Pistachios vs Peanuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to peanuts, we picked the peanuts.
Why?
The choice might be surprising; after all, peanuts are usually the cheapest and most readily available nuts, popularly associated with calories and not much else. However! This one was super-close, and peanuts won very marginally, as you’ll see.
In terms of macros, pistachios have slightly more fiber and nearly 2x the carbs, while peanuts have slightly more protein and fats. What we all as individuals might prioritize more there is subjective, but this could arguably be considered a tie. About the fiber and carbs: peanuts have the lower glycemic index, but not by much. And about those fats: yes, they are healthy, and the fat breakdown for each is almost identical: pistachios have 53% monounsaturated, 33% polyunsaturated, and 14% saturated, while peanuts have 53% monounsaturated, 34% polyunsaturated, and 14% saturated. Yes, that adds up to 101% in the case of peanuts, but that’s what happens with rounding things to integers. However, the point is clear: both of these nuts have almost identical fats.
In the category of vitamins, pistachios have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and C, while peanuts have more of vitamins B3, B5, B9, E, and choline, So, a 5:5 tie on vitamins.
When it comes to minerals, pistachios have more calcium, copper, phosphorus, and potassium, while peanuts have more iron, magnesium, manganese, selenium, and zinc. So, a marginal victory for peanuts (and yes, the margins of difference were similar in each case).
Adding up the tie, the other tie, and the marginal victory for peanuts, means a marginal victory for peanuts in total.
A quick note in closing though: this was comparing raw unsalted nuts in both cases, so do take that into account when buying nuts, and at the very least, skip the salted, unless you are deficient in sodium. Or if you’re using them for cooking, then buying salted nuts because they’re usually cheaper is fine; just soak and rinse them to remove the salt.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How we can prepare for future public health emergencies
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The U.S. is experiencing an increasing number of disease outbreaks and extreme weather events. While state and national preparedness for public health emergencies has improved in some areas, dangerous gaps remain, says a recent report from Trust for America’s Health.
Titled, “Ready or Not 2024: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism,” the report identifies gaps in national and state preparedness for public health emergencies and provides recommendations for improvement.
Using nine key indicators, the report categorizes all U.S. states and the District of Columbia into three readiness levels: high, medium, and low. The writers hope the report will help policymakers in under-performing states improve public health infrastructure.
Read on to learn more about what the research found and how we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies.
There’s work to be done
The report highlights areas with strong performance as well as those that need improvement.
Some areas with strong performance:
- State public health funding: Most states and the District of Columbia either maintained or increased their public health funding during the 2023 fiscal year.
- Health care labor force preparedness: Most states have started expanding the health care labor force for improved emergency response. As of 2023, 39 states participated in the Nurse Licensure Compact, which allows nurses to work in multiple member states without the need for additional state licenses.
Some areas that need improvement:
- Hospital safety scores: Only 25 percent of acute care hospitals earned the highest patient safety grade in fall 2023. These scores measure health care-associated infection rates, intensive care unit capacity, and other metrics. More high-scoring hospitals would improve preparedness for future public health emergencies.
- Access to paid time off: From March 2018 to March 2023, only 55 percent of U.S. workers used paid time off. Access to paid time off is important for reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
We can all do our part by staying up to date on vaccines
While the report focuses on policy changes that would improve emergency preparedness, Trust for America’s Health’s research identifies one way that we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies: staying up to date on vaccines.
The report found that during the 2022-2023 flu season, only 49 percent of those eligible for the flu vaccine received it. Public health experts are concerned that false claims about COVID-19 vaccines have resulted in overall vaccine hesitancy.
A decline in vaccination rates has led to an uptick in life-threatening, vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles. Increasing vaccine uptake would prevent the spread of vaccine-preventable diseases and reduce strain on hospital systems during public health crises.
Make sure that you and your children have received all recommended vaccines to prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Learn more about recommended vaccines for adults and children from the CDC.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
How Does Alcohol Cause Blackouts?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes people who have never experienced an alcoholic blackout wonder “is it real, or is it just a convenient excuse to avoid responsibility/embarrassment with regard to things done while drunk?”
In 1969 (so, still in the era of incredibly unethical psychological experiments that ranged from the 50s into the 70s), Dr. Donald Goodwin conducted a study in which intoxicated participants were asked to recall an object they had just seen. Most succeeded initially, but half were unable to remember the object just 30 minutes later, demonstrating alcohol-induced memory blackouts.
But, is it any different from regular forgetting? And the answer is: yes, it is indeed different.
The memories that never got stored
Ethanol, the active compound in alcohol, is lipophilic, enabling it to cross the blood-brain barrier and disrupt brain function. It impairs all kinds of things, including decision-making, impulse control, motor skills, and, notably, memory networks—which is what we’re looking at today.
Memory formation (beyond “working memory”, which is the kind that enables you to have an idea of what you were just doing, and carry out simple plans like “pick up this cup, raise it to my mouth, and take a sip”, without forgetting partway through) relies on a process called long-term potentiation (LTP), which strengthens neural connections to store information. Ethanol disrupts this process, preventing memory storage and causing blackouts.
In effect, this means you didn’t just forget a memory; you never stored it in the first place. For this reason, experiences from during an alcoholic blackout cannot be retrieved in the same ways we might retrieve other memories (e.g. in regular forgetting, it’s possible that a context clue jogs our memory and then we remember the experience—because in regular forgetting, the memory was in there; we just didn’t recall it until we were reminded).
Blackouts (in which the memory is never stored in the first place) typically occur when blood alcohol concentration (BAC) exceeds 0.16, while lower levels can result in partial memory loss (brownouts) in which some things may be recalled, but not others. Factors such as dehydration, genetics, medications, food consumption, and age influence the likelihood of complete blackouts.
While alcohol’s residual effects typically subside within a day, repeated over-drinking can cause permanent neuron damage, as well as of course plenty of damage to other organs in the body (especially the liver and gut).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Mung Beans vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mung beans to black beans, we picked the black beans.
Why?
Both are great! But…
In terms of macros, black beans have more protein, carbs, and fiber, as well as the lower glycemic index (although both are already low). So, a clear win for black beans here.
In the category of vitamins, mung beans have more of vitamins A, B5, B9, and C, while black beans have more of vitamins B1, B6, E, K, and choline. Thus, a slight win for black beans this time.
When it comes to minerals, mung beans have more selenium and zinc, while black beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. An easy win for black beans.
Of course, enjoy either or both—but if you’re going to pick one, we say black beans win the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head-to-Head
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Genius Gut – by Dr. Emily Leeming
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to the gut-brain information interchange, 90% of it is the gut talking to the brain (the brain is a good listener). As such, one of the best things we can do for our brain is ensure our gut has good things to say.
Dr. Leeming talks us through doing a quick initial assessment to judge the general goodness/badness of our current gut situation (based on output, not input, so it’s about the actual goodness/badness, not what we expect it should be), before going on to explain a lot of the anatomy and physiology at hand.
The hacks themselves may be, in their titles, things you already know—but where the real value of this book lies is in all the data and science collated under each of those hacks, allowing the reader to optimize everything rather than just guessing. Which can mean optimize by doing things as close to perfectly as possible, or it can mean optimize by doing/using the things that get the best results for the minimum effort. It’s up to you!
The style is very casual and friendly, even conversational, while not skimping on science (and indeed, citations are frequently provided for such).
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your gut health, especially with the goal of improving your brain health, this is an excellent book for that.
Click here to check out Genius Gut, and make yours better for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eating Disorders: More Varied (And Prevalent) Than People Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Disordered Eating Beyond The Stereotypes
Around 10% of Americans* have (or have had) an eating disorder. That might not seem like a high percentage, but that’s one in ten; do you know 10 people? If so, it might be a topic that’s near to you.
*Source: Social and economic cost of eating disorders in the United States of Americ
Our hope is that even if you yourself have never had such a problem in your life, today’s article will help arm you with knowledge. You never know who in your life might need your support.
Very misunderstood
Eating disorders are so widely misunderstood in so many ways that we nearly made this a Friday Mythbusting edition—but we preface those with a poll that we hope to be at least somewhat polarizing or provide a spectrum of belief. In this case, meanwhile, there’s a whole cluster of myths that cannot be summed up in one question. So, here we are doing a Psychology Sunday edition instead.
“Eating disorders aren’t that important”
Eating disorders are the second most deadly category of mental illness, second only to opioid addiction.
Anorexia specifically has the highest case mortality rate of any mental illness:
Source: National Association of Anorexia Nervosa & Associated Disorders: Eating Disorder Statistics
So please, if someone needs help with an eating disorder (including if it’s you), help them.
“Eating disorders are for angsty rebellious teens”
While there’s often an element of “this is the one thing I can control” to some eating disorders (including anorexia and bulimia), eating disorders very often present in early middle-age, very often amongst busy career-driven individuals using it as a coping mechanism to have a feeling of control in their hectic lives.
13% of women over 50 report current core eating disorder symptoms, and that is probably underreported.
Source: as above; scroll to near the bottom!
“Eating disorders are a female thing”
Nope. Officially, men represent around 25% of people diagnosed with eating disorders, but women are 5x more likely to get diagnosed, so you can do the math there. Women are also 1.5% more likely to receive treatment for it.
By the time men do get diagnosed, they’ve often done a lot more damage to their bodies because they, as well as other people, have overlooked the possibility of their eating being disordered, due to the stereotype of it being a female thing.
Source: as above again!
“Eating disorders are about body image”
They can be, but that’s far from the only kind!
Some can be about control of diet, not just for the sake of controlling one’s body, but purely for the sake of controlling the diet itself.
Still yet others can be not about body image or control, like “Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder”, which in lay terms sometimes gets dismissed as “being a picky eater” or simply “losing one’s appetite”, but can be serious.
For example, a common presentation of the latter might be a person who is racked with guilt and/or anxiety, and simply stops eating, because either they don’t feel they deserve it, or “how can I eat at a time like this, when…?” but the time is an ongoing thing so their impromptu fast is too.
Still yet even more others might be about trying to regulate emotions by (in essence) self-medicating with food—not in the healthy “so eat some fruit and veg and nuts etc” sense, but in the “Binge-Eating Disorder” sense.
And that latter accounts for a lot of adults.
You can read more about these things here:
Psychology Today | Types of Eating Disorder ← it’s pop-science, but it’s a good overview
Take care! And if you have, or think you might have, an eating disorder, know that there are organizations that can and will offer help/support in a non-judgmental fashion. Here’s the ANAD’s eating disorder help resource page, for example.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
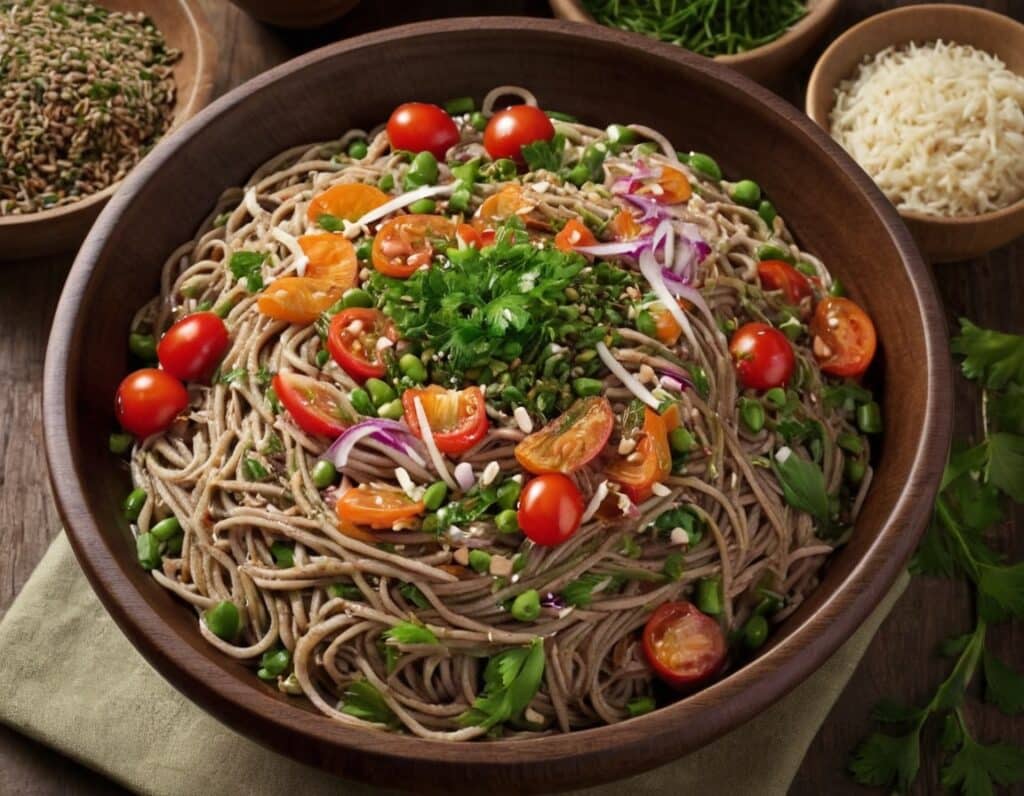
Superfood Soba Noodle Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This Japanese dish is packed with nutrients and takes very little preparation time, involving only one cooked ingredient, and a healthy one at that!
You will need
- 8 oz dried soba noodles
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp avocado oil
- 2 tsp soy sauce
- ¼ cucumber, cut into thin batons (don’t peel it first)
- ½ carrot, grated (don’t peel it first)
- 6 cherry tomatoes, halved (you wouldn’t peel these, right? Please don’t)
- ½ red onion, finely sliced (ok, this one you can peel first! Please do)
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tsp crushed red chili flakes
- Garnish: fresh parsley, chopped
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the soba noodles (boil in water for 10 mins or until soft). Rinse with cold water (which lowers the glycemic index further, and also we want them cold anyway) and set aside.
2) Make the dressing by blending the garlic, avocado oil, and soy cauce. Set it aside.
3) Assemble the salad by thoroughly but gently mixing the noodles with the cucumber, carrot, tomatoes, and onion. Add the dressing, the chia seeds, and the chili flakes, and toss gently to combine.
4) Serve, adding the parsley garnish.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Rice vs Buckwheat – Which is Healthier? ← soba noodles are made from buckwheat, which by the way is also a good source of rutin, which can strengthen blood vessel walls against damage, reducing the risk of atheroma
- Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: