Spirulina vs Nori – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing spirulina to nori, we picked the nori.
Why?
In the battle of the seaweeds, if spirulina is a superfood (and it is), then nori is a super-dooperfood. So today is one of those “a very nutritious food making another very nutritious food look bad by standing next to it” days. With that in mind…
In terms of macros, they’re close to identical. They’re both mostly water with protein, carbs, and fiber. Technically nori is higher in carbs, but we’re talking about 2.5g/100g difference.
In the category of vitamins, spirulina has more vitamin B1, while nori has a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a little closer but still a clear win for nori; spirulina has more copper, iron, and magnesium, while nori has more calcium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc.
Want to try some nori? Here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nori was an important part of the diet enjoyed here
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
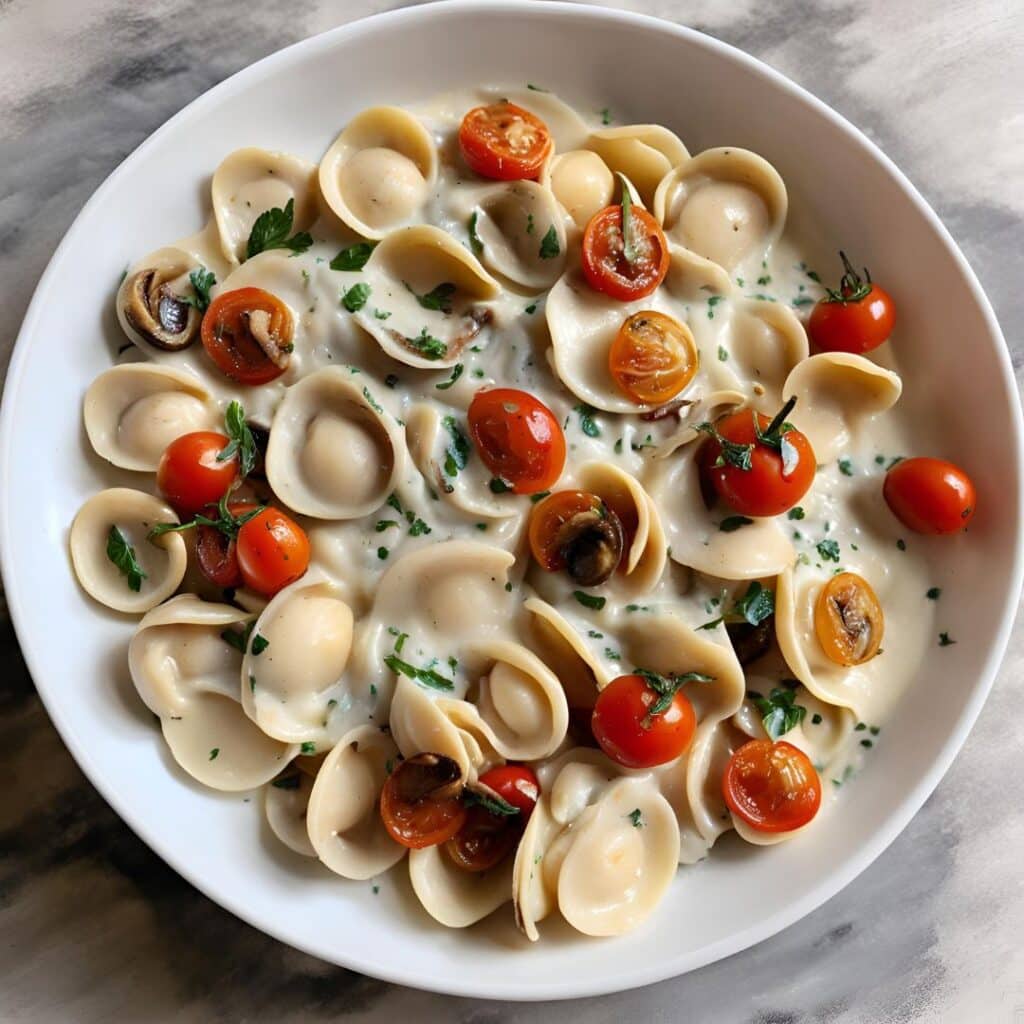
Gut-Healthy Labneh Orecchiette
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Labneh (a sort of yogurt-cheese made from strained yogurt) is a great probiotic, and there’s plenty of resistant starch in this dish too, from how we cook, cool, and reheat the pasta. Add to this the lycopene from the tomatoes, the ergothioneine from the mushrooms, and the healthful properties of the garlic, black pepper, and red chili, and we have a very healthy dish!
You will need
- 10 oz labneh (if you can’t buy it locally, you can make your own by straining Greek yogurt through a muslin cloth, suspended over a bowl to catch the water that drips out, overnight—and yes, plant-based is also fine if you are vegan, and the gut benefits are similar because unlike vegan cheese, vegan yogurt is still fermented)
- 6 oz wholegrain orecchiette (or other pasta, but this shape works well for this sauce)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated
- Juice of ½ lemon
- Large handful chopped parsley
- Large handful chopped dill
- 9 oz cherry tomatoes, halved
- 9 oz mushrooms (your choice what kind), sliced (unless you went for shiitake or similar, which don’t need it due to already being very thin)
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the pasta as you normally would. Drain, and rinse with cold water. Set aside.
2) Combine the labneh with the garlic, black pepper, dill, parsley, and lemon juice, in a large bowl. Set aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil in a skillet; add the chili flakes, followed by the mushrooms. Cook until soft and browned, then add the tomatoes and fry for a further 1 minute—we want the tomatoes to be blistered, but not broken down. Stir in the MSG/salt, and take off the heat.
4) Refresh the pasta by passing a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander, then add the hot pasta to the bowl of labneh sauce, stirring to coat thoroughly.
5) Serve, spooning the mushrooms and tomatoes over the labneh pasta.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
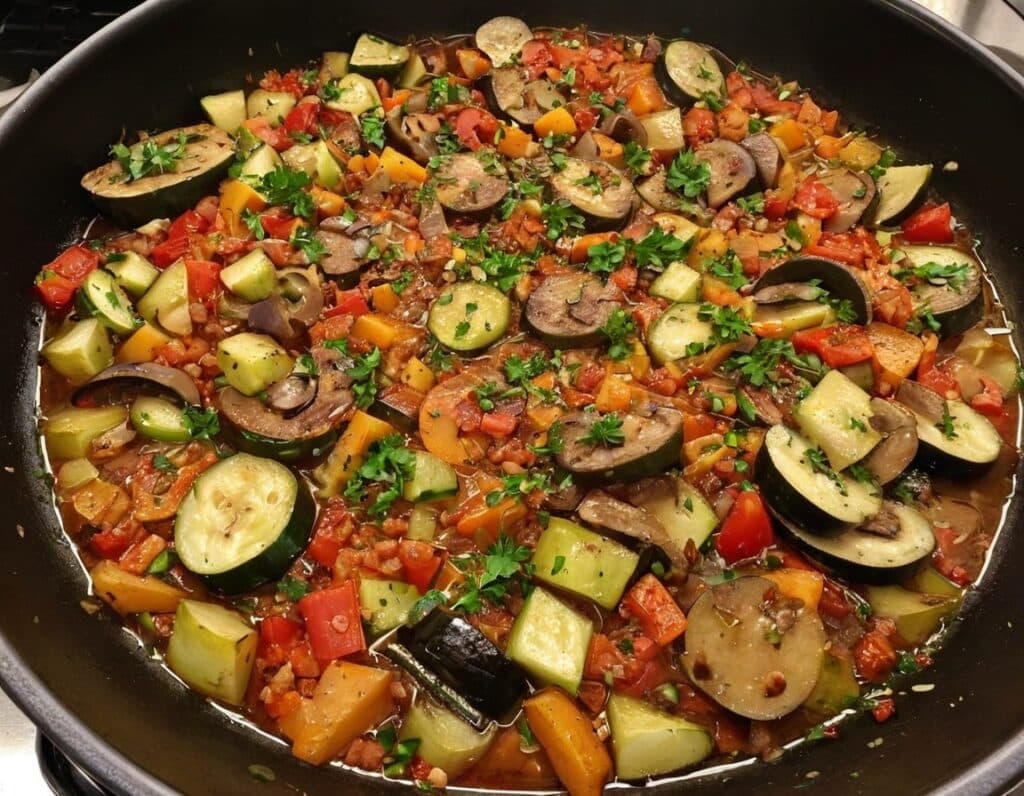
Speedy Easy Ratatouille
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One of the biggest contributing factors to unhealthy eating? The convenience factor. To eat well, it seems, one must have at least two of the following: money, time, and skill. So today we have a health dish that’s cheap, quick, and easy!
(You won’t need a rat in a hat to help you with this one)
You will need
- 3 ripe tomatoes, roughly chopped
- 2 zucchini, halved and chopped into thick batons
- 2 portobello mushrooms, sliced into ½” slices
- 1 large red pepper, cut into thick chunks
- 3 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tbsp finely chopped parsley
- 2 tsp garlic paste
- 2 tsp thyme leaves, destalked
- 1 tsp rosemary leaves, destalked
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper
- Optional: 1 tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low sodium salt (the MSG is the healthier option as it contains less sodium than even low sodium salt)
- Optional: other vegetables, chopped. Use what’s in your fridge! This is a great way to use up leftovers. Particularly good options include chopped eggplant, chopped red onion, and/or chopped carrot.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the olive oil into a sauté pan and set the heat on medium. When hot but smoking, add the mushrooms and any optional vegetables (but not the others from the list yet), and fry for 5 minutes.
Note: if you aren’t pressed for time, then you can diverge from the “speedy” part of this by cooking each of the vegetables separately before combining, which allows each to keep its flavor more distinct.
2) Add the garlic, followed by the zucchini, red pepper, chili flakes, and thyme; stir periodically (you shouldn’t have to stir constantly) for 10 minutes.
3) Add the tomatoes and a cup of water to the pan, along with any MSG/salt. Cover with the lid and allow to simmer for a further 10 minutes.
4) Serve, adding the garnish.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- The Magic Of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we had 3/5 today!
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
- MSG vs Salt: Sodium Comparison
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Aging Minds: Normal vs Abnormal Cognitive Decline
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Having a “senior moment” and having dementia are things that are quite distinct from one another; while we may very reasonably intend to fight every part of it, it’s good to know what’s “normal” as well as what is starting to look like progress into something more severe:
Know the differences
Cognitive abilities naturally decline with age, often beginning around 30 (yes, really—the first changes are mostly metabolic though, so this is far from set in stone). Commonly-noticed changes include:
- slower thinking
- difficulty multitasking
- reduced attention
- weaker memory.
Over time, these changes have what is believed to be a two-way association (as in, each causes/worsens the other) with changes in brain structure, especially reduced hippocampal and frontal lobe volume.
- Gradual cognitive changes are normal with age, whereas dementia involves a pathological decline affecting memory, problem-solving, and behavior.
- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) involves noticeable cognitive decline without disrupting daily life, while dementia affects everyday tasks like cooking or driving.
- Dementia causes significant impairments, including motor challenges like falls or tremors, and dementia-induced cognitive decline symptoms include forgetfulness, getting lost, personality changes, and planning difficulties, often worsening with stress or illness.
To best avoid these, consider: regular exercise, a nutritious diet, good quality sleep, social interaction, and mentally stimulating activities.
Also, often forgotten (in terms of its relevance at least): managing cardiovascular health is very important too. We’ve said it before, and we’ll say it again: what’s good for your heart is good for your brain (since the former feeds the latter with oxygen and nutrients, and also takes away detritus that will otherwise build up in the brain).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Is It Dementia? Spot The Signs (Because None Of Us Are Immune) ← we go into more specific detail here
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
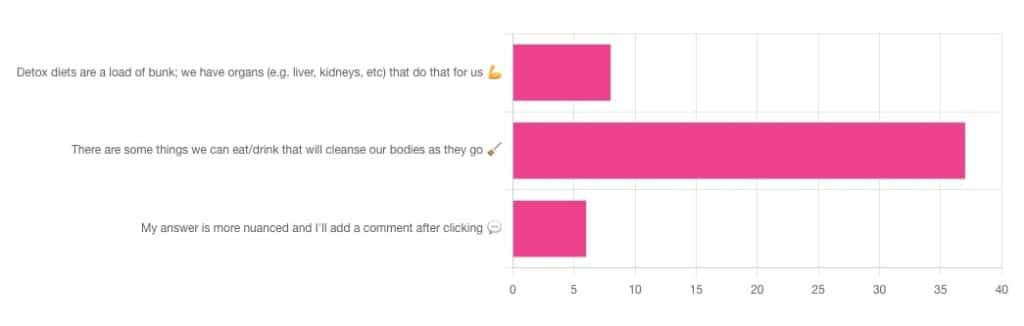
Out of the subscribers who engaged in the poll, it looks like we have a lot of confidence in at least some detox approaches being useful!
Celery juice is most people’s go-to, and indeed it was the only one to get mentioned in the comments added. So let’s take a look at that first…
Celery juice
Celery juice is enjoyed by many people, with many health benefits in mind, including to:
- reduce inflammation
- lower blood pressure
- heal the liver
- fight cancer
- reduce bloating
- support the digestive system
- increase energy
- support weight loss
- promote good mental health
An impressive list! With such an impressive list, we would hope for an impressive weight of evidence, so regular readers might be wondering why those bullet-pointed items aren’t all shiny hyperlinks to studies backing those claims. The reason is…
There aren’t any high-quality studies that back any of those claims.
We found one case study (so, a study with a sample size of one; not amazing) that observed a blood pressure change in an elderly man after drinking celery juice.
Rather than trawl up half of PubMed to show the lacklustre results in a way more befitting of Research Review Monday, though, here’s a nice compact article detailing the litany of disappointment that is science’s observations regards celery juice:
Why Are People Juicing Their Celery? – by Allison Webster, PhD, RD
A key take-away is: juicing destroys the fiber that is celery’s biggest benefit, and its phytochemicals are largely unproven to be of use.
If you enjoy celery, great! It (when not juiced) is a great source of fiber and water. If you juice it, it’s a great source of water.
Activated Charcoal
Unlike a lot of greenery—whose “cleansing” benefits mostly come from fiber and disappear when juiced—activated charcoal has a very different way of operating.
Activated charcoal is negatively charged on a molecular level*, and that—along with its porous nature—traps toxins. It really is a superpowered detox that actually works very well indeed.
But…
It works very well indeed. It will draw out toxins so well, that it’s commonly used to treat poisonings. “Wait”, we hear you say, “why was that a but”?
It doesn’t know what a toxin is. It just draws out all of the things. You took medicine recently? Not any more you didn’t. You didn’t even take that medication orally, you took it some other way? Activated charcoal does not care:
- The effect of activated charcoal on drug exposure following intravenous administration: A meta-analysis
- Activated charcoal for acute overdose: a reappraisal
Does this mean that activated charcoal can be used to “undo” a night of heavy drinking?
Sadly not. That’s one of the few things it just doesn’t work for. It won’t work for alcohol, salts, or metals:
The Use of Activated Charcoal to Treat Intoxications
*Fun chemistry mnemonic about ions:
Cations are pussitive
Anions (by process of elimination) are negative
Onions taste good in salad (remember also: Cole’s Law)
Bottom line on detox foods/drinks:
- Fiber is great; juicing removes fiber. Eat your greens (don’t drink them)!
- Activated charcoal is the heavy artillery of detoxing
- Sometimes it will remove things you didn’t want removed, though
- It also won’t help against alcohol, sadly
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
CBD Oil
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Q&A with the 10almonds Team
Q: Very interested in this article on CBD oil in the states. hope you do another one in the future with more studies done on people and more information on what’s new as far as CBD oil goes
A: We’re glad you enjoyed it! We’ll be sure to revisit CBD in the future—partly because it was a very popular article, and partly because, as noted, there is a lot going on there, research-wise!
And yes, we prefer human studies rather than mouse/rat studies where possible, too, and try to include those where we find them. In some cases, non-human animal studies allow us to know things that we can’t know from human studies… because a research institution’s ethics board will greenlight things for mice that it’d never* greenlight for humans.
Especially: things that for non-human animals are considered “introduction of external stressors” while the same things done to humans would be unequivocally called “torture”.
Animal testing in general is of course a moral quagmire, precisely because of the suffering it causes for animals, while the research results (hopefully) can be brought to bear to reduce to suffering of humans. We’re a health and productivity newsletter, not a philosophical publication, but all this to say: we’re mindful of such too.
And yes, we agree, when studies are available on humans, they’re always going to be better than the same study done on mice and rats.
As a topical aside, did you know there’s a monument to laboratory mice and all they’ve (however unintentionally) done for us?
❝The quirky statue depicts an anthropomorphic mouse as an elderly woman, complete with glasses balanced atop its nose. Emerging from two knitting needles in its hands is the recognizable double-helix of a strand of DNA.❞
~ Smithsonian Magazine
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does This Practice Really Hold A Candle To Evidence-Based Medicine?
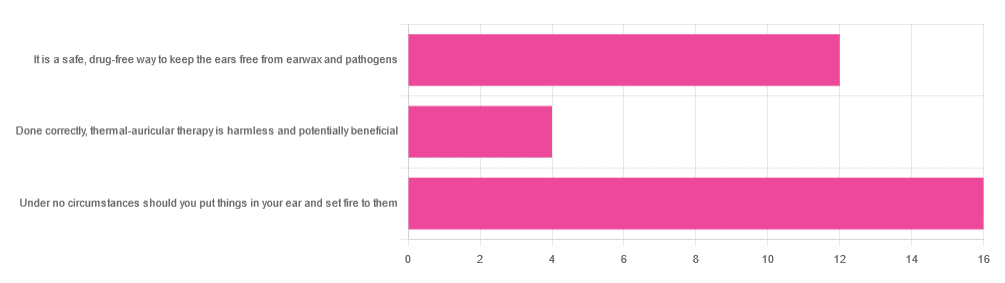
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion of ear candling, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- Exactly 50% said “Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them”
- About 38% said “It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens”
- About 13% said “Done correctly, thermal-auricular therapy is harmless and potentially beneficial”
This means that if we add the two positive-to-candling answers together, it’s a perfect 50:50 split between “do it” and “don’t do it”.
(Yes, 38%+13%=51%, but that’s because we round to the nearest integer in these reports, and more precisely it was 37.5% and 12.5%)
So, with the vote split, what does the science say?
First, a quick bit of background: nobody seems keen to admit to having invented this. One of the major manufacturers of ear candles refers to them as “Hopi” candles, which the actual Hopi tribe has spent a long time asking them not to do, as it is not and never has been used by the Hopi people. Other proposed origins offered by advocates of ear candling include Traditional Chinese Medicine (not used), Ancient Egypt (no evidence of such whatsoever), and Atlantis:
Quackwatch | Why Ear Candling Is Not A Good Idea
It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens: True or False?
False! In a lot of cases of alternative therapy claims, there’s an absence of evidence that doesn’t necessarily disprove the treatment. In this case, however, it’s not even an open matter; its claims have been actively disproven by experimentation:
- It doesn’t remove earwax; on the contrary, experimentation “showed no removal of cerumen from the external auditory canal. Candle wax was actually deposited in some“
- It doesn’t remove pathogens, and the proposed mechanism of action for removing pathogens, that of the “chimney effect”: the idea that the burning candle creates a vacuum that draws wax out of the ear along with debris and bacteria, simply does not work; on the contrary, “Tympanometric measurements in an ear canal model demonstrated that ear candles do not produce negative pressure”.
- It isn’t safe; on the contrary, “Ear candles have no benefit in the management of cerumen and may result in serious injury”
In a medium-sized survey (n=122), the following injuries were reported:
- 13 x burns
- 7 x occlusion of the ear canal
- 6 x temporary hearing loss
- 3 x otitis externa (this also called “swimmer’s ear”, and is an inflammation of the ear, accompanied by pain and swelling)
- 1 x tympanic membrane perforation
Indeed, authors of one paper concluded:
❝Ear candling appears to be popular and is heavily advertised with claims that could seem scientific to lay people. However, its claimed mechanism of action has not been verified, no positive clinical effect has been reliably recorded, and it is associated with considerable risk.
No evidence suggests that ear candling is an effective treatment for any condition. On this basis, we believe it can do more harm than good and we recommend that GPs discourage its use❞
Source: Canadian Family Physician | Ear Candling
Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them: True or False?
True! It’s generally considered good advice to not put objects in general in your ears.
Inserting flaming objects is a definite no-no. Please leave that for the Cirque du Soleil.
You may be thinking, “but I have done this and suffered no ill effects”, which seems reasonable, but is an example of survivorship bias in action—it doesn’t make the thing in question any safer, it just means you were one of the one of the ones who got away unscathed.
If you’re wondering what to do instead… Ear oils can help with the removal of earwax (if you don’t want to go get it sucked out at a clinic—the industry standard is to use a suction device, which actually does what ear candles claim to do). For information on safely getting rid of earwax, see our previous article:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: