Reversing Alzheimer’s – by Dr. Heather Sandison
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The title here is bold, isn’t it? But, if the studies so far are anything to go by, she is, indeed, reversing Alzheimer’s. By this we mean: her Alzheimer’s patients have enjoyed a measurable reversal of the symptoms of cognitive decline (this is not something that usually happens).
The science here is actually new, and/but references are given aplenty, including Dr. Sandison’s own research and others—there’s a bibliography of several hundred papers, which we love to see.
Dr. Sandison’s approach is of course multivector, but is far more lifestyle medicine than pills, with diet in particular playing a critical role. Indeed, it’s worth mentioning that she is a naturopathic doctor (not an MD), so that is her focus—though she’s had a lot of MDs looking in on her work too, as you may see in the book. She has found best results in a diet low in carbs, high in healthy fats—and it bears emphasizing, healthy ones. Many other factors are also built in, but this is a book review, not a book summary.
Nor does the book look at diet in isolation; other aspects of lifestyle are also taken into account, as well as various medical pathways, and how to draw up a personalized plan to deal with those.
The book is written with the general assumption that the reader is someone with increased Alzheimer’s risk wishing to reduce that risk, or the relative of someone with Alzheimer’s disease already. However, the information within is beneficial to all.
The style is on the hard end of pop-science; it’s written for the lay reader, but will (appropriately enough) require active engagement to read effectively.
Bottom line: if Alzheimer’s is something that affects or is likely to affect you (directly, or per a loved one), then this is a very good book to have read
Click here top check out Reversing Alzheimer’s, and learn how to do it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Foods That Cause You to Lose Weight – by Dr. Neal Barnard
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We previously reviewed Dr. Barnard’s “The Power Foods Diet”, and this time his work is about weight loss.
This time there are more recipes (which take up most of the book, so this one could be reasonably described as a cookbook), but not until after nearly a hundred pages of concepts, principles, and tips.
The recipes themselves are again very respectable, even if some may be a little redundant (e.g. the double-page recipe for blueberry muffins is followed by a double-page recipe for banana and date muffins, instead of just saying “or substitute this”—things like that) and run the gamut from salad dressings to hearty main meals.
A strength of the book is that it’s about what you eat, not how much of it you eat, so if you love eating (which is a very healthy trait to have in general), then you’ll enjoy that aspect.
Bottom line: if you’d like to eat more and weigh less, then this is a top-tier book for you.
Click here to check out “Foods That Cause You To Lose Weight”, and enjoy eating!
Share This Post
-
10 Powerful Tips To Improve Lymph Flow – by Laurel West
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The lymphatic system is a large part of the body’s “clean-up” system, as well having an important role in fighting cancer specifically. As such, while it doesn’t get nearly as much popular attention as our circulatory system or our nervous system, say, it is critically important.
The author, a massage therapist, knows her stuff when it comes to lymph, and shows that here.
As this is a very lean book, weighing in at a mere 87 pages, you can imagine it gets straight to the point.
So will we! The titular “10 powerful tips” are:
- Drink water
- Matcha meditation
- Breathwork
- Dry brushing
- Hydrotherapy
- Stretching
- Sweating
- Lymphatic facial massage
- Advanced lymphatic massage
- Anti-inflammatory diet
Of course, she does explain each of those; some are more obvious than others; “drink water” takes less explanation than “advanced lymphatic massage”, say.
The style is, as you might expect, concise. It’s more of a primer than a textbook, and it does communicate its ideas clearly.
Bottom line: if you’d like to manage your lymph better, this book is an excellent way to get started.
Click here to check out 10 Powerful Tips To Improve Lymph Flow, and improve your lymph flow.
Share This Post
-
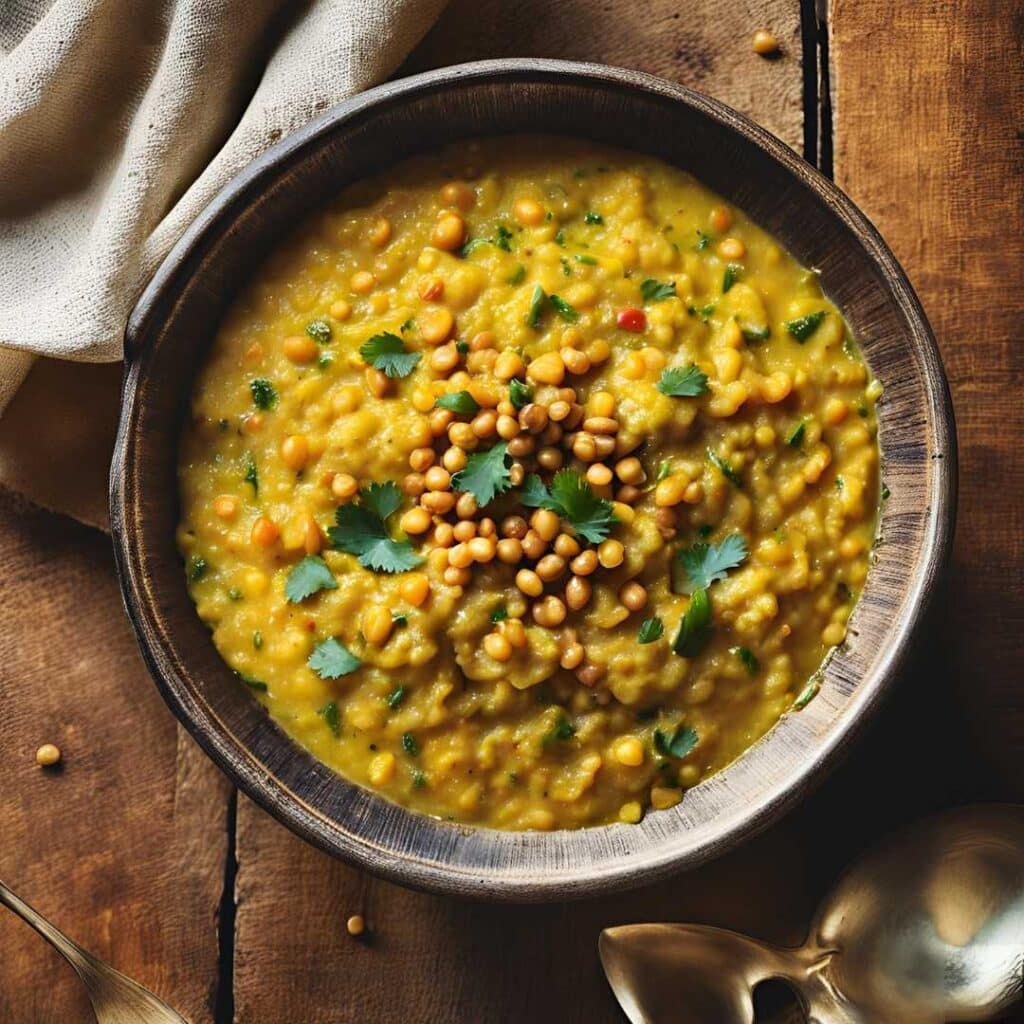
Anti-Inflammatory Khichri & Tadka
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is halfway between a daal and a risotto; it’s delicious and it’s full of protein, fiber, heathy fats, and flavors. And those flavors? Mostly from health-giving phytochemicals of one kind of another.
You will need
For the khichri:
- 1 oz chana dal
- 1 oz red lentils
- 1 oz brown lentils
- 1 oz quinoa
- 4 oz wholegrain basmati rice
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
For the tadka:
- 2 tbsp avocado oil (or other oil suitable for high temperatures—so, not olive oil on this occasion!)
- ¼ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 1 fresh red chili (adjust per heat preferences)
- 1 fresh green chili (adjust per heat preferences)
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 6 curry leaves
- 12 twists of freshly ground black pepper
To serve:
- Optional: flatbreads or poppadoms
- Optional: lemon wedges or lime wedges
- Optional: chopped cilantro or parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Simmer the khichri ingredients in 5 cups of water, stirring occasionally if necessary, until it has a risotto-like consistency; this will probably take about 30–40 minutes. This time can be greatly reduced by using a pressure cooker, but obviously you won’t be able to check or stir, so do that only if you know what you’re doing cooking those grains and pseudograins in there, and what settings/timings to use for your specific device.
2) Make the tadka when the khichri is nearly ready, by heating the 2 tbsp of avocado oil in a skillet until very hot but not smoking, Add the rest of the ingredients from the tadka section, and cook until the garlic is nice and golden.
3) Pour the tadka over the khichri to serve, with any of the optional accompaniments we mentioned.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Good Is Your Sleep, Really?
This is Dr. Marie-Pierre St-Onge, Director of Columbia University’s Center of Excellence for Sleep and Circadian Research.
The focus of Dr. St-Onge’s research is the study of the impact of lifestyle, especially sleep and diet, on cardio-metabolic risk factors.
She conducts clinical research combining her expertise on sleep, nutrition, and energy regulation.
What kind of things do her studies look at?
Her work focuses on questions about…
- The role of circadian rhythms (including sleep duration and timing)
- Meal timing and eating patterns
…and their impact on cardio-metabolic risk.
What does she want us to know?
First things first, when not to worry:
❝Getting a bad night’s sleep once in a while isn’t anything to worry about. That’s what we would describe as transient insomnia. Chronic insomnia occurs when you spend three months or more without regular sleep, and that is when I would start to be concerned.❞
But… as prevention is (as ever) better than cure, she also advises that we do pay attention to our sleep! And, as for how to do that…
The Six Dimensions of Sleep
One useful definition of overall sleep health is the RU-Sated framework, which assesses six key dimensions of sleep that have been consistently associated with better health outcomes. These are:
- regularity
- satisfaction with sleep
- alertness during waking hours
- timing of sleep
- efficiency of sleep
- duration of sleep
You’ll notice that some of these things you can only really know if you use a sleep-monitoring app. She does recommend the use of those, and so do we!
We reviewed and compared some of the most popular sleep-monitoring apps! You can check them out here: Time For Some Pillow Talk
You also might like…
We’re not all the same with regard to when is the best time for us to sleep, so:
Use This Sleep Cycle Calculator To Figure Out the Optimal Time for You To Go to Bed and Wake Up
AROUND THE WEB
What’s happening in the health world…
- Aspirin may make your breathing worse
- Taking naps for more than 30 minutes may raise your metabolic disease risk
- How to ease back into exercise after surgery
- Study provides evidence that breathing exercises may reduce your Alzheimer’s risk
- No one in movies knows how to swallow a pill
More to come tomorrow!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Women are less likely to receive CPR than men. Training on manikins with breasts could help
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If someone’s heart suddenly stops beating, they may only have minutes to live. Doing CPR (cardiopulmonary resusciation) can increase their chances of survival. CPR makes sure blood keeps pumping, providing oxygen to the brain and vital organs until specialist treatment arrives.
But research shows bystanders are less likely to intervene to perform CPR when that person is a woman. A recent Australian study analysed 4,491 cardiac arrests between 2017–19 and found bystanders were more likely to give CPR to men (74%) than women (65%).
Could this partly be because CPR training dummies (known as manikins) don’t have breasts? Our new research looked at manikins available worldwide to train people in performing CPR and found 95% are flat-chested.
Anatomically, breasts don’t change CPR technique. But they may influence whether people attempt it – and hesitation in these crucial moments could mean the difference between life and death.
Pixel-Shot/Shutterstock Heart health disparities
Cardiovascular diseases – including heart disease, stroke and cardiac arrest – are the leading cause of death for women across the world.
But if a woman has a cardiac arrest outside hospital (meaning her heart stops pumping properly), she is 10% less likely to receive CPR than a man. Women are also less likely to survive CPR and more likely to have brain damage following cardiac arrests.
Bystanders are less likely to intervene if a woman needs CPR, compared to a man. doublelee/Shutterstock These are just some of many unequal health outcomes women experience, along with transgender and non-binary people. Compared to men, their symptoms are more likely to be dismissed or misdiagnosed, or it may take longer for them to receive a diagnosis.
Bystander reluctance
There is also increasing evidence women are less likely to receive CPR compared to men.
This may be partly due to bystander concerns they’ll be accused of sexual harassment, worry they might cause damage (in some cases based on a perception women are more “frail”) and discomfort about touching a woman’s breast.
Bystanders may also have trouble recognising a woman is experiencing a cardiac arrest.
Even in simulations of scenarios, researchers have found those who intervened were less likely to remove a woman’s clothing to prepare for resuscitation, compared to men. And women were less likely to receive CPR or defibrillation (an electric charge to restart the heart) – even when the training was an online game that didn’t involve touching anyone.
There is evidence that how people act in resuscitation training scenarios mirrors what they do in real emergencies. This means it’s vital to train people to recognise a cardiac arrest and be prepared to intervene, across genders and body types.
Skewed to male bodies
Most CPR training resources feature male bodies, or don’t specify a sex. If the bodies don’t have breasts, it implies a male default.
For example, a 2022 study looking at CPR training across North, Central and South America, found most manikins available were white (88%), male (94%) and lean (99%).
It’s extremely rare for a manikin to have breasts or a larger body. M Isolation photo/Shutterstock These studies reflect what we see in our own work, training other health practitioners to do CPR. We have noticed all the manikins available to for training are flat-chested. One of us (Rebecca) found it difficult to find any training manikins with breasts.
A single manikin with breasts
Our new research investigated what CPR manikins are available and how diverse they are. We identified 20 CPR manikins on the global market in 2023. Manikins are usually a torso with a head and no arms.
Of the 20 available, five (25%) were sold as “female” – but only one of these had breasts. That means 95% of available CPR training manikins were flat-chested.
We also looked at other features of diversity, including skin tone and larger bodies. We found 65% had more than one skin tone available, but just one was a larger size body. More research is needed on how these aspects affect bystanders in giving CPR.
Breasts don’t change CPR technique
CPR technique doesn’t change when someone has breasts. The barriers are cultural. And while you might feel uncomfortable, starting CPR as soon as possible could save a life.
Signs someone might need CPR include not breathing properly or at all, or not responding to you.
To perform effective CPR, you should:
- put the heel of your hand on the middle of their chest
- put your other hand on the top of the first hand, and interlock fingers (keep your arms straight)
- press down hard, to a depth of about 5cm before releasing
- push the chest at a rate of 100-120 beats per minute (you can sing a song) in your head to help keep time!)
https://www.youtube.com/embed/Plse2FOkV4Q?wmode=transparent&start=94 An example of how to do CPR – with a flat-chested manikin.
What about a defibrillator?
You don’t need to remove someone’s bra to perform CPR. But you may need to if a defibrillator is required.
A defibrillator is a device that applies an electric charge to restore the heartbeat. A bra with an underwire could cause a slight burn to the skin when the debrillator’s pads apply the electric charge. But if you can’t remove the bra, don’t let it delay care.
What should change?
Our research highlights the need for a range of CPR training manikins with breasts, as well as different body sizes.
Training resources need to better prepare people to intervene and perform CPR on people with breasts. We also need greater education about women’s risk of getting and dying from heart-related diseases.
Jessica Stokes-Parish, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Bond University and Rebecca A. Szabo, Honorary Senior Lecturer in Critical Care and Obstetrics, Gynaecology and Newborn Health, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing extra virgin olive oil to cold-pressed coconut oil, we picked the olive oil.
Why?
While the cold-pressed coconut oil may offer some health benefits due to its lauric acid content, its 80–90% saturated fat content isn’t great for most people. It’s a great oil when applied topically for healthy skin and hair, though!
The extra virgin olive oil has a much more uncontroversially healthy blend of triglycerides, and (in moderation) is universally recognized as very heart-healthy.
Your local supermarket, most likely, has a good extra virgin olive oil, but if you’d like to get some online, here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: