Pomegranate vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pomegranate to cherries, we picked the pomegranate.
Why?
In terms of macros, pomegranate is slightly higher in carbs, and/but 4x higher in fiber. That’s already a good start for pomegranates. Lest we be accused of cherry-picking, though, we’ll mention that pomegranate is also slightly higher in protein and fat, for what it’s worth—which is not a lot. As with most fruits, the protein and fat numbers are low importance next to the carb:fiber ratio.
When it comes to vitamins, pomegranate has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B9. E. K, and choline. On the other hand, cherries have more of vitamins A and B3. The two fruits are equal in vitamin C. This all makes for a clear win for pomegranate.
In the category of minerals, pomegranate boasts more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. In contrast, cherries have slightly more calcium. Another win for pomegranate.
Both of these fruits have beneficial polyphenols, each with a slightly different profile, but neither pressingly better than the other.
In short: as ever with healthy foods, enjoy both—diversity is good! But if you’re going to pick on, we recommend the pomegranate.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Pomegranate Peel’s Potent Potential ← so don’t throw it away!
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Turmeric (Curcumin) Dos and Don’ts With Dr. Kim
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Turmeric is a fabulous spice, most well-known for its anti-inflammatory powers; its antioxidant effects benefit all of the body, including the brain. While it fights seemingly everything from arthritis to atherosclerosis to Alzheimer’s and more, it also boosts brain-derived neurotrophic factor, looks after your cardiovascular health, holds back diabetes, reduces the risk of cancer, fights depression, slows aging, and basically does everything short of making you sing well too.
Dr. Leonid Kim goes over the scientific evidence for these, and also talks about some of the practicalities of taking turmeric, and safety considerations.
For the most part, turmeric is very safe even at high doses (up to 8g at least); indeed, at smaller doses (e.g. 500mg) it largely does the same job as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, with fewer problems.
It also does the job of several antidiabetic medications, by increasing uptake of glucose (thus reducing blood sugar levels) while simultaneously decreasing the glucose secretion from the liver. It does this by regulating the AMPK signalling pathway, just like metformin—while again, being safer.
Dr. Kim also looks at the (good!) evidence for turmeric in managing PCOS and undoing NAFLD; so far, so good.
Dosage: he bids us pay attention whether we’re taking it as turmeric itself or as curcumin standardized extract. The latter is the active compound, and in principle more powerful, but in practice it can get metabolized too quickly and easily—before it can have its desired effect. So, turmeric itself is a very good choice.
Absorption: since we do want it to be absorbed well, though, he does recommend taking it with piperine (as in black pepper).
You may be thinking: isn’t this going to cause the same problem you were just talking about, and cause it to be metabolized too quickly? And the answer is: no! How piperine works is almost the opposite; it protects the curcumin in the turmeric from our digestive enzymes, and thus allows them to get absorbed without being broken down too quickly—thus increasing the bioavailability by slowing the process down.
Lipophilia: no, that’s not a disease (or a fetish), rather it means that curcumin is soluble in fats, so we should take it near in time to a meal that contains at least a tablespoon of oil in total (so if you’re cooking a curry with your turmeric, this need is covered already, for example).
Supplement provenance: he recommends picking a supplement that’s been tested by a reputable 3rd party, as otherwise turmeric can be quite prone to impurities (which can include lead and arsenic, so, not great).
Contraindications: for some people, curcumin can cause gastrointestinal issues (less likely if taking with meals), and also, it can interact with blood-thinners. While taking aspirin or curcumin alone might help avoid circulatory problems, taking both could increase the bleeding risk for some people, for example. Similarly, if taking curcumin and metformin while diabetic, one must watch out for the combination being too effective at lowering blood sugar levels, and thus causing hypoglycemia instead. Similar deal with blood pressure medications.
There’s more in the video though (yes really; we know we wrote a lot but it’s information-dense), so do check it out:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Want to know more?
You can also check out our related articles:
Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)Share This Post
-
Burned Out By Tuesday?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Avoiding Burnout, The Active Way
This is Dr. Claudine Holt. She’s double board-certified, in Occupational & Environmental Medicine, and Lifestyle Medicine.
In short: preventative medicine in all parts of our life.
Hopefully, you are reading this bright-eyed and bushy-tailed and ready to take on another exciting day in this wonderful, beautiful world!
On the other hand, it’s possible that you’re reading this semi-focussed, looking for a crumb of dopamine as much as you are looking for information.
If you’ve ever had the “What a week!” / “It’s only Tuesday” moment, this one’s for you.
What does Dr. Holt want us to know?
You can recover from burnout without guilt
Sometimes, we overreach ourselves. Sometimes, life overreaches us! Sometimes it’s not that we overcommitted—it’s just that we were taking each day as it comes, but sometimes several days gang up on us at once.
Sometimes, even, we can feel exhausted when it seems like we haven’t done anything.
Note: if you feel exhausted and it seems like you haven’t done anything, then be aware: you are exhausted for a reason!
What that reason might be may vary, but contrary to popular belief, energy does not just vanish. It went somewhere.
This goes double if you have any chronic illness(es), even if you’re not aware of having had a flare-up, chances are you were just exceptionally busy (on a cellular level).
And it’s easy to think that “mere” cellular activity shouldn’t be exhausting, but that is 100% of where our energy transactions happen—whether or not we are consciously aware of them!
See also: Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue ← yes, this also covers when you are too exhausted to shop and cook like a TV chef
Dr. Holt specializes in working with burned out medical professionals (and also specifically specializes in working with women), but there are lessons for everyone in her advice. For example:
Fiction: ”Medicine is my calling–it’s who I am.”
Fact: You are more than medicine! Remember that your career is just one aspect of your life. Don’t forget to create your big-picture vision and tend the garden of the other areas of your life too.
Read more: Dr. Claudine Holt | Burnout: Fact vs Fiction
This same thing can go for whatever part of your identity frequently follows “I’m a…”, and is somewhere that you put a lot of your energy; it could equally be a non-professional job like “homemaker”, or a relational status like “husband”, or a cultural identifier like “Christian”, or a hobby like “gardener” (assuming that is not also your profession, in which case, same item, different category).
Indeed, a lot of women especially get hit by “the triple burden” of professional work, housework, and childcare. And it’s not even necessarily that we resent any of those things or feel like they’re a burden; we (hopefully) love our professions, homes, children. But, here’s the thing:
No amount of love will add extra hours to the day.
So what does she recommend doing about it, when sometimes we’re juggling things that can’t be dropped?
Start simple, but start!
Dr. Holt recommends to start with a smile (yes even if, and sometimes especially when, the circumstances do not feel like they merit it), and deploy some CBT tools:
Two Hacks to Quickly Rise Above Burnout (Or Any Circumstance)
We’ve expanded on this topic here:
With a more level head on, it becomes easier to take on the next step, which creating healthy boundaries—and that doesn’t just mean with other people!
It also means slaying our own perfectionism and imposter syndrome—both things that will have us chasing our tails 36 hours per day if we let them.
See also:
- Perfectionism, And How To Make Yours Work For You
- Imposter Syndrome (And Why Almost Everyone Has It)
❝Burnout is the culture of our times. A culture that expects us to do more and think our way out of everything. A culture that asks for more than the body can bear. Unfortunately, even though the situation might not be of our creation, burnout culture is our inheritance.
An inheritance we can either perpetuate—or change—depending on what we embody.❞
Source: The Embodied MD on Burnout with Dr Claudine Holt
That “embodiment” is partly our choices and actions that we bring and own just as we bring and own our body—and it’s partly our relationship with our body itself, and learning to love it, and work with it to achieve wonderful things, instead of just getting through the day.
Which yes, does also mean making space for good diet, exercise, sleep and so forth, per:
These Top Five Things Make The Biggest Difference To Health
Want to know more?
You might like to check out Dr. Holt’s website:
The Embodied M.D. | Burnout Coach
…where she also offers resources such as a blog and a podcast.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Wheat Belly, Revised & Expanded Edition – by Dr. William Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This review pertains to the 2019 edition of the book, not the 2011 original, which will not have had all of the same research.
We are told, by scientific consensus, to enjoy plenty of whole grains as part of our diet. So, what does cardiologist Dr. William Davis have against wheat?
Firstly, not all grains are interchangeable, and wheat—in particular, modern strains of wheat—cannot be described as the same as the wheat of times past.
While this book does touch on the gluten aspect (and Celiac disease), and notes that modern wheat has a much higher gluten content than older strains, most of this book is about other harms that wheat can do to us.
Dr. Davis explores and explains the metabolic implications of wheat’s unique properties on organs such as our pancreas, liver, heart, and brain.
The book does also have recipes and meal plans, though in this reviewer’s opinion they were a little superfluous. Wheat is not hard to cut out unless you are living in a food desert or are experiencing food poverty, in which case, those recipes and meal plans would also not help.
Bottom line: this book, filled with plenty of actual science, makes a strong case against wheat, and again, mostly for reasons other than its gluten content. You might want to cut yours down!
Click here to check out Wheat Belly, and see if skipping the wheat could be good for you!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Boundary-Setting Beyond “No”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
More Than A “No”
A lot of people struggle with boundary-setting, and it’s not always the way you might think.
The person who “can’t say no” to people probably comes to mind, but the problem is more far-reaching than that, and it’s rooted in not being clear over what a boundary actually is.
For example: “Don’t bring him here again!”
Pretty clear, right?
And while it is indeed clear, it’s not a boundary; it’s a command. Which may or may not be obeyed, and at the end of the day, what right have we to command people in general?
Same goes for less dramatic things like “Don’t talk to me about xyz”, which can still be important or trivial, depending on whether the topic of xyz is deeply traumatizing for you, or mildly annoying, or something else entirely.
Why this becomes a problem
It becomes a problem not because of any lack of clarity about your wishes, but rather, because it opens the floor for a debate. The listener may be given to wonder whether your right to not experience xyz is greater or lesser than their right to do/say/etc xyz.
“My right to swing my fist ends where someone else’s nose begins”
…does not help here, firstly because both sides will believe themself (or nobody) to be the injured party; for the fist-swinger, the other person’s nose made a vicious assault on their freedom. Or secondly, maybe there was some higher principle at stake; a reason why violence was justified. And then ten levels of philosophical debate. We see this a lot when it comes to freedom of expression, and vigorous debate over whether this entails freedom from social consequences of one’s words/actions.
How a good boundary-setting works (if this, then that)
Consider two signs:
- No trespassing!
- Trespassers will be shot!
Superficially, the second just seems like a more violent rendition of the first. But in fact, the second is more informationally useful: it explains what will happen if the boundary is not respected, and allows the reader to make their own informed decision with regard to what to do with that information.
We can employ this method (and can even do so gently, if we so wish and hopefully we mostly do wish to be gentle) when it comes to social and interpersonal boundary-setting:
- If you bring him here again, I will refuse you entrance
- If you bring up that topic again, I will ask you to leave
- If you do that, I will never speak to you again
- If you don’t stop drinking, I will divorce you
This “if-this-then-that” model does the very first thing that any good boundary does: make itself clear.
It doesn’t rely on moral arguments; it doesn’t invite debate. For example in that last case, it doesn’t argue that the partner doesn’t have the right to drink—it simply expresses what the speaker will exercise their own right to do, in that eventuality.
(as an aside, the situation that occurs when one is enmeshed with someone who is dependent on a substance is a complex topic, and if you’re interested in that, check out: Codependency Isn’t What Most People Think)
Back on track: boundary-setting is not about what’s right or good—it’s about nothing more nor less than a clear delineation between what we will and won’t accept, and how we’ll enforce that.
We can also, in particularly personal boundary-setting (such as with sexual boundaries’ oft-claimed “gray areas”), fix an improperly-set boundary that forgot to do the above, e.g:
“How about [proposition]?”
“No thank you” ← casually worded answer; contextually reasonable, and yet not a clear boundary per what we discussed above
“Come on, I think you’d like it”
“I said no. No means no. Ask me again and I will [consequences that are appropriate and actionable]”What’s “appropriate and actionable” may vary a lot from one situation to another, but it’s important that it’s something you can do and are prepared to do and will do if the condition for doing it is met.
Anything less than that is not a boundary—it’s just a request.
Note: this does not require that we have power, by the way. If we have zero power in a situation, well, that definitely sucks, but even then we can still express what is actionable, e.g. “I will never trust you again”.
“Price of entry”
You may have wondered, upon reading “boundary-setting is not about what’s right or good—it’s about nothing more nor less than a clear delineation between what we will and won’t accept, and how we’ll enforce that”, can’t that be used to control and manipulate people, essentially coercing them to do or not do things with the threat of consequences (specifically: bad ones)?
And the answer is: yes, yes it can.
But that’s where the flipside comes into play—the other person gets to set their boundaries, too.
For all of us, if we have any boundaries at all, there is a “price of entry” and all who want to be in our lives, or be close to us, have to decide for themselves whether that price of entry is worth it.
- If a person says “do not talk about topic xyz to me or I will leave”, that is a price of entry for being close to them.
- If you are passionate about talking about topic xyz to the point that you are unwilling to shelve it when in their presence, then that is the price of entry for being close to you.
- If one or more of you is not willing to pay the price of entry, then guess what, you’re just not going to be close.
In cases of forced proximity (e.g. workplaces or families) this is likely to get resolved by the workplace’s own rules (i.e. the price of entry that you agreed to when signing a contract to work there), and if something like that doesn’t exist (such as in families), well, that forced proximity is going to reach a breaking point, and somebody may discover it wasn’t enforceable after all.
See also: Family Estrangement: More Common Than Most People Think
…which also details how to fix it, where possible.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10almonds Tells The Tea…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s Bust Some Myths!
It’s too late after puberty, hormones won’t change xyz
While yes, many adult trans people dearly wish they’d been able to medically transition before going through the “wrong” puberty, the truth is that a lot of changes will still occur later… even to “unchangeable” things like the skeleton.
The body is remaking itself throughout life, and hormones tell it how to do that. Some parts are just quicker or slower than others. Also: the skeleton is pulled-on constantly by our muscles, and in a battle of muscle vs bone, muscle will always win over time.
Examples of this include:
- trans men building bigger bones to support their bigger muscles
- trans women getting smaller, with wider hips and a pelvic tilt
Trans people have sporting advantages
Assuming at least a year’s cross-sex hormonal treatment, there is no useful advantage to being trans when engaging in a sport. There are small advantages and disadvantages (which goes for any person’s body, really). For example:
- Trans women will tend to be taller than cis women on average…
- …but that larger frame is now being powered by smaller muscles, because they shrink much quicker than the skeleton.
- Trans men taking T are the only athletes allowed to take testosterone…
- …but they will still often be smaller than their fellow male competitors, for example.
Read: Do Trans Women Athletes Have Advantages? (A rather balanced expert overview, which does also cover trans men)
There’s a trans population explosion; it’s a social contagion epidemic!
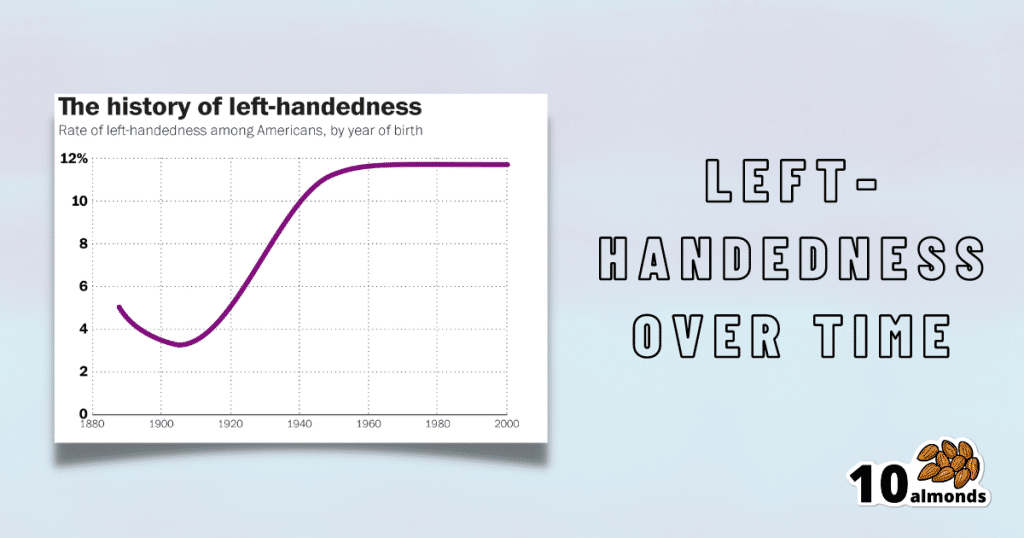
Source for figures: The Overall Rate Of Left-Handedness (Researchgate)
Left-handed people used to make up around 3% of the population… Until the 1920s, when that figure jumped sharply upwards, before plateauing at around 12% in around 1960, where it’s stayed since. What happened?! Simple, schools stopped forcing children to use their right hand.
Today, people ask for trans healthcare because they know it exists! Decades ago, it wasn’t such common knowledge.
The same explanation can be applied to other “population explosions” such as for autism and ADHD.
Fun fact: Mt. Everest was “discovered” in 1852, but scientists suspect it probably existed long before then! People whose ancestors were living on it long before 1852 also agree. Sometimes something exists for a long time, and only comes to wider public awareness later.
Transgender healthcare is too readily available, especially to children!
To believe some press outlets, you’d think:
- HRT is available from school vending machines,
- kids can get a walk-in top surgery at recess,
- and there’s an after-school sterilization club.
In reality, while availability varies from place to place, trans healthcare is heavily gatekept. Even adults have trouble getting it, often having to wait years and/or pay large sums of money… and get permission from a flock of doctors, psychologists, and the like. For those under the age of 18, it’s almost impossible in many places, even with parental support.
Puberty-blockers shouldn’t be given to teenagers, as the effects are irreversible
Quick question: who do you think should be given puberty-blockers? For whom do you think they were developed? Not adults, for sure! They were not developed for trans teens either, but for cis pre-teens with precocious puberty, to keep puberty at bay, to do it correctly later. Nobody argues they’re unsafe for much younger cis children, and only object when it’s trans teens.
They’re not only safe and reversible, but also self-reversing. Stop taking them, and the normally scheduled puberty promptly ensues by itself. For trans kids, the desired effect is to buy the kid time to make an informed and well-considered decision. After all, the effects of the wrong puberty are really difficult to undo!
A lot of people rush medical transition and regret it!
Trans people wish it could be rushed! It’s a lot harder to get gender-affirming care as a trans person, than it is to get the same (or comparable) care as a cis person. Yes, cis people get gender-affirming care, from hormones to surgeries, and have done for a long time.
As for regret… Medical transition has around a 1% regret rate. For comparison, hip replacement has a 4.8% regret rate and knee replacement has a 17.1% regret rate.
A medical procedure with a 99% success rate would generally be considered a miracle cure!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat Real Food and Love It – by Kari McCloskey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Half the battle of healthy eating is enjoying it—because once you do, it’s no longer a battle!
So that’s what this book focuses on. The author, a Registered Nutritionist, does indeed dispense nutritional advice, as you might expect, but also bids us pay attention to what nature’s foods do for us, and notice what less healthy foods take from us. She goes through these category by category, quite comprehensively, before moving on to the more “active” parts of the book.
There’s a lot about training our senses, and about taking a holistic approach to eating, as well as renewing not just our relationship with food, but also various other parts of our life that are inextricably linked to it (from sleep and exercise, to social considerations, and medical issues that healthier eating will help us to avoid or at least tame).
The style is… Joyful. Much like this reviewer, the author loves food, and it shows. She also (again much like this reviewer) cares deeply about the impact food has on her, and (for a third time: like this reviewer!) wants to share that joy and care with the reader. The priority is readability and helpfulness; scientific references are still provided wherever appropriate, though.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your eating but it seems like a chore, this book can help turn it into an excitingly enjoyable journey instead.
Click here to check out Eat Real Food And Love It, and eat real food and love it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: