Rushing Woman’s Syndrome – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-known that very many women suffer from “the triple burden” of professional work, housework, and childcare. And it’s not even necessarily that we resent any of those things or feel like they’re a burden; we (hopefully) love our professions, homes, children. But, here’s the thing: no amount of love will add extra hours to the day!
On the psychological level, a lot is about making more conscious decisions and fewer automatic reactions. For example, everyone wants everything from us right now, if not by yesterday, but when do they need it? And, is it even our responsibility? Not everything is, and many of us take on more than we should in our effort to be “enough”.
On the physical level, she covers hormones, including the menstrual/menopausal and the metabolic, as well as liver health, digestive issues, and sleep.
The style is direct and friendly, making frequent references to science but not getting deep into it.
It’s worth noting that while she acknowledges other demographics exist, she’s writing mainly for an audience of otherwise healthy straight white women with children and at least moderate financial resources, so if you fall outside of those things, there may be things that society will penalize you for and expect more from you in return for less, so that is a limitation of the book.
Bottom line: if the above describes you, you will probably get value out of this book.
Click here to check out Rushing Woman’s Syndrome, and take care of yourself too!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How worried should I be about cryptosporidiosis? Am I safe at the pool?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You might have heard of something called “cryptosporidiosis” recently, closely followed by warnings to stay away from your local swimming pool if you’ve had diarrhoea.
More than 700 cases of this gastrointestinal disease were reported in Queensland in January, which is 13 times more than in January last year. Just under 500 cases have been recorded in New South Wales this year to-date, while other states have similarly reported an increase in the number of cryptosporidiosis infections in recent months.
Cryptosporidiosis has been listed as a national notifiable disease in Australia since 2001.
But what exactly is it, and should we be worried?What causes cryptosporidiosis, and who is affected?
Cryptosporidiosis is the disease caused by the parasite Cryptosporidium, of which there are two types that can make us sick. Cryptosporidum hominis only affects humans and is the major cause of recent outbreaks in Australia, while Cryptosporidium parvum can also affect animals.
The infection is spread by spores called oocysts in the stools of humans and animals. When ingested, these oocysts migrate and mature in the small bowel. They damage the small bowel lining and can lead to diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, fever and abdominal discomfort.
Most people develop symptoms anywhere from one to 12 days after becoming infected. Usually these symptoms resolve within two weeks, but the illness may last longer and can be severe in those with a weakened immune system.
Children and the elderly tend to be the most commonly affected. Cryptosporidiosis is more prevalent in young children, particularly those under five, but the disease can affect people of any age.
A number of public pools have been closed lately due to cryptosporidiosis outbreaks.
LBeddoe/ShutterstockSo how do we catch it?
Most major outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis have been due to people drinking contaminated water. The largest recorded outbreak occurred in Milwaukee in 1993 where 403,000 people were believed to have been infected.
Cryptosporidium oocysts are very small in size and in Milwaukee they passed through the filtration system of one of the water treatment plants undetected, infecting the city’s water supply. As few as ten oocysts can cause infection, making it possible for contaminated drinking water to affect a very large number of people.
Four days after infection a person with cryptosporidiosis can shed up to ten billion oocysts into their stool a day, with the shedding persisting for about two weeks. This is why one infected person in a swimming pool can infect the entire pool in a single visit.
Cryptosporidium oocysts excreted in the faeces of infected humans and animals can also reach natural bodies of water such as beaches, rivers and lakes directly through sewer pipes or indirectly such as in manure transported with surface runoff after heavy rain.
One study which modelled Cryptosporidium concentrations in rivers around the world estimated there are anywhere from 100 to one million oocysts in a litre of river water.
In Australia, cryptosporidiosis outbreaks tend to occur during the late spring and early summer periods when there’s an increase in recreational water activities such as swimming in natural water holes, water catchments and public pools. We don’t know exactly why cases have seen such a surge this summer compared to other years, but we know Cryptosporidium is very infectious.
Oocysts have been found in foods such as fresh vegetables and seafood but these are not common sources of infection in Australia.
What about chlorine?
Contrary to popular belief, chlorine doesn’t kill off all infectious microbes in a swimming pool. Cryptosporidium oocysts are hardy, thick-walled and resistant to chlorine and acid. They are not destroyed by chlorine at the normal concentrations found in swimming pools.
We also know oocysts can be significantly protected from the effects of chlorine in swimming pools by faecal material, so the presence of even small amounts of faecal matter contaminated with Cryptosporidium in a swimming pool would necessitate closure and a thorough decontamination.
Young children and in particular children in nappies are known to increase the potential for disease transmission in recreational water. Proper nappy changing, frequent bathroom breaks and showering before swimming to remove faecal residue are helpful ways to reduce the risk.
Cryptosporidium can spread in other bodies of water, not just swimming pools.
Yulia Simonova/ShutterstockSome sensible precautions
Other measures you can take to reduce yours and others’ risk of cryptosporidiosis include:
- avoid swimming in natural waters such as rivers and creeks during and for at least three days after heavy rain
- avoid swimming in beaches for at least one day after heavy rain
- avoid drinking untreated water such as water from rivers or springs. If you need to drink untreated water, boiling it first will kill the Cryptosporidium
- avoid swallowing water when swimming if you can
- if you’ve had diarrhoea, avoid swimming for at least two weeks after it has resolved
- avoid sharing towels or linen for at least two weeks after diarrhoea has resolved
- avoid sharing, touching or preparing food that other people may eat for at least 48 hours after diarrhoea has resolved
- wash your hands with soap and water after going to the bathroom or before preparing food (Cryptosporidium is not killed by alcohol gels and sanitisers).
Not all cases of diarrhoea are due to cryptosporidiosis. There are many other causes of infectious gastroenteritis and because the vast majority of the time recovery is uneventful you don’t need to see a doctor unless very unwell. If you do suspect you may have cryptosporidiosis you can ask your doctor to refer you for a stool test.
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How Estrogen & Progesterone Affect Your Pain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s been long-established that pain perception in women and men is quite different—on average, at least, since the datasets are usually somewhat overlapping.
If that last statement is confusing, think of it like height: on average, men are taller than women, but the datasets of “men’s height” and “women’s height” will be overlapping, because indeed some women are taller than some men.
So it is with pain also: women generally have heightened pain sensitivity compared to men, although reporting of that pain can vary a lot depending on the circumstances and experimental methodology.
An additional consideration is that women are overrepresented when it comes to people with chronic pain (i.e., more women have chronic pain than men).
In some cases, this is because a given chronic condition (as for example many autoimmune diseases) predominantly affects women for reasons that are often not well-explored, and in other cases, the reason is more obvious (for example, you will not find many men with endometriosis).
See also: What you need to know about endometriosis
Researchers, namely, Dr. Élora Midavaine et al., have found another common reason for the disparity in pain perception:
From estrogen to opioids
It turns out that the main female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, can suppress pain by prompting immune cells near the spinal cord to produce opioids.
The immune cells in question are immune-regulatory T-cells (colloquially called “Tregs” by scientists who don’t want to have to say/write that in full every time), whose main job is usually simply reducing inflammation. In other words, they’re the immune cells that tell your other immune cells to kindly chill a little bit and not overdo it.
In this case, the estrogen and progesterone stimulate the Tregs to produce the opioids (specifically, enkephalin) to block the pain signals before they reach the brain.
You may be thinking: but hang on, wouldn’t this mean that women experience less pain than men?
And the answer is: it depends!
A while back we wrote an article about how Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear, and it’s a similar principle in this case: the female sex hormones are protective… Until they’re not!
In other words: in menopause, for example. And just like Alzheimer’s, chronic pain increasingly affects people the older we get, so the majority of people experiencing it at any time will tend to be postmenopausal. Symptoms get brushed off with “well, you are older now”, and while yes indeed many things may be age-related, in some cases their pathogenesis can be very clearly traced to “this hormone was doing the job for you, and now your levels of that hormone are very low, so you no longer get that protection”.
You can find the paper itself here: Meningeal regulatory T cells inhibit nociception in female mice ← yes, it’s a mouse study, but all the systems exist the same way in humans, so there is no reason to assume it would be different for us. Just, scientists can’t persuade an ethics board to let them knock out humans’ Tregs with toxins and then do nerve damage to measure the pain processing.
Takeaway idea: if you are postmenopausal and suffer chronic pain, then it’s an extra reason you might want to consider bioidentical HRT if you haven’t already.
See also: What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
Want to learn more?
We’ve written quite a bit about pain management, including:
- Before You Reach For That Tylenol…
- How To Stop Pain Spreading
- How To Dial Down Your Pain
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- Get The Right Help For Your Pain
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief (When Painkillers Aren’t Helping, These Things Might)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Is More Likely Than You Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): More Likely Than You Think
COPD is not so much one disease, as rather a collection of similar (and often overlapping) diseases. The main defining characteristic is that they are progressive lung diseases. Historically the most common have been chronic bronchitis and emphysema, though Long COVID and related Post-COVID conditions appear to have been making inroads.
Lung cancer is generally considered separately, despite being a progressive lung disease, but there is crossover too:
COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history
COPD can be quite serious:
“But I don’t smoke”
Great! In fact we imagine our readership probably has disproportionately few smokers compared to the general population, being as we all are interested in our health.
But, it’s estimated that 30,000,000 Americans have COPD, and approximately half don’t know it. Bear in mind, the population of the US is a little over 340,000,000, so that’s a little under 9% of the population.
Click here to see a state-by-state breakdown (how does your state measure up?)
How would I know if I have it?
It typically starts like any mild respiratory illness. Likely shortness of breath, especially after exercise, a mild cough, and a frequent need to clear your throat.
Then it will get worse, as the lungs become more damaged; each of those symptoms might become stronger, as well as chest tightness and a general lack of energy.
Later stages, you guessed it, the same but worse, and—tellingly—weight loss.
The reason for the weight loss is because you are getting less oxygen per breath, making carrying your body around harder work, meaning you burn more calories.
What causes it?
Lots of things, with smoking being up at the top, or being exposed to a lot of second-hand smoke. Working in an environment with a lot of air pollution (for example, working around chemical fumes) can cause it, as can inhaling dust. New Yorkers: yes, that dust too. It can also develop from other respiratory illnesses, and some people even have a genetic predisposition to it:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: a commonly overlooked cause of lung disease
Is it treatable?
Treatment varies depending on what form of it you have, and most of the medical interventions are beyond the scope of this article. Suffice it to say, there are medications that can be taken (including bronchodilators taken via an inhaler device), corticosteroids, antibiotics and antivirals of various kinds if appropriate. This is definitely a “see your doctor” item though, because there are is far too much individual variation for us to usefully advise here.
However!
There are habits we can do to a) make COPD less likely and b) make COPD at least a little less bad if we get it.
Avoiding COPD:
- Don’t smoke. Just don’t.
- Avoid second-hand smoke if you can
- Avoid inhaling other chemicals/dust that may be harmful
- Breathe through your nose, not your mouth; it filters the air in a whole bunch of ways
- Seriously, we know it seems like nostril hairs surely can’t do much against tiny particles, but tiny particles are attracted to them and get stuck in mucous and dealt with by our immune system, so it really does make a big difference
Managing COPD:
- Continue the above things, of course
- Exercise regularly, even just light walking helps; we realize it will be difficult
- Maintain a healthy weight if you can
- This means both ways; COPD causes weight loss and that needs to be held in check. But similarly, you don’t want to be carrying excessive weight either; that will tire you even more.
- Look after the rest of your health; everything else will now hit you harder, so even small things need to be taken seriously
- If you can, get someone to help / do your household cleaning for you, ideally while you are not in the room.
Where can I get more help/advice?
As ever, speak to your doctor if you are concerned this may be affecting you. You can also find a lot of resources via the COPD Foundation’s website.
Take care of yourself!
Share This Post
- Don’t smoke. Just don’t.
Related Posts
-
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not there?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not There?
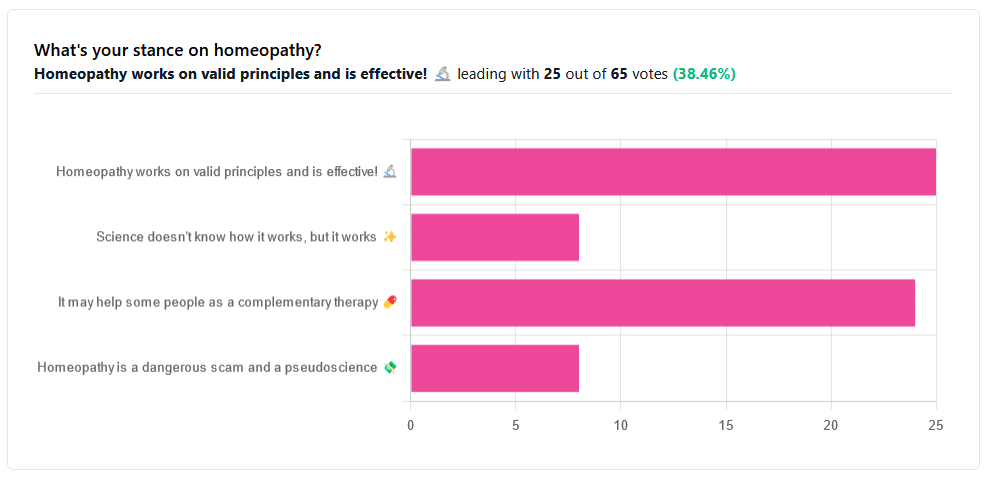
Yesterday, we asked you your opinions on homeopathy. The sample size of responses was a little lower than we usually get, but of those who did reply, there was a clear trend:
- A lot of enthusiasm for “Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective”
- Near equal support for “It may help some people as a complementary therapy”
- Very few people voted for “Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works”; this is probably because people who considered voting for this, voted for the more flexible “It may help some people as a complementary therapy” instead.
- Very few people considered it a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience.
So, what does the science say?
Well, let us start our investigation by checking out the position of the UK’s National Health Service, an organization with a strong focus on providing the least expensive treatments that are effective.
Since homeopathy is very inexpensive to arrange, they will surely want to put it atop their list of treatments, right?
❝Homeopathy is a “treatment” based on the use of highly diluted substances, which practitioners claim can cause the body to heal itself.
There’s been extensive investigation of the effectiveness of homeopathy. There’s no good-quality evidence that homeopathy is effective as a treatment for any health condition.❞
The NHS actually has a lot more to say about that, and you can read their full statement here.
But that’s just one institution. Here’s what Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council had to say:
❝There was no reliable evidence from research in humans that homeopathy was effective for treating the range of health conditions considered: no good-quality, well-designed studies with enough participants for a meaningful result reported either that homeopathy caused greater health improvements than placebo, or caused health improvements equal to those of another treatment❞
You can read their full statement here.
The American FDA, meanwhile, have a stronger statement:
❝Homeopathic drug products are made from a wide range of substances, including ingredients derived from plants, healthy or diseased animal or human sources, minerals and chemicals, including known poisons. These products have the potential to cause significant and even permanent harm if they are poorly manufactured, since that could lead to contaminated products or products that have potentially toxic ingredients at higher levels than are labeled and/or safe, or if they are marketed as substitute treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases and conditions, or to vulnerable populations.❞
You can read their full statement here.
Homeopathy is a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience: True or False?
False and True, respectively, mostly.
That may be a confusing answer, so let’s elaborate:
- Is it dangerous? Mostly not; it’s mostly just water. However, two possibilities for harm exist:
- Careless preparation could result in a harmful ingredient still being present in the water—and because of the “like cures like” principle, many of the ingredients used in homeopathy are harmful, ranging from heavy metals to plant-based neurotoxins. However, the process of “ultra-dilution” usually removes these so thoroughly that they are absent or otherwise scientifically undetectable.
- Placebo treatment has its place, but could result in “real” treatment going undelivered. This can cause harm if the “real” treatment was critically needed, especially if it was needed on a short timescale.
- Is it a scam? Probably mostly not; to be a scam requires malintent. Most practitioners probably believe in what they are practising.
- Is it a pseudoscience? With the exception that placebo effect has been highly studied and is a very valid complementary therapy… Yes, aside from that it is a pseudoscience. There is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “like cures like” principle, and there is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “water memory” idea. On the contrary, they go against the commonly understood physics of our world.
It may help some people as a complementary therapy: True or False?
True! Not only is placebo effect very well-studied, but best of all, it can still work as a placebo even if you know that you’re taking a placebo… Provided you also believe that!
Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works: True or False?
False, simply. At best, it performs as a placebo.
Placebo is most effective when it’s a remedy against subjective symptoms, like pain.
However, psychosomatic effect (the effect that our brain has on the rest of our body, to which it is very well-connected) can mean that placebo can also help against objective symptoms, like inflammation.
After all, our body, directed primarily by the brain, can “decide” what immunological defenses to deploy or hold back, for example. This is why placebo can help with conditions as diverse as arthritis (an inflammatory condition) or diabetes (an autoimmune condition, and/or a metabolic condition, depending on type).
Here’s how homeopathy measures up, for those conditions:
(the short answer is “no better than placebo”)
Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective: True or False?
False, except insofar as placebo is a valid principle and can be effective.
The stated principles of homeopathy—”like cures like” and “water memory”—have no scientific basis.
We’d love to show the science for this, but we cannot prove a negative.
However, the ideas were conceived in 1796, and are tantamount to alchemy. A good scientific attitude means being open-minded to new ideas and testing them. In homeopathy’s case, this has been done, extensively, and more than 200 years of testing later, homeopathy has consistently performed equal to placebo.
In summary…
- If you’re enjoying homeopathic treatment and that’s working for you, great, keep at it.
- If you’re open-minded to enjoying a placebo treatment that may benefit you, be careful, but don’t let us stop you.
- If your condition is serious, please do not delay seeking evidence-based medical treatment.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat – by Aubrey Gordon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are books aplenty to encourage and help you to lose weight. This isn’t one of those.
There are also books aplenty to encourage and help you to accept yourself and your body at the weight you are, and forge self-esteem. This isn’t one of those, either—in fact, it starts by assuming you already have that.
There are fair arguments for body neutrality, and fat acceptance. Very worthy also is the constant fight for bodily sovereignty.
These are worthy causes, but they’re for the most-part not what our author concerns herself with here. Instead, she cares for a different and very practical goal: fat justice.
In a world where you may be turned away from medical treatment if you are over a certain size, told to lose half your bodyweight before you can have something you need, she demands better. The battle extends further than healthcare though, and indeed to all areas of life.
Ultimately, she argues, any society that will disregard the needs of the few because they’re a marginal demographic, is a society that will absolutely fail you if you ever differ from the norm in some way.
All in all, an important (and for many, perhaps eye-opening) book to read if you are fat, care about fat people, are a person of any size, or care about people in general.
Pick Up Your Copy of “What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat”, on Amazon Today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tech Bliss – by Clo S., MSc.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The popular idea of a “digital detox” is simple enough, “just unplug!”, they say.
But here in the real world, not only is that often not practical for many of us, it may not always even be entirely desirable. The Internet (and our devices with all their bells and whistles) can be a source of education, joy, and connection!
So, how to find out what’s good for us and what’s not, in our daily digital practices? Clo. S. has answers… Or rather, experiments for us to do and find out for ourselves.
These experiments range from the purely practical “try this to streamline your experience” to the more personal “how does this thing make you feel?”. A lot of the experiments will be performed via your digital devices—some, without! Others are about online interpersonal dynamics, be they one-on-one or navigating a world in which it seems everyone is out to get us, our outrage, and/or our money. Still yet others are about optimizing what you do get from the parts of your digital experience that are enriching for you.
As the title suggests, there are 30 experiments, and it’s not a stretch to do them one per day for a month. But, as the author notes, it’s by no means necessary to do them like that; it’s a workbook and reference guide, not a to-do list!
(On the topic of it being a reference guide…There’s also an extensive tools directory towards the end!)
In short: this is a great book for optimizing your online experience—whatever that might mean for you personally; you can decide for yourself along the way!
Click here to get a copy of Tech Bliss: 30 Experiments For Your Digital Wellness today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: