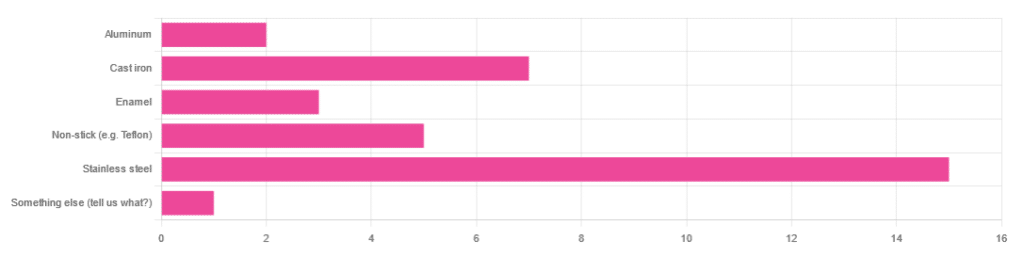
Salmon vs Tuna – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing salmon to tuna, we picked the tuna.
Why?
It’s close, and there are merits and drawbacks to both!
In terms of macros, tuna is higher in protein, while salmon is higher in fats. How healthy are the fats, you ask? Well, it’s a mix, because while there are plenty of “good” fats in salmon, salmon is also 10x higher in saturated fat and 150% higher in cholesterol.
So when it comes to fats, if you want to eat fish and have the healthiest fats, one option is to skip the salmon, and instead serve tuna with some extra virgin olive oil.
We’ll call this section a clear win for tuna.
On the vitamin front, they are close to equal. Salmon has more of some vitamins, tuna has more of others; all in all we’d say the balance is in salmon’s favor, but by the time a portion of salmon is giving you 350% of your daily requirement, does it really matter that the same portion of tuna is “only” giving you 294% of the daily requirement? It goes like that for a lot of the vitamins they both contain.
Still, we’ll call this section a nominal win for salmon.
In the category of minerals, tuna is much higher in iron while salmon is higher in calcium. The rest of the minerals they both have, tuna is comfortably higher—and since the “% of RDA in a portion” figures are double-digit here rather than triple, those margins are relevant this time.
We’ll call this section a moderate win for tuna.
Both fish carry a risk of mercury poisoning, but this varies more by location than by fish, so it hasn’t been a consideration in this head-to-head.
Totting up the sections, this a modest but clear win for tuna.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild-Caught: Important Differences!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mythbusting Cookware Materials
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you what kind of cookware you mostly use, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 45% said stainless steel
- About 21% said cast iron
- About 15% said non-stick (e.g. Teflon)
- About 9% said enamel
- About 6% said aluminum
- And 1 person selected “something else”, but then commented to the contrary, writing “I use all of the above”
So, what does the science say about these options?
Stainless steel cookware is safe: True or False?
True! Assuming good quality and normal use, anyway. There really isn’t a lot to say about this, because it’s very unexciting. So long as it is what it is labelled as: there’s nothing coating it, nothing comes out of it unless you go to extremes*, and it’s easy to clean.
*If you cook for long durations at very high temperatures, it can leach nickel and chromium into food. What this means in practical terms: if you are using stainless steel to do deep-frying, then maybe stop that, and also consider going easy on deep-frying in general anyway, because obviously deep-frying is unhealthy for other reasons.
Per normal use, however: pretty much the only way (good quality) stainless steel cookware will harm you is if you touch it while it’s hot, or if it falls off a shelf onto your head.
That said, do watch out for cheap stainless steel cookware that can contain a lot of impurities, including heavy metals. Since you probably don’t have a mass spectrometer and/or chemistry lab at home to check for those impurities, your best guard here is simply to buy from a reputable brand with credible certifications.
Ceramic cookware is safe: True or False?
True… Most of the time! Ceramic pans usually have metal parts and a ceramic cooking surface coated with a very thin layer of silicon. Those metal parts will be as safe as the metals used, so if that’s stainless steel, you’re just as safe as the above. As for the silicon, it is famously inert and body-safe (which is why it’s used in body implants).
However: ceramic cookware that doesn’t have an obvious metal part and is marketed as being pure ceramic, will generally be sealed with some kind of glaze that can leach heavy metals contaminants into the food; here’s an example:
Lead toxicity from glazed ceramic cookware
Copper cookware is safe: True or False?
False! This is one we forgot to mention in the poll, as one doesn’t see a lot of it nowadays. The copper from copper pans can leach into food. Now, of course copper is an important mineral that we must get from our diet, but the amount of copper that that can leach into food from copper pans is far too much, and can induce copper toxicity.
In addition, copper cookware has been found to be, on average, highly contaminated with lead:
Non-stick cookware contaminates the food with microplastics: True or False?
True! If we were to discuss all the common non-stick contaminants here, this email would no longer fit (there’s a size limit before it gets clipped by most email services).
Suffice it to say: the non-stick coating, polytetrafluoroethylene, is itself a PFAS, that is to say, part of the category of chemicals considered environmental pollutants, and associated with a long list of health issues in humans (wherein the level of PFAS in our bloodstream is associated with higher incidence of many illnesses):
You may have noticed, of course, that the “non-stick” coating doesn’t stick very well to the pan, either, and will tend to come off over time, even if used carefully.
Also, any kind of wet cooking (e.g. saucepans, skillets, rice cooker inserts) will leach PFAS into the food. In contrast, a non-stick baking tray lined with baking paper (thus: a barrier between the tray and your food) is really not such an issue.
We wrote about PFAS before, so if you’d like a more readable pop-science article than the scientific paper above, then check out:
PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
Aluminum cookware contaminates the food with aluminum: True or False?
True! But not usually in sufficient quantities to induce aluminum toxicity, unless you are aluminum pans Georg who eats half a gram of aluminum per day, who is a statistical outlier and should not be counted.
That’s a silly example, but an actual number; the dose required for aluminum toxicity in blood is 100mg/L, and you have about 5 liters of blood.
Unless you are on kidney dialysis (because 95% of aluminum is excreted by the kidneys, and kidney dialysis solution can itself contain aluminum), you will excrete aluminum a lot faster than you can possibly absorb it from cookware. On the other hand, you can get too much of it from it being a permitted additive in foods and medications, for example if you are taking antacids they often have a lot of aluminum oxide in them—but that is outside the scope of today’s article.
However, aluminum may not be the real problem in aluminum pans:
❝In addition, aluminum (3.2 ± 0.25 to 4.64 ± 0.20 g/kg) and copper cookware (2.90 ± 0.12 g/kg) were highly contaminated with lead.
The time and pH-dependent study revealed that leaching of metals (Al, Pb, Ni, Cr, Cd, Cu, and Fe, etc.) into food was predominantly from anodized and non-anodized aluminum cookware.
More metal leaching was observed from new aluminum cookware compared to old. Acidic food was found to cause more metals to leach during cooking.❞
~ the same paper we cited when talking about copper
Cast iron cookware contaminates the food with iron: True or False?
True, but unlike with the other metals discussed, this is purely a positive, and indeed, it’s even recommended as a good way to fortify one’s diet with iron:
The only notable counterpoint we could find for this is if you have hemochromatosis, a disorder in which the body is too good at absorbing iron and holding onto it.
Thinking of getting some new cookware?
Here are some example products of high-quality safe materials on Amazon, but of course feel free to shop around:
Stainless Steel | Ceramic* | Cast Iron
*it says “non-stick” in the description, but don’t worry, it’s ceramic, not Teflon etc, and is safe
Bonus: rice cooker with stainless steel inner pot
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Dealing With Hearing Loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hearing is important, not only for convenience, but also for cognitive health—as an inability to participate in what for most people is an important part of social life, has been shown to accelerate cognitive decline:
14 Powerful Strategies To Prevent Dementia ← one of them is looking after your hearing
To this end, we’ve written before about ways to retain (or at least slow the loss of) your hearing, here:
But, what if, despite our best efforts, your hearing is declining regardless, or is already impaired in some way?
Working with the hand we’ve been dealt
So, your hearing is bad and/or deteriorating. Assuming you’ve ruled out possibilities of fixing it, the next step is how to manage this new state of affairs.
One thing to seriously consider, sooner than you think you need to, is using hearing aids. This is because they will not only help you in the obvious practical way, but also, they will slow the associated decline of the parts of your brain that process the language you hear:
ACHIEVE study finds hearing aids cut cognitive decline by 48%
…and here’s the paper itself:
Furthermore, hearing aid use can significantly reduce all-cause mortality:
Your ears are not the only organs
Remember, today’s about dealing with hearing loss, not preventing it (for preventing it, see the second link we dropped up top).
With this in mind: do not underestimate the usefulness of learning to lipread.
Lipreading is not a panacea; it has its limitations:
- You can’t lipread an audio-only phonecall, or a podcast, or the radio
- You can’t lipread a video call if the video quality is poor
- You can’t lipread if someone is wearing a mask (as in many healthcare settings)
- You can’t lipread multiple people at once; you have to choose whose mouth to watch (or at least, you will miss the first word(s) each time while switching)
- You can’t lipread during sex if your/their face is somewhere else (may seem like a silly example, but actually communication can be important in sex, and the number of times this writer has had to say “Say again?” in intimate moments is ridiculous)
However, it can also make a huge difference the rest of the time, and can even be a superpower in times/places when other people’s hearing is nullified, such as a noisy environment, or a video call in which someone’s mic isn’t working.
The good news is, it’s really very easy to learn to lipread. There are many valid ways (often involving consciously memorizing mouth-shapes from charts, and then putting them together one by one to build a vocabulary), but this writer recommends a more organic, less effort-intensive approach:
- Choose a video of someone who speaks clearly, and for which video you already know what is being said (such as by using subtitles first, or a transcript, or perhaps the person is delivering a famous speech or reciting a poem that you know well, or it’s your favorite movie that you’ve watched many times).
- Now watch it with the sound off (assuming you do normally have some hearing; if you don’t, then you’re probably ahead of the game here) and just pay close attention to the lips. Do this on repeat; soon you’ll be able to “hear” the sounds as you see them made.
- Now choose a video of someone who speaks clearly, for which video you do not already know what is being said. You’ll probably only get parts of it at first; that’s ok.
- Now learn the rest of what they said in that video (by reading a transcript or such), and use it like you used the first video.
- Now repeat steps 3 and 4 until you are lipreading most people easily unless there is some clear obfuscation preventing you.
This process should not take long, as there are only about 44 phonemes (distinct sounds) in English, and once you’ve learned them, you’re set. If you speak more languages, those same 44 phonemes should cover most of most of them, but if not, just repeat the above process with the next language.
Remember, if you have at least some hearing, then most of the time your lipreading and your hearing are going to be working together, and neither will be as strong without the other—but if necessary, well-practised lipreading can indeed often stand in for hearing when hearing isn’t available.
A note on sign language:
Sign language is great, and cool, and useful. However, it’s only as useful as the people who know it, which means that it’s top-tier in the Deaf community (where people will dodge hearing-related cognitive decline entirely, because their social interaction is predominantly signed rather than spoken), and can be useful with close friends or family members who learn it (or at least learn some), but isn’t as useful in most of the wider world when people don’t know it. But if you do want to learn it, don’t let that hold you back—be the change you want to see!
Most of our readers are American, so here’s a good starting place for American Sign Language ← this is a list of mostly-free resources
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
7 Days Of Celery Juice: What’s The Verdict?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Laura “Try” tries many popular trends, and reports on the benefits (or problems, or both). In this case, it’s 7 days of celery juice… Not as a fast, though, i.e. she doesn’t just have celery juice for 7 days, but rather, it’s how she kicks off each morning, with half a liter (16oz) on an empty stomach.
What she found
First, she bought a masticating juicer and organic celery. So, those are expenses to consider, especially the one-off expense of the juicer, and the ongoing expense of organic celery—estimated $90/month).
In terms of taste, she was surprised it wasn’t as bitter as expected, but from the second day onwards, she did use the juicer’s filter to remove the frothy sludge, and she also switched to juicing only the stalks, not the leaves—which are more bitter.
10almonds note: the leaves are more bitter because that’s where the polyphenols are more densely concentrated. The leaves are better for you than the stalks. Enjoy the leaves. Really: if you chop them finely you can use them as herbs in your cooking, and if you’re making a salad, just chop them into that too.
The reason she picked the quantity of half a liter is because this is what she found recommended to coat the stomach lining—on the promise of increased stomach acid production, reduced bacteria overgrowth, as well as antiviral, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties. As she’s just one woman without a personal lab, she couldn’t test and thus verify any of these though—but she did still have benefits to report:
She did experience clearer skin, more energy, and better sleep after a few days.
Ultimately, she decided to continue to do it just at the weekends, due to its positive effects, despite the cost and time consumption.
For more personal insights, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Artichoke vs Asparagus – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing artichoke to asparagus, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Both are great and it was close!
In terms of macros, artichoke has a little more protein and around 3x the carbs and fiber: the ratio there means that both vegetables have an identical glycemic index, so we’ll go with the “most food per food” reckoning of nutritional density, and call it for the artichoke.
When it comes to vitamins, artichoke has more of vitamins B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline, while asparagus has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, E, and K. Both very respectable nutritional sets, but artichoke gets a marginal 6:5 win on strength of numbers.
In the category of minerals, artichoke has more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while asparagus has more iron, selenium, and zinc. A clearer 6:3 win for artichoke this time.
Once again, both of these are great foods, so by all means enjoy either or both. But if you’re looking for the nutritionally densest option, it’s the artichoke!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Zuranolone: What to know about the pill for postpartum depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In the year after giving birth, about one in eight people who give birth in the U.S. experience the debilitating symptoms of postpartum depression (PPD), including lack of energy and feeling sad, anxious, hopeless, and overwhelmed.
Postpartum depression is a serious, potentially life-threatening condition that can affect a person’s bond with their baby. Although it’s frequently confused with the so-called “baby blues,” it’s not the same.
The baby blues include similar, temporary symptoms that affect up to 80 percent of people who have recently given birth and usually go away within the first few weeks. PPD usually begins within the first month after giving birth and can last for months and interfere with a person’s daily life if left untreated. Thankfully, PPD is treatable and there is help available.
On August 4, the FDA approved zuranolone, branded as Zurzuvae, the first-ever oral medication to treat PPD. Until now, besides other common antidepressants, the only medication available to treat PPD specifically was the IV injection brexanolone, which is difficult to access and expensive and can only be administered in a hospital or health care setting.
Read on to find out more about zuranolone: what it is, how it works, how much it costs, and more.
What is zuranolone?
Zurzuvae is the brand name for zuranolone, an oral medication to treat postpartum depression. Developed by Sage Therapeutics in partnership with Biogen, it’s now available in the U.S. Zurzuvae is typically prescribed as two 25 mg capsules a day for 14 days. In clinical trials, the medication showed to be fast-acting, improving PPD symptoms in just three days.
How does zuranolone work?
Zuranolone is a neuroactive steroid, a type of medication that helps the neurotransmitter GABA’s receptors, which affect how the body reacts to anxiety, stress, and fear, function better.
“Zuranolone can be thought of as a synthetic version of [the neuroactive steroid] allopregnanolone,” says Dr. Katrina Furey, a reproductive psychiatrist, clinical instructor at Yale University, and co-host of the Analyze Scripts podcast. “Women with PPD have lower levels of allopregnenolone compared to women without PPD.”
How is it different from other antidepressants?
“What differentiates zuranolone from other previously available oral antidepressants is that it has a much more rapid response and a shorter course of treatment,” says Dr. Asima Ahmad, an OB-GYN, reproductive endocrinologist, and founder of Carrot Fertility.
“It can take effect as early as on day three of treatment, versus other oral antidepressants that can take up to six to 12 weeks to take full effect.”
What are Zurzuvae’s side effects?
According to the FDA, the most common side effects of Zurzuvae include dizziness, drowsiness, diarrhea, fatigue, the common cold, and urinary tract infection. Similar to other antidepressants, the medication may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions in people 24 and younger. However, NPR noted that this type of labeling is required for all antidepressants, and researchers didn’t see any reports of suicidal thoughts in their trials.
“Drug trials also noted that the side effects for zuranolone were not as severe,” says Ahmad. “[There was] no sudden loss of consciousness as seen with brexanolone or weight gain and sexual dysfunction, which can be seen with other oral antidepressants.”
She adds: “Given the lower incidence of side effects and more rapid-acting onset, zuranolone could be a viable option for many,” including those looking for a treatment that offers faster symptom relief.
Can someone breastfeed while taking zuranolone?
It’s complicated. In clinical trials, participants were asked to stop breastfeeding (which, according to Furey, is common in early clinical trials).
A small study of people who were nursing while taking zuranolone found that 0.3 percent of the medication dose was passed on to breast milk, which, Furey says, is a pretty low amount of exposure for the baby. Ahmad says that “though some data suggests that the risk of harm to the baby may be low, there is still overall limited data.”
Overall, people should talk to their health care provider about the risks and benefits of breastfeeding while on the medication.
“A lot of factors will need to be weighed, such as overall health of the infant, age of the infant, etc., when making this decision,” Furey says.
How much does Zurzuvae cost?
Zurzuvae’s price before insurance coverage is $15,900 for the 14-day treatment. However, the Policy Center for Maternal Mental Health says insurance companies and Medicaid are expected to cover it because it’s the only drug of its kind.
Less than 1 percent of U.S. insurers have issued coverage guidelines so far, so it’s still unknown how much it will cost patients after insurance. Some insurers require patients to try another antidepressant first (like the more common SSRIs) before covering Zurzuvae. For uninsured and underinsured people, Sage Therapeutics said it will offer copay assistance.
The hefty price tag and potential issues with coverage may widen existing health disparities, says Ahmad. “We need to ensure that we are seeking out solutions to enable wide-scale access to all PPD treatments so that people have access to whatever treatment may work best for them.”
If you or anyone you know is considering suicide or self-harm or is anxious, depressed, upset, or needs to talk, call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or text the Crisis Text Line at 741-741. For international resources, here is a good place to begin.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
In Praise of Slowness – by Carl Honoré
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This isn’t just about “taking the time to smell the roses” although yes, that too. Rather, it’s mostly about looking at what drives us to speed everything up in the first place, and correcting where appropriate.
If your ancestors had time to eat fruit and lie in the sun, then why, with all of modern technology now available, are you harangued 16+ hours a day by the pressures of universally synchronized timepieces?
Honoré places a lot of the blame squarely on the industrial revolution; whereas previously our work would be limited by craftsmen who take a year to complete something, or the pace of animals in a field, now humans had to keep up with the very machines that were supposed to serve us—and it’s only got worse from there.
This book takes a tour of many areas affected by this artificial “need for speed”, and how it harms not just our work-life balance, but also our eating habits, the medical attention we get, and even our love lives.
The prescription is deceptively simple, “slow down”. But Honoré dedicates the final three chapters of the book to the “how” of this, when of course there’s a lot the outside world will not accommodate—but where we can slow down, there’s good to be gained.
Bottom line: if you’ve ever felt that you could get all of your life into order if you could just pause the outside world for a week or two, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out In Praise of Slowness, and make time for what matters most!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: