They Were Injured at the Super Bowl Parade. A Month Later, They Feel Forgotten.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
KFF Health News and KCUR are following the stories of people injured during the Feb. 14 mass shooting at the Kansas City Chiefs Super Bowl celebration. Listen to how one Kansas family is coping with the trauma.
Jason Barton didn’t want to attend the Super Bowl parade this year. He told a co-worker the night before that he worried about a mass shooting. But it was Valentine’s Day, his wife is a Kansas City Chiefs superfan, and he couldn’t afford to take her to games since ticket prices soared after the team won the championship in 2020.
So Barton drove 50 miles from Osawatomie, Kansas, to downtown Kansas City, Missouri, with his wife, Bridget, her 13-year-old daughter, Gabriella, and Gabriella’s school friend. When they finally arrived home that night, they cleaned blood from Gabriella’s sneakers and found a bullet in Bridget’s backpack.
Gabriella’s legs were burned by sparks from a ricocheted bullet, Bridget was trampled while shielding Gabriella in the chaos, and Jason gave chest compressions to a man injured by gunfire. He believes it was Lyndell Mays, one of two men charged with second-degree felony murder.
“There’s never going to be a Valentine’s Day where I look back and I don’t think about it,” Gabriella said, “because that’s a day where we’re supposed to have fun and appreciate the people that we have.”
One month after the parade in which the U.S. public health crisis that is gun violence played out on live television, the Bartons are reeling from their role at its epicenter. They were just feet from 43-year-old Lisa Lopez-Galvan, who was killed. Twenty-four other people were injured. Although the Bartons aren’t included in that official victim number, they were traumatized, physically and emotionally, and pain permeates their lives: Bridget and Jason keep canceling plans to go out, opting instead to stay home together; Gabriella plans to join a boxing club instead of the dance team.
During this first month, Kansas City community leaders have weighed how to care for people caught in the bloody crossfire and how to divide more than $2 million donated to public funds for victims in the initial outpouring of grief.
The questions are far-reaching: How does a city compensate people for medical bills, recovery treatments, counseling, and lost wages? And what about those who have PTSD-like symptoms that could last years? How does a community identify and care for victims often overlooked in the first flush of reporting on a mass shooting: the injured?
The injured list could grow. Prosecutors and Kansas City police are mounting a legal case against four of the shooting suspects, and are encouraging additional victims to come forward.
“Specifically, we’re looking for individuals who suffered wounds from their trying to escape. A stampede occurred while people were trying to flee,” said Jackson County Prosecutor Jean Peters Baker. Anyone who “in the fleeing of this event that maybe fell down, you were trampled, you sprained an ankle, you broke a bone.”
Meanwhile, people who took charge of raising money and providing services to care for the injured are wrestling with who gets the money — and who doesn’t. Due to large donations from celebrities like Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce, some victims or their families will have access to hundreds of thousands of dollars for medical expenses. Other victims may simply have their counseling covered.
The overall economic cost of U.S. firearm injuries is estimated by a recent Harvard Medical School study at $557 billion annually. Most of that — 88% — represented quality-of-life losses among those injured by firearms and their families. The JAMA-published study found that each nonfatal firearm injury leads to roughly $30,000 in direct health care spending per survivor in the first year alone.
In the immediate aftermath of the shootings, as well-intentioned GoFundMe pages popped up to help victims, executives at United Way of Greater Kansas City gathered to devise a collective donation response. They came up with “three concentric circles of victims,” said Jessica Blubaugh, the United Way’s chief philanthropy officer, and launched the #KCStrong campaign.
“There were folks that were obviously directly impacted by gunfire. Then the next circle out is folks that were impacted, not necessarily by gunshots, but by physical impact. So maybe they were trampled and maybe they tore a ligament or something because they were running away,” Blubaugh said. “Then third is folks that were just adjacent and/or bystanders that have a lot of trauma from all of this.”
PTSD, Panic, and the Echo of Gunfire
Bridget Barton returned to Kansas City the day after the shooting to turn in the bullet she found in her backpack and to give a statement at police headquarters. Unbeknownst to her, Mayor Quinton Lucas and the police and fire chiefs had just finished a press conference outside the building. She was mobbed by the media assembled there — interviews that are now a blur.
“I don’t know how you guys do this every day,” she remembered telling a detective once she finally got inside.
The Bartons have been overwhelmed by well wishes from close friends and family as they navigate the trauma, almost to the point of exhaustion. Bridget took to social media to explain she wasn’t ignoring the messages, she’s just responding as she feels able — some days she can hardly look at her phone, she said.
A family friend bought new Barbie blankets for Gabriella and her friend after the ones they brought to the parade were lost or ruined. Bridget tried replacing the blankets herself at her local Walmart, but when she was bumped accidentally, it triggered a panic attack. She abandoned her cart and drove home.
“I’m trying to get my anxiety under control,” Bridget said.
That means therapy. Before the parade, she was already seeing a therapist and planning to begin eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, a form of therapy associated with treating post-traumatic stress disorder. Now the shooting is the first thing she wants to talk about in therapy.
Since Gabriella, an eighth grader, has returned to middle school, she has dealt with the compounding immaturity of adolescence: peers telling her to get over it, pointing finger guns at her, or even saying it should have been her who was shot. But her friends are checking on her and asking how she’s doing. She wishes more people would do the same for her friend, who took off running when the shooting started and avoided injury. Gabriella feels guilty about bringing her to what turned into a horrifying experience.
“We can tell her all day long, ‘It wasn’t your fault. She’s not your responsibility.’ Just like I can tell myself, ‘It wasn’t my fault or my responsibility,’” Bridget said. “But I still bawled on her mom’s shoulder telling her how sorry I was that I grabbed my kid first.”
The two girls have spent a lot of time talking since the shooting, which Gabriella said helps with her own stress. So does spending time with her dog and her lizard, putting on makeup, and listening to music — Tech N9ne’s performance was a highlight of the Super Bowl celebration for her.
In addition to the spark burns on Gabriella’s legs, when she fell to the concrete in the pandemonium she split open a burn wound on her stomach previously caused by a styling iron.
“When I see that, I just picture my mom trying to protect me and seeing everyone run,” Gabriella said of the wound.
It’s hard not to feel forgotten by the public, Bridget said. The shooting, especially its survivors, have largely faded from the headlines aside from court dates. Two additional high-profile shootings have occurred in the area since the parade. Doesn’t the community care, she wonders, that her family is still living with the fallout every day?
“I’m going to put this as plainly as possible. I’m f—ing pissed because my family went through something traumatic,” Bridget vented in a recent social media post. “I don’t really want anything other [than], ‘Your story matters, too, and we want to know how you’re doing.’ Have we gotten that? Abso-f—lutely not.”
‘What Is the Landscape of Need?’
Helped in part by celebrities like Swift and Kelce, donations for the family of Lopez-Galvan, the lone fatality, and other victims poured in immediately after the shootings. Swift and Kelce donated $100,000 each. With the help of an initial $200,000 donation from the Kansas City Chiefs, the United Way’s #KCStrong campaign took off, reaching $1 million in the first two weeks and sitting at $1.2 million now.
Six verified GoFundMe funds were established. One solely for the Lopez-Galvan family has collected over $406,000. Smaller ones were started by a local college student and Swift fans. Churches have also stepped up, and one local coalition had raised $183,000, money set aside for Lopez-Galvan’s funeral, counseling services for five victims, and other medical bills from Children’s Mercy Kansas City hospital, said Ray Jarrett, executive director of Unite KC.
Money for Victims Rolls In
Donations poured in for those injured at the Super Bowl Parade in Kansas City after the Feb. 14 shootings. The largest, starting with a $200,000 donation from the Kansas City Chiefs, is at the United Way of Greater Kansas City. Six GoFundMe sites also popped up, due in part to $100,000 donations each from Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce. Here’s a look at the totals as of March 12.United Way#KCStrong: $1.2 million.Six Verified GoFundMe AccountsLisa Lopez-Galvan GoFundMe (Taylor Swift donated): $406,142Reyes Family GoFundMe (Travis Kelce donated): $207,035Samuel Arellano GoFundMe: $11,896Emily Tavis GoFundMe: $9,518Cristian Martinez’s GoFundMe for United Way: $2,967Swifties’ GoFundMe for Children’s Mercy hospital: $1,060ChurchesResurrection (Methodist) “Victims of Violence Fund”: $53,358‘The Church Loves Kansas City’: $183,000
Meanwhile, those leading the efforts found models in other cities. The United Way’s Blubaugh called counterparts who’d responded to their own mass shootings in Orlando, Florida; Buffalo, New York; and Newtown, Connecticut.
“The unfortunate reality is we have a cadre of communities across the country who have already faced tragedies like this,” Blubaugh said. “So there is an unfortunate protocol that is, sort of, already in place.”
#KCStrong monies could start being paid out by the end of March, Blubaugh said. Hundreds of people called the nonprofit’s 211 line, and the United Way is consulting with hospitals and law enforcement to verify victims and then offer services they may need, she said.
The range of needs is staggering — several people are still recovering at home, some are seeking counseling, and many weren’t even counted in the beginning. For instance, a plainclothes police officer was injured in the melee but is doing fine now, said Police Chief Stacey Graves.
Determining who is eligible for assistance was one of the first conversations United Way officials had when creating the fund. They prioritized three areas of focus: first were the wounded victims and their families, second was collaborating with organizations already helping victims in violence intervention and prevention and mental health services, and third were the first responders.
Specifically, the funds will be steered to cover medical bills, or lost wages for those who haven’t been able to work since the shootings, Blubaugh said. The goal is to work quickly to help people, she said, but also to spend the money in a judicious, strategic way.
“We don’t have a clear sightline of the entire landscape that we’re dealing with,” Blubaugh said. “Not only of how much money do we have to work with, but also, what is the landscape of need? And we need both of those things to be able to make those decisions.”
Firsthand Experience of Daily Kansas City Violence
Jason used his lone remaining sick day to stay home with Bridget and Gabriella. An overnight automation technician, he is the family’s primary breadwinner.
“I can’t take off work, you know?” he said. “It happened. It sucked. But it’s time to move on.”
“He’s a guy’s guy,” Bridget interjected.
On Jason’s first night back at work, the sudden sound of falling dishes startled Bridget and Gabriella, sending them into each other’s arms crying.
“It’s just those moments of flashbacks that are kicking our butts,” Bridget said.
Tell Us About Your Experience
We are continuing to report on the effects of the parade shooting on the people who were injured and the community as a whole. Do you have an experience you want to tell us about, or a question you think we should look into? Message KCUR’s text line at (816) 601-4777. Your information will not be used in an article without your permission.
In a way, the shooting has brought the family closer. They’ve been through a lot recently. Jason survived a heart attack and cancer last year. Raising a teenager is never easy.
Bridget can appreciate that the bullet lodged in her backpack, narrowly missing her, and that Gabriella’s legs were burned by sparks but she wasn’t shot.
Jason is grateful for another reason: It wasn’t a terrorist attack, as he initially feared. Instead, it fits into the type of gun violence he’d become accustomed to growing up in Kansas City, which recorded its deadliest year last year, although he’d never been this close to it before.
“This crap happens every single day,” he said. “The only difference is we were here for it.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Water Fluoridation, Atheroma, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I watched a documentary recently on Fluoride in our drinking water & the dangers of it. Why are we poisoning our water?❞
This is a great question, and it certainly is controversial. It sounds like the documentary you watched was predominantly or entirely negative, but there’s a lot of science to back both sides of this, and it’s not even that the science is contradictory (it’s not). It’s that what differs is people’s opinions about whether benefiting one thing is worth creating a risk to another, and that means looking at:
- What is the risk associated with taking no action (error of omission)?
- What is the risk associated with taking an action (error of commission)?
The whole topic is worth a main feature, but to summarize a few key points:
- Water fluoridation is considered good for the prevention of dental cavities
- Water fluoridation aims to deliver fluoride and doses far below dangerous levels
- This requires working on consumer averages, though
- ”Where do we put the safety margins?” is to some extent a subjective question, in terms of trading off one aspect of health for another
- Too much fluoride can also be bad for the teeth (at least cosmetically, creating little white* spots)
- Detractors of fluoride tend to mostly be worried about neurological harm
- However, the doses in public water supplies are almost certainly far below the levels required to cause this harm.
- That said, again this is working on consumer averages, though.
- However, the doses in public water supplies are almost certainly far below the levels required to cause this harm.
- A good guide is: watch your teeth! Those white* spots will be “the canary in the coal mine” of more serious harm that could potentially come from higher levels due to overconsumption of fluorine.
*Teeth are not supposed to be pure white. The “Hollywood smile” is a lie. Teeth are supposed to be a slightly off-white, ivory color. Anything whiter than that is adding something else that shouldn’t be there, or stripping something off that should be there.
❝How does your diet change clean out your arteries of the bad cholesterol?❞
There’s good news and bad news here, and they can both be delivered with a one-word reply:
Slowly.
Or rather: what’s being cleaned out is mostly not the LDL (bad) cholesterol, but rather, the result of that.
When our diet is bad for cardiovascular health, our arteries get fatty deposits on their walls. Cholesterol gets stuck here too, but that’s not the main physical problem.
Our body’s natural defenses come into action and try to clean it up, but they (for example macrophages, a kind of white blood cell that consumes invaders and then dies, before being recycled by the next part of the system) often get stuck and become part of the buildup (called atheroma), which can lead to atherosclerosis and (if calcium levels are high) hardening of the arteries, which is the worst end of this.
This can then require medical attention, precisely because the body can’t remove it very well—especially if you are still maintaining a heart-unhealthy diet, thus continuing to add to the mess.
However, if it is not too bad yet, yes, a dietary change alone will reverse this process. Without new material being added to the arterial walls, the body’s continual process of rejuvenation will eventually fix it, given time (free from things making it worse) and resources.
In fact, your arteries can be one of the quickest places for your body to make something better or worse, because the blood is the means by which the body moves most things (good or bad) around the body.
All the more reason to take extra care of it, since everything else depends on it!
You might also like our previous main feature:
Share This Post
-
The Purple Parsnip’s Bioactive Brain Benefits (& more)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This Root Might Be A Guardian Angel
Sometimes we go searching for supplements to research; sometimes supplements present themselves for examination! In this case, our attention was grabbed by a headline:
Angelica gigas extract emerges as a potential treatment for vascular disease
Angelica who?
Angelica gigas, also called the purple parsnip (amongst other names), is a flowering plant native to Korea. It has assorted medicinal properties, and in this case, it was its heart-healthy benefits that were making news:
❝Ultimately, this study presents clearly evidence that Angelica gigas extract is a promising natural product-based functional food/herbal medicine candidate for preventing or regulating hyperlipidemic cardiovascular complications❞
But it has a lot more to offer…
The root has various bioactive metabolites, but the compounds that most studies are most interested in are decursin and decursinol, for their neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement effects:
❝[C]rude extracts and isolated components from the root of A. gigas exhibited neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement effects.
Neuronal damage or death is the most important factor for many neurodegenerative diseases.
In addition, recent studies have clearly demonstrated the possible mechanisms behind the neuroprotective action of extracts/compounds from the root of A. gigas.❞
That middle paragraph there? That’s one of the main pathogenic processes of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Multiple Sclerosis.
Angelica gigas attenuates (reduces the force of) that process:
❝The published reports revealed that the extracts and isolated components from the root of A. gigas showed neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement properties through various mechanisms such as anti-apoptosis, antioxidative actions, inhibiting mRNA and protein expressions of inflammatory mediators and regulating a number of signaling pathways.
In conclusion, the A. gigas root can serve as an effective neuroprotective agent by modulating various pathophysiological processes❞
Read more: Neuroprotective and Cognitive Enhancement Potentials of Angelica gigas Nakai Root: A Review
Beyond neuroprotection & cognitive enhancement
…and also beyond its protection against vascular disease, which is what got our attention…
Angelica gigas also has antioxidant properties, anti-cancer properties, and general immune-boosting properties.
We’ve only so much room, so: those links above will take you to example studies for those things, but there are plenty more where they came from, so we’re quite confident in this one.
Of course, what has antioxidant properties is usually anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-aging, because these things are reliant on many of the same processes as each other, with a lot of overlap.
Where can we get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
A Cold Shower A Day Keeps The Doctor Away?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Cold Shower A Day Keeps The Doctor Away?
This is Dutch extreme athlete Wim Hof, also known as “The Iceman”! He’s broken many world records mostly relating to the enduring the cold, for example:
- climbing Mount Kilimanjaro in shorts
- running a half-marathon above the Arctic Circle barefoot
- standing in a container completely covered with ice cubes for more than 112 minutes
You might not want to do yoga in your pyjamas on an iceberg, but you might like…
- better circulatory health
- reduced risk of stroke
- a boosted immune system
- healthier skin
- more energy and alertness
…and things like that. Wim Hof’s method is not just about extreme athletic achievements; most of what he does, the stuff that can benefit the rest of us, is much more prosaic.
The Wim Hof Method
For Wim Hof, three things are key:
- Breathing (See: Wim Hof Method Breathing Exercises)
- Commitment (See: How to Increase Willpower)
- Cold therapy (See: Benefits of Cold Therapy)
Today, we’re going to be focusing on the last one there.
What are the benefits of Cold Therapy?
Once upon a time, we didn’t have central heating, electric blankets, thermal underwear, and hot showers. In fact, once upon a time, we didn’t have houses or clothes. We used to be a lot more used to the elements! And while it’s all well and good to enjoy modern comforts, it has left our bodies lacking practice.
Practice at what? Most notably: vasodilation and vasoconstriction, in response to temperature changes. Either:
- vasodilation, because part of our body needs more blood to keep it warm and nourished, or
- vasoconstriction, because part of our body needs less blood running through it to get cooled down.
Switching between the two gives the blood vessels practice at doing it, and improves vascular muscle tone. If your body doesn’t get that practice, your blood vessels will be sluggish at making the change. This can cause circulation problems, which in turn have a big impact in many other areas of health, including:
- cardiovascular disease
- stroke risk
- mood instability
- nerve damage in extremities
On the flipside, if the blood vessels do get regular practice at dilating and constricting, you might enjoy lower risk of those things, and instead:
- improved immune response
- healthier skin
- better quality sleep
- more energy and alertness
- improved sexual performance/responsiveness
So, how to get that, without getting extreme?
As today’s title suggests, “a cold shower a day” is a great practice.
You don’t have to jump straight in, especially if you think your circulation and vascular responses might be a bit sluggish in the first instance. In fact, Wim Hof recommends:
- Week 1: Thirty seconds of cold water at the end of a warm shower each morning
- Week 2: One minute of cold water at the end of a warm shower each morning
- Week 3: A minute and a half of cold water at the end of a warm shower each morning
- Week 4: Two minutes of cold water at the end of a warm shower each morning
How cold is cold?
The benefits of cold exposure begin at around 16ºC / 60ºF, so in most places, water from the cold water mains is sufficiently cold.
As your body becomes more used to making the quick-change on a vascular level, the cold water will seem less shocking to your system. In other words, on day 30 it won’t hit you like it did on day one.
At that point, you can either continue with your two-minutes daily cold shower, and reap the benefits, or if you’re curious to push it further, that’s where ice baths come in!
Can anyone do it, or are any conditions contraindicated?
As ever, we’re a health and productivity newsletter, not doctors, let alone your doctors. Nothing here is medical advice. However, Wim Hof himself says:
❝Listen to your body, and never force the practices. We advise against doing Wim Hof Method if you are dealing with any of the following:
- Epilepsy
- High blood pressure
- Coronary heart disease
- A history of serious healthy issues like heart failure or stroke
- Pregnancy*
- Childhood*❞
*There is simply not enough science regarding the effects of cold exposure on people who are pregnant, or children. Obviously, we don’t expect this to be remedied anytime soon, because the study insitutions’ ethics boards would (rightly!) hold up the study.
As for the other conditions, and just generally if unsure, consult a doctor.
As you can see, this does mean that a limitation of Cold Therapy is that it appears to be far better as a preventative, since it helps guard against the very conditions that could otherwise become contraindications.
We haven’t peppered today’s main feature with study papers, partly because Wim Hof’s own website has kindly collated a collection of them (with links and summaries!) onto one page:
Further reading: The Science Behind The Wim Hof Method
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Drug companies pay doctors over A$11 million a year for travel and education. Here’s which specialties received the most
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Drug companies are paying Australian doctors millions of dollars a year to fly to overseas conferences and meetings, give talks to other doctors, and to serve on advisory boards, our research shows.
Our team analysed reports from major drug companies, in the first comprehensive analysis of its kind. We found drug companies paid more than A$33 million to doctors in the three years from late 2019 to late 2022 for these consultancies and expenses.
We know this underestimates how much drug companies pay doctors as it leaves out the most common gift – food and drink – which drug companies in Australia do not declare.
Due to COVID restrictions, the timescale we looked at included periods where doctors were likely to be travelling less and attending fewer in-person medical conferences. So we suspect current levels of drug company funding to be even higher, especially for travel.
Monster Ztudio/Shutterstock What we did and what we found
Since 2019, Medicines Australia, the trade association of the brand-name pharmaceutical industry, has published a centralised database of payments made to individual health professionals. This is the first comprehensive analysis of this database.
We downloaded the data and matched doctors’ names with listings with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (Ahpra). We then looked at how many doctors per medical specialty received industry payments and how much companies paid to each specialty.
We found more than two-thirds of rheumatologists received industry payments. Rheumatologists often prescribe expensive new biologic drugs that suppress the immune system. These drugs are responsible for a substantial proportion of drug costs on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS).
The specialists who received the most funding as a group were cancer doctors (oncology/haematology specialists). They received over $6 million in payments.
This is unsurprising given recently approved, expensive new cancer drugs. Some of these drugs are wonderful treatment advances; others offer minimal improvement in survival or quality of life.
A 2023 study found doctors receiving industry payments were more likely to prescribe cancer treatments of low clinical value.
Our analysis found some doctors with many small payments of a few hundred dollars. There were also instances of large individual payments.
Why does all this matter?
Doctors usually believe drug company promotion does not affect them. But research tells a different story. Industry payments can affect both doctors’ own prescribing decisions and those of their colleagues.
A US study of meals provided to doctors – on average costing less than US$20 – found the more meals a doctor received, the more of the promoted drug they prescribed.
Pizza anyone? Even providing a cheap meal can influence prescribing. El Nariz/Shutterstock Another study found the more meals a doctor received from manufacturers of opioids (a class of strong painkillers), the more opioids they prescribed. Overprescribing played a key role in the opioid crisis in North America.
Overall, a substantial body of research shows industry funding affects prescribing, including for drugs that are not a first choice because of poor effectiveness, safety or cost-effectiveness.
Then there are doctors who act as “key opinion leaders” for companies. These include paid consultants who give talks to other doctors. An ex-industry employee who recruited doctors for such roles said:
Key opinion leaders were salespeople for us, and we would routinely measure the return on our investment, by tracking prescriptions before and after their presentations […] If that speaker didn’t make the impact the company was looking for, then you wouldn’t invite them back.
We know about payments to US doctors
The best available evidence on the effects of pharmaceutical industry funding on prescribing comes from the US government-run program called Open Payments.
Since 2013, all drug and device companies must report all payments over US$10 in value in any single year. Payment reports are linked to the promoted products, which allows researchers to compare doctors’ payments with their prescribing patterns.
Analysis of this data, which involves hundreds of thousands of doctors, has indisputably shown promotional payments affect prescribing.
Medical students need to know about this. LightField Studios/Shutterstock US research also shows that doctors who had studied at medical schools that banned students receiving payments and gifts from drug companies were less likely to prescribe newer and more expensive drugs with limited evidence of benefit over existing drugs.
In general, Australian medical faculties have weak or no restrictions on medical students seeing pharmaceutical sales representatives, receiving gifts, or attending industry-sponsored events during their clinical training. They also have no restrictions on academic staff holding consultancies with manufacturers whose products they feature in their teaching.
So a first step to prevent undue pharmaceutical industry influence on prescribing decisions is to shelter medical students from this influence by having stronger conflict-of-interest policies, such as those mentioned above.
A second is better guidance for individual doctors from professional organisations and regulators on the types of funding that is and is not acceptable. We believe no doctor actively involved in patient care should accept payments from a drug company for talks, international travel or consultancies.
Third, if Medicines Australia is serious about transparency, it should require companies to list all payments – including those for food and drink – and to link health professionals’ names to their Ahpra registration numbers. This is similar to the reporting standard pharmaceutical companies follow in the US and would allow a more complete and clearer picture of what’s happening in Australia.
Patients trust doctors to choose the best available treatments to meet their health needs, based on scientific evidence of safety and effectiveness. They don’t expect marketing to influence that choice.
Barbara Mintzes, Professor, School of Pharmacy and Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney and Malcolm Forbes, Consultant psychiatrist and PhD candidate, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Yes, you still need to use sunscreen, despite what you’ve heard on TikTok
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Summer is nearly here. But rather than getting out the sunscreen, some TikTokers are urging followers to chuck it out and go sunscreen-free.
They claim it’s healthier to forgo sunscreen to get the full benefits of sunshine.
Here’s the science really says.
Karolina Grabowska/Pexels How does sunscreen work?
Because of Australia’s extreme UV environment, most people with pale to olive skin or other risk factors for skin cancer need to protect themselves. Applying sunscreen is a key method of protecting areas not easily covered by clothes.
Sunscreen works by absorbing or scattering UV rays before they can enter your skin and damage DNA or supportive structures such as collagen.
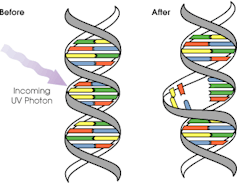
When UV particles hit DNA, the excess energy can damage our DNA. This damage can be repaired, but if the cell divides before the mistake is fixed, it causes a mutation that can lead to skin cancers.
The energy from a particle of UV (a photon) causes DNA strands to break apart and reconnect incorrectly. This causes a bump in the DNA strand that makes it difficult to copy accurately and can introduce mutations. NASA/David Herring The most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Melanoma is less common, but is the most likely to spread around the body; this process is called metastasis.
Two in three Australians will have at least one skin cancer in their lifetime, and they make up 80% of all cancers in Australia.
Around 99% of skin cancers in Australia are caused by excessive exposure to UV radiation.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation also affects the appearance of your skin. UVA rays are able to penetrate deep into the skin, where they break down supportive structures such as elastin and collagen.
This causes signs of premature ageing, such as deep wrinkling, brown or white blotches, and broken capillaries.
Sunscreen can help prevent skin cancers
Used consistently, sunscreen reduces your risk of skin cancer and slows skin ageing.
In a Queensland study, participants either used sunscreen daily for almost five years, or continued their usual use.
At the end of five years, the daily-use group had reduced their risk of squamous cell carcinoma by 40% compared to the other group.
Ten years later, the daily use group had reduced their risk of invasive melanoma by 73%
Does sunscreen block the health-promoting properties of sunlight?
The answer is a bit more complicated, and involves personalised risk versus benefit trade-offs.
First, the good news: there are many health benefits of spending time in the sun that don’t rely on exposure to UV radiation and aren’t affected by sunscreen use.
Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not all light. Ron Lach/Pexels Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not visible light or infrared light (which we feel as heat). And importantly, some of the benefits of sunlight are obtained via the eyes.
Visible light improves mood and regulates circadian rhythm (which influences your sleep-wake cycle), and probably reduces myopia (short-sightedness) in children.
Infrared light is being investigated as a treatment for several skin, neurological, psychiatric and autoimmune disorders.
So what is the benefit of exposing skin to UV radiation?
Exposing the skin to the sun produces vitamin D, which is critical for healthy bones and muscles.
Vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly common among Australians, peaking in Victoria at 49% in winter and being lowest in Queensland at 6% in summer.
Luckily, people who are careful about sun protection can avoid vitamin D deficiency by taking a supplement.
Exposing the skin to UV radiation might have benefits independent of vitamin D production, but these are not proven. It might reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis or cause release of a chemical that could reduce blood pressure. However, there is not enough detail about these benefits to know whether sunscreen would be a problem.
What does this mean for you?
There are some benefits of exposing the skin to UV radiation that might be blunted by sunscreen. Whether it’s worth foregoing those benefits to avoid skin cancer depends on how susceptible you are to skin cancer.
If you have pale skin or other factors that increase you risk of skin cancer, you should aim to apply sunscreen daily on all days when the UV index is forecast to reach 3.
If you have darker skin that rarely or never burns, you can go without daily sunscreen – although you will still need protection during extended times outdoors.
For now, the balance of evidence suggests it’s better for people who are susceptible to skin cancer to continue with sun protection practices, with vitamin D supplementation if needed.
Katie Lee, PhD Candidate, Dermatology Research Centre, The University of Queensland and Rachel Neale, Principal research fellow, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Simple, 10-Minute Hip Opening Routine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hips Feeling Stiff?
If so, Flow with Adee’s video (below) has just the solution with a quick 10-minute hip-opening routine. Designed for intermediates but open to all, we love Adee’s work and recommend that you reach out to her to tell her what you’d like to see next.
Other Methods
If you’re a book lover, we’ve reviewed a fantastic book on reducing hip pain. Alternatively, learn stretching from a ballerina with Jasmine McDonald’s ballet stretching routine.
Otherwise, enjoy today’s video:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: