Scheduling Tips for Overrunning Tasks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Your Questions, Our Answers!
Q: Often I schedule time for things, but the task takes longer than I think, or multiplies while I’m doing it, and then my schedule gets thrown out. Any ideas?
A: A relatable struggle! Happily, there are remedies:
- Does the task really absolutely need to be finished today? If not, just continue it in scheduled timeslots until it’s completed.
- Some tasks do indeed need to be finished today (hi, writer of a daily newsletter here!), so it can be useful to have an idea of how long things really take, in advance. While new tasks can catch us unawares, recurring or similar-to-previous tasks can be estimated based on how long they took previously. For this reason, we recommend doing a time audit every now and again, to see how you really use your time.
- A great resource that you should include in your schedule is a “spare” timeslot, ideally at least one per day. Call it a “buffer” or a “backup” or whatever (in my schedule it’s labelled “discretionary”), but the basic idea is that it’s a scheduled timeslot with nothing scheduled in it, and it works as an “overflow” catch-all.
Additionally:
- You can usually cut down the time it takes you to do tasks by setting “Deep Work” rules for yourself. For example: cut out distractions, single-task, work in for example 25-minute bursts with 5-minute breaks, etc
- You can also usually cut down the time it takes you to do tasks by making sure you’re prepared for them. Not just task-specific preparation, either! A clear head on, plenty of energy, the resources you’ll need (including refreshments!) to hand, etc can make a huge difference to efficiency.
See Also: Time Optimism and the Planning Fallacy
Do you have a question you’d like to see answered here? Hit reply or use the feedback widget at the bottom; we’d love to hear from you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Surgery won’t fix my chronic back pain, so what will?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This week’s ABC Four Corners episode Pain Factory highlighted that our health system is failing Australians with chronic pain. Patients are receiving costly, ineffective and risky care instead of effective, low-risk treatments for chronic pain.
The challenge is considering how we might reimagine health-care delivery so the effective and safe treatments for chronic pain are available to millions of Australians who suffer from chronic pain.
One in five Australians aged 45 and over have chronic pain (pain lasting three or more months). This costs an estimated A$139 billion a year, including $12 billion in direct health-care costs.
The most common complaint among people with chronic pain is low back pain. So what treatments do – and don’t – work?
Opioids and invasive procedures
Treatments offered to people with chronic pain include strong pain medicines such as opioids and invasive procedures such as spinal cord stimulators or spinal fusion surgery. Unfortunately, these treatments have little if any benefit and are associated with a risk of significant harm.
Spinal fusion surgery and spinal cord stimulators are also extremely costly procedures, costing tens of thousands of dollars each to the health system as well as incurring costs to the individual.
Addressing the contributors to pain
Recommendations from the latest Australian and World Health Organization clinical guidelines for low back pain focus on alternatives to drug and surgical treatments such as:
- education
- advice
- structured exercise programs
- physical, psychological or multidisciplinary interventions that address the physical or psychological contributors to ongoing pain.

Pain education is central. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Two recent Australian trials support these recommendations and have found that interventions that address each person’s physical and psychological contributors to pain produce large and sustained improvements in pain and function in people with chronic low back pain.
The interventions have minimal side effects and are cost-effective.
In the RESOLVE trial, the intervention consists of pain education and graded sensory and movement “retraining” aimed to help people understand that it’s safe to move.
In the RESTORE trial, the intervention (cognitive functional therapy) involves assisting the person to understand the range of physical and psychological contributing factors related to their condition. It guides patients to relearn how to move and to build confidence in their back, without over-protecting it.
Why isn’t everyone with chronic pain getting this care?
While these trials provide new hope for people with chronic low back pain, and effective alternatives to spinal surgery and opioids, a barrier for implementation is the out-of-pocket costs. The interventions take up to 12 sessions, lasting up to 26 weeks. One physiotherapy session can cost $90–$150.
In contrast, Medicare provides rebates for just five allied health visits (such as physiotherapists or exercise physiologists) for eligible patients per year, to be used for all chronic conditions.
Private health insurers also limit access to reimbursement for these services by typically only covering a proportion of the cost and providing a cap on annual benefits. So even those with private health insurance would usually have substantial out-of-pocket costs.
Access to trained clinicians is another barrier. This problem is particularly evident in regional and rural Australia, where access to allied health services, pain specialists and multidisciplinary pain clinics is limited.
Higher costs and lack of access are associated with the increased use of available and subsidised treatments, such as pain medicines, even if they are ineffective and harmful. The rate of opioid use, for example, is higher in regional Australia and in areas of socioeconomic disadvantage than metropolitan centres and affluent areas.
So what can we do about it?
We need to reform Australia’s health system, private and public, to improve access to effective treatments for chronic pain, while removing access to ineffective, costly and high-risk treatments.
Better training of the clinical workforce, and using technology such as telehealth and artificial intelligence to train clinicians or deliver treatment may also improve access to effective treatments. A recent Australian trial, for example, found telehealth delivered via video conferencing was as effective as in-person physiotherapy consultations for improving pain and function in people with chronic knee pain.
Advocacy and improving the public’s understanding of effective treatments for chronic pain may also be helpful. Our hope is that coordinated efforts will promote the uptake of effective treatments and improve the care of patients with chronic pain.
Christine Lin, Professor, University of Sydney; Christopher Maher, Professor, Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney; Fiona Blyth, Professor, University of Sydney; James Mcauley, Professor of Psychology, UNSW Sydney, and Mark Hancock, Professor of Physiotherapy, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post

Foot Drop!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Interesting about DVT after surgery. A friend recently got diagnosed with foot drop. Could you explain that? Thank you.❞
First, for reference, the article about DVT after surgery was:
DVT Risk Management Beyond The Socks
As for foot drop…
Foot drop is descriptive of the main symptom: the inability to raise the front part of the foot due to localized weakness/paralysis. Hence, if a person with foot drop dangles their feet over the edge of the bed, for example, the affected foot will simply flop down, while the other (if unaffected) can remain in place under its own power. The condition is usually neurological in origin, though there are various more specific causes:
When walking unassisted, this will typically result in a distinctive “steppage gait”, as it’s necessary to lift the foot higher to compensate, or else the toes will scuff along the ground.
There are mobility aids that can return one’s walking to more or less normal, like this example product on Amazon.
Incidentally, the above product will slightly shorten the lifespan of shoes, as it will necessarily pull a little at the front.
There are alternatives that won’t like this example product on Amazon, but this comes with the different problem that it limits the user to stepping flat-footedly, which is not only also not an ideal gait, but also, will serve to allow any muscles down there that were still (partially or fully) functional to atrophy. For this reason, we’d recommend the first product we mentioned over the second one, unless your personal physiotherapist or similar advises otherwise (because they know your situation and we don’t).
Both have their merits, though:
Trends and Technologies in Rehabilitation of Foot Drop: A Systematic Review
Of course, prevention is better than cure, so while some things are unavoidable (especially when it comes to neurological conditions), we can all look after our nerve health as well as possible along the way:
Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
…as well as the very useful:
What Does Lion’s Mane Actually Do, Anyway?
…which this writer personally takes daily and swears by (went from frequent pins-and-needles to no symptoms and have stayed that way, and that’s after many injuries over the years).
If you’d like a more general and less supplements-based approach though, check out:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Share This Post

How to Find Happiness In Yourself – by Michelle Mann
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of books about happiness tell you what to pursue, generally. What things to focus on, and that’s good, but incomplete. This book does cover those things too (complete with academic sources to back up what really works), but also goes further:
Michelle Mann gives 25 key habits that will cumulatively build happiness, which is what it’s really about. After all:
- If you watch your favourite movie, you’ll be happy for 90 minutes (or 9 hours if it’s The Lord of the Rings).
- If you build daily habits that add happiness to you, your surroundings, and those around you, you’ll be happy for life.
They do also cover happiness while going through difficult times, such as divorce, job loss, illness, or bereavement.
Sometimes, knowing what we “should” do in theory is the easy part. Where Mann excels here is in providing explanations of each habit. This means that rather than it being some platitude, the principles underlying it are truly understood… and thus motivate us to actually apply the advice and build the habits into our life.
While the explanations are therefore the greatest value of the book, we do recommend copying out the 25 habits (which are effectively subchapter headings) and putting them somewhere to read often.
Bottom line: we recommend getting yourself (and/or your loved ones!) a copy of this book. You (and/or they) will be happy you did!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Coconut Milk vs Soy Milk – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing coconut milk to soy milk, we picked the soy.
Why?
First, because there are many kinds of both, let’s be clear which ones we’re comparing. For both, we picked the healthiest options commonly available, which were:
- Soy milk, unsweetened, fortified
- Coconut milk, raw (liquid expressed from grated meat and water)
Macronutrients are our first consideration; coconut milk has about 3x the carbs and about 14x the fat. Now, the fats are famously healthy medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), but still, one cup of coconut milk contains about 2.5x the recommended daily amount of saturated fat, so it’s wise to go easy on that. Coconut milk also has about 4x the fiber, but still, because the saturated fat difference, we’re calling this one a win for soy milk.
In the category of vitamins, the fortified soy milk wins. In case you’re curious: milk in general (animal or plant) is generally fortified with vitamin D (in N. America, anyway; other places may vary), and vitamin B12. In this case, the soy milk has those, plus some natural vitamins, meaning it has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and D, while coconut milk has more of vitamins B3, B5, and C. A fair win for soy milk.
When it comes to minerals, the only fortification for the soy milk is calcium, of which it has more than 7x what coconut milk has. The coconut milk, however, has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium. An easy win for coconut milk.
Adding up the sections gives us a win for soy milk—but if consumed in moderation as part of a diet otherwise low in saturated fat, a case could be made for the coconut.
The real take-away here today is not this specific head-to-head but rather: milks (animal or plant) vary a lot, have a lot of different fortifications and/or additives, and yes that goes even for brands (cow milk brands do this a lot) who don’t advertise their additives because their branding is going for a “natural” look. So, read labels, and make informed decisions about which additives you do or don’t want.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Reduce Caffeine’s Impact on Kidneys
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Avid coffee drinker so very interested in the results Also question Is there something that you could take or eat that would prevent the caffeine from stimulating the kidneys? I tried to drink decaf from morning to night not a good result! Thanks❞
That is a good question! The simple answer is “no” (but keep reading, because all is not lost)
There’s no way (that we yet know of) to proof the kidneys against the stimulating effect of caffeine. This is especially relevant because part of caffeine’s stimulating effect is noradrenergic, and that “ren” in the middle there? It’s about the kidneys. This is just because the adrenal gland is situated next to them (actually, it’s pretty much sitting on top of them), hence the name, but it does mean that the kidneys are about the hardest thing in the body to have not effected by caffeine.
However! The effects of caffeine in general can be softened a little with l-theanine (found in tea, or it can be taken as a supplement). It doesn’t stop it from working, but it makes the curve of the effect a little gentler, and so it can reduce some unwanted side effects.
You can read more about l-theanine here:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

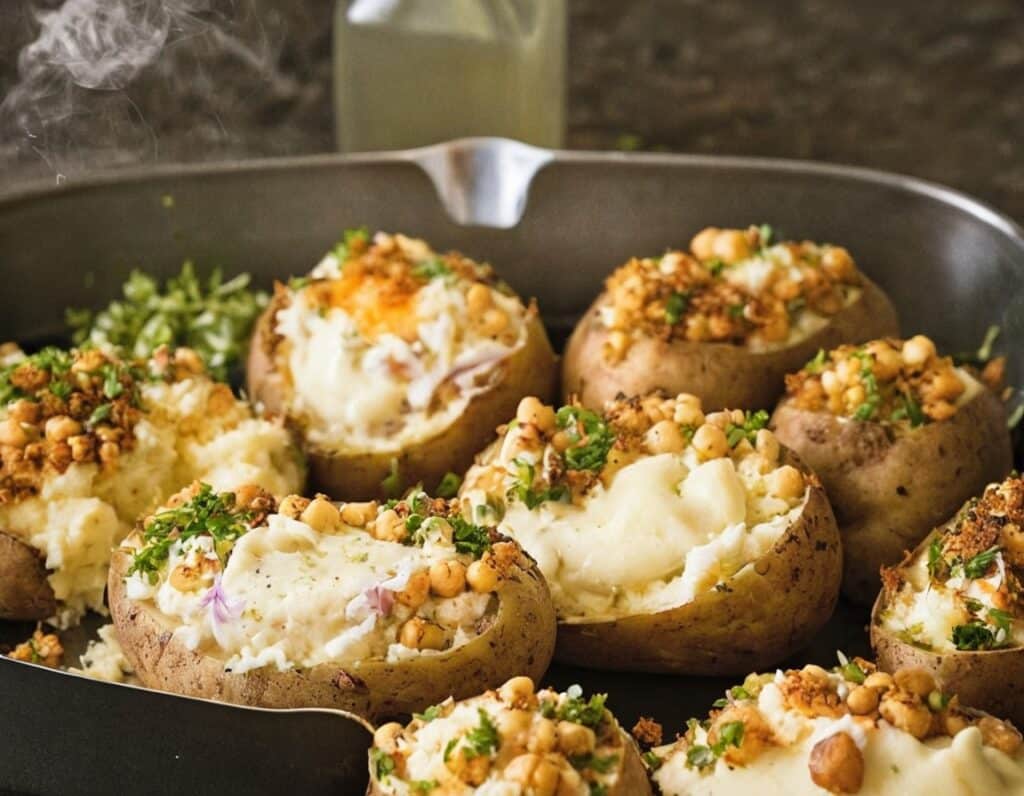
Twice-Baked Stuffed Potatoes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Packed with protein and fiber and dosed with healthy spices, these tasty treats can be enjoyed hot as they are, or cold as part of a salad dinner.
You will need
- 4 large baking potatoes
- 2 cans chickpeas, drained
- 1 can coconut milk
- ½ cup shredded mozzarella cheese, or plant-based alternative
- 1 bulb garlic (sounds like a lot, but this is about three cloves per potato; adjust if you want, though)
- 3 tbsp chopped pickled jalapeños
- 1 tbsp black pepper
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp dried thyme
- 1 tsp onion powder
- Toppings: smoked paprika, finely chopped parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Wash, prick, and bake the potatoes—the latter being for an hour, or until tender.
3) Remove them from the oven and lower the temperature to 350℉ / 175℃.
4) Cut the potatoes lengthways and scoop out the insides into a food processor, leaving enough in the potato that it can hold its shape.
5) Add the remaining ingredients (except the toppings, and half the chickpeas) to the food processor, and blend until smooth.
6) Stuff the filling back into the potato shells (by simple physics of volume, you’ll have a little more than you need, but make it heaped mounds rather than a flat fill-in, and you can probably use most of it, if not all), add the other half of the chickpeas on top and then finally the paprika dusting, and bake for a further 20 minutes.
7) Serve, adding the chopped parsley garnish.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: