Tips For Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis is the umbrella term for a cluster of joint diseases involving inflammation of the joints, hence “arthr-” (joint) “-itis” (suffix used to denote inflammation). These are mostly, but not all, autoimmune diseases, in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks our own joints.
Inflammatory vs Non-Inflammatory Arthritis
Arthritis is broadly divided into inflammatory arthritis and non-inflammatory arthritis.
You may be wondering: how does one get non-inflammatory inflammation of the joints?
The answer is, in “non-inflammatory” arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, the damage comes first (by general wear-and-tear) and inflammation generally follows as part of the symptoms, rather than the cause. So the name can be a little confusing. In the case of osteo- and other “non-inflammatory” forms of arthritis, you definitely still want to keep your inflammation at bay as best you can, but it’s not as absolutely critical a deal as it is for “inflammatory” forms of arthritis.
We’ll tackle the beast that is osteoarthritis another day, however.
Today we’re going to focus on…
Rheumatoid Arthritis
This is the most common of the autoimmune forms of arthritis. Some quick facts:
- It affects a little under 1% of the global population, but the older we get, the more likely it becomes
- Early onset of rheumatoid arthritis is most likely to show up around the age of 50 (but it can show up at any age)
- However, incidence (not onset) of rheumatoid arthritis peaks in the 70s age bracket
- It is 2–4 times more common in women than in men
- Approximately one third of people stop work within two years of its onset, and this increases thereafter.
Well, that sounds gloomy.
Indeed it’s not fun. There’s a lot of stiffness and aching of joints (often with swelling too), loss of joint function can be common, and then there are knock-on effects like fatigue, weakness, and loss of appetite.
Beyond that it’s an autoimmune disorder, its cause is not known, and there is no known cure.
Is there any good news?
If you don’t have rheumatoid arthritis at the present time, you can reduce your risk factors in several ways:
- Having an anti-inflammatory diet. Get plenty of fiber, greens, and berries. Fatty fish is great too, as are oily nuts. On the other side of things, high consumption of salt, sugar, alcohol, and red meat are associated with a greater risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
- Not smoking. Smoking is bad for pretty much everything, including your chances of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
- Not being obese. This one may be more a matter of correlation than causation, because of the dietary factors (if one eats an anti-inflammatory diet, obesity is less likely), but the association is there.
There are other risk factors that are harder to control, such as genetics, age, sex, and having a mother who smoked.
See: Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis
What if I already have rheumatoid arthritis?
If you already have rheumatoid arthritis, it becomes a matter of symptom management.
First, reduce inflammation any (reasonable) way you can. We did a main feature on this before, so we’ll just drop that again here:
Next, consider the available medications. Your doctor may or may not have discussed all of the options with you, so be aware that there are more things available than just pain relief. To talk about them all would require a whole main feature, so instead, here’s a really well-compiled list, along with explanations about each of them, up to date as of this year:
Rheumatoid Arthritis Medication List (And What They Do, And How)
Finally, consider other lifestyle adjustments to manage your symptoms. These include:
- Exercise—gently, though! You do not want to provoke a flare-up, but you do want to maintain your mobility as best you can. There’s a use-it-or-lose-it factor here. Swimming and yoga are great options, as is tai chi. You may want to avoid exercises that involve repetitive impacts to your joints, like running.
- Rest—while keeping mobility going. Get good sleep at night (this is important), but don’t make your bed your new home, or your mobility will quickly deteriorate.
- Hot & cold—both can help, and alternating them can reduce inflammation and stiffness by improving your body’s ability to respond appropriately to these stimuli rather than getting stuck in an inappropriate-response state of inflammation.
- Mobility aids—if it helps, it helps. Maybe you only need something during a flare-up, but when that’s the case, you want to be as gentle on your body as possible while keeping moving, so if crutches, handrails etc help, then by all means get them and use them.
- Go easy on the use of braces, splints, etc—these can offer short-term relief, but at a long term cost of loss of mobility. Only you can decide where to draw the line when it comes to that trade-off.
You can also check out our previous article:
Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
Take good care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Unchoke Yourself If You Are Dying Alone
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The first things that most people think of, won’t work. This firefighter advises on how to actually do it:
Steps to take
Zero’th step: he doesn’t mention this, but try coughing first. You might think coughing will be a natural reaction anyway, but that tends only to happen automatically with small partial obstructions, not a complete blockage. Either way, try to cough forcefully to see if it dislodges whatever you’re choking on. If that doesn’t work…
Firstly: don’t rely on calling for help if you’re alone and cannot speak; you’re unlikely to be able to communicate and you will just waste time (when you don’t have time to waste). Even if you call emergency services and they trace your location, chances are that, at most, a cop car will show up some hours later to see what it was about. They will not dispatch an ambulance on the strength of “someone called and said nothing”.
Secondly, it is probable that will not be able to perform an abdominal thrust (also called Heimlich maneuvre in the US) on yourself the way you could on another person, and hitting your chest with your hand will produce insufficient force even if you’re quite strong. Nor are you likely to be able to slap yourself on the back to way you might another person.
Instead, he advises:
- Find a sturdy object: use a chair, table, countertop, or another firm surface that has an edge.
- Use gravity to perform self-Heimlich: position yourself with the edge of the object just below your sternum (he says ribcage, but the visuals show he clearly means the bottom of the sternum, where the diaphragm is, not the lower ribs). Fall onto the object forcefully to create pressure and dislodge the obstruction. This will not be fun.
- If it doesn’t work indoors: move to a visible outdoor location like your yard or a neighbor’s lawn. Falling visibly on the ground will likely alert someone to call for help.
While doing the above, remain as calm as possible, as this will not only increase the length of time you have before passing out, but will also help avoid your throat muscles tightening even more, worsening the choking.
After doing the above, seek medical attention now that you can communicate; you’ve probably broken some ribs and you might have organ damage.
For more on all this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Survive A Heart Attack When You’re Alone ← very different advice for this scenario!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Science and Technology of Growing Young – by Sergey Young
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are a lot of very optimistic works out there that promise the scientific breakthroughs that will occur very soon. Even amongst the hyperoptimistic transhumanism community, there is the joke of “where’s my flying car?” Sometimes prefaced with “Hey Ray, quick question…” as a nod to (or sometimes, direct address to) Ray Kurzweil, the Google computer scientist and futurist.
So, how does this one measure up?
Our author, Sergey Young, is not a scientist, but an investor with fingers in many pies. Specifically, pies relating to preventative medicine and longevity. Does that make him an unreliable narrator? Not necessarily, but it means we need to at least bear that context in mind.
But, also, he’s investing in those fields because he believes in them, and wants to benefit from them himself. In essense, he’s putting his money where his mouth is. But, enough about the author. What of the book?
It’s a whirlwind tour of the main areas of reseach and development, in the recent past, the present, and the near future. He talks about problems, and compelling solutions to problems.
If the book has a weak point, it’s that it doesn’t really talk about the problems to those solutions—that is, what can still go wrong. He’s excited about what we can do, and it’s somebody else’s job to worry about pitfalls along the way.
As to the “and what you can do now?” We’ll summarize:
- Mediterranean diet, mostly plant-based
- Get moderate exercise daily
- Get good sleep
- Don’t drink or smoke
- Get your personal health genomics data
- Get regular medical check-ups
- Look after your mental health too
Bottom line: this is a great primer on the various avenues of current anti-aging research and development, with discussion ranging from the the technological to the sociological. It has some health tips too, but the real meat of the work is the insight into the workings of the longevity industry.
Share This Post
-
No Equipment Muscle Gain Routine for Ages 50+
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sarcopenia, the loss of muscle mass commonly associated with aging, can be a big problem as it leaves us vulnerable to injury (and also isn’t great for the metabolism—keeping adequate muscle mass ensures keeping the metabolism ticking over nicely). Will Harlow, over-50s specialist physiotherapist, is here to share a routine that works without weights:
Where it counts
There’s a fair amount of emphasis here on the lower body and core. That’s because in practical terms, this is what matters more for our health than having bulging biceps:
- First exercise: donkey calf raises to build strength in the calves using a chair.
- Second exercise: single-leg elevated lunge to work the quads and glutes, using a step or books for elevation.
- Third exercise: slow sit-to-stand for quads, glutes, and core strength, focusing on a slow descent.
- Fourth exercise: wall press-up to strengthen the chest, shoulders, and arms, with a variation using towels for increased resistance.
- Final exercise: shoulder raises using bottles or similar weights to target the shoulders and rotator cuffs.
Ok, so that last one was a slight cheat on his part as it does require grabbing a weight, but it’s not specialist equipment at least, and can just be something you grabbed at home. It’s also the least important of the five exercises, and can be skipped if necessary.
For more on all of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Do Probiotics Work For Weight Loss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Can you talk about using probiotics for weight loss? Thanks❞
Great question! First, a quick catch-up:
How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make, Really?
Our above-linked article covers a number of important benefits of probiotic supplements, but we didn’t talk about weight loss at all. So let’s examine whether probiotics are useful for weight loss.
Up-front summary: the science is unclear
This 2021 systematic review found that they are indeed very effective:
❝The intake of probiotics or synbiotics could lead to significant weight reductions, either maintaining habitual lifestyle habits or in combination with energy restriction and/or increased physical activity for an average of 12 weeks.
Specific strains belonging to the genus Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium were the most used and those that showed the best results in reducing body weight.
Both probiotics and synbiotics have the potential to help in weight loss in overweight and obese populations.❞
This slightly older (2015) systematic review and meta-analysis found the opposite:
❝Collectively, the RCTs examined in this meta-analysis indicated that probiotics have limited efficacy in terms of decreasing body weight and BMI and were not effective for weight loss.❞
Source: Probiotics for weight loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis
And in case that’s not balanced enough, this 2020 randomized controlled trial got mixed results:
❝Regression analysis performed to correlate abundance of species following supplementation with body composition parameters and biomarkers of obesity found an association between a decrease over time in blood glucose and an increase in Lactobacillus abundance, particularly in the synbiotic group.
However, the decrease over time in body mass, BMI, waist circumstance, and body fat mass was associated with a decrease in Bifidobacterium abundance.❞
Source: Effects of Synbiotic Supplement on Human Gut Microbiota, Body Composition and Weight Loss in Obesity
Summary
Probiotics may or may not work for weight loss.
In all likelihood, it depends on the blend of cultures contained in the supplement. It’s possible that Lactobacillus is more beneficial for weight loss than Bifidobacterium, which latter may actually reduce weight loss.
Or it might not, because that was just one study and correlation ≠ causation!
We’d love to give you a hard-and-fast answer, but if the data doesn’t support a hard-and-fast answer, we’re not going to lie to you.
What we can say for sure though is that probiotics come with very many health benefits, so whether or not weight loss is one of them, they’re a good thing to have for most people.
Some further articles that may interest you:
- How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make, Really? ← the aforementioned article
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later) ← gut health 101
- Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism ← these things can help change your metabolic base rate, which is highly relevant to weight loss
- How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body) ←unlike most forms of exercise, which cause the body to slow the metabolism afterwards to compensate, high-intensity interval training results in an increased metabolic rate (so generally: fat-burning) for several hours after training.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
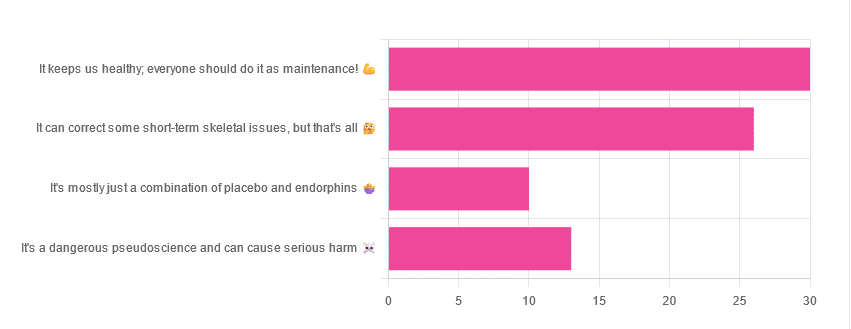
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on chiropractic medicine, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- 38% of respondents said it keeps us healthy, and everyone should do it as maintenance
- 33% of respondents said it can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all
- 16% of respondents said that it’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause serious harm
- 13% of respondents said that it’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins
Respondents also shared personal horror stories of harm done, personal success stories of things cured, and personal “it didn’t seem to do anything for me” stories.
What does the science say?
It’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause harm: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
That is to say, chiropractic in its simplest form that makes the fewest claims, is not a pseudoscience. If somebody physically moves your bones around, your bones will be physically moved. If your bones were indeed misaligned, and the chiropractor is knowledgeable and competent, this will be for the better.
However, like any form of medicine, it can also cause harm; in chiropractic’s case, because it more often than not involves manipulation of the spine, this can be very serious:
❝Twenty six fatalities were published in the medical literature and many more might have remained unpublished.
The reported pathology usually was a vascular accident involving the dissection of a vertebral artery.
Conclusion: Numerous deaths have occurred after chiropractic manipulations. The risks of this treatment by far outweigh its benefit.❞
Source: Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases
From this, we might note two things:
- The abstract doesn’t note the initial sample size; we would rather have seen this information expressed as a percentage. Unfortunately, the full paper is not accessible, and nor are many of the papers it cites.
- Having a vertebral artery fatally dissected is nevertheless not an inviting prospect, and is certainly a very reasonable cause for concern.
It’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins: True or False?
True or False, depending on what you went in for:
- If you went in for a regular maintenance clunk-and-click, then yes, you will get your clunk-and-click and feel better for it because you had a ritualized* experience and endorphins were released.
- If you went in for something that was actually wrong with your skeletal alignment, to get it corrected, and this correction was within your chiropractor’s competence, then yes, you will feel better because a genuine fault was corrected.
*this is not implying any mysticism, by the way. Rather it means simply that placebo effect is strongest when there is a ritual associated with it. In this case it means going to the place, sitting in a pleasant waiting room, being called in, removing your shoes and perhaps some other clothes, getting the full attention of a confident and assured person for a while, this sort of thing.
With regard to its use to combat specifically spinal pain (i.e., perhaps the most obvious thing to treat by chiropractic spinal manipulation), evidence is slightly in favor, but remains unclear:
❝Due to the low quality of evidence, the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulation compared with a placebo or no treatment remains uncertain. ❞
Source: Clinical Effectiveness and Efficacy of Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation for Spine Pain
It can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all: True or False?
Probably True.
Why “probably”? The effectiveness of chiropractic treatment for things other than short-term skeletal issues has barely been studied. From this, we may wish to keep an open mind, while also noting that it can hardly claim to be evidence-based—and it’s had hundreds of years to accumulate evidence. In all likelihood, publication bias has meant that studies that were conducted and found inconclusive or negative results were simply not published—but that’s just a hypothesis on our part.
In the case of using chiropractic to treat migraines, a very-related-but-not-skeletal issue, researchers found:
❝Pre-specified feasibility criteria were not met, but deficits were remediable. Preliminary data support a definitive trial of MCC+ for migraine.❞
Translating this: “it didn’t score as well as we hoped, but we can do better. We got some positive results, and would like to do another, bigger, better trial; please fund it”
Source: Multimodal chiropractic care for migraine: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Meanwhile, chiropractors’ claims for very unrelated things have been harshly criticized by the scientific community, for example:
Misinformation, chiropractic, and the COVID-19 pandemic
About that “short-term” aspect, one of our subscribers put it quite succinctly:
❝Often a skeletal correction is required for initial alignment but the surrounding fascia and muscles also need to be treated to mobilize the joint and release deep tissue damage surrounding the area. In combination with other therapies chiropractic support is beneficial.❞
This is, by the way, very consistent with what was said in the very clinically-dense book we reviewed yesterday, which has a chapter on the short-term benefits and limitations of chiropractic.
A truism that holds for many musculoskeletal healthcare matters, holds true here too:
❝In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win❞
In other words…
Chiropractic can definitely help put misaligned bones back where they should be. However, once they’re there, if the cause of their misalignment is not treated, they will just re-misalign themselves shortly after you walking out of your session.
This is great for chiropractors, if it keeps you coming back for endless appointments, but it does little for your body beyond give you a brief respite.
So, by all means go to a chiropractor if you feel so inclined (and you do not fear accidental arterial dissection etc), but please also consider going to a physiotherapist, and potentially other medical professions depending on what seems to be wrong, to see about addressing the underlying cause.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Broccoli vs Cauliflower – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing broccoli to cauliflower, we picked the broccoli.
Why?
This one is quite straightforward. Superficially, they’re very similar:
Both are great cruciferous vegetables with many health benefits to offer. Even for those keen to avoid oxalates, which cruciferous vegetables in general can be high in, these ones are quite low.
However, if you have IBS, you might want to avoid both, for their raffinose content that may cause problems for you.
For pretty much everyone else, unless you have a special reason why it’s not the case for you, both are a good source of abundant vitamins and minerals, and yet…
Anything cauliflower can do, broccoli can do better!
Broccoli contains more of the vitamins they both contain, and more of the minerals they both contain.
Broccoli also beats cauliflower on amino acids (except lysine), and contains a lot more lutein and zeaxanthin, carotenoids important for healthy eyes and brain.
So by all means enjoy both, but if you’re going to pick one, pick broccoli!
Want to know more?
Check out: Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: