Holding Back The Clock on Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Holding Back The Clock on Aging

This is Dr. Eric Verdin, President and CEO of the Buck Institute of Research on Aging. He’s also held faculty positions at the University of Brussels, the NIH, and the Picower Institute for Medical Research. Dr. Verdin is also a professor of medicine at University of California, San Francisco.
Dr. Verdin’s laboratory focuses on the role of epigenetic regulators (especially the behaviors of certain enzymes) in the aging process. He studies how metabolism, diet, and chemical factors regulate the aging process and its associated diseases, including Alzheimer’s.
He has published more than 210 scientific papers and holds more than 15 patents. He is a highly cited scientist and has been recognized for his research with a Glenn Award for Research in Biological Mechanisms of Aging.
And that’s just what we could fit here! Basically, he knows his stuff.
What we can do
Dr. Verdin’s position is bold, but rooted in evidence:
❝Lifestyle is responsible for about 93% of our longevity—only about 7% is genetics. Based on the data, if implementing health lifestyle choices, most people could live to 95 in good health. So there’s 15 to 17 extra years of healthy life that is up for grabs❞
~ Dr. Eric Verdin
See for example:
- From discoveries in aging research to therapeutics for healthy aging
- Optimism, lifestyle, and longevity in a racially diverse cohort of women
- Well-being, food habits, and lifestyle for longevity—evidence from supercentenarians
How we can do it
Well, we all know “the big five”:
- Good diet (Mediterranean Diet as usual is recommended)
- Good exercise (more on this in a moment)
- Good sleep (more on this in a moment)
- Avoid alcohol (not controversial)
- Don’t smoke (need we say more)
When it comes to exercise, generally recognized as good is at least 150 minutes per week of moderate intensity exercise (for example, a brisk walk, or doing the gardening), and at least three small sessions a week of high intensity exercise, unless contraindicated by some medical condition.
As for Dr. Verdin’s take on this…
What Dr. Verdin recommends is:
- make it personalized
- make it pre-emptive
- make it better
The perfect exercise plan is only perfect if you actually do it. And if you actually can do it, for that matter.
Prevention is so much better (and easier) than cure for a whole array of maladies. So while there may be merit in thinking “what needs fixing”, Dr. Verdin encourages us to take extra care to not neglect factors of our health that seem “good enough”. Because, give them time and neglect, and they won’t be!
Wherever we’re at in life and health, there’s always at least some little way we could make it a bit better. Dr. Verdin advises us to seek out those little improvements, even if it’s just a nudge better here, a nudge better there, all those nudges add up!
About sleep…
It’s perhaps the easiest one to neglect (writer’s note: as a writer, I certainly feel that way!), but his biggest take-away tip for this is:
Worry less about what time you set an alarm for in the morning. Instead, set an alarm for the evening—to remind you when to go to bed.
Want to hear directly from the man himself?
Here he is speaking on progress we can expect for the next decade in the field of aging research, as part of the 100 Minutes of Longevity session at The Longevity Forum, a few months ago:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Minimum Method – by Joey Thurman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Trying to squeeze out an extra 0.5% from every effort in life can be exhausting, especially with diminishing marginal returns when it comes to linear increases in effort.
Surely there must be a sweet spot of getting the best returns on the least effort and call it a day?
That’s what this book is about. Thurman examines and explains how to get “the most for least” in various important areas of health, including diet, exercise, sleep, breathwork, recovery, and a chapter specifically on brain health, though of course all the aforementioned things do affect brain health too.
An interesting feature of the book is that at the end of each chapter, he’ll give different advice for different levels of experience/commitment, so that essentially there’s an easy/medium/hard way to proceed each time.
The style is light and personal, without much hard science. The advice given is nonetheless consistent with prevailing scientific consensus, and there are still occasional scientific references throughout, with links to appropriate studies. Mostly though, the focus is on being practical.
Bottom line: if you’ve been looking for a “most for least” way of going about health, this is a fine option.
Click here to check out The Minimum Method, and enjoy benefits disproportionate to your effort!
Share This Post
-
Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong?
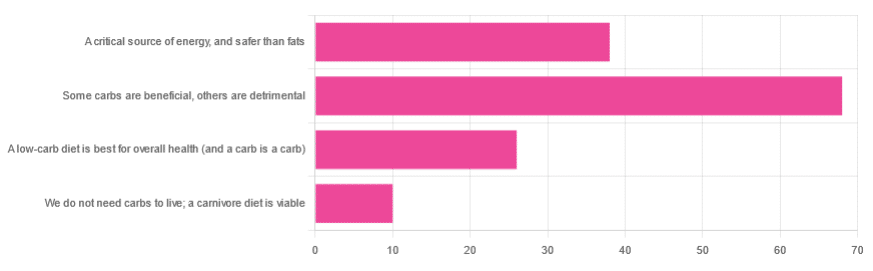
We asked you for your health-related view of carbs, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses
- About 48% said “Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental”
- About 27% said “Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats”
- About 18% said “A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb)”
- About 7% said “We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable”
But what does the science say?
Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats: True or False?
True and False, respectively! That is: they are a critical source of energy, and carbs and fats both have an important place in our diet.
❝Diets that focus too heavily on a single macronutrient, whether extreme protein, carbohydrate, or fat intake, may adversely impact health.❞
Source: Low carb or high carb? Everything in moderation … until further notice
(the aforementioned lead author Dr. de Souza, by the way, served as an external advisor to the World Health Organization’s Nutrition Guidelines Advisory Committee)
Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental: True or False?
True! Glycemic index is important here. There’s a big difference between eating a raw carrot and drinking high-fructose corn syrup:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
While some say grains and/or starchy vegetables are bad, best current science recommends:
- Eat some whole grains regularly, but they should not be the main bulk of your meal (non-wheat grains are generally better)
- Starchy vegetables are not a critical food group, but in moderation they are fine.
To this end, the Mediterranean Diet is the current gold standard of healthful eating, per general scientific consensus:
A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb): True or False?
True-ish and False, respectively. We covered the “a carb is a carb” falsehood earlier, so we’ll look at “a low-carb diet is best”.
Simply put: it can be. One of the biggest problems facing the low-carb diet though is that adherence tends to be poor—that is to say, people crave their carby comfort foods and eat more carbs again. As for the efficacy of a low-carb diet in the context of goals such as weight loss and glycemic control, the evidence is mixed:
❝There is probably little to no difference in weight reduction and changes in cardiovascular risk factors up to two years’ follow-up, when overweight and obese participants without and with T2DM are randomised to either low-carbohydrate or balanced-carbohydrate weight-reducing diets❞
Source: Low-carbohydrate versus balanced-carbohydrate diets for reducing weight and cardiovascular risk
❝On the basis of moderate to low certainty evidence, patients adhering to an LCD for six months may experience remission of diabetes without adverse consequences.
Limitations include continued debate around what constitutes remission of diabetes, as well as the efficacy, safety, and dietary satisfaction of longer term LCDs❞
~ Dr. Joshua Goldenberg et al.
Source: Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission
❝There should be no “one-size-fits-all” eating pattern for different patient´s profiles with diabetes.
It is clinically complex to suggest an ideal percentage of calories from carbohydrates, protein and lipids recommended for all patients with diabetes.❞
Source: Current Evidence Regarding Low-carb Diets for The Metabolic Control of Type-2 Diabetes
We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable: True or False?
False. For a simple explanation:
The Carnivore Diet: Can You Have Too Much Meat?
There isn’t a lot of science studying the effects of consuming no plant products, largely because such a study, if anything other than observational population studies, would be unethical. Observational population studies, meanwhile, are not practical because there are so few people who try this, and those who do, do not persist after their first few hospitalizations.
Putting aside the “Carnivore Diet” as a dangerous unscientific fad, if you are inclined to meat-eating, there is some merit to the Paleo Diet, at least for short-term weight loss even if not necessarily long-term health:
What’s The Real Deal With The Paleo Diet?
For longer-term health, we refer you back up to the aforementioned Mediterranean Diet.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
16/8 Intermittent Fasting For Beginners
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health Insider explains in super-simple fashion why and how to do Intermittent Fasting (IF), which is something that can sound complicated at first, but becomes very simple and easy once understood.
What do we need to know?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a good, well-evidenced way to ease your body’s metabolic load, and
give your organs a chance to recover from the strain of digestion and its effects. That’s not just your gastrointestinal organs! It’s your pancreas and liver too, amongst others—this is about glucose metabolism as much as it is about digestion.This, in turn, allows your body some downtime to do its favorite thing, which is: maintenance!
This maintenance takes the form of enhanced cellular apoptosis and autophagy, helping to keep cells young and cancer-free.
In other words, with well-practised intermittent fasting, we can reduce our risk of metabolic disease (including heart disease and diabetes) as well as cancer and neurodegeneration.
You may be wondering: this sounds miraculous; what’s the catch? There are a couple:
- While fasting from food, the body’s enhanced metabolism requires more water, so you’ll need to take extra care keep on top of your hydration (this is one reason why Ramadan fasting, while healthy for most people, is not as healthy as IF—because Ramadan fasting means abstaining from water, too).
- If you are diabetic, and especially if you have Type 1 Diabetes, fasting may not be a safe option for you, since if you get a hypo in the middle of your fasting period, it’s obviously not a good idea to wait another many hours before fixing it.
Extra note on that last one: it’s easy to think “can’t I just lower my bolus insulin instead of eating?” and while superficially yes that will raise your blood sugar levels, it’s because the sugar will be sticking around in your blood, and not actually getting released into the organs that need it. So while your blood glucose monitor may say you’re fine, you will be starving your organs and if you keep it up they may suffer serious damage.
Disclaimer: our standard legal/medical disclaimer applies, and this is intended for educational purposes only; please do speak with your endocrinologist before changing anything you usually do with regard to your blood sugar maintenance.
Ok, back onto the cheerier topic at hand:
Aside from the above: for most people, IF is a remarkably healthful practice in very many ways.
For more on the science, practicalities, and things to do/avoid, enjoy this short (4:53) video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Want to know more?
Check out our previous main feature on this topic:
Intermittent Fasting: Mythbusting Edition
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What is PMDD?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is a mood disorder that causes significant mental health changes and physical symptoms leading up to each menstrual period.
Unlike premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which affects approximately three out of four menstruating people, only 3 percent to 8 percent of menstruating people have PMDD. However, some researchers believe the condition is underdiagnosed, as it was only recently recognized as a medical diagnosis by the World Health Organization.
Read on to learn more about its symptoms, the difference between PMS and PMDD, treatment options, and more.
What are the symptoms of PMDD?
People with PMDD typically experience both mood changes and physical symptoms during each menstrual cycle’s luteal phase—the time between ovulation and menstruation. These symptoms typically last seven to 14 days and resolve when menstruation begins.
Mood symptoms may include:
- Irritability
- Anxiety and panic attacks
- Extreme or sudden mood shifts
- Difficulty concentrating
- Depression and suicidal ideation
Physical symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Headaches
- Changes in appetite
- Body aches
- Bloating
- Abdominal cramps
- Breast swelling or tenderness
What is the difference between PMS and PMDD?
Both PMS and PMDD cause emotional and physical symptoms before menstruation. Unlike PMS, PMDD causes extreme mood changes that disrupt daily life and may lead to conflict with friends, family, partners, and coworkers. Additionally, symptoms may last longer than PMS symptoms.
In severe cases, PMDD may lead to depression or suicide. More than 70 percent of people with the condition have actively thought about suicide, and 34 percent have attempted it.
What is the history of PMDD?
PMDD wasn’t added to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders until 2013. In 2019, the World Health Organization officially recognized it as a medical diagnosis.
References to PMDD in medical literature date back to the 1960s, but defining it as a mental health and medical condition initially faced pushback from women’s rights groups. These groups were concerned that recognizing the condition could perpetuate stereotypes about women’s mental health and capabilities before and during menstruation.
Today, many women-led organizations are supportive of PMDD being an official diagnosis, as this has helped those living with the condition access care.
What causes PMDD?
Researchers don’t know exactly what causes PMDD. Many speculate that people with the condition have an abnormal response to fluctuations in hormones and serotonin—a brain chemical impacting mood— that occur throughout the menstrual cycle. Symptoms fully resolve after menopause.
People who have a family history of premenstrual symptoms and mood disorders or have a personal history of traumatic life events may be at higher risk of PMDD.
How is PMDD diagnosed?
Health care providers of many types, including mental health providers, can diagnose PMDD. Providers typically ask patients about their premenstrual symptoms and the amount of stress those symptoms are causing. Some providers may ask patients to track their periods and symptoms for one month or longer to determine whether those symptoms are linked to their menstrual cycle.
Some patients may struggle to receive a PMDD diagnosis, as some providers may lack knowledge about the condition. If your provider is unfamiliar with the condition and unwilling to explore treatment options, find a provider who can offer adequate support. The International Association for Premenstrual Disorders offers a directory of providers who treat the condition.
How is PMDD treated?
There is no cure for PMDD, but health care providers can prescribe medication to help manage symptoms. Some medication options include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), a class of antidepressants that regulate serotonin in the brain and may improve mood when taken daily or during the luteal phase of each menstrual cycle.
- Hormonal birth control to prevent ovulation-related hormonal changes.
- Over-the-counter pain medication like Tylenol, which can ease headaches, breast tenderness, abdominal cramping, and other physical symptoms.
Providers may also encourage patients to make lifestyle changes to improve symptoms. Those lifestyle changes may include:
- Limiting caffeine intake
- Eating meals regularly to balance blood sugar
- Exercising regularly
- Practicing stress management using breathing exercises and meditation
- Having regular therapy sessions and attending peer support groups
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
If you or anyone you know is considering suicide or self-harm or is anxious, depressed, upset, or needs to talk, call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or text the Crisis Text Line at 741-741. For international resources, here is a good place to begin.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
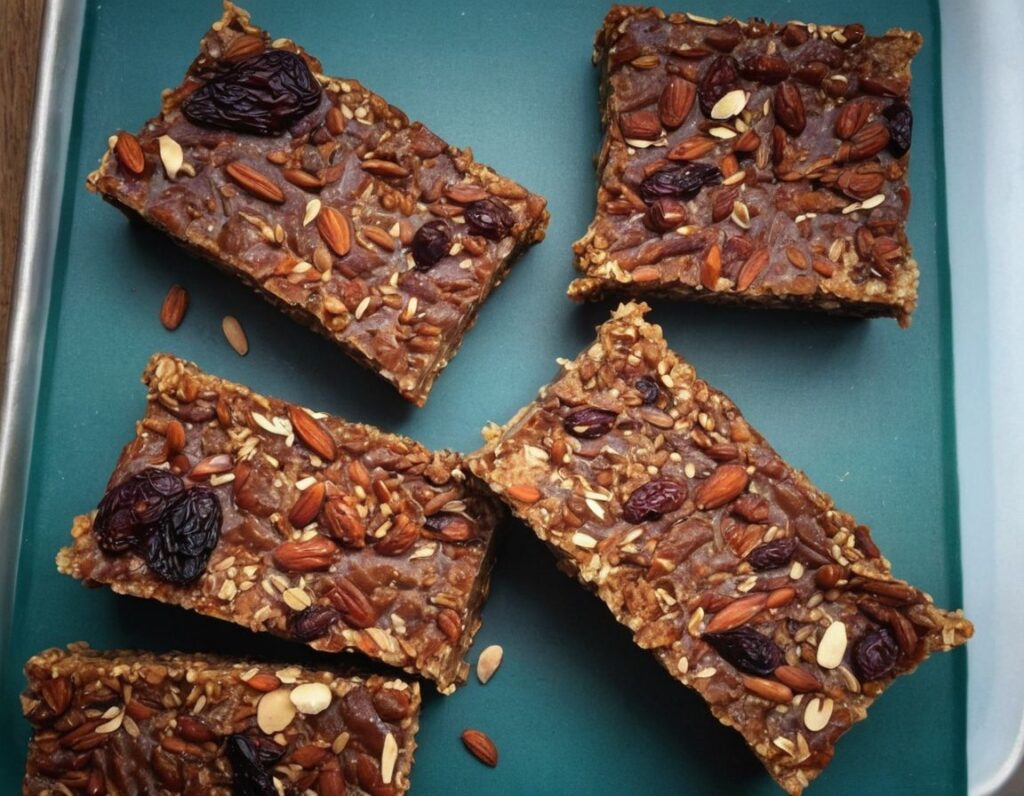
Balanced Energy Cake Bars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Unlike a lot of commercially available products, these bars won’t spike your blood sugars in the same way. There’s technically plenty of sugar in them, mostly from the chopped dates, but they’re also full of fiber, protein, and healthy fats. This means they can give you an energy boost (along with lots of gut-healthy, heart-healthy, and brain-healthy ingredients) without any crash later. They’re also delicious, and make for a great afternoon snack!
You will need
- 1 cup oats
- 15 Medjool dates, pitted and soaked in hot water for 15 minutes
- 3 carrots, grated
- 4oz almond butter
- 2 tbsp tahini
- 2 tbsp flaxseeds, milled
- 1 tbsp sesame seeds, toasted
- Optional: your choice of dried fruit and/or chopped nuts (mix it up; diversity is good!)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Steam the grated carrots for 3–4 minutes; pat dry and allow to cool
2) Drain and pat dry the dates, roughly chop them and add them to a bowl with the carrots. Because we chopped the dates rather than blended them (as many recipes do), they keep their fiber, which is important.
3) Add the oats, seeds, almond butter, and tahini. Also add in any additional dried fruit and/or chopped nuts you selected for the optional part. Mix well; the mixture should be quite firm. If it isn’t, add more oats.
4) Press the mixture into a 10″ square baking tin lined with baking paper. Refrigerate for a few hours, before cutting into bar shapes (or squares if you prefer). These can now be eaten immediately or stored for up to a week.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Behind Book Recommendations
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: What’s the process behind the books you recommend? You seem to have a limitless stream of recommendations
We do our best!
The books we recommend are books that…
- are on Amazon—it makes things tidy, consistent, and accessible. And if you end up buying one of the books, we get a small affiliate commission*.
- we have read—we would say “obviously”, but you might be surprised how many people write about books without having read them.
- pertain in at least large part to health and/or productivity.
- are written by humans—bookish people (and especially Kindle Unlimited users) may have noticed lately that there are a lot of low quality AI-written books flooding the market, sometimes with paid 5-star reviews to bolster them. It’s frustrating, but we can tell the difference and screen those out.
- are of a certain level of quality. They don’t have to be “top 5 desert-island books”, because well, there’s one every day and the days keep coming. But they do have to genuinely deliver the value that we describe, and merit a sincere recommendation.
- are varied—we try to not give a run of “samey” books one after another. We will sometimes review a book that covers a topic another previously-reviewed book did, but it must have something about it that makes it different. It may be a different angle or a different writing style, but it needs something to set it apart.
*this is from Amazon and isn’t product-specific, so this is not affecting our choice of what books to review at all—just that they will be books that are available on Amazon.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: