsuit against foodmakers draws from documents made public in litigation against tobacco companies that owned some of the biggest brands in the food industry.
Similar allegations were made against opioid manufacturers, distributors, and retailers before they agreed to pay tens of billions of dollars in a 2021 settlement with states.
The FDA ultimately put restrictions on the labeling and marketing of tobacco, and the opioid epidemic led to legislation that increased access to lifesaving medications to treat addiction.
But the Trump administration’s zeal in taking on Big Food may face unique challenges.
The ability of the FDA to impose regulation is hampered in part by funding. While the agency’s drug division collects industry user fees, its division of food relies on a more limited budget determined by Congress.
Change can take time because the agency moves at what some critics call a glacial pace. Last year, the FDA revoked a regulation allowing brominated vegetable oil in food products. The agency determined in 1970 that the additive was not generally recognized as safe.
Efforts to curtail the marketing of ultra-processed food could spur lawsuits alleging that any restrictions violate commercial speech protected by the First Amendment. And Kennedy — if he is confirmed as HHS secretary — may struggle to get support from a Republican-led Congress that champions less federal regulation and a president-elect who during his previous term served fast food in the White House.
“The question is, will RFK be able to make a difference?” said David L. Katz, a doctor who founded True Health Initiative, a nonprofit group that combats public health misinformation. “No prior administration has done much in this space, and RFK is linked to a particularly anti-regulatory administration.”
Meanwhile, the U.S. population is recognized as among the most obese in the world and has the highest rate of people with multiple chronic conditions among high-income countries.
“There is a big grassroots effort out there because of how sick we are,” said Jerold Mande, who served as deputy undersecretary for food safety at the Department of Agriculture from 2009 to 2011. “A big part of it is people shouldn’t be this sick this young in their lives. You’re lucky if you get to 18 without a chronic disease. It’s remarkable.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Soy Allergy? No Problem! Turn Any Legume Into Tofu (Here’s How)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Legumes have similar chemical composition, which means they can generally be used in the same ways as each other:
Variety is the spice of life
In the video, he demonstrates this with green peas, red lentils, and green lentils, and mentions that it is the same for chickpeas too. The process is:
- Soak 100g dried legumes overnight in plenty of water.
- Drain and blend with 250ml fresh water until smooth.
- Pour into a nonstick frying pan, add ½ tsp salt, and stir.
- Cook until it thickens into a paste, then cook for another 2–3 minutes on low heat.
- Transfer to a 500ml mold, smooth the top, and set in the fridge for 1 hour.
- If properly set, it can be eaten as-is or fried into crispy cubes.
- Stir-fry tofu with: ginger, spring onions, garlic, and chili.
- Sauce: suggestions include soy sauce, rice wine vinegar, mirin, sesame oil.
- Garnish with: sesame and coriander seeds
Science behind it: heating alters protein bonds and starches, forming a thick paste that sets.
Note: legumes contain natural toxins that are destroyed by cooking. For some, like those mentioned above, frying for a few minutes is sufficient. However, kidney beans are high in phytohemagglutinin, which requires at least 20 minutes of cooking to be safe, making them unsuitable for this process.
For more on all of this, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Six Ways To Eat For Healthier Skin
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: